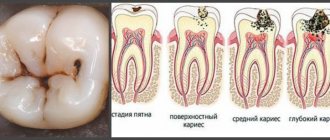
Function of tonsils in the body
The main task of these organs, located at the entrance to the pharyngeal ring, is to protect the respiratory organs from the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into them.
They produce special substances that can destroy microbes, as well as lymphocytes.
It is these cells that play a primary role in the formation and maintenance of immunity. Only the tonsils are able to differentiate the type of pathogen that has entered the body and transmit this information to the immune system.
The child has enlarged tonsils: photo
Thanks to this, even before the microorganism multiplies and serious inflammation develops in the body, highly specific antibodies begin to be produced in increased quantities, rushing to the affected area to destroy the infectious agents.
That is why these organs are no longer removed for preventive purposes, but on the contrary, they try to preserve them with all their might, even with the development of chronic diseases.
If a child has enlarged tonsils: causes of inflammation
The main reason that tonsils grow, regardless of their location, is inflammation of a bacterial nature. In most cases, it is caused by streptococci and staphylococci.
Healthy tonsils in a child: photo (right)
Large tonsils are usually observed after a sore throat, that is, an acute inflammatory process. If treatment is not carried out correctly or is not completed, microorganisms can develop resistance to the drugs used and continue to infect the tissues of the oral cavity.
Thus, after the disease, chronic tonsillitis gradually begins to develop, which is the main cause of hypertrophy of the tonsils.
Coping with it completely is far from easy, and in severe cases, only timely surgery can protect the body from the occurrence of severe and life-threatening complications.
However, sometimes the cause of swollen tonsils can be infectious diseases such as:
- diphtheria;
- scarlet fever;
- typhoid fever;
- ARVI.
Also in children, the pharyngeal tonsil often enlarges. If it has grown, doctors diagnose adenoiditis.
This disease is in most cases first diagnosed in children at 2 or 3 years of age. But, unlike damage to the tonsils, adenoids often arise against the background of endocrine or autoimmune disorders.
The following can also trigger the development of the disease:
- poor nutrition that does not meet the needs of a growing body for vitamins and other substances;
- unsatisfactory living conditions;
- frequent transmission of infectious diseases.
Treatment of tonsillitis in a child
Treatment of tonsillitis in children is accompanied by bed rest and a diet that is gentle on the irritated throat. The palate must be washed and treated with antiseptics (chlorhexidine, iodinol or Lugol) and decoctions of chamomile, juniper, sage or calendula. Taking into account the nature of the detected microflora, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. Physiotherapeutic procedures help in restoring the body's strength - ultraphonophoresis, ultraviolet irradiation, UHF, laser light beam therapy.
In case of acute inflammation of the tonsils, abscess, the abscesses are opened, and in the chronic form of the disease, tonsillectomy is prescribed - an operation to remove the tonsils.
Pages of history. Currently, tonsolectomy is used as a last resort. In the 70-80s in the USSR, appointments for excision of palatine tonsils were widespread; it was believed that the human body did not need tonsils. Often the operation was a preventive measure: there is no organ in which angina develops, which means there will be no disease in the future.
To improve the protective functions of the child’s body, vitamins, immunomodulators and sanatorium treatment at sea are prescribed. Preventive measures to prevent recurrences of the disease include hardening , antibacterial treatment of the oral cavity and avoiding contact with infected patients.
For conservative treatment of tonsillitis, the doctor may recommend:
- Sanitation of lesions with pus using various antiseptics (rinsing, vacuum aspiration, washing, irrigation);
- General strengthening therapy, including taking multivitamin complexes. Strengthening the immune system is necessary to resist bacterial exposure;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures and herbal medicine;
- Ultrasound therapy;
- Homeopathic treatment;
- Drug therapy twice a year (courses).
It is usually recommended to alternate courses of conservative treatment in order to select the most effective methods that provide a long-term stage of remission. Treatment of chronic tonsillitis involves transferring an exacerbation into remission, but it should be remembered that the signs of the disease will persist.
The use of antibiotics for rinsing in the treatment of chronic tonsillitis is inappropriate, since their local use leads to the growth of flora that will be antibiotic-resistant.
Surgical treatment is necessary for the decompensated form of the disease, if its conservative forms are ineffective. Removal of tonsils is carried out when symptoms of rheumatism, rheumatic carditis are detected, which can cause heart valve defects, peritonsillar abscesses, and frequent sore throats.
If hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils is detected (grade 2-3), and their function is not impaired, the tonsil tissue is only partially removed.
