Tonsil cancer is an oncological disease resulting from mutation of healthy cells in the tonsils and their subsequent growth and reproduction. Externally, this type of cancer looks like swollen ulcers. In the early stages, the disease is asymptomatic. Therefore, oncology is detected at a later stage, when the prognosis for survival decreases. It ranks second in terms of the frequency of deaths. To detect the focus of a malignant tumor at the initial stage, it is necessary to promptly contact a specialist if there is discomfort in the tonsils.
Description of the disease
Under the influence of various factors, healthy cells of lymphoid tissue mutate, grow, and multiply rapidly. The result of this process is a malignant type of formation on the lymphoid tissue. In a healthy state, the lymphoid layer of the larynx serves as protection for the respiratory organs. Cancer of the tonsils (tonsils) is part of the group of oncological diseases of the oral cavity.
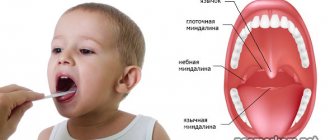
The throat consists of tonsils: lingual, pharyngeal (adenoids), 2 tubal, 2 palatine. Most often, the palatine gland is affected by squamous cell carcinoma, but sometimes lymphoma can be diagnosed. The disease affects the lymph nodes located on the palatine tonsil. The rate of development determines the aggressiveness of tonsil cancer: in a short time, the disease moves from the initial stage to the terminal stage. This is due to the fact that the initial stage of cancer does not show signs of discomfort, allowing cancer cells to develop freely.
It was previously believed that tonsil cancer develops in men over 50 years of age. But the disease is getting younger, and tonsil cancer is increasingly being diagnosed in women.
Symptoms
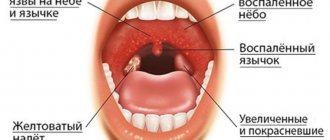
Doctors believe that the reason for the late detection of a malignant tumor is its similarity to a sore throat, ARVI, and influenza. It is important to know the symptoms of a malignant tumor of the tonsils:
- When swallowing, the presence of a lump is felt.
- Sore throat. As the disease progresses, the pain is constant.
- Soreness and coughing, sometimes accompanied by blood. This symptom indicates trouble in the respiratory tract.
- Tonsils and lymph nodes enlarge either on the right or left side. On the side on which growth occurs, the tumor focus is located on that side.
- Swelling of the neck.
- Voice change.
Symptoms of the initial stage of the disease resemble symptoms of sore throat, flu, and sinusitis. Potential patients do not attach importance to symptoms, allowing the disease to develop.
Late stages are indicated by weight loss, weakness, ongoing coughing, causing chest pain, cutting pain in the throat, followed by pain in the ears, paratemporal area, and cheeks.
Symptoms of tumor growth:
- Saliva contains purulent and bloody discharge.
- Difficulty breathing through the nose.
- Continuous sore throat. Swallowing increases the pain, and it radiates into the ear on the side where the source of the disease is located.
- Feeling like there is a lump stuck in the throat.
- Asymmetrical size of the tonsils. The affected tonsil is larger in size.
- Upon self-examination, ulcers are found on the tonsils.
- Lymph nodes become enlarged and painful.
The ingrowth of cancer cells into the mucous tissue of the oropharynx is indicated by untreatable otitis media with severe pain. As a result of tumor spread to the oropharynx, deafness may occur.
When the tumor penetrates the skull, compression of the brain and nerves occurs. The following signs indicate this:
- causeless visual impairment;
- loss of function of the muscles that provide motor functions of the eyeballs;
- trigeminal nerve disease;
- difficulty swallowing;
- deterioration of the soft palate;
- loss of sensitivity in the oropharynx and tongue.
Metastasis of cancer cells to other organs is indicated by symptoms common to all types of tumor:
- weight loss;
- poor appetite, vomiting, nausea caused by intoxication of waste products of cancer cells;
- decrease in hemoglobin level;
- weakness;
- dental problems;
- elevated temperature;
- inflamed gums.
Reticulosarcoma of the tonsils
For what reason does it occur?
