Changing teeth is an important event for both the child and his parents. It is not surprising that many questions arise regarding whether this process is proceeding correctly, and how to understand that it is broken.
One of the most common causes of concern is an empty tooth in a child - a fallen baby tooth is not filled with anything from the inside and looks “unhealthy”.
The tooth hurts, but there is no caries: what to do, causes and treatment
Various problems with teeth are familiar to everyone, and even a person who understands little about dentistry can roughly determine what is associated with this or that ailment. We usually go to the dentist with specific complaints: caries, tooth breakage, increased sensitivity, but sometimes we cannot independently determine the cause. It happens that a person’s entire tooth begins to hurt or immediately after treatment. What to do when a tooth hurts, but there is no caries? What reasons can cause discomfort and unpleasant sensations?
Causes of toothache in the absence of caries
Toothache in the absence of visible reasons is a common practice; the reasons for this can be related both to the oral cavity and to other human organs and systems, because, as you know, everything in our body is interconnected. Before identifying and treating the cause of the pain, the dentist will determine whether the tooth has been treated. This greatly influences further measures.
Complications after treatment
Most often, pain in a supposedly healthy tooth is treated some time after treatment of that same tooth. Sometimes it only takes a couple of days for the patient to return to the dentist, and for some, the tooth begins to hurt only after a while. In the first case, the pain is often residual. This happens especially often after nerve removal. The anesthesia wears off and the tooth begins to ache. To eliminate such pain, it is enough to take special medications, and dentists simply recommend to endure it. In some cases, pain after treatment may be caused by a relapse of the disease or an error at certain stages of treatment. Relapses quite often occur after treatment of deep caries. In this case, the disease is already approaching the nerve endings of the tooth and can easily damage them. When a relapse occurs, the tooth invariably begins to hurt. Dentists are people just like you and me, and they are also not immune to mistakes. True, their mistakes can result in severe aching pain for the patient. If there were errors at any stage of treatment or filling, they will sooner or later make themselves felt. For example, if, after removing the nerve, the tooth root was not closed with special gutta-percha pins, the filling material gets into the soft tissue, the body rejects it as a foreign object and inflammation begins.
Another common mistake is using a low-quality filling compound, which may leave voids inside when it dries. Bacteria develop in them, which soon affect the nerve endings. One of the few causes of toothache after treatment is an allergic reaction to the composition. It is quite rare, and it is almost impossible to find pathologies at the treatment stage. That's why pain occurs. When you go to a specialist, they will simply replace the filling with a composition with other components, or make a ceramic filling. If a tooth hurts, but there is no caries, and it was cured relatively recently, the reasons are more or less clear. However, pain can also occur in the teeth, with complaints about which the patient has never consulted a dentist. This is usually associated with various diseases of the dental system.
Diseases of the dental system
• Caries. Even if you do not see a carious cavity on your teeth, this does not mean that it does not exist. The disease does not have to occur only in the visible area; it can also develop near the gums. It is most difficult to notice such caries if it occurs on a chewing tooth. What is most remarkable is that with this development of the disease, pain begins to appear first of all. Caries is located as close as possible to the nerve endings.
• Increased sensitivity of enamel. This disease can be either congenital or caused by mechanical damage to the enamel. Sensitivity can be distinguished by a sharp reaction to cold or hot. Then the aching pain sharply develops into acute pain. Increased tooth sensitivity can affect only one tooth, for example, after recent treatment of neighboring ones. Then the dentist, through negligence, could damage its enamel, a natural defense against external irritants.
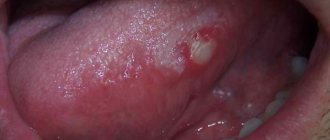
• Gum inflammation. The problem is usually accompanied by bleeding, redness and increased sensitivity to temperature changes. There may be additional symptoms such as fever and general malaise. However, despite all this, it is not always possible to identify the exact cause of pain on your own. The gums sometimes become inflamed in places where they are invisible to the patient. The causes of gum inflammation can be external damage, and this problem is often a symptom of a number of oral diseases.
• Tooth cyst. You will definitely not be able to identify such a disease on your own. This requires an x-ray examination. The cyst occurs in the area of the tooth root. It is a round cavity filled with fluid, resembling pus. The reason for the appearance of a cyst is an infection in the soft tissues, and for this it is not even necessary that the tooth near which it develops be damaged. The most interesting thing is that before the first symptoms in the form of pain, you could have had a cyst for more than one year. Pain appears only when the cavity is already of impressive size and begins to affect the nerve endings. We have listed the most common problems, but all of them are associated only with specific diseases of the dental system, and sometimes such pain occurs for reasons not related to dentistry. Other reasons
• Neurology of the trigeminal nerve. The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the cranial nerves. It is directly connected to the nerve endings in the teeth, so if it is damaged, the pain can spread to the oral cavity. The patient will think that his teeth hurt, although the reason is far from them.
