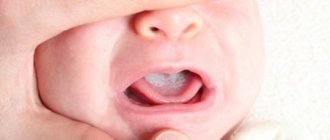
An allergic reaction is the indirect cause of many diseases. One of the most common is allergic stomatitis. The disease affects the oral mucosa and, if left untreated for a long time, can become chronic. Allergic stomatitis requires complex treatment, including taking antihistamines, treating affected tissues and following a diet. Let's take a closer look at how to avoid this problem and defeat it if it does arise.
Description of the disease
Allergic stomatitis is the name given to inflammatory changes that manifest themselves in the oral mucosa, stimulated by immunopathological reactions that are consequences of allergies. Find out why teeth decay and what you need to do to protect them here.
The disease usually has three key stages:
- Immunological. The early stage at which the corresponding antibodies are formed and histamine is synthesized. The reason is contact with one or another allergen.
- Pathological. Inflammatory mediators begin to appear.
- Pathophysiological. This is the moment when the disease can finally be visually identified - inflammation of the oral cavity appears, which can be seen with the naked eye.
Read about the treatment of ulcerative stomatitis in the mouth here.
As a rule, the nature of the disease can be divided into acute, subacute, and chronic recurrent.
Reasons for the development of the disease
A negative reaction develops after contact of the oral mucosa with various allergens. External agents are plant pollen and mold spores.
Allergic stomatitis often develops in the following cases:
- negative reaction to installed crowns, fillings, prostheses, especially those made from cheap, low-quality materials;
- in children - an acute response to certain types of food;
- irritation of oral tissues due to decreased immunity due to a course of treatment with sulfonamides or antibacterial drugs;
- advanced caries, bleeding gums, inflammatory processes accompanied by the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms;
- as a complication of Lyme disease, recurrent aphthous stomatitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, hemorrhagic diathesis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
According to the international classification of diseases, negative reactions in the oral cavity are included in a special section. Allergic stomatitis code according to ICD 10 - K12 “Stomatitis and other related lesions” and subsection K12.1 “Other forms of stomatitis”.
Learn about the use of bay leaves in folk medicine to treat allergic diseases.
Read about the first signs and symptoms of a gluten allergy in a child at this address.
Symptoms
There are a number of symptoms that can be used to identify the occurrence of this disease. These include:
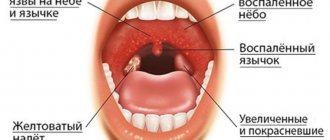
- increased bleeding of the oral cavity;
- hyperemia;
- swelling of the mouth;
- painful sensations when eating any food;
- characteristic burning sensation in the mouth;
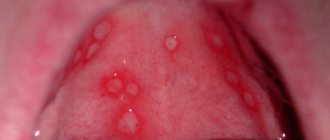
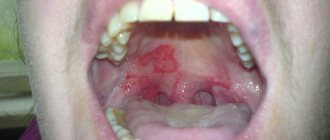
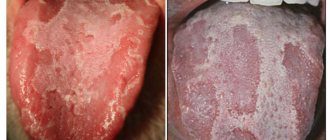
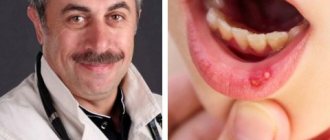
- erosion of the mucous membrane and the appearance of ulcers on its surface and palate.
- Sometimes, in addition to the described symptoms, a person may feel a general deterioration in their condition.
It is also worth paying attention to the symptoms of individual diseases, which are indicated in the next paragraph - their presence is not yet a sign of the presence of stomatitis, but may be a sign that the problem will soon appear.
Symptoms of allergic stomatitis
Depending on the form of allergic stomatitis, the symptoms and clinical picture will differ slightly.
The simplest symptoms and course of the disease can be observed in the catarrhal form of stomatitis. Basically, the patient feels severe itching in the oral cavity. Sometimes there is a burning sensation. As symptoms increase, difficulties begin with chewing and swallowing food, to the point that this process becomes impossible. In this case, the patient loses his sense of taste and cannot distinguish between spicy and salty. There is a constant desire to drink water due to dry mouth.
When a patient has erosive-ulcerative stomatitis, the oral mucosa is covered with small blisters, which over time burst and form an open wound - an ulcer that has a tendency to bleed. Disruption of the microflora in the oral cavity leads to the appearance of pathogenic bacteria that penetrate the open ulcer and cause an increase in body temperature, lymph nodes may become inflamed, and soft tissues have severe swelling. Pain is present not only during eating, but also when the patient is at rest.
