Today, brushing your teeth twice a day is the norm for modern people. But teeth are only 25%, and the entire oral cavity is another 75%, where microbes also remain that can adversely affect our health. Therefore, today, mouth rinses are included in mandatory hygiene procedures, which help preserve enamel, remove plaque, and destroy pathogenic microbes.
Choice of product
So how to choose the right rinse aid, which rinsing solutions are considered the best, we suggest talking about this in detail.
The first thing you need to pay attention to is the composition of the rinse aid.
If the rinse is chosen for the purpose of daily oral care, then it should not contain chlorhexidine and triclosan. These two antibacterial drugs can only be used if there is some kind of acute inflammation.
Even then, triclosan and chlorhexidine mouthwash should not be used for more than five days in a row. Because if you use it longer, the microflora that is in the oral cavity and is normal for your body begins to die. As a result, bacteria begin to be produced that become resistant to these antiseptics, and already turn into an enemy of your body.
You need to choose products that are approved by the Russian Dental Association; this is the only way to say that the product is clinically proven effective and safe.
Popular brands of daily care rinses on the market include Listerine and Forest Balm.
MANIPULATION No. 76 “TREATMENT OF THE ORAL MUCOSA AND LIPS”
Goal: maintaining the patient’s personal hygiene.
Indications: patient's serious condition.
Equipment: rubber gloves, sterile spatulas, gauze wipes, beakers, wooden sticks with a cotton swab at the end, Janet syringe, rubber spray can, towel, oilcloth, kidney-shaped tray, boiled water or one of the antiseptic solutions: 2% baking soda solution, 0.02% solution of furatsilin, pale pink solution of potassium permanganate; glycerin, fatty cosmetic cream or hygienic lipstick, safety glasses, containers with disinfectant solution.
Sequencing
1. It is convenient to sit the patient in bed (or give him an elevated position) and cover the chest with oilcloth.
2. Wash your hands, put on gloves, and put on safety glasses.
3. Pour boiled water or one of the prepared solutions into a beaker.
4. With your left hand, wrap the tip of the patient’s tongue with a sterile gauze pad and carefully pull it out of the mouth.
5. With your right hand, moisten another napkin with an antiseptic solution, wipe your tongue, removing plaque in the direction from root to tip, using 2-3 napkins, then release your tongue.
6. Place the wipes in the waste tray.
7. Pull back the patient’s upper lip with a spatula and wipe the teeth from the inside and outside with a swab on a wooden stick, soaked in the prepared solution, from the inside and outside in the direction from bottom to top.
8. Place used swabs in the waste tray.
9. Treat the mucous membrane of the lower gum and teeth in the same way.
10. Help the patient rinse his mouth or irrigate the oral mucosa:
- turn the patient’s head to one side, cover the body and chest with oilcloth, place a kidney-shaped tray under the chin;
- pull back the corner of the mouth with a spatula and use a Janet syringe (or a rubber can) to rinse alternately the left and then the right cheek space with a stream of liquid under moderate pressure.
11. Place used care items in the waste tray.
12. Apply cream to a sterile napkin with a spatula and lubricate the patient’s lips with a thin layer (or use hygienic lipstick).
13. Place the cloth and spatula in the waste tray.
14. Disinfect care items.
15. Remove gloves, immerse in a container with a disinfectant solution, and wash your hands.
Complications : aspiration of antiseptic solutions into the respiratory tract during irrigation of the oral mucosa.
Note: if your tongue is dry, lubricate it with sterile glycerin.
How to use mouthwash correctly
Dosage. As a rule, the packaging of the rinse aid already contains a dispenser cap, which determines the amount of the product. If there is no cap, then take about 20 ml of liquid, which is about 4 teaspoons.
Time. To be effective, rinse for at least 30 seconds. You also need to remember that the mouthwash is a product for personal use.