Symptoms
Typically, a red throat with swollen glands is rarely the only sign of problems in the body. In addition to the fact that red veins, a white, gray or yellowish coating appear on them, they also:
- Sore throat when at rest or when swallowing;
- difficulties arise when swallowing, as expanded loose tissues interfere with the free passage of food;
- lethargy and irritability appear;
- lymph nodes enlarge;
- body temperature rises;
- There is a nasal voice.
Depending on the developing infection and the degree of involvement of other organs of the respiratory system, a dry or wet cough may additionally be present. In severe cases, when the tissue is too swollen, breathing difficulties may occur.
As a result, the baby will suffer not only from lack of air, but also from sleep problems, snoring, and fear of suffocation. In such situations, it is necessary to show the child to the doctor as soon as possible and carry out a number of measures to eliminate the swelling.
However, sometimes even against the background of the fact that the child has large tonsils, the inflammatory process can occur without fever or discomfort in the throat. Other signs may be present to a greater or lesser extent, which is not always a positive indicator.
This may indicate the disease has become chronic. Therefore, the tonsils are often enlarged, but do not hurt.
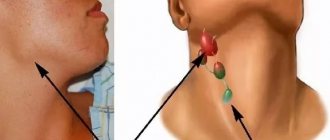
Degrees of tonsil enlargement
Depending on the size of these organs, there are 4 degrees of hypertrophy:
1
The tonsils occupy 1/3 of the space between the edge of the anterior palatine arch and the center line of the pharynx. This position of the organs has virtually no effect on the state of nasal breathing, which may worsen slightly during sleep. Pathology at the 1st stage can be suspected by the slightly open mouth of a child in a dream.
2
The tonsils cover half of the vomer (Located in the nasal cavity). This is accompanied by discomfort while eating and opening the mouth at night.
3
Most of the vomer is covered by one or another enlarged tonsil. Difficulties in swallowing and breathing are typical for this degree of hypertrophy.
4
The affected gland occupies all the free space and completely covers the vomer, and with bilateral damage they can even overlap each other. This is an indication for surgical intervention, since it makes proper nutrition and breathing almost impossible.
Adenoid hypertrophy: treatment
At the first stage of treatment, the doctor determines the tactics - to be treated on an outpatient basis or to prepare for surgical removal. If adenoids interfere with breathing, prevent sleep, cause breathing apnea during sleep, or cause complications - hearing loss, damage to the cardiovascular system, kidneys - consider the possibility of surgery. If there is evidence, you shouldn’t be afraid of her. In case of exacerbation of chronic diseases, in the acute period of infections, blood clotting disorders, severe heart diseases, surgery is contraindicated. We are ready to organize treatment, including surgery, in clinics in St. Petersburg or partner clinics abroad, in Finland, Switzerland, Austria, and accompany patients from the first visit to recovery. Even grade 1 adenoid hypertrophy must be treated. At the second stage of treatment, if conservative methods are indicated, the doctor prescribes drugs - antiviral, antibacterial, antiallergic. Plus, local procedures are carried out to cleanse the nasal cavity of mucus and physiotherapy. It is important to restore the immune function of the adenoids. This is carried out by qualified doctors. You should not interfere with the functioning of the immune system yourself. At the third stage of treatment, the doctor evaluates the effect and adjusts the therapy. Follow the rules:
- avoid provoking factors - cold drinks, dust, air polluted by industrial emissions and tobacco smoke,
- humidify the air and ventilate more often,
- take a walk in the fresh air
- Avoid contact with people with colds.
At the fourth stage of treatment, the doctor determines the frequency of follow-up examinations and studies in order to monitor the condition and notice a relapse in time.
What result should I expect?
- Nasal breathing is normalized,
- Nasal discharge stops,
- Snoring disappears
- The frequency of viral infections is reduced,
- The general condition improves - vigor and energy appear, memory and attention improve.
Prevention of adenoid hypertrophy in children and adults
- Reduce the infectious load,
- Treat ARVI - you should not take a child who has not fully recovered to school or kindergarten,
- Moisturize the nasal cavity with saline solutions,
- Humidify the air in the apartment,
- Ventilate more often
- Give your child enough to drink
- Avoid contact with aggressive substances, including tobacco smoke,
- Strengthen your immune system: less stress and TV and computer, more fresh air and physical activity. Plus proper nutrition.
All these activities improve local immunity, which means they reduce the likelihood of “catching” a virus or bacteria. And then you won’t have to search for “adenoid hypertrophy symptoms and treatment” in a search engine.