• Migraine. Migraine is a neurological disease accompanied by periodic acute headaches. For those who have not encountered it before, it is quite difficult to classify the disease. During sudden attacks there is a feeling that not only the head hurts, but also specific teeth. Not finding a connection between these symptoms, patients turn to the dentist. If he does not find it, make an accurate diagnosis.
• Inflammation of the middle ear. Otitis media is often accompanied by pain in the chewing teeth. The pain resembles the symptoms of deep caries, or even pulpitis. It is aching, but with any irritation it becomes acute. Immediately after complete treatment of otitis media, additional symptoms will disappear.
• Sinusitis. The roots of the teeth of the upper jaw are connected to the paranasal sinus, so when inflammation of sinusitis occurs, a feeling of toothache appears. The most interesting thing is that inflammation of sinusitis can really lead to further problems with teeth, because it is one of the causes of cysts in the smile area.
Causes of pain
If a tooth is sore, if the patient assumes that there is no caries, it is worth starting to look for the cause with the tooth. Upon examination you can identify:
- non-carious infection. Tooth structure can wear down, which in turn causes pain, which usually occurs when eating sweet or sour foods, brushing teeth, or touching dental appliances. Significant tissue loss leads to pulpitis with prolonged reactions to provoking factors;
- pulpitis. Forms on teeth that have not received timely treatment for caries. To identify a problematic tooth, hardware methods are used. Pulpitis can spread under the filling, which also eliminates visible symptoms. Inflammatory reactions manifest themselves in the form of spontaneous pain. The chronic condition is characterized by acute and aching pain;
Pulpitis
- Periodontitis is a disease of the gums that causes the appearance of gum pockets and overhanging gums. This phenomenon increases the sensitivity of the teeth, and sometimes pain is felt when biting. Gum pathology in many cases is caused by caries or non-carious causes that increase pain;
- periodontitis – damage to the root of the tooth. It can even appear on teeth that visually appear healthy. It is also possible that it may appear on perfectly healthy teeth after damage or in the event of a cyst developing. This process is characterized by pain when biting, which can worsen and spread to nearby teeth;
- periodontal disease is a phenomenon in which there is no caries and other inflammatory processes. The first symptom is pain from eating too hot or cold;
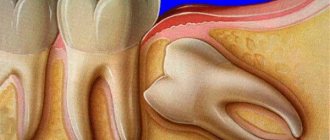
- retained wisdom tooth. Horizontally located “eights” cannot come out, putting pressure on nearby teeth, causing unpleasant pain. Delayed teething often causes inflammation on top of the gum;
When wisdom teeth erupt, a person may experience severe discomfort.
- gingivitis. It manifests itself as pain in one or several teeth at once, sometimes worsening as a result of suppuration in periodontal pockets. The tooth begins to loosen, and an unpleasant odor appears from the mouth. The mucous membrane becomes red and may bleed and swell. This disease occurs when oral hygiene is not observed, the immune system is weakened, or the gums are damaged. It can be treated with anti-inflammatory medications prescribed by your dentist. Preventive measures include regular oral hygiene. Pain is felt when exposed to a mechanical, chemical or temperature stimulus. It appears quickly and ends just as quickly. The pain can spread to several teeth at once or affect only one specific one. Pain may occur during pregnancy due to a viral infection;
- increased sensitivity of enamel. This phenomenon can be congenital or acquired as a result of mechanical trauma to the enamel. Sensitivity can be recognized by the sharp pain that occurs when consuming hot and cold food or liquid. In this case, the pain becomes acute. This problem, as a rule, affects only one specific tooth, for example, after treatment of a nearby one. In this case, the doctor could accidentally damage the enamel, which protects against irritants;
Increased sensitivity of enamel
- tooth cyst Accompanied by aching pain, often worsening when eating hot food or from touching. A pus ball forms near the root area. At first he doesn't show any warning signs. Can be detected by X-ray examination. Surgery causes an increase in body temperature and swelling of the mucous membrane. The main thing is to contact your dentist in time to prevent serious complications.
Important ! If no results were obtained during a detailed examination, it is worth paying attention to neighboring areas of the oral cavity.
Toothache is felt when:
- salivary stone disease;
- otitis;
- sinusitis;
- gum tumors
Salivary stone disease
Video - Causes of periodontal disease and periodontitis
Relieving pain at home
The most correct decision on your part in case of toothache is to make an appointment with the dentist at your next appointment. As you already understand, almost all causes of toothache without caries are associated with quite serious diseases of the dental system. While you wait for your appointment with the dentist, you can only help yourself endure the pain. First of all, painkillers are needed for this. Since pain is often accompanied by inflammation, it is best to select painkillers that will also combat additional symptoms; Nurofen and other analgesic tablets are excellent for this.