A more severe form of allergic stomatitis is ulcerative-necrotic; this type usually manifests itself against the background of a decrease in the protective function of the body. In this case, the symptoms are expressed in general weakness, constant headache and decreased appetite.
In addition, with any form of the disease, the patient has a characteristic taste in the mouth, and, accordingly, an unpleasant odor emanates. The inability to swallow causes increased accumulation of saliva in the mouth.
Causes
The name of the disease already indicates that its main cause is an allergic reaction. But allergies can also be triggered by various factors:
- The allergen may enter the body or may come into contact with the oral mucosa. Accordingly, either a systemic reaction or a local one will develop.
- A systemic reaction can be caused by incorrectly selected medications, food, mold, pollen or plant spores, and the like.
Local allergies can be caused by dentures, toothpaste, oral hygiene fluids and other things that are present in the oral cavity but do not enter directly into the mouth.
Not all patients are equally predisposed to local, contact allergic stomatitis. It most often occurs in people who suffer from chronic gastrointestinal diseases, such as colitis or gastritis, as well as diabetes and other endocrine pathologies. With these problems, organic disorders occur, resulting in increased sensitivity to contact type allergens. This material will tell you about the symptoms and treatment of stomatitis in the throat.
Hives occur when exposed to strong allergens and can affect the entire body.
Sometimes the problem can be provoked by other allergic-type diseases that occur in the body, for example, Quincke's edema, eczema or urticaria. Often, allergic stomatitis can also be part of diathesis, lupus, vasculitis and other systematic diseases, although in the vast majority of cases it occurs in isolation.
Oddly enough, even dental care can cause this disease. Often, allergies can be caused by materials used in dentistry, for example, anesthesia drugs, metal fillings and dentures, and much more. Therefore, it is necessary to quickly respond to any reaction after visiting the dentist - and inform the specialist that you require a different approach.
Treatment regimen
Treatment measures must be carried out comprehensively. The success of treatment largely depends on the correct identification of the provoking factor and its elimination. Treatment also includes combating the symptoms of the disease with the help of medications and traditional medicine.
In addition to the dentist, a patient with this type of stomatitis will need to consult an allergist. Contact with the provoking factor is eliminated using:
- Hypoallergenic diet. Spicy foods and pickles are excluded. Smoked meats and marinades. Brightly colored fruits and vegetables are removed from the menu.
- Careful oral care. After each meal, the mouth is rinsed with antiseptic solutions or cleaned with an irrigator.
- Cancellation of medications taken (with the permission of the therapist);
- Refusal from temporary orthodontic structures - braces, mouth guards, etc.
- Changing dental care products.
Drug treatment
Treatment of allergic stomatitis includes the use of general and local drugs - tablets, creams, ointments, solutions. To relieve symptoms in children, it is recommended to use local teething gels - Cholisal, Kamistad, Kalgel, Dentol-baby. Often, treatment of allergic stomatitis in young patients is supported by antibiotic therapy. This is due to the fact that inflammatory diseases in children are quickly complicated by bacterial infection.
Kamistad gel is safe for the treatment of stomatitis in children
The following groups of drugs are used in the fight against the disease:
- Antihistamines - Suprastin, Zodak, Zyrtec, Fenistil, Cetrin. For children under 3 years of age, antihistamines are given in the form of syrups.
- Antiseptic solutions for local treatment of damaged areas - Cholisal, Ingaalipt, Miramistin, Hexoral, Vinilin. The latter medicine is not used to treat children under 3 years of age, since there is no clinical data on its use in children.
- Local painkillers - Lidocaine, Lidochlor. Apply into the oral cavity using cotton swabs. Adults are recommended to purchase painkillers in spray form.
- Regenerating agents – Solcoseryl, Propolis spray. Medicines in this group are not recommended for patients under 12 years of age.
You should know! For severe allergic disease, the dentist may prescribe corticosteroid medications for oral administration or drip administration. Corticosteroids are not prescribed to children because the likelihood of recurrence of the disease is high.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine methods are used to complement diet and drug treatment. Before using natural remedies, consult a doctor, as some of them cause allergic reactions. It is recommended to use natural products only when fighting stomatitis in adults.
Among the most popular recipes it should be noted:
- Potato compress: 1 tuber is grated on a fine grater and applied to the affected areas for 15 minutes. The previously obtained mass is wrapped in sterile gauze.