Enlarged tonsil on one side
Sometimes one of the two tonsils is enlarged: the left or the right. This is also accompanied by the appearance of a sore throat and redness of the tissues, but if it is enlarged on one side in a child, but the throat does not hurt, this in the vast majority of cases is a clear sign of a chronic infection.
Thus, an enlarged tonsil on one side may indicate the same diseases as listed above, but tonsils of different sizes may also indicate that an injury has been sustained or is forming:
- pharyngeal abscess;
- phlegmon.
Only after a thorough examination is the doctor able to say what it means when the tonsil is enlarged on one side and prescribe treatment appropriate to the situation.
If one tonsil is larger than the other, this more than ever requires examination by a specialist, because the patient may need urgent surgical intervention.
Otherwise, the abscess may rupture and its contents will spill out either into the oral cavity and pharynx, or into the thickness of the tissues. The latter option poses the greatest danger, since this is always fraught with the development of complications, one of which is sepsis.
When should you see a doctor? How dangerous is the pathology?
Swollen tonsils in a child always require timely consultation with a specialist, and if pathologies are detected, full treatment. Indeed, in the absence of competent therapy, a child may develop quite serious health problems:
- the occurrence of disturbances in the structure of the facial bones;
- bite distortion;
- violation of chest development;
- anemia;
- mental retardation (in especially severe cases).
To avoid such sad consequences, it is necessary, when the first signs of tissue proliferation appear, to contact a pediatric otolaryngologist and strictly follow all his recommendations.
You should immediately make an appointment with an ENT specialist if your baby constantly:
- choking while eating;
- breathes through his mouth and snores in his sleep;
- nasal, has problems with pronunciation;
- often catches colds;
- suffers from inattention and fatigue.
How to treat enlarged tonsils in a child?
How to treat pathology depends on the causes of its occurrence. The choice of treatment tactics is determined by the doctor on an individual basis.
In most cases, patients are prescribed:
1
Gargling with antiseptic solutions (Furacilin, Givalex, Angilex, Chlorophyllipt alcohol, Chlorgesidine, Miramistin and others). This measure is necessary to wash away pathogenic microflora from the surface of the mucous membranes.
2
Inhalations. Homeopathic remedies, for example Tonsilgon, or synthetic drugs, in particular Rotokan, Malavit, Dioxidin, can be used as solutions for inhalation therapy. They help eliminate the inflammatory process and swelling of tissues.
3
Antibiotics for topical use (Polydex, Isofra, Rinil) are prescribed if the bacterial nature of the disease is confirmed.
4
Systemic antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Vilprafen, Sumamed, Ospamox, Flemoxin Solutab, Tetracycline, Doxy-M) are used when topical drugs are ineffective in especially severe cases.
5
Corticosteroids. Drugs in this group are indicated when a child’s tonsils are very enlarged; treatment is carried out under the supervision of a specialist, and its duration usually does not exceed a week. However, in particularly severe cases, a longer period of time – up to several months – may be required.
6
Homeopathic remedies (Umkalor, Tonsilgon) are used to increase immunity.
For tonsillitis accompanied by the formation of purulent plugs, rinsing the tonsils with antiseptic solutions in an ENT office is often prescribed. The procedure can be performed on different devices and usually requires at least 10 sessions to achieve positive results.
Measures to help with hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils
Grade 1 does not require special treatment . For prevention, periodic rinsing with a warm solution of chamomile, sage or baking soda and maintaining oral hygiene will not hurt. We need to try to increase the child’s immunity and make him healthier in a sea or mountain climate.
Hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils of the 2nd degree in a child requires close attention. It is necessary to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations to prevent even greater pathology. Usually the doctor prescribes gargling with antiseptic solutions and lubricating the tonsils with cauterizing solutions. To prevent inflammation, lubricating the nasopharyngeal mucosa . Often, the doctor recommends tonsil rinsing procedures, which are performed in the clinic. Today, innovations include vacuum washing of the tonsils. It is not available everywhere, but it is very effective and the procedure is easily tolerated by the child.
Grade 3 requires an integrated approach, which may include both conservative and surgical treatment. Conservative treatment includes not only locally applied drugs, but also internal anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as physical therapy.
interruptions in breathing occur due to contact of the tonsils , a tonsillectomy may be recommended, in which part of the tonsil tissue is surgically removed under local anesthesia. It is usually carried out when the child is 5–7 years old.
Treatment of enlarged tonsils in children with folk remedies
As an addition to the main therapy, the otolaryngologist may recommend the use of traditional medicine.
In many situations, they give good results and help the growing body recover faster, but it is usually not possible to completely cure the disease with their help.
But before the first use, you must make sure that your baby is not allergic to the selected components. After all, children are more prone to developing allergic reactions than adults.
To cope with the problem, you can use:
1
Propolis tincture. 20 g of beekeeping product is finely ground and added to 100 ml of vodka. After 3 days they begin to use it for gargling. Procedures should be carried out before meals. The tincture has an antiseptic and wound-healing effect.
2
A mixture of sugar and lemon juice. Mix 20 ml of juice and 20 g of granulated sugar in a glass container. Take it three times a day to strengthen the immune system.
3
A decoction of sage leaves with garlic. The raw materials are crushed and poured with a liter of boiling water. Place the container in a steam bath and leave for 25 minutes. The finished product is left to infuse and filtered after 45 minutes. Take it 50 ml three times a day or use it for rinsing.
4
Sea buckthorn oil. It has pronounced anti-inflammatory, regenerating and immunostimulating properties. It is recommended to consume 1 teaspoon daily. During ingestion, it is possible to lubricate almost all areas of the tonsils, which helps reduce unpleasant symptoms and accelerate the elimination of inflammation.
Why does overgrowth occur?
The first line of human defense against harmful bacteria and viruses are the tonsils and adenoids. With their help, the body prevents uninvited guests from entering the respiratory tract, develops immune memory and thus learns to defeat subsequent infectious attacks.
In addition, the lymphoid cells of the tonsils perform another function, no less important for the human body - hematopoietic. They serve as suppliers of lymphocytes to the bloodstream.
One of the six that a person has - the paired tonsils - can be easily seen in a mirror if you open your mouth wide. They are located on the sides of the pharynx and are usually medium in size. Although in some people anatomically they can be quite large and even extend beyond the arches of the pharynx.
Tonsil hypertrophy in children is a pathological situation when the tonsil tissue grows excessively. Typically, hypertrophy is a non-inflammatory process. In adults, large, loose tonsils mean that there is an old inflammatory process - chronic tonsillitis.
It is still not known for certain what is the trigger for the uncontrolled growth of cells in the palatine tonsils. They only talk about the obvious relationship between tonsil hypertrophy in children and certain risk factors. This:
- quite frequent infectious viral diseases - not only of the child himself, but also of the mother during the gestation period;
- unfavorable birth;
- frequent hypothermia of tonsil tissue, etc.
You should also not discount the general environmental situation and hereditary predisposition.
At the same time, regression of the disease is possible. When, against the background of trained immunity and rare respiratory viral diseases, the tonsils gradually take on their previous size.
Enlarged tonsils in a child: treatment by Komarovsky. Recommendations
Dr. Evgeny Olegovich Komarovsky recommends treating inflamed tonsils in a child under the supervision of a pediatrician or ENT specialist. As for what parents should do before visiting the doctor, he advises:
- bed rest if the baby is weak;
- drinking plenty of water;
- regular ventilation of the nursery and wet cleaning;
- for fever, give paracetamol and ibuprofen.
In case of chronic inflammatory processes, the doctor recommends, in the absence of exacerbations, in moderate quantities, but regularly give the baby ice cream, cold drinks, etc. This helps to harden the body and “train” the tonsils.
Symptoms
Inflammation of the tonsils occurs in many diseases. Each of them has its own specific symptoms.
But there are general signs characteristic of damage to the tonsils:
- Bad breath. Small pieces of food are retained on loose lymphoid tissues. They begin to decompose, causing an unpleasant odor. For babies with tonsil hypertrophy, it is important to gargle regularly to flush out any leftover food.
- Pain. The inflammatory process in the throat is often accompanied by painful sensations that intensify when swallowing.
- Changes in the structure and color of the tonsils. Lymphoid tissue turns from pink to red. In a healthy state it is smooth, but when inflamed it becomes loose (bumps appear on its surface). A white coating may also appear.
- Weakness. It is provoked by intoxication of the body associated with the entry of a virus into it.
- Headache. They are provoked by the onset of swelling of the mucous membrane and difficulty breathing.
It is possible to increase body temperature either slightly (up to 37.5°) or up to 39°.
When the first symptoms appear, consult a pediatrician or ENT specialist. Self-medication can harm your child's health.
How to reduce tonsils in a child without surgery?
For chronic diseases, physiotherapy is indicated. As part of this, patients are often prescribed ultrasound treatment. This method is considered highly effective and can often reduce the severity of hyperemia and avoid surgical intervention.
Ultrasound treatment of tonsils in a child allows:
- cleanse them of accumulations of pus;
- reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process;
- accelerate tissue regeneration.