Pain in the teeth - the root cause of which was diseases of other organs
Quite often, the patient thinks that the tooth hurts, but in fact it is a disease of adjacent organs. Pain similar to a toothache can be caused by:
- Paranasal sinuses;
- Pharynx;
- Cervical vertebrae;
- Hearing organs;
- Diseases of the heart, blood vessels, etc.
Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear that almost always radiates to the back of the lower and upper jaw. Another unpleasant, but unfortunately quite common disease is sinusitis, also characterized by toothache. If there are complaints of discomfort in the lower jaw on the left side, we can assume that the cause is the development of angina, which is a harbinger of an acute heart attack. An inconspicuous, but slightly unpleasant feeling of dry mouth is the first sign of the onset of sialolithiasis. As they develop, the stones begin to block the flow of saliva, after which swelling appears in the area under the jaw, and it feels like a toothache.
Professional treatment of the cause of pain
When you go to the dentist, the first thing you will do is a thorough examination and medical history. If external causes of pain cannot be identified, an x-ray examination is performed. During this procedure, a cyst can be identified. In the event that the pain is caused by complications or errors from a recent illness, treatment of its causes will be most simple. In most cases, the old filling is simply removed from the tooth, a new treatment is performed, and the restoration is repeated.
Deep caries that occurs in the gum area is cured in much the same way. The dentist removes the affected tissue and then places a filling. The longest treatment awaits you if the pain is due to increased sensitivity. The dentist will apply a special mineralizing composition to the affected teeth, and then everything depends on you. The period of enamel restoration can take up to several months, but it will still not be possible to restore it to its original state. The cyst is usually removed surgically. The most common type of disease is cystectomy or cystotomy. In both cases, the dentist makes an incision at the front of the gum and removes the accumulated pus from the cavity. Only with cystectomy of a tooth cyst is the damaged soft tissue completely removed, and then a part of the root is also resectioned. It turns out that after such an operation there are no tissues affected by the cyst and the disease will definitely not arise again. If the pain is caused by neurology, the dentist will simply send you to the appropriate specialist, and he will deal with the treatment.
Painless dental treatment in a modern dental center
Whatever the nature and type of pain, the sooner you seek help from a specialist, the faster the problem will be solved. A qualified dentist will conduct all the necessary research and, using modern methods and technologies, will relieve you of unpleasant sensations completely painlessly. If the cause is a disease of other organs, an experienced doctor will definitely refer you to the appropriate specialists to treat the root cause. After using the dental implantation service, sometimes pain may also occur in the neighboring incisors. This may occur due to the adaptation of the “new” tooth and its pressure on the adjacent incisors. This feeling may soon pass, however, it would still be a good idea to visit a doctor. Pay attention to the condition of your oral cavity, and do not be afraid to consult a specialist. After all, timely treatment in most cases always has a positive result, lasts much faster and will significantly save the amount of money it will require!
Why is there a problem?
A seemingly healthy tooth at first glance may already be affected by caries. This pathology first destroys the enamel, and only then “gets” to the hard bone tissue. It seems to the patient that a healthy tooth hurts (after all, there is no hole on it yet), but this is not so.
First, on the affected unit, “thanks to” the pathogenic microflora that lives in the oral cavity, a dark spot appears, which only after some time will turn into “full-fledged” caries and lead to the appearance of a more pronounced pain syndrome. Odontogenic sinusitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses due to secondary infection during dental treatment) also causes pain in visually healthy teeth.
Another explanation for why a healthy tooth hurts is increased sensitivity of the enamel. Dentin, located under the tooth enamel, contains many nerve endings. This means that when the protective layer of the tooth becomes thinner, it becomes susceptible to hot, cold, and rough foods.
There are many reasons why enamel becomes sensitive:
- unbalanced diet;
- hormonal changes in the body;
- poor quality oral care;
- problems with the nervous system.
Why do teeth that do not have carious lesions still hurt: the cause of discomfort can be a cyst - a benign neoplasm located on the gum. A cyst occurs due to the increased activity of pathogenic microorganisms that live en masse in the oral cavity.
The main danger of such a tumor is that it grows rapidly. Pain from a cyst usually occurs when pressure is applied (and then only when the formation reaches a significant size). Among the reasons for the appearance of this neoplasm it is worth noting:
- poorly treated caries;
- partial filling of dental canals;
- pulpitis.
Gingivitis (inflammation of the gums near the front or chewing tooth) is another explanation for the appearance of pain. Additional symptoms: the “affected” unit staggers, when biting on it there is an acute piercing pain, the gums themselves are swollen, hyperemic, there is bad breath, and when brushing your teeth, blood may be found on the brush.