Oncologists cannot come to a consensus on the cause of cancer damage to the respiratory tract. Doctors hypothesize about the factors that cause tonsil cancer:
- The chemical composition, the resin contained in tobacco, leads to a change in the structure of lymphoid tissue. The change leads to atypicality of healthy cells. The combination of alcohol and tobacco increases the likelihood of malignant neoplasms. If a man smokes and drinks alcohol for a long time, the risk of malignancy increases.
- Epstein-Barr disease, characterized by sore throat and enlarged lymph nodes, can become a precursor to cancer.
- Long-term uncontrolled treatment with immunosuppressants.
- Received chemotherapy, radiation.
- The oncogenic human papillomavirus increases the risk of tonsil cancer by 30 times.
- Harmful working conditions, presence of constant contact with chlorine, benzene, arsenic.
- Weakening the body's protective function.
- Unfavorable environmental situation.
Stages of tonsil cancer
Based on the characteristic signs of the lesions, 4 stages of a malignant tumor are distinguished.
The first stage is diagnosed if the cancer has not spread beyond the tonsils. The mucous membrane is involved in the process. The size of the lesion is no more than 2 centimeters. At this stage, the lymph nodes are not affected, and metastasis to distant organs has not occurred. There are no symptoms characteristic of cancer. Detection of the lesion is possible during a medical examination.
When moving to the second stage, the patient notes the presence of pain in the throat area. The volume of the neoplasm reaches 4 centimeters. Doctors diagnose damage to the tonsil, an increase in the size of the lymph nodes on the side of the localization of the tumor.
When cancer cells spread to the tongue and nasopharynx, the third stage is diagnosed. There is unilateral or bilateral enlargement of the lymph nodes. Metastasis to other organs begins. Symptoms appear, characterized by pain when swallowing, the presence of blood and pus in the salivary secretion, and bad breath.
The fourth stage is characterized by metastases in the jaw bone, ear canals, nasopharynx, and larynx. Nearby lymph nodes are involved in the damage process. There is a division of stage 4 into the following stages:
- The diameter of the lesion is less than 6 centimeters. There are no metastases.
- Presence of metastases. There is progression of cancer cells to nearby organs.
- Metastasis to the cervical region, cranium.
Recovery depends on the stage at which the disease was discovered and treatment began. Determining the stage is necessary to prescribe an adequate course of treatment to avoid relapses and increase survival.
Kinds
With regular trauma to the tonsils, the body starts the process of regenerating tonsil tissue. First, one atypical cell appears and begins to develop rapidly. A focus of a malignant tumor appears.
According to external signs, tonsil cancer is of three types:
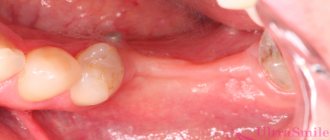
- The shape of a papillomatous tumor is similar to a polyp. The connection with the mucous tissue is due to the presence of a stalk.
- Ulcerative cancer looks like damage to the mucous membrane of various sizes. The difference is the thickened edges.
- An infiltrative tumor is characterized by compaction of nodes, the edges of which resemble tubercles.
Types of tonsil cancer
As a result of histological analysis, tonsil cancer is divided into the following types:
- sarcoma affects the connective tissue of the tonsils;
- in lymphosarcoma, connective and lymphoid tissue cells are involved in the process;
- squamous cell carcinoma affects the top layer of tissue;
- epithelioma affects the cells of the mucous membrane;
- lymphoepithelioma affects the mucous and lymphoid tissue types;
- in reticulosarcoma, reticulocytes become participants in the process.
Every type of cancer requires immediate treatment. The sooner it is started, the greater the chances of recovery.
What does it lead to?
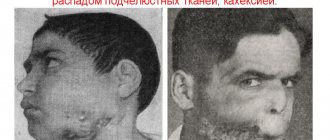
Lymphoid cancer does not go away without a trace for a person. It leads to partial or complete hearing loss. Surgery in the oral cavity can cause respiratory failure. Foci of tumor in the larynx lead to speech impairment. The waste products of mutated cells cause intoxication, poor health, and reduce the body's resistance.