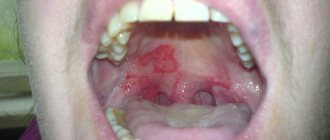
How to treat stomatitis - the best means for treatment
Local treatment of stomatitis is the main one. It is aimed at combating pathogens and preventing the spread of infection to healthy tissue. But many people do not know exactly how to treat stomatitis in the mouth and how often they should use products to combat pain and inflammation. Typically, local treatment is carried out at home. But in children, stomatitis can be accompanied by severe intoxication and require constant medical supervision. Therefore, a consultation with a dentist will not be superfluous, especially in childhood.
Decoction of chamomile, calendula, oak bark
You can prepare a one-component solution, but if you add other herbs, this will only increase the effectiveness.
To prepare an infusion of chamomile or calendula, add 1 tablespoon of the product to a glass of boiled water and leave for 1 hour. During this time, the infusion will cool down and can be used.
Oak bark is poured with boiling water in the proportion of 2 tablespoons to 1 glass of water. Then you need to keep the broth in a steam bath for half an hour.
Goals of local treatment of stomatitis
Treatment of stomatitis is the main method of treating the disease. Systemic therapy for this pathology is rarely used, mainly when there is a high risk of complications and the detection of a large number of infectious pathogens.
The main goals of local treatment of stomatitis:
- tissue disinfection;
- destruction of viruses, fungi and other pathogenic microorganisms that support the inflammatory process in the oral cavity;
- significant relief of well-being;
- prevention of complications;
- increasing the effectiveness of other treatment methods.
To treat stomatitis, antiseptic solutions, ointments and gels are most often used. Whether it is possible to treat stomatitis with a specific remedy - only the attending physician will say for sure.
But some people limit themselves only to local treatment of foci of stomatitis, while first of all it is necessary to influence the etiological factors of the disease and, if possible, eliminate their influence on the patient’s body.
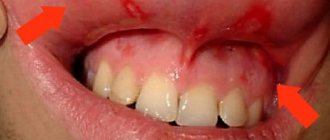
Photos of oral solutions

2
Join the discussion of the article:
Faith
I started using solutions about 10 years ago, when I was more attracted to the whitening effect of rinses. Now I only use Listerine. But what’s interesting is that when I was abroad, I bought myself Listerine antiseptic, a blue liquid, and there it is completely different, it is so concentrated that I couldn’t even hold it in my mouth for a couple of seconds!
Vote for0Vote against Reply
Nika
Holy shit... I didn’t even know that there was a duration of treatment with rinses. Hmm.. I used it without thinking about it at all. I prefer Forest Balsam. Cheap and cheerful. Sometimes I brew furacelin, and sometimes I brew herbs. Furacelin, by the way, is a good thing. It helps quickly, the effect is noticeable in a day or two. Herbs relieve inflammation well, and I usually use balms-rinses as a refresher.
Vote for0Vote against Reply
Site search
Recommendations
Sangviritrin - instructions for use of the solution and indications for use for dental problems
Mouth spray: the best formulations with prebiotics, their cost and application features
Falimint - reviews, instructions for use and expert assessment of effectiveness
Stomatofit - complete instructions for use, dosage, selection of analogues and price comparison
Ketorol for toothache - reviews of use and effectiveness. Cost and dentists’ opinions about the medicine
Antibiotics for flux: the most effective remedies and tips on choosing medications for children and adults
Metrogil denta - analogues, advantages of use, composition features and indications for use
Periodontocide - means for prevention, release form, methods of application and indications for use
Medicine for teeth - rating of the best remedies for eliminating pain and relieving swelling. Doctors' advice and cost of the most effective drugs
Medicine for gums - the most effective gels, ointments and tablets for relieving pain and discomfort
Blue for stomatitis - methods and features of using the medicine for children and adults
Cholisal is a dental gel for gums and oral cavity. Price and instructions for use
Kamistad gel - instructions for use, features of use, composition, indications and contraindications
Lincomycin - instructions for use, cost, reviews from patients and doctors
Ointment for gums - the choice of the most effective healing and anti-inflammatory agents
Ibuprofen - clinical practice, instructions for use and safety tips