Gingivitis is caused by improper oral care, trauma to soft tissues from dental stones, vitamin deficiency, immune failure, endocrine disorders and other dental and non-odontogenic pathologies. If there is no caries, but the tooth hurts, it may be a consequence of a migraine - in this case, the nature of the pain is pulsating, it occurs at the same time as a headache and goes away after taking painkillers.
Trigeminal neuralgia is another well-known “provocateur” of tooth and jaw pain. This disease can be the result of injury, inflammation, muscle spasm and a host of other problems. In this case, it is not the dentist who can help the patient, but an experienced neurologist.
Cysts, fistulas, gumboils and other purulent-inflammatory lesions of the soft tissues of the oral cavity can cause pain in healthy teeth. Toothache can accompany the course of sinusitis in a child or adult patient. This ENT disease is an acute or chronic inflammatory process localized in the maxillary (maxillary) sinuses.
It is noteworthy that there is also the so-called odontogenic sinusitis, which develops as a result of infection falling into the sinuses during dental treatment. The list of classic signs of this pathology includes: impaired nasal breathing, headaches, if the process occurs in an acute form - increased body temperature, nasal congestion. The combination of these symptoms is a reason to seek advice from an ENT doctor.
Dull pain in a tooth: why it appeared and how to quickly remove it
Practice shows that dull pain in a tooth does not cause much concern for the patient, especially if it occurs periodically and not very often. But this symptom always indicates the presence of a dental problem that must be addressed without delay. Otherwise, the development of complications and the need for lengthy and expensive treatment is only a matter of time.
Causes and associated symptoms
The pain, which can be described as dull and aching, can occur for a number of reasons:
- Violations of the integrity of the enamel . The appearance of chips and cracks on the surface of a tooth or caries in the chalk stain stage may go unnoticed by the person himself, especially if the damage is microscopic. But this is the beginning of a pathological process that is gradually gaining momentum. In this case, pain most often occurs when brushing your teeth and rinsing your mouth with cold water - the enamel no longer fully protects the dentin, and it becomes sensitive to cold.
- Enamel hypoplasia . Congenital thinning of the enamel or its abrasion due to malocclusion is the cause of increased tooth sensitivity and dull pain, which develops mainly as a reaction to sour and sweet foods.
- Root granuloma . The formation of a root apex cyst or granuloma may be accompanied by dull pain during chewing food or chewing gum. This symptom most often appears after hypothermia or an acute respiratory viral infection, and after some time goes away on its own. But as the cyst grows, episodes of pain become more frequent and more intense. In addition to pain, slight soreness of the gums, redness and swelling may be observed.
- Allergy . If you have recently undergone dental caries treatment and are then left with a dull, aching pain in a tooth that has been filled, the cause may be an allergy to the materials used by the dentist. In this case, the pain develops 1-2 days after visiting the doctor, and remains at the same level constantly - neither intensifying nor weakening. In addition to pain, other allergy symptoms are often observed - sore throat and nose, excessive nasal discharge, conjunctivitis. These manifestations of immune system hypersensitivity do not necessarily develop simultaneously with pain, and can occur both before and after it.
- Periodotosis or periodontitis . This is a lesion of the tissues of the supporting apparatus of the tooth, in which they become inflamed (periodontitis) or degenerate (periodontitis). In this case, pain is felt in several teeth located nearby, and abnormal mobility may be observed in them. Periodontitis is characterized by redness and swelling of the gums, and periodontal disease, on the contrary, is pallor and a decrease in the size of the gums involved in the pathological process.
A dull pain in a tooth, no matter how insignificant it may seem, is always a symptom of the onset of some pathological process. All the diseases and conditions described above, except allergies, which lead to pain, continue to develop and worsen without treatment, resulting in the loss of one or more teeth.
Intermediate stages between dull pain (the initial stage of the disease) and the need to remove a tooth can be caries, gingivitis, and periostitis.
Allergies to dental materials deserve special attention.
Left unattended, this condition leads to general sensitization of the body - it becomes overly sensitive to various substances that are potentially allergenic.
The result of this can be systemic allergic reactions that are not limited to the runny nose or conjunctivitis. The most serious consequences are considered to be Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock.
Treatment methods
The chosen method of treating pain syndrome is directly dependent on its causes.
- When tooth enamel is damaged or thinned, special restoration materials are applied to the surface of the teeth, which not only “repair” cracks and chips, but also restore the normal level of minerals in the enamel.
- Root granuloma can be treated conservatively only in the very first stages, when it does not yet threaten the tooth and neighboring structures. In this case, systemic immunostimulating treatment, antibiotic therapy, anti-inflammatory and vitamin preparations are used, and physiotherapeutic procedures (UV irradiation, ultrasound therapy, etc.) and gum massage are prescribed. If the granuloma grows rapidly or if conservative methods are ineffective, surgical removal of the cyst and adjacent tissues altered by the pathological process is prescribed.