If the disease is detected at the first stage, complications can be avoided or their destructive effect can be reduced. During the first 2-3 years, there remains an increased risk of relapse. Outbreaks may occur at a previous location or in distant parts. It is impossible to prevent relapse, but it is possible to recognize it at the initial stage. To do this, you need to regularly visit a doctor and take control tests. Recurrent cancer is more aggressive than the primary disease. Therefore, doctors use complex therapy to destroy a recurrent tumor.
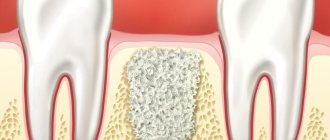
Causes of hypertrophy
Changes in the structure of the tonsil can occur in several ways:
- vascular-glandular, which is observed in the case of local changes in the form of proliferation and plethora of blood vessels, while the volume of tissue decreases;
- lymphoid, when lymphoid hyperplasia occurs due to prolonged inflammation and the presence of infectious intoxication.
An increase in lymphoid formation occurs for the following reasons:
- chronic inflammation of the tonsils (pharyngeal or palatine) - with adenoids and tonsillitis, when microbes persist in the folds of the mucous membrane and maintain inflammation;
- inflammation of the lingual tonsil (glossitis) when it is injured;
- burdened heredity. If the parents had adenoids or had tonsils removed, the child may also have problems with the tonsils;
- negative effects of dry, dusty air, industrial hazards;
- smoking;
- oncological diseases of the pharynx;
- previous operations to remove adenoids or tonsils, when the remaining tonsils take on the function of the removed lymphoid formations, which leads to their hyperplasia;
- occupational hazards when the vocal apparatus has a heavy load (singers, speakers, announcers).
In children, the pathology is extremely rare, but for mature men and women in the premenopausal period, hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil is not uncommon. Most cases occur during puberty.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing the disease at an early stage allows you to begin the fight against the cancer outbreak in a timely manner and increase survival rate. Diagnosis at an early stage is difficult due to the absence or mild symptoms. At the appointment, the doctor examines the patient, as a result of which the clinical picture is revealed and a preliminary diagnosis is announced. Redness of the tonsil, an increase in the volume of the lymph nodes, pain during palpation, swelling of the neck, and its deformation allow us to judge the presence of a tumor process. The doctor prescribes a range of studies aimed at confirming or refuting the diagnosis.
- Laryngoscopy - examination of the oral cavity - determines the condition of the tonsils and mucous membrane.
- A general biochemical blood test reveals anemia and an inflammatory process.
- An analysis of tumor markers confirms or denies the presence of an oncological process.
- Bronchoscopy and esophagoscopy reveal the presence of lesions that have spread to the respiratory tract and digestive canal. These studies allow us to judge the stage of the disease and the size of the lesions.
- Biopsy is the removal of an element of a neoplasm for histological analysis. It provides information about the structure of cells, the rate of division, and the type of tumor.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) visualizes the inflammation on a screen. The procedure makes it possible to judge the size, boundaries of the tumor, and the presence of metastases.
- Positron emission tomography provides information about the quality of the tumor. This method is used to detect cancer at the initial stage.
- Ultrasound allows you to determine the presence of cancer foci located in the deep layers of tissue and provides information about metastasis.
Prevention
Leading a healthy lifestyle is one of the main rules
To avoid diseases of the lingual tonsil, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system. All methods are suitable for this - from hardening to taking vitamins. However, no preventive measures will work if there is a chronic source of infection in the body. First of all, you need to cure your teeth, chronic tonsillitis and other advanced diseases. Smokers should give up smoking, otherwise sooner or later chronic diseases of the tonsils will appear, including tissue hypertrophy.
If you suspect inflammation of the lingual tonsil, you should consult a doctor and not self-medicate. An advanced inflammatory process is dangerous due to an abscess of the lingual tonsil and inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Treatment
The course of treatment is selected depending on the type, stage of the disease, the degree of involvement of the lymph nodes in the process, and the presence of metastases in the body.
- Surgery involves removing the affected parts of the oropharynx. The type of intervention is determined by the size of the tumor focus:
- If the formation is small, laser surgery is indicated. This operation minimizes complications and does not lead to injuries to the oral cavity.
- The destruction of the lesion by ultra-low temperatures is called cryodestruction. Liquid nitrogen kills cancer cells. The method is effective at the initial stage.
