Exudative erythema multiforme is an acute disease of the skin and mucous membranes of an infectious-allergic nature, characterized by a recurrent course with exacerbations, usually in the autumn-spring period. In 5% of cases, only the oral mucosa is affected, and in more than a third of patients, the rashes are localized simultaneously on both the skin and mucous membranes. Young (aged 20 to 40) men are most often affected, but women, children, and the elderly can also be affected.
You will learn about why exudative erythema multiforme occurs in the mouth, clinical manifestations, principles of diagnosis and treatment of this pathology, including physical therapy techniques, from our article.
Causes
Depending on the causative factor, there are 2 forms of pathology:
- infectious-allergic (or idiopathic) – infection (bacteria, viruses) plays an important role in its development;
- toxic-allergic (or symptomatic) – occurs as an allergic reaction to taking medications (antibiotics, sulfonamides, vaccines, serums and others).
Risk factors are:
- foci of chronic infection of any location - chronic otitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, caries, periodontal disease and others;
- a person’s tendency to develop allergic reactions (including a burdened hereditary history - frequent allergic diseases in close relatives);
- decreased functions of the immune system (including immunodeficiencies after severe acute respiratory viral infections, pneumonia, during chemotherapy for cancer, and so on).
Multimorphic erythema: symptoms
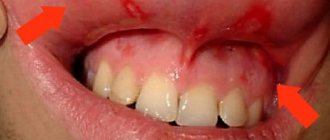
Exudative erythema (photo of which is posted below) begins to manifest itself clinically with prodromal symptoms that develop under the influence of provoking factors.
The photo shows exudative erythema
The symptomatic form develops while taking medications or after vaccinations. Further, both forms of the disease proceed approximately the same.
With erythema multiforme, widespread skin lesions are observed on the extremities (mainly hands and forearms), less often on the neck and face. Exudative erythema multiforme often occurs
Initially, bright red round spots appear on the skin, with clearly defined boundaries and a diameter of 2-15 millimeters.
Ridges form along the edges of the rash, and over time the center acquires a bluish tint. The spots merge, forming bizarre ring-shaped patterns on the patient’s skin.
Along with the spots, separately located blisters and blisters may appear. In this case, they talk about the bullous form of erythema.
The rash may appear on the reproductive organs and in skin folds. In this case, over time they turn into erosions covered with purulent or bloody crusts. The appearance of new rashes is accompanied by headaches, general weakness and fever.
This whole process lasts about one and a half to two weeks and ends with complete recovery. Sometimes hyperpigmentation may be observed in areas where there were rashes.
Symptomatic polymorphic exudative erythema has similar clinical signs, but its occurrence is not associated with exposure to infections, and relapses are not associated with changing seasons. Symptomatic erythema occurs after repeated administration of a drug that is an allergen for the patient's body.
With this form, rashes are more common; they can be observed not only on the skin, but also on the oral mucosa. In addition to spots, painful blisters often form, which significantly impair the patient’s quality of life.
Clinical manifestations
The disease is characterized by a sudden onset. The patient notes weakness, general malaise, headache, body aches, pain in muscles and joints. His body temperature rises to febrile levels and chills appear. At this stage, there are still no rashes on the skin and mucous membranes.
1-2 days after the onset of the above symptoms of intoxication, elements of a rash appear on the extensor surfaces of the patient’s lower and upper extremities (symmetrically), on the neck and face - bluish-red spots, slightly raised above the surface of healthy tissues, gradually increasing in size. The center of the spots seems to be slightly depressed, has a bluish color, and a bubble with contents of a serous or bloody nature can form here. The periphery of the spot is red-pink, has the appearance of a border - a cockade.
Over time, the spots merge with each other, forming large areas of lesions of various shapes. There is a polymorphism of rashes: spots, blisters, and bumps (papules) can be found on one area of the skin. Often the rash does not cause subjective discomfort to the patient, in other cases it is accompanied by burning or itching.
The first sign of disease of the oral mucosa is its swelling and erythema - limited or diffuse. Then, bubbles of various shapes and sizes appear on the hyperemic (reddened) areas. This is a very painful condition - a person experiences pain even at rest, not to mention eating. After a few days, the blisters open, leaving behind erosions that tend to merge. Erosions localized on the lips become covered with crusts, making it difficult for the patient to open his mouth and eat food.
Since the oral cavity of any person contains a large number of different microorganisms, erosions quickly become infected, which aggravates the course of the disease. The risk of infection is also increased by foci of chronic infection in the patient's mouth. In this case, erosions become covered with a thick yellow-gray coating, salivation increases, submandibular or cervical lymph nodes become enlarged, and an unpleasant (putrid) odor from the mouth appears.
In some patients, there are no symptoms of general intoxication of the body, and the rashes on both the mucous membranes and the skin are not clearly expressed.