- Periodontitis requires antibacterial therapy, the use of immunostimulating agents and drugs that improve blood supply to tissues.
- For periodontal disease, treatment is carried out comprehensively, and it begins with identifying the causes of this condition. Since periodontal degeneration is often caused by missing teeth, malocclusions, crowding and other orthodontic conditions, treatment may include bite correction, removal of supernumerary teeth, and replacement of missing teeth.
How to remove dull pain in a tooth
Nise tablets for dull toothache
If it is not possible to see a doctor, and the pain syndrome disrupts the usual rhythm of life and reduces its quality, you should know how to relieve dull pain in a tooth at home:
- Avoid any thermal stress on the tooth. Food and drinks should be heated or cooled to a temperature of 34-37°C, the same condition should be observed when brushing your teeth and rinsing your mouth after eating: water and mouthwash should not be hot or cold.
- Take an analgesic that suits you (Tempalgin, Baralgin, Analgin) or NSAIDs (Ibuklin, Bral, Nimesil, Nise, Aspirin, etc.).
- Carefully remove food debris and soft plaque from your teeth, even if it makes you feel uncomfortable.
- If the pain is localized not in the root of the tooth or pulp (in the depths of the tooth, judging by the sensations), but closer to the crown, you can use local anesthetics based on lidocaine or novocaine (provided that you are not allergic to them).
Loading…
Source: https://vzube.com/tupaya-bol-v-zube.html
Solution
Next, traditional treatment and ways to get rid of pain at home are discussed.
First aid at home
Before visiting the dentist and establishing the cause of the pain syndrome, you can cope with the discomfort at home using proven folk remedies. Thus, it is recommended to rinse the oral cavity with a soda solution (1 tsp of powder/glass of warm water), decoctions, infusions of sage, chamomile, calendula and other herbs with anti-inflammatory properties (1 tbsp of plant material/250 ml of boiling water).
In addition, you can chew a clove of garlic or apply a slice of raw potato to the “affected” tooth. A cold compress applied to the cheek on the “sick” side and rinsing with alcohol are well-known home remedies for aching and throbbing tooth pain.
Professional treatment
What medical measures will be taken depends on the cause of pain in a visually healthy tooth. If the dentist, upon examination, discovers caries or pulpitis, he will remove the affected areas of bone (soft) tooth tissue, fill the canals, install a permanent composite, and, if necessary, perform prosthetics.
If the pain is non-odontogenic, the doctor will refer the patient to an ENT specialist - he will prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and other drugs for sinusitis, local remedies, physiotherapy for the treatment of otitis media - or to a neurologist (the fight against neuralgia involves a whole range of therapeutic measures - from massage to taking antidepressants).
Nature of pain
The following pain characteristics are important for diagnosis:
- appears in response to irritants - mechanical (when cleaning, touching), thermal (cold, hot), chemical (sweet, sour);
- spontaneous - for no apparent reason;
- short-term – passes within 10-15 minutes;
- prolonged pain, difficult to respond to painkillers, often at night, preventing sleep;
- pulling, aching;
- sharp, cutting;
- with irradiation into adjacent teeth, into the teeth of the opposite jaw, along the nerve trunk, into the eye, into the ear;
- without irradiation with a clear sensation of the causative tooth;
- when biting during or without eating.
Why does a tooth without caries hurt?
If a tooth hurts, but, according to the patient, there is no caries, the search for the cause should begin with the tooth itself. In this case you can find:
- After all, caries - quite often carious lesions are located under the enamel, on the contact surfaces of the teeth, below the gum level. All this prevents their detection during visual inspection. Especially if it is carried out without special lighting and tools (that is, at home).
- Pulpitis – on intact (untreated) teeth, the development of pulpitis occurs from undiagnosed caries. Hardware methods are used to recognize the affected tooth. Pulpitis can also develop under a filling, but there will also be no visible changes in the tooth. Inflammation in the pulp makes itself felt by prolonged spontaneous pain. In a chronic process it is aching, in an acute process it is sharp and nocturnal. Read more about pulpitis →
- Non-carious lesions - with erosions, wedge-shaped defects, increased abrasion, complaints are most often associated with the fact that teeth hurt from sweets, sours, from touching with a brush or dental instruments. With significant tissue loss, symptoms of pulpitis appear with a long-term reaction to the stimulus.
- Periodontitis is inflammation of the root of a tooth. It very often happens on apparently healthy teeth with good fillings and previously treated root canals. Also possible on intact teeth after trauma or as a result of the spread of a granuloma (or cyst). Periodontitis is characterized by pain when biting, which during exacerbation becomes severe and radiates to adjacent teeth. Read more about periodontitis →
- Periodontitis is an inflammatory process in the gums that leads to the formation of periodontal pockets and receding gums. As a result, the teeth become sensitive and pain may occur when biting. Gum diseases are often accompanied by root caries and non-carious lesions, which aggravate pain. Read more about periodontitis→
- Periodontal disease is a degenerative process in which there is neither caries nor signs of inflammation. But one of its first signs is that the teeth begin to hurt from temperature irritants. Read more about periodontal disease →
- Impacted (unerupted) wisdom teeth - horizontally located eights do not have the opportunity to erupt, while with their crown part they put pressure on neighboring teeth, causing pain most often in the second molar. The slow growth of figure eights is often accompanied by inflammation of the gums covering them (pericoronitis).