- Carrot juice. The vegetable is grated and the juice is squeezed out, which is diluted with boiled water in a 1:1 ratio. The liquid is held in the mouth for several minutes and then spat out.
- Honey tincture. The product is used with caution as it causes allergies. Cooking recipe: 1 tbsp. l. chamomile, pour 150 ml of boiling water and leave for 10 minutes. Add 2 tbsp to the cooled liquid. l. honey and rinse your mouth with it 3-4 times a day.
- Herbal tincture: mix 1 tsp. chamomile and calendula and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Infuse the medicine for 30 minutes and rinse your mouth with it no more than 4 times a week.
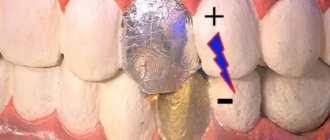
Chemical silver plating
Often, aphthous allergic stomatitis is associated with wearing metal structures to correct the bite. Many of these devices are of a permanent type. In this case, patients are prescribed chemical silver plating.
The essence of the procedure is to apply a thin layer of silver to the inside of the device. This prevents the appearance of new ulcers and erosions in the oral cavity.
After silvering, the surface of the prosthesis is covered with wax to protect it from blackening. The procedure has a significant drawback - the fragility of the effect. The patient will have to visit the dentist frequently to repeat the procedure.
Treatment of children
The main goal of pathology therapy in children is to identify the allergen and remove it from the body as quickly as possible. To do this, parents must provide the child with a hypoallergenic diet and stop taking medications (with the permission of the pediatrician). The baby is shown to the dentist so that he can evaluate the condition of the fillings and dentures in the oral cavity.
If there is a problem, the child’s mouth is treated with antiseptic compounds. It is desirable that these drugs additionally have an analgesic effect - Lyzomycin. The ulcers are cauterized with a mixture of vitamins B1 and antibiotics.
Treatment
When a person develops the problem in question, comprehensive treatment must be carried out. The first thing that is critical to do is to eliminate contact with the allergen. For example, if the cause is a reaction to dentures, contact with them must be eliminated as quickly as possible. If the reason is caused by something unclear, then you need to visit a dentist who will help you figure it out. If the dentist cannot help, then you need to contact a therapist, endocrinologist or other similar specialists. This link will tell you how to relieve toothache during pregnancy.
In general, treatment of allergic stomatitis consists of several elements:
- taking antihistamines, which include Fenistil, Solcoseryl, Suprastin, Metrogyl Denta, Clarotadine, Vinilin or others prescribed by the attending physician;
- maintaining a special diet, which, on the one hand, contains the required amount of vitamins and microelements, on the other hand, excludes everything that can provoke allergies. For example, you definitely cannot eat citrus fruits, eggs and similar foods, as well as anything spicy, salty, and so on;
- taking folic acid and vitamins B, PP and C separately;
- treatment of inflamed areas of the mucous membrane using special antiseptics and healing solutions.
Only an integrated approach can fully cope with the disease, but remember that in each individual case the treatment will be different - and it should be determined not by the patient, but by the attending physician.
Clinical course in children and adults
In the first stages, allergic stomatitis causes virtually no symptoms. There may be a slight burning sensation in the mouth, reminiscent of a burn, which intensifies when eating hot, sour or spicy foods.
If you exclude contact with the allergen, the disease may go away on its own, but more often it goes into the second stage. It is characterized by increased discomfort, redness of the mucous membrane, and the appearance of blisters or rashes.
The third stage is the formation of ulcers and general manifestations of the disease (fever, headache, irritability, etc.). A person cannot eat, and sometimes talk - if treatment is not started, serious complications are possible.
Allergic stomatitis is diagnosed in adults and children of any age, including infants. Diagnosing the disease in patients under 2 years of age is difficult due to the lack of complaints and the similarity of symptoms with other diseases. If a child refuses to eat, is capricious and constantly puts his hands to his mouth, you should consult a doctor. Signs of allergic stomatitis resemble teething, and only a pediatrician can make a correct diagnosis.
Complications
If you do not treat this disease in time, complications may arise, and quite serious ones, although, if you think about it, stomatitis itself is a complication. In his case, this can be called a chronic form, when the inflammation remains stable and is difficult to treat. This article will tell you how to get rid of bad breath during pregnancy.
On average, the prognosis for the disease is optimistic; if you respond at sufficiently early stages, then in most cases any complications can be avoided.