Magnetic therapy is also indicated. The essence of the method is the influence of a magnetic field, which achieves:
- anesthetic;
- anti-inflammatory;
- bacteriostatic;
- sedative effect.
Treatment
The variability of treatment for large tonsils in a child depends on the severity and degree of development of the disease.
Stage 1 therapy
In the case of initial stage I, no special treatment is required. It is enough to gargle periodically, once a week, adding salt, furatsilin tablets or baking soda to the water and using herbal decoctions.
If there are problems with nasal breathing, they must be eliminated. It is especially important to do this in cold weather. For one of the prerequisites for the occurrence of loose tonsils in a child is their hypothermia, which occurs when breathing through the mouth.
Mountain and sea air are healing.
Stage 2 treatment methods
Treatment of grade 2 hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils combines an impressive complex of special drugs and procedures. The goal of treatment is to prevent the disease from developing into an even more dangerous stage.
The doctor may prescribe lubrication of the tonsils and mucous membrane of the nasopharynx with anti-inflammatory and astringent drugs. As well as frequent rinsing with antiseptic solutions. Procedures can be either daily or course-based. For example, lubrication with Karotolin every day, before bed, every day, and with Collargol 3% according to the “2-3 weeks - month of rest” scheme.
If necessary, drug therapy can be enhanced by the administration of immune system stimulants, such as IRS-19, Lysobact or Imudon.
If the underlying disease is accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membranes, allergic rhinitis, adenoiditis or sinusitis, hormonal steroid drugs (topical corticosteroids) in the form of sprays - Avamis or Nasonex - are justifiably prescribed.
Another option for how to reduce tonsils in a child without surgery is hardware physiotherapeutic treatment methods. Most Popular:
- inhalations based on mineralized water,
- mud applications-compresses for the submandibular area,
- phono- and electrophoresis,
- ultrasound, microwave, laser therapy
- ozone, balneotherapy,
- tube-quartz and others.
In case of ineffectiveness of conservative treatment and the presence of threatening conditions with hypertrophy II and passing into III degree, when the baby has difficulty breathing and swallowing, surgical intervention is recommended. The child's overgrown, loose tonsils are partially removed and a tonsillotomy is performed. In some cases they can be removed completely.
It should be noted that the tissue of this organ of the immune system is capable of self-healing and even after conditionally complete removal it can grow again after some time.
Should I delete it and when?
The operation is performed only at the last stages of disease progression, when the tonsils have long been large, conservative therapy does not produce results, and exacerbations are observed more than 5 times a year. Also indications for surgical intervention may be:
- severe difficulty breathing;
- formation of abscesses, phlegmon, peritonsillar abscess;
- development of allergies;
- the occurrence of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, joints.
If the palatine tonsils are affected, a tonsillectomy is performed. Often, swollen tonsils in a child are removed with a laser, although other methods can be used.
However, doctors usually try to delay the operation as much as possible in order to save the organs. Indeed, in many situations, as you grow older, the severity of the problem decreases, and the need for surgical intervention disappears.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Breathe deeply, sing, run, have fun - it’s so natural for a baby. It is worth being wary even when he is constantly bothered by a runny nose and a nasal voice.
First symptoms to see a doctor
Signs confirming changes in the tissue organs of the tonsils:
- change in voice, the child speaks through his nose;
- mouth breathing;
- night snoring.
List of symptoms of the inflammatory process in the tonsils and adenoids
There are a number of general indicators that indicate damage to the tonsils and adenoids.
- Sore throat and constant nasal congestion.
- Frequent spontaneous sneezing.
- Nasal voice.
- Low-grade fever and severe sweating during sleep.
- Grinding of teeth in sleep and profuse salivation.
- Frequent otitis and tonsillitis.
Diagnosis of the disease
Any diagnosis begins with an examination. The doctor interviews the patient, makes a superficial examination of the nasopharynx, determines whether there is an inflammatory process, whether there is an enlargement of the tonsils, and diagnoses the condition of the adenoids. If necessary, gives the patient a referral for tests or prescribes an instrumental diagnostic method if there is a suspicion of a serious pathology.
Instrumental methods include:
- Pharyngoscopy.
- Fiberendoscopy.
- Ultrasound of the larynx.
Exclusion of other pathologies is very important for correct treatment of the underlying diagnosis.
Therefore, if a doctor recommends tonsil removal for a child, you should weigh everything first. Hypertrophy of the tonsils in children by adolescence can decrease naturally, since as the child grows up, the growth of lymphoid tissue stops, and it even atrophies.