Photo from website: huxfluxdeluxe.wordpress.com/
If a thorough examination does not yield any results, attention should be paid to the areas adjacent to the oral cavity. Tooth pain can occur when:
- sinusitis,
- otitis,
- trigeminal neuralgia,
- salivary stone disease,
- migraine,
- tumors of the jaws.
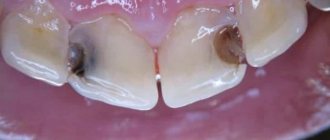
Signs and appearance of teeth with deep caries
The photo below shows internal caries on the tissues under the destroyed enamel. This is a typical type of disease that develops inside the tooth. The dark areas of the affected dentin are clearly visible:
It is the changed color of tissues damaged by caries that is the main diagnostic sign of the disease. In the vast majority of cases, it is precisely by the black dots on the enamel or on the fissures that the doctor clearly diagnoses “caries”.
From the practice of a dentist
Black dots on teeth can indicate either congenital or acquired (most often) pigmentation (“smoker’s plaque”, etc.), but more often – hidden caries. When you start to drill out such points, they go so deep that 70-80% of the points within the enamel are completely removed, and 20-30% reach the dentin, and sensitivity appears (if the patient, due to refusal of anesthesia, asked to manipulate the conditions, until it becomes painful). Since the patient is always right, we act according to the situation: it becomes painful - we agree and administer anesthesia to the brave client according to the protocol.
Sometimes even severely damaged teeth with internal caries can appear completely healthy. So, if the surface from which the damage began is tightly adjacent to another tooth, caries can develop deep in the internal tissues, and even with a close examination of the oral cavity with the naked eye it remains unnoticed. The situation is similar when caries inside a tooth develops from damage in the enamel located below the soft gum tissue (root caries).
In most cases, at the first examination of teeth, their walls (surfaces) affected by caries are striking. These are often not carious cavities at all, but simply gray, tarnished enamel that has lost its healthy appearance due to demineralization.
Often, the dentist sees a certain “tunnel” in the space between the teeth, but the probe may, due to the density of the interdental space, not pass into the hidden internal carious cavity. Usually, the doctor shows the patient in the mirror the grayish shades of the enamel against the background of developed internal caries and begins treating the tooth after anesthesia.
When a bur touches gray enamel, in almost 90% of cases it breaks off within a couple of seconds and the bur falls into the internal cavity with an abundance of carious, pigmented, infected and softened dentin. If the anesthesia is administered correctly by the doctor, there is absolutely no pain.
The doctor cleans and seals the tooth strictly according to the caries treatment protocol. If the tooth already has a connection with the pulp chamber (the cavity where the nerve is located), then the doctor performs depulpation and filling of the canals, followed by a permanent filling in one or two visits.
The photo below shows a tooth in which deep internal carious cavities are visible under bright light:
The following photo shows fissure caries, that is, localized in the area of the natural relief of the teeth. Such darkening inside also often hides significantly destroyed tissues that are not immediately detectable during a normal examination:
At home, such “internal caries” is almost impossible to detect. It will reveal itself only if there is extensive damage to the dentin and pain appears in the tooth when the pulp is included in the pathological process. That is why preventive visits to the dentist are so important, who, using special methods, will be able to detect caries in any location and treat the tooth before it requires pulp removal (nerve removal).
Diagnostics
In the dental office, the doctor focuses on a visual examination. For accurate diagnosis, the following are additionally used:
- X-ray – targeted images and orthopantomogram to assess the condition of the alveolar processes;
- electroodontometry – exposure to electric current, which makes it possible to distinguish a diseased tooth from a healthy one and determine the degree of damage;
- transillumination - examination under special lighting (most often a halogen lamp is used);
- laser – the modified reflection of the laser beam is assessed.
If it is suspected that the pain is not related to the teeth, the patient is referred to specialized specialists.
Diagnosis of caries
When the dentist does not find the causes of the patient’s pain, he tries to find them using various diagnostic methods.
- X-rays are usually used to look for carious cavities in teeth if an external examination reveals nothing. The image clearly shows damage caused by deep caries, but the diagnostic method cannot determine the disease in the early stages. However, not all clinics have an expensive device that allows you to take dental x-rays, which is worth considering when choosing private dentistry.