Diagnostics
If the mucous membranes and tongue are affected, it is important to consult a dentist in a timely manner. The doctor will examine the oral cavity, clarify the clinical picture, and listen to the patient’s complaints. An analysis of background diseases is carried out, the doctor identifies the strength and nature of negative symptoms.
If allergic stomatitis is suspected, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out:
- checking structures: dentures, braces, fillings;
- general clinical examinations of urine and blood;
- immunogram to monitor the state of the immune system;
- determination of the acidity level and composition of saliva;
- identification of the activity of enzymes contained in saliva;
- leukopenic test;
- provocative tests with removal and subsequent installation of dentures to confirm or refute an allergic reaction to inappropriate material of structures in the mouth.
Important! Only with an integrated approach to diagnosis can the cause of a negative reaction be determined. Difficulties often arise in determining the factor that provokes tissue damage.
Prevention
It is best not to treat this disease, but to ensure its high-quality prevention so that there are no reasons for its manifestation. You need to do the following:
- Provide constant high-quality hygienic care for your oral cavity. It is important not only to brush your teeth, but also to regularly visit the dentist, treat caries, gum disease, remove plaque and change dentures.
- Provide an individual approach to dental treatment/prosthetics. As mentioned earlier, even the products used in dentistry can easily become one of the causes of the development of the disease. Therefore, you need to either carefully monitor what reacts to and what doesn’t, or simply always use hypoallergenic materials, even if they are somewhat more expensive.
- Avoid contact with allergens. If you know that you have a predisposition to an allergic reaction to a particular irritant, you need to take measures to minimize contact with it. For example, if it is dust, then you need to clean the house as often and effectively as possible - and so on.
- Treat common diseases. Often it is general diseases of the body that can cause such particular phenomena as allergic stomatitis. Therefore, if something is wrong in the body, it needs to be dealt with, otherwise the consequences can be even more serious than stomatitis.
Causes
To date, doctors cannot accurately determine the exact root causes of allergic reactions. Signs of individual intolerance occur when various substances enter the oral cavity, provoking an atypical reaction of the immune system. A similar situation can happen when:
- Consumption of chewing gum and certain foods.
- Using oral hygiene products (which contain substances that provoke allergies).
- The presence of synthetic elements in the oral cavity that cause allergies (they can be dentures, filling material, onlays, etc.).
- Chronic infectious lesions of the oral cavity (for example, caries or periodontal disease).
- Contact with certain substances, such as metal from wind instruments.
- Consumption of any medications, including the use of various medications during dental procedures. Also, seemingly safe traditional medicine can play the role of a provocateur.
- Insect bites, etc.
Allergies in the mouth can be caused by various factors. So, such a violation can develop when:
- Individual predisposition.
- Decreased immune activity.
- The presence of damage to the mucous membranes.
- Bad habits, in particular smoking, etc.
Scientists suspect that the prevalence of allergic reactions is associated with the progressive development of humanity. However, to date there is no exact explanation for why exposure to the same substances is dangerous for some people, but does not affect the health and well-being of others.
Manifestations of allergies
An allergic reaction can appear either immediately after contact with the allergen or after some time. In the first case, symptoms appear within a few hours or even minutes. In the case of a delayed reaction, the allergy may not manifest itself in any way even for up to two weeks.
Local reactions develop most quickly, for example, urticaria, as well as Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock. There is no particular difference in treatment between the two types, so it is not so important how soon clinical manifestations began.
Preventive recommendations
Patients cannot always prevent the development of an allergic form of stomatitis. When installing dentures, corrective structures or fillings, it is impossible to predict what the reaction of the oral mucosa to a foreign substance will be. Even to high-quality, expensive prostheses, some patients are allergic.
Basic preventive measures:
- treat carious teeth, gingivitis, stomatitis in a timely manner;
- control the course, reduce the frequency and severity of relapses in chronic diseases;
- do not consume large amounts of foods with a high risk of allergic reactions;
- strengthen immunity;
- do not frequently use refreshing balms with alcohol, which irritate delicate mucous membranes;
- At the first signs of stomatitis, consult a doctor. If an immune reaction is suspected, the dentist will refer you to an allergist for consultation.
Symptoms of allergic stomatitis cause noticeable discomfort to the patient, interfere with eating, talking, and often cause breathing problems due to a swollen tongue, palate, and larynx. In the early stages, treatment is successful; therapy for advanced forms of the disease is often fraught with difficulties.
In the following video you can see recipes for folk remedies for the treatment of allergic stomatitis: