Causes and symptoms of the disease
Pericoronitis is caused by the proliferation of bacteria in the air space between the gum and the crown of the erupting tooth. A moist environment remains under the swollen gum, which promotes the activation of the infectious process.
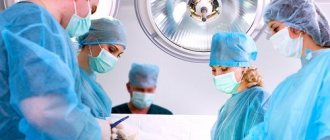
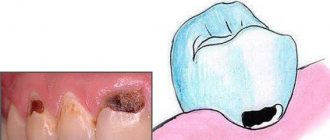
This is what surgical treatment of pericoronitis looks like
Pericoronitis of traumatic origin is less commonly diagnosed. For example, if the antagonist tooth has already erupted, it can irritate the exposed gum during chewing.
Having understood what pericoronitis is, it is necessary to study the symptoms. The most common signs of pathology:
- redness of the gums in the area of the erupting tooth;
- aching pain that spreads to the temporomandibular joint;
- high temperature (if the infection was not stopped at an early stage);
- bad breath.
The intensity of negative sensations directly depends on the degree of infection of the gum tissue.
What is pericoronitis
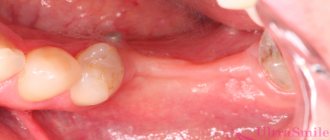
Pericoronitis is an inflammation of the gum tissue around the wisdom tooth.
It is most often observed on the tissues around the figure eights on the lower jaw. It develops after a tooth partially cuts through the gum. If the growth process slows down, bacteria accumulate around the emerging piece of tooth, causing infection and inflammation of the gums. The process can spread to the cheeks and neck. The development of the disease is complicated by food debris that forms plaque on the surface of the tooth. Plaque can accumulate under the gum tissue and it simply won’t be possible to clean it. While eating, the gums become injured and swell, and inflammation of the gingival margin begins.
If teething is difficult, the figure eight will put pressure on neighboring teeth, damaging both soft tissue and bone. The reasons for such complications can be different - from incorrect position of tooth roots to thickening of the mucous membrane, which does not allow the tooth to erupt.
Acute pericoronitis
Acute pericoronitis (also called serous) is characterized by pain that worsens with chewing. If you ignore the disease, painful sensations will occur with every movement of the jaw. Palpation of the gums may result in bleeding.
In the acute form, the pain intensifies during chewing
With the least pressure on the area of the erupting tooth, pulsation appears. When applying local anesthetics, as well as after drainage, the pain goes away. But relapses occur until the tooth completely erupts.
Chronic
The chronic form of pericoronitis is diagnosed in patients who chose to “endure” the pain that appeared during teething. The most pronounced symptoms of this stage of the disease are:
- periodic non-sharp pain;
- halitosis;
- closed abscesses.
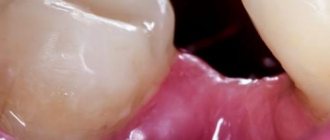
During the examination, the dentist may see that the semi-erupted tooth is covered with a sensitive, erythematous, swollen hood. A typical sign of the chronic form of the disease is unilateral pharyngitis.
Forms
There are several varieties of this disease, which differ depending on many factors - severity of manifestation, localization, complexity of development, and so on. It is worth talking in more detail about each of them.
Catarrhal
In fact, it is the catarrhal form that is the beginning of the disease . If left untreated, it can develop into a more complex form, which can lead to various complications.
The clinical picture of catarrhal pericoronitis is characterized by almost all the main symptoms, except for the appearance of pus. However, they appear in a fairly mild form .
This is precisely the main danger. Due to the mildness of symptomatic manifestations, patients rarely immediately seek help from a specialist. Accordingly, treatment does not begin on time, and the disease becomes more serious.
Ulcerative
A characteristic feature of this form of the disease is an ulcerative-necrotic process in inflamed tissues . It is caused by certain types of anaerobic bacteria. The most striking manifestation is that an ulcerative rim appears along the edge of the gum.
Bleeding of soft tissues in this area increases if the characteristic plaque is removed from the gums. This form involves the use of only conservative treatment without surgery .
Retromolar
In some cases, when the purulent focus is hidden, the outflow of exudate becomes difficult. It accumulates in the soft tissues, and the inflammation spreads further deeper, affecting the periosteum of the retromolar fossa . Then an abscess begins to form there.
This whole process, in fact, is a complicated form of this disease and has another name - retromolar periostitis. Its symptoms are much more pronounced than with other forms, and are very similar to the manifestations of the purulent acute form of pericoronitis.
The body temperature rises in some cases to almost 39°C, and the pain becomes almost unbearable.
The swelling in the gum area spreads to the adjacent areas and becomes very severe. In the area located at the end of the jaw, when you press on it, an infiltrate may be detected.
Spicy
In addition to fairly pronounced characteristic symptoms, the acute form may be accompanied by associated problems:
- Clinical manifestations develop very quickly.
- From general discomfort in this area and aching pain in just 2-3 days, the pain becomes acute.
- At the same time, a slowly oozing exudate appears.
It is acute pericoronitis that, in the absence of immediate treatment, can quite easily turn into recurrent and chronic forms .