X-ray image
- Laser diagnostics. An accurate diagnostic method for which a device called “Diagnodont” is used. The affected teeth are found with a laser beam. “Diagnodont” allows you to find the disease in remote and hidden areas at an early stage of the development of the disease; the method is safe and can be used by both adults and children.
Transluminescence is based on the principle of illuminating the tooth with bright light. Ultraviolet light is used and passed through a filter. In this light, healthy teeth look very white, the tongue appears orange, and caries occurring inside the tooth appears dark.
Other diagnostic methods: tooth staining with markers and temperature diagnostics are not suitable for searching for teeth damaged by disease.
Diagnosis of hidden damage using the DIAGNOdent-pen-C4 device
How to eliminate tooth pain without caries at home
To relieve pain, it is allowed to take painkillers: such as Paracetamol, Nise, Nurofen, Pentalgin, Ketanov. However, you should not take these drugs in large doses or for a long time. Elimination of the symptom does not lead to a cure, complicates diagnosis and worsens the effect of local anesthesia.
To treat hypersensitivity, pastes with a high fluoride content are used. There will be no result from their use if hyperesthesia is associated with the destruction of tooth tissue.
Periodontitis pain (when biting) is relieved by rinsing with a warm soda solution.
Which specialist should I visit?
The first thing you should do is visit your dentist. If problems in the oral cavity are not identified, you may need help from the following specialists:
Caries is deservedly considered the most common disease, since it affects more than 90% of people. But tooth pain is not always associated with the presence of caries, and such conditions require careful diagnosis, since they may hide much more serious problems.
Author: Irina Kirk, dentist, especially for Karies.pro
Reasons for the development of deep caries
The causes of caries in deep tooth tissues are similar to those for caries with any other types of its localization. The disease develops due to the following factors:
- The constant presence of acids in the oral cavity, both those that came here with food (fruits, vegetables), and those produced by bacteria that consume the remains of almost any carbohydrate food - flour, sweets, cereals.
- Reduced secretion of saliva or its low bactericidal activity. This may be caused by other diseases or metabolic disorders.
- Mechanical and thermal damage to tooth enamel.
- Hereditary factors.
Typically, caries develops under the influence of a complex of several such factors.
In any case, it is in the deep parts of the tooth, located under the enamel, that caries develops most quickly due to the greater susceptibility of the tissues here to the action of acids. Therefore, there are often situations when, under a barely noticeable (or even completely invisible to the naked eye) hole, there is a large cavity destroyed by the carious process.
On a note:
This is why the enamel almost always breaks off (comes off in pieces) when a large carious cavity has already formed, affecting the layers of softened, infected dentin. That is, the enamel can hold the load for a long time, hanging over a hidden carious cavity, often without giving it away.
A tooth hurts, but there is no hole: causes and methods of eliminating pain
Sometimes a person may be bothered by severe toothaches, but the problem is not visible visually. What could this pain be a symptom of? Is it worth contacting a specialist? How to relieve painful sensations?
If your tooth hurts, but there is no hole, then this may indicate the development of caries, inflammation of the gums, increased sensitivity of the teeth, etc. Let's take a closer look at the causes and methods of treatment.
Rules for treating the disease
In all cases of caries development inside a tooth, its treatment requires opening the enamel, removing the affected dentin and filling the cleaned cavities. In its advanced form, internal caries leads to the need to remove the nerve and fill the canals.
Even more serious are situations when a very significant amount of tissue is damaged by caries from inside the tooth, and it either after their removal or simply due to softening, splits. In this situation, it is often necessary to remove a tooth according to indications, followed by installation of an implant at the request of the patient, or to make do with modern prosthetic techniques.
On a note
There is a difference between a split and a split, so tooth-preserving techniques may involve, for example, restoration of a tooth on a titanium (anchor, fiberglass) pin after thorough intra-canal treatment + installation of a crown (metal-ceramic, stamped, solid-cast, etc.), may involve tooth preparation under the tab, installing the tab + crown. There can be many options.
Sometimes the damage is quite extensive, but it is possible to save the roots of the tooth by removing the pulp from them. In such cases, it is possible to get by with installing a crown.
In any case, after detecting a carious cavity, the doctor cleans it out with a bur. If such tissues come close to the pulp, their removal can be painful and is most often done using local anesthesia.
From dental practice
There are ambiguous situations when the pulp area has not yet been opened when cleaning the carious cavity, but the patient already begins to experience pain during the doctor’s work. It is impossible to say for sure whether it is worth carrying out depulpation here or not. Without depulpation after installing the filling, when chewing, it may begin to disturb the nerve endings and cause pain. Some doctors are inclined to depulpate such a tooth so that they do not have to carry out repeated work if, after installing the filling, the patient begins to experience pain. Other dentists explain the situation to the patient in detail and make a decision together with him. It should be borne in mind that many patients are very sensitive to the preservation of their teeth in a “living” form and are willing to take risks in order to walk around with a tooth with preserved pulp for several more years, if after a simple filling there is no pain.