- Electroresection involves removing foci of a malignant tumor using an electric scalpel.
- During a classic operation, the doctor removes the tumor and nearby tissue. Used in case of a large area of affected tissue.
In extremely advanced cases, doctors remove the lower jaw, which will later be replaced by an implant. Classic surgery is fraught with swelling in the respiratory tract, making breathing difficult, and voice impairment. To make breathing easier during the recovery period, a hole is made in the trachea.
- During chemotherapy, the patient is prescribed medications that inhibit the growth of cancer cells. The dose is selected taking into account the patient's condition. It is used as an independent method of treatment at an early stage of the disease. For large areas of damage, a course of chemotherapy reduces the size of the tumor. At the terminal stage, the use of chemotherapy can delay death.
- Radiation is used if the tumor is small. Adjuvant radiation therapy is used after surgery to prevent tumor cells from regrowing. Dental treatment is recommended before radiation, which reduces the risk of complications during therapy.
- A new method in the treatment of cancer is photodynamic therapy, which involves the introduction of certain substances into the human body that accumulate in areas of cancer. Under the influence of certain light rays, substances begin to destroy mutated cells.
- Doctors do not approve of self-medication with traditional medicine, since methods of treatment with folk remedies have not been studied by science. During the time spent on self-medication, cancer can develop into an inoperable form.
- Psychological treatment for any form of cancer is important. Diagnosis of cancer leads to stressful situations and prolonged depression. They take away the patient’s strength, which is necessary to fight the disease. Support from loved ones and professional psychological assistance allow the patient to achieve psychological balance.
The type of treatment depends on the stage of the cancer. The first two stages of cancer allow the use of surgery or radiation therapy. This choice of treatment is associated with the small size of the lesion. By combining control methods, doctors achieve a reduction in the risk of relapse and an increase in the level of effectiveness.
In the third and fourth stages, the treatment regimen is different. Surgery is used after radiotherapy and chemotherapy are used to reduce the area of the tumor.
Tonsil cancer in childhood, childbearing and old age
Gland cancer is rarely diagnosed in children. In childhood, early diagnosis of the disease is associated with frequent visits to doctors. Detection of the disease at the initial stage and adequate treatment make it possible to achieve effectiveness in the fight against this type of cancer.
This type of pathology is more common in older people. Therefore, cases of tonsil cancer in women during pregnancy and breastfeeding are rarely recorded. Doctors believe that chronic inflammations such as laryngitis and tonsillitis provoke the atyping of healthy cells. In obstetrics, these inflammations are perceived as a gateway for pathogenic microorganisms. For this reason, tonsillitis in pregnant women is treated in a timely manner. When a tonsil tumor is diagnosed in a pregnant woman, gynecologists and oncologists develop tactics to combat the disease together, taking into account the duration of pregnancy and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Elderly men constitute the main risk group for this cancer. In women, this risk is reduced by 10 times. The symptoms are the same. Early detection allows for optimistic survival predictions.
Causes of hypertrophy
Causes of hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil:
- The most common cause is inflammation of other tonsils, namely the nasopharyngeal and palatine tonsils. This inflammation is most often caused by infectious diseases such as tonsillitis.
- Inflammation can spread from the tongue with glossitis.
- An important factor is hereditary predisposition. Often, persistent hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil is observed in relatives.
- The cause of hypertrophy can be regular or constant thermal, chemical and other effects, such as smoking, eating hot, cold, spicy, salty or pickled foods.
- Cysts and tumors (both benign and malignant) located in close proximity to the root of the tongue or at the root itself.
- In some cases, hypertrophy occurs after removal of the palatine tonsils (this is a kind of compensatory process by which the body tries to compensate for the lack of lymphoid tissue, part of which was removed).
- An enlarged palatine tonsil is often found in people whose professions involve the need to increase intrathoracic pressure (this includes singers, glassblowers, swimmers, and speakers).
- Another reason is diseases of the digestive system, especially those accompanied by an increase in the acidity of gastric juice and its release through the esophagus.
- To begin effective treatment, you should find out the exact causes of hypertrophy.