As a rule, the process lasts up to 2 weeks, after which it ends with recovery.
The infectious-allergic form of the disease lasts for years, exacerbating 2-3, and in some cases more often, times a year. Toxic-allergic erythema recurs only after the patient comes into contact with a drug to which his body is overly sensitive.
Redness of the oral mucosa in an adult: symptoms, causes of formations, treatment methods
The oral mucosa is characterized by increased sensitivity to external and internal factors. So, when consuming hot foods, redness forms on it at the points of contact. However, some types of rashes on the surface of the mucous membrane inside the mouth indicate the course of pathological processes in the body.
Causes
The rash on the surface of the oral mucosa consists of small red spots. Its appearance indicates the course of the pathological process. In rare cases, such a rash occurs against the background of a serious illness.
In adults, the appearance of red spots is caused by the following pathological conditions:
- allergic reaction;
- infectious infection of the body;
- vascular and cardiac pathologies.
Initially, the rash appears on the back wall of the throat. As the pathological process develops, red spots appear in other areas of the mucous membrane, affecting the tongue, the inside of the cheeks and spreading to the skin.
The most common cause of rashes in the mouth is considered to be an infectious infection of the body. In such circumstances, other symptoms, including increased body temperature and sore throat, also indicate the presence of pathology.
There are many infectious diseases, the course of which is accompanied by the appearance of red spots on the surface of the oral mucosa. Commonly encountered diseases include the following:
- infection with staphylococcus;
- flu;
- herpes simplex;
- rubella;
- chicken pox;
- measles.
Less commonly, patients with red spots inside the mouth are found to have:
- mononucleosis;
- erythema of infectious etiology;
- roseola;
- syphilis;
- stomatitis and its herpetic form;
- herpetic sore throat;
- tonsillitis;
- typhus;
- meningitis.
Separately, you should pay attention to fungal infections of the body. This disease is accompanied by the formation of a white coating on the surface of the mucous membrane, under the surface of which areas of redness are hidden.
Also, red dots may indicate the course of rare pathologies:
- pyogenic granuloma;
- petechiae appearing on the palate;
- sarcoma ;
- syndrome .
It is impossible to determine the true cause of the formation of red dots on the surface of the mucous membrane only by this symptom. It is necessary to identify other characteristic signs indicating a specific pathology.
Symptoms of stomatitis
With stomatitis, spots on the surface of the mucous membrane have a pale pink or bright red tint. Such points are located at a distance from each other or merge with each other. Depending on the type of stomatitis, the course of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of the following symptoms:
- ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane;
- pain in the mouth;
- bad breath ;
- bleeding gums;
- increased temperature ;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- general weakness;
- headache ;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Herpetic stomatitis is considered the most common due to the fact that approximately 90% of the population are carriers of the virus. Redness of the mucous membrane usually occurs against the background of decreased immunity.
Symptoms of sore throat
Agina is an infectious disease characterized by an acute course. It mainly occurs in minors. Infection occurs by airborne droplets.
With angina, the following phenomena are observed:
- increased temperature that does not decrease for several days;
- cramping pain localized in the abdominal area;
- redness of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity;
- the formation of papules with cloudy liquid in the oral cavity;
- pain that occurs when swallowing;
- itching;
- active work of the salivary glands;
- formation of erosions at the site of papules;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Sore throat heals within about 10 days.
Symptoms of tonsillitis
Tonsillitis develops against the background of infection of the oral cavity with streptococcal infection. The course of this disease is indicated by:
- increased temperature ;
- headache ;
- general weakness;
- body aches
- pain in the throat, neck, ears;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- change in the shape of the tonsils (their surface becomes loose);
- the appearance of a characteristic white coating on the surface of the tonsils.
Red dots in the mouth with tonsillitis appear during the first days after infection. The danger of the disease is that it causes complications on the heart and kidneys. Problems with these organs occur approximately 10 days after the first symptoms of tonsillitis appear.
Allergy symptoms
Red spots on the oral mucosa often indicate an allergic reaction. It occurs due to the consumption of certain foods, medications or the use of hygiene products. An allergic reaction, which manifests itself in the form of red spots, does not cause a feeling of discomfort in a person.
This pathological phenomenon can be separated from other diseases by the following signs:
- the spots are located symmetrically relative to each other;
- between the spots there are areas not affected by the allergic rash;
- fusion occurs ;
- there are no other symptoms characteristic of an allergic reaction (pain, itching, burning);
- rashes appear on the skin.
Regardless of the nature of the clinical picture, if red spots appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor. These symptoms may indicate the course of more dangerous diseases.
Symptoms for other pathologies
Red spots on the mucous membrane are often the result of injury to the latter. However, they can also indicate the course of diseases dangerous to the body.