In general, even with deep caries, the nerve has to be removed, according to statistics, in less than a third of cases, and the removal of the tooth itself due to deep caries is generally a rather rare situation.
Possible reasons
Toothache can be a symptom of several diseases at once. Moreover, these diseases are not always associated with the field of dentistry. Before starting treatment, it is always worth identifying the problem. Without a correct diagnosis, treatment will not bring fruitful results.
So, toothache for no apparent reason can be due to caries, increased sensitivity of teeth, cysts, inflammation of the gums, trigeminal neuralgia, as well as migraines, sinusitis, inflammation of the middle ear. Let's talk about each possible illness in more detail.
Caries
The most popular dental disease, which is an obvious reason to visit the dentist. In caries, the enamel is initially destroyed, after which the disease spreads to the hard tissues of the tooth. If this disease is not treated, the tooth will most likely be removed.
Causes of pain in teeth that look healthy on the outside
Sometimes, pain occurs upon contact with hot or too cold food. It is characterized by severity and is usually associated with increased tooth sensitivity. If the pain is aching and practically does not stop, then most likely the reason is the presence of an inflammatory process. When a sharp pain occurs when eating something sweet or cold, and after the stimulus is removed, the discomfort immediately goes away - this is considered the main signs of advanced caries. Sometimes it is invisible outwardly, but hides between the teeth. Overloading the incisor due to malocclusion is another cause of pain. One of the serious diseases that is accompanied by toothache is periodontitis. An externally healthy incisor hurts because inflammation of the gum tissue that holds it to the bone occurs. Pain is felt not only in the tooth, but also in the gum, when pressing on it, unpleasant sensations arise. Acute and never-ending pain occurs when the incisor nerve becomes inflamed. Hidden and neglected caries, which is often the cause, causes excruciating pain that intensifies as evening approaches. In order to identify the factor that led to the pain, the dentist may prescribe an x-ray or computed tomography in Kharkov. Having initially identified the problem, the treatment will go much faster and quickly give a positive result.
How to relieve pain at home?
Garlic is great for toothache
Toothache by its nature is very strong and persistent. When it starts, any person focuses only on it.
Such a disease can strike anywhere, far from the city and dentists who are always ready to help. But how can you help yourself relieve pain before you have the opportunity to seek treatment from a doctor?
The problem of painful sensations in the oral cavity is not new, so people have long had their own methods of relieving discomfort:
- Rinse with soda solution , an infusion of herbs that have an anti-inflammatory effect (chamomile, sage).
- Taking painkillers , which are in every first aid kit for all occasions.
- A piece of raw potato , which should be pressed against a sore tooth, can draw out unpleasant sensations.
- Garlic , which can be chewed on a sore tooth, or made into a paste with salt and applied to the sore spot.
- Clove oil. A couple of drops can be applied to the problem area, or dissolved in a glass of water and rinsed with the mixture.
- a piece of ice in a bag, wrap it in cotton cloth, and apply it to your cheek on the side where the tooth hurts. This will help to cope with pain very effectively for a short time.
- Rinsing your mouth with drinks containing alcohol is very successful in relieving tooth pain.
- Massage certain points on the face.
The danger of hidden caries
The unnoticed progression of the disease is the main danger of this type of caries. It is impossible to find and determine it on your own. The peculiarity of hidden caries is that the patient does not usually suffer from toothache and the teeth do not react to hot and cold, at least until the destructive process involves the pulp. In rare cases, caries spreads to neighboring teeth, and there is a possibility that the disease will proceed hidden on them too.
Usually, visiting a doctor with hidden caries happens too late, so it is recommended to undergo a preventive dental examination every six months. Sometimes the doctor can only perform depulpation. In advanced cases, caries infects most of the dentin, reducing the strength of the tooth, which can break under any unfortunate pressure.
The problem is that even during an examination by a dentist, he may not notice the caries developing inside the tooth.
In order for him to make a decision on diagnosis, either the patient must have complaints about a healthy tooth or multiple caries. Hidden caries usually occurs against the background of carious lesions in other teeth.
Interdental hidden view affects 2 teeth
Professional treatment
If even mild pain occurs, you should contact a specialist as soon as possible. Before consulting a doctor, you should not heat the sore spot to soothe the pain, as this will only provoke further development of inflammation.
Rinsing with a warm solution or plain water after eating can relieve tissue swelling. Only an experienced dentist will finally relieve suffering; it is rare that you can do without dental treatment. Even if the pain subsides, after some time it will return with renewed vigor.
When a tooth hurts, but there is no hole, this may indicate numerous possible diseases. To determine the exact problem and begin timely treatment of the tooth, you need to consult a dentist.