Recovery period
After treatment, a rehabilitation period is necessary. The effectiveness of fighting the disease depends on how the recovery goes. The effectiveness of chemotherapy is achieved by destroying malignant tumor cells. The effect of chemicals is not selective; in parallel with the destruction of cancer cells, healthy ones are also destroyed. The result of chemotherapy is a weakened body and a decrease in protective functions.
The patient spends the first postoperative hours in bed without eating. After a day, a painkiller is administered, and you are allowed to drink and eat liquid food, the temperature of which is equal to the human body temperature. This is done to avoid injury to the surgical area. The scarring process ends after 3 weeks. By this time, mucous tissue will have formed at the operation site. At first, physical activity, stress, and long journeys are not allowed. After the healing period, the oncologist conducts a second examination and prescribes control tests.
Basic recommendations for the recovery period:
- good nutrition with sufficient amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins;
- exclude visiting the sauna, bathhouse;
- avoid exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- Do not take dietary supplements without a doctor's recommendation.
The diet for the recovery period should be thoughtful. The rehabilitated person's menu includes vegetables, fruits, cereals, and vegetable oils. Consumption of natural antioxidants - garlic, onions - helps reduce the risk of secondary cancer. To restore wasted energy, use natural juices: beet, carrot, birch, maple. To provide the body with vegetable protein and polyunsaturated fats, it is recommended to consume legumes and seeds. Drinking clean water in the required amount (at least 2 liters per day) helps remove toxins.
The total ban includes animal fats, caviar, nuts, bee products, glucose-containing products, and baked goods.
Food is prepared by boiling and stewing, avoiding the addition of vinegar, artificial flavors, and spices. To avoid irritation of the oral cavity, hot food is cooled to human body temperature.
These nutritional recommendations should be followed during the treatment and recovery phase. Taking into account the advice, they create a diet that they adhere to throughout their lives.
How to prevent the disease?
Prevention is easier than cure. There are a number of preventive measures that can reduce the likelihood of disease:
- The chemicals contained in alcoholic beverages irritate the mucous tissue of the tonsils. The tar of tobacco products constantly injures lymphoid tissue. Regular trauma to the tonsils accelerates the process of mutation of healthy cells. Conclusion - eliminate bad habits.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Frequent visits to specialists: otolaryngologist, dentist.
- Eliminate or reduce exposure to ultraviolet rays, carcinogens, ions.
- Review your sex life, eliminating frequent changes of partners.
Localization and type of lingual tonsils
The lingual tonsil can be singular or paired
The lingual tonsil is located under the surface of the back of the tongue. It is a formation of lymphoid tissue in which the process of maturation of immune cells and the production of antibodies occurs.
Despite the fact that it is designated as an unpaired organ, most people have two such tonsils. This is explained by the symmetrical division of the organ’s lymphoid tissue into two parts.
The lingual tonsil in the photo is determined by an accumulation of lymphoid tissue consisting of follicles, so its structure appears heterogeneous. To determine how many lingual tonsils a person has, it is enough to carefully examine the groove at the base of the tongue. If it is very clear and noticeable, it means that the lymphoid tissue is divided into two organs and two tonsils. Interestingly, this division is not a pathology.
The anatomy of the lingual tonsil is simple. Having figured out where the lingual or uvular tonsil is located, you should understand the functions that this organ performs. Along with the palatine tonsils, the lingual tonsil is an organ of the immune system, acting as a barrier to germs and viruses that enter the body through the mouth. When there is a threat of penetration of pathogenic microorganisms, immune cells are formed and released in this tonsil, designed to protect against the disease.
Survival prognosis
The survival prognosis is worsened by late detection of the disease. If tonsil cancer is detected at an early stage, the prognosis for 5-year survival is 100%. When detected at stage 2, 83% of patients survive up to 5 years. This figure drops to 58% if the disease is detected at stage 3. Detection at the end stage gives a 5-year survival rate of 19%. These survival statistics prove that the earlier treatment begins, the longer the life of patients!
It is important to remember that tonsil cancer, like other cancers, is not the end of the world. The right tactics to combat the disease and a positive attitude will lead to a complete recovery.