Monnucleosis
The disease is characterized by pinpoint hemorrhages that occur on the tongue and palate. With mononucleosis, the patient experiences:
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- problems ;
- pain that occurs when swallowing;
- jumps .
In case of chronicity, the course of the disease leads to an increase in the size of the spleen and liver.
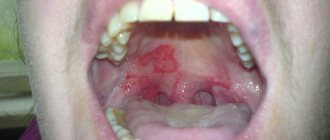
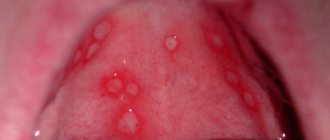
Exudative erythema
The pathology is characterized by rapid development. During the first 24 hours, the patient experiences headaches, a sharp increase in body temperature and a sore throat. Red dots on the surface of the mucosa form about a day after the first symptoms of erythema appear.
They are localized in the language. Subsequently, the red spots transform into blisters filled with cloudy liquid. Over time they spread across the sky. These blisters self-open, and small ulcers form in their place.
Kawasaki syndrome
Kawasaki syndrome spots take on a bright crimson hue. They also appear on the surface of the skin. Kawasaki syndrome is characterized by swollen lips and increased body temperature. At the same time, the skin on the fingers and toes peels off.
Syphilis
Syphilis is characterized by the formation of red spots on the tongue that have a hard surface. The disease is not accompanied by the appearance of pain.
Kaposi's sarcoma
Kaposi's sarcoma is a malignant tumor. Red spots affecting the mucous membrane have a bluish tint. When pressing on them, the patient experiences pain. Kaposi's sarcoma occurs in people with HIV infection.
If the above symptoms appear, you should seek help from a specialist. If left untreated, these pathologies are fatal.
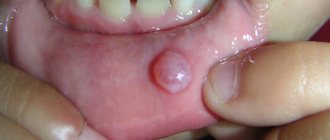
Pyogenic granuloma
It develops in the place most susceptible to trauma. Pyogenic granuloma is a single papule with a diameter of less than 1 cm. A rim consisting of microscopic scales often appears at its base.
Petechiae on the sky
Petechiae are large red spots that spread along the entire palate. They often occur simultaneously with mononucleosis. The surface of such spots is flat.
Diagnostics
Patient examination methods are selected based on his complaints. First of all, the doctor collects information about the symptoms that bother the patient. To confirm a preliminary diagnosis, the following is carried out:
- blood test (general and biochemical);
- bacterial culture to identify the causative agent of infectious pathology;
- PCR research;
- laboratory testing for the presence of antibodies to HIV infection;
- biopsy of tumors in the oral cavity if a cancerous tumor is suspected;
- other events.
Initially, the dentist examines the oral cavity.
Treatment
Treatment is selected based on the results obtained during the diagnosis. Treatment of stomatitis involves the use of the following drugs:
- Famciclovir;
- Valacyclovir;
- Miramistin;
- Viferon-gel;
- Amiksin.
General strengthening therapy aimed at restoring immunity is mandatory. If you suspect the presence of other pathologies that provoked stomatitis, their treatment is prescribed.
Treatment for sore throat caused by herpes infection includes the following:
- refusal to use antibiotics;
- bed rest;
- taking liquid food;
- regular rinsing ;
- taking analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
If complications caused by herpetic sore throat are suspected, the patient is admitted to a hospital.
Treatment of tonsillitis includes:
- taking penicillins or macrolides;
- rinsing the mouth with antiseptic substances;
- use of antibacterial sprays to treat the mouth;
- use of Lugol's solution .
Antihistamines help relieve the symptoms of an allergic reaction. Also, in such circumstances, it is necessary to exclude the influence of the factor that caused redness of the mucous membrane.
Treatment of pyogenic granuloma is carried out by removing it. To eliminate petechiae, vitamins of groups C, P and K, liver extracts and globulins are used. In the treatment of Kaposi's sarcoma, a central place is occupied by measures aimed at strengthening the immune system. At the same time, intensive chemotherapy is carried out.
Prevention
Prevention of red spots that appear on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity includes:
- regular adherence to hygiene rules;
- timely treatment of acute and chronic diseases;
- regular examination by a doctor to detect immunodeficiency pathologies;
- active lifestyle ;
- taking multivitamin complexes.
Red spots are one of the symptoms of a number of diseases. They usually occur within the first day after infection of the body and in rare cases create discomfort for the person.
Source: https://dentalblog.ru/pyatna/krasnye-vo-rtu/
Diagnostic principles
In most cases, the doctor makes a diagnosis based on complaints, medical history and the results of an objective examination of the patient. To confirm the diagnosis, the patient can undergo specific immunological tests, as well as cytological and histological examination of scrapings taken from erosions.