What are the specifics of chronic fibrous periodontitis? What is the main danger?
Read here about ways to treat gingivitis in pregnant women at home.
In this article https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/desnyi/sposobyi-v-domashnih-usloviyah.html we will talk about the effectiveness of gum treatment with folk remedies.
Purulent subacute isolated
In this case, this disease occurs in a chronic form , which occurs due to lack of treatment in the acute stage.
It is characterized by periodic attenuation of inflammatory processes , which subsequently reappear. When pressing on the site of inflammation, in most cases exudate begins to appear from under the gum fold.
In addition to the gum itself, inflammation spreads to the cheek, palatoglossal arch and palate. This provokes not only quite severe pain, which increases while eating, but also difficulty opening the mouth and swallowing.
This is also accompanied by resorption of bone tissue in the area of inflammation. Due to a decrease in bone density, loosening of the causative tooth and the adjacent tooth may also occur .
Pericoronitis of wisdom teeth
With pericoronaritis "figure eight" intense pain appears in the tonsils and ears. The symptoms are practically no different from the acute form of the disease. However, the erythema may spread towards the pharynx.
Pain may radiate to the throat, temple, ear
There is also discharge of pus during palpation and an enlargement of the submandibular lymph node.
How is pericoronitis differentiated?
Disease code according to the International Classification of Diseases: K05.3 (chronic form). Periodontitis also belongs to this group. The primary task of the attending physician is to differentiate pericoronitis from other diseases with similar symptoms.
For diagnosis, it is enough to take an x-ray of the pathological area. If the image shows an impacted tooth, then classic gum inflammation is excluded.
Treatment of pericoronitis
When developing a therapy program, the doctor must take into account the degree of inflammation and the volume of affected areas. Conservative treatment includes:
- use of antimicrobial drugs, analgesics;
- anti-inflammatory applications;
- washing with antiseptic solutions.
In later stages, dental pericoronitis is treated surgically. Most often, excision or complete removal of the hood is performed.
This is what the hood looks like
Therapy aimed at preserving the tooth
To avoid removing impacted teeth, it is recommended to thoroughly clean the area under the hood. To prevent the spread of infection, it is necessary to use mouthwashes that contain chlorhexidine daily.
The dentist can clean the problem area using a irrigator. If it is noticed that pus has begun to accumulate under the hood, antibiotics are additionally prescribed.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment methods will help eliminate pain and prevent the development of a chronic form of the disease. Most often, dentists prescribe:
- quartzing;
- treatment of the affected area with microcurrents;
- laser treatment of tissue.
It should be borne in mind that undergoing physical therapy does not replace the use of prescribed medications, as well as daily oral hygiene.
In some situations it is better to remove the tooth
Are traditional methods of treatment effective?
Some patients prefer traditional methods to official medicine. In particular, healers recommend rinsing with oak bark and chamomile decoction. Dentists warn that traditional recipes, like physical therapy, will help temporarily eliminate unfavorable symptoms. You should not refuse to use medications prescribed by your doctor.
Excision of the hood for pericoronitis
If regular rinsing and drainage of the affected area does not produce positive results, then excess tissue is excised above the impacted tooth. Surgical manipulation is performed under local anesthesia with a scalpel or laser.
Bleeding may occur after the procedure. Some patients experience gum regrowth.
How to treat
Treatment begins with removing the inflammation. The mucous membrane covering the dental crown is excised to make it easier for the figure eight to emerge. After the inflammation has passed, you can assess the condition of the tooth itself. If the mucous membrane has returned to normal, there is enough free space in the dentition and the bite is not disturbed, the tooth can be left alone.
If the position of the figure eight is incorrect, it cannot be preserved: the position of the root will not change, and growth “in the wrong direction” will provoke new inflammations endlessly, worsening the condition of neighboring teeth. A wisdom tooth located in the gum will have to be removed surgically.
Some dentists offer laser treatment: a beam through the skin affects inflammation, while an infrared laser has anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effects. After the procedure, microcirculation improves, tissues are filled with oxygen and pain is completely relieved. This treatment will take up to ten days, the procedures will need to be repeated daily until acute pericoronitis passes.
Complications of pericoronitis
Do not ignore painful symptoms and prescribed treatment. The progression of the disease is indicated by the appearance of pain when chewing, swallowing or opening the mouth wide. The patient may also notice the appearance of swelling.
Untreated infection spreads to the lymph nodes of the neck and tonsils. Chronic pericoronitis is often complicated by:
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis;
- pharyngitis;
- hyperplasia of the tonsils;
- tonsillitis.
Pericoronitis can be treated non-surgically. You should not ignore the dentist’s recommendations, because in the early stages you can get rid of the disease using conservative methods.
ethnoscience
Some people try to get rid of the inflammation that accompanies tooth growth at home using various rinses and baths.
Dentists categorically do not recommend doing this. The fact is that it is impossible to completely get rid of plaque and pathogenic microorganisms present in the gum pocket on your own.
Lack of timely treatment can lead to the accumulation of purulent contents in the soft tissues and the occurrence of complications, which can only be eliminated through surgery.