Differential diagnosis of exudative erythema multiforme is carried out with:
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- pemphigus;
- acute urticaria;
- fixed sulfanilamide erythema;
- erythema nodosum;
- periarteritis nodosa;
- vasculitis of an allergic nature.
Erythema multiforme exudative
- print version
- Download or send a file
Approved by the Joint Commission on the Quality of Medical Services of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Republic of Kazakhstan on August 16, 2020
Protocol No. 9
Exudative erythema multiforme is an inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa and skin, characterized by true polymorphism of the lesion elements, associated with bacterial and drug allergies. It is characterized by an acute onset followed by a relapsing course.
Correlation of ICD-10 and ICD-9 codes:
| ICD-10 | ICD-9 | ||
| Code | Name | Code | Name |
| L51 | Erythema multiforme | – | – |
| L51.0 | Nonbullous erythema multiforme | ||
| L51.1 | Bullous erythema multiforme |
Protocol development date: 2020.
Users of the protocol : therapists, dermatologists, infectious disease specialists, allergists, dentists.
Patient category: adults.
Level of evidence scale:
| A | A high-quality meta-analysis, systematic review of RCTs, or large RCTs with a very low probability (++) of bias, the results of which can be generalized to an appropriate population. |
| IN | High-quality (++) systematic review of cohort or case-control studies, or High-quality (++) cohort or case-control studies with very low risk of bias, or RCTs with low (+) risk of bias, the results of which can be generalized to an appropriate population . |
| WITH | Cohort or case-control study or controlled trial without randomization with low risk of bias (+). The results of which can be generalized to the relevant population or RCTs with very low or low risk of bias (++ or +), the results of which cannot be directly generalized to the relevant population. |
| D | Case series or uncontrolled study or expert opinion. |
Mobile application “MedElement”
Download the application for ANDROID / for iOS
Mobile application “MedElement”
Principles of treatment
Treatment is usually carried out by a dermatologist, but since the rash can be localized in the mouth, the dentist is also confronted with this disease.
Mild forms of pathology require only local therapy. Can be used:
- ointments containing an antibacterial drug and a glucocorticosteroid (Triderm, Pimafucort);
- antiseptic solutions (for rinsing the mouth) - Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, chamomile decoction and others;
- to reduce pain - anesthetics (Lidocaine, Trimecaine);
- wound healing agents - sea buckthorn oil, Solcoseryl dental gel and others.
For moderate and severe forms of the disease, drugs for systemic use are added to the above recommendations:
- broad-spectrum antibiotics (in particular, cephalosporins);
- antiviral agents (Acyclovir) – for secondary infection with the herpes virus;
- antihistamines (cetirizine, loratadine and others);
- enterosorbents (Atoxil, Enterosgel) – accelerate the removal of the allergen from the body;
- corticosteroids (prednisolone, methylprednisolone) orally, less often intramuscularly, for a short course;
- multivitamins.
Also, during the treatment period, the patient is recommended to follow a gentle diet. It is based on drinking plenty of fluids and warm dishes with a soft, puree-like consistency. Dishes with a strong taste, as well as rough foods that can injure the affected mucous membranes, are excluded from the diet. Alcohol is prohibited, since the alcohol it contains will cause chemical burns to already damaged tissues.
Physiotherapy
Ultraviolet irradiation has a good effect in the treatment of this pathology.
Treatment with physical factors can be used in complex therapy of exudative erythema multiforme both in the subacute stage of the disease and during its remission. It is used to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, stimulate restoration processes in affected tissues, and also to activate the immune system.
For this pathology, preference is given to the following physiotherapy methods:
- general ultraviolet irradiation (it is carried out for patients with frequently recurrent forms of pathology in courses 2-3 times a year in periods between exacerbations);
- local ultraviolet irradiation of affected areas (prevents their secondary infection with opportunistic flora of the oral cavity, stimulates healing processes; procedures are carried out every day in a course of 5-6 sessions; therapy begins with 1 biodose and increases it by 1 with each subsequent procedure; in parallel, they are exposed to ultraviolet light on the collar area, adrenal glands and chest area);
- laser therapy (used in the subacute period of the disease, when the symptoms of intoxication have already been eliminated; the duration of 1 session is from 30 seconds to 5 minutes, depending on the power flux density used (it can vary from 1 to 100 mW/cm2); maximum course duration treatment – 13 procedures; if the patient notes the absence of pain in the mouth while eating, therapy is stopped);
- galvanotherapy;
- electrophoresis with magnesium on the collar area.
The last 2 methods are prescribed during the period of remission of erythema. Their most desirable effect in this case is stimulation of the patient’s immune system. The effect is carried out for 20 minutes, the number of procedures per course of treatment is no more than 10.