Pain after wisdom tooth removal - possible complications and duration of pain after removal
Removal of a wisdom tooth - indications, features and main stages of the removal operation
Toothpicks - benefits, harm and tips for choosing safe toothpicks from the best materials
Bone dental implantation – myths and truth about bone tissue augmentation. Step-by-step description of the operation
Sections
Most read on the site:
A tooth hurts at night The sky in the mouth hurts Vitamins for teeth Inflammation of the gums Inflammation of the tooth Gel for gums Herpes in the mouth Dental hygiene Gorpils Dekasan Dental floss Tartar Plaque Ibuprofen Irrigator How to choose a mouthwash How to brush your teeth Kamistad gel Bleeding gums Medicine for gums Medicine for teeth Cavity treatment mouth Lincomcin ointment for gum metrogil denta nystatin swollen upper lip whitening paste gums gums periodontocide Prevention Pomic in the mouth Solution to the oral cavity of Sinki sinky from stomatitis spray spray stomatophytite dentistry in the gums, ultrasound halitosis Hepilor Holisal Crunches the jaw Itchy teeth Cleaning gums Splinting teeth Mouth ulcers
Copyright © 2020 ZubkiExpert.Ru is a leading online portal about dentistry. Modern methods of diagnostics and dental treatment! Home | Sitemap | Dentist consultation
Symptoms of tooth erosion
At the superficial stage of development of the disease, it is quite difficult to notice changes with the naked eye. The enamel loses its natural shine, but this is not very noticeable to others. Erosion can be detected at this stage only if the surface of the tooth is thoroughly dried and then an iodine infusion is applied. Those places where the enamel is damaged by erosion will turn yellow-brown. This stage of the disease occurs without pain, which often becomes the reason that the patient does not notice changes in time and does not seek medical help.
With moderate severity of erosion, the erosive defect looks like a whitish cup-shaped spot. With deep erosion, the erosive defect has a yellow or brown color.
Erosion of enamel is accompanied not only by its destruction, but also by abrasion of hard tooth tissues, as well as other destructive processes. In the deep stage of dental erosion, the patient may experience symptoms of dental hypersensitivity or pain. Such unpleasant sensations intensify many times over with thermal, mechanical or any other effect on the teeth.
How to treat stomatitis?
To treat stomatitis, standard antiseptics are most often used - Chlorhexidine solution 0.05% and Miramistin . These products are used for daily antiseptic mouth rinses. The course of treatment usually does not exceed 7-10 days. Hydrogen peroxide is also used. Additionally, it is recommended to use painkillers and anti-inflammatory dental ointments.
The use of Chlorhexidine for the treatment of stomatitis
Chlorhexidine has a wide spectrum of action. It is effective against most infectious pathogens, including those that are considered opportunistic and are present in small quantities in the healthy microflora of the oral cavity.
The drug has no age restrictions. You can treat stomatitis in children and adults with Chlorhexidine by simply injecting a small amount of antiseptic onto the oral mucosa. Rinse for at least 30 seconds. It is this time interval that is sufficient for the formation of a protective film, which prevents the active reproduction of pathogens for several hours after Chlorhexidine enters the oral cavity.
The use of Miramistin for the treatment of stomatitis
Miramistin, in addition to its broad antimicrobial effect, is active against the herpes virus. Just like Chlorhexidine, it does not need to be diluted, but can be used immediately for local treatment. How to properly treat stomatitis with the antiseptic Miramistin is described in detail in the instructions from the official manufacturer. The product can be used not only by adults, but also by children.
Miramistin can be used as a standard antiseptic for any form of stomatitis, but it is most effective in treating diseases of viral etiology. The drug has several forms of release: spray, solution and ointment. You can choose the appropriate tool.
Miramistin is not recommended for use for longer than 10 days. Long-term use may cause disturbances in the local microflora of the oral cavity. Miramistin is used to treat the mucous membrane several times a day, before meals.
What to choose - Miramistin or Chlorhexidine?
If you choose a drug that can be used to treat stomatitis in the mouth at home based on the level of antimicrobial activity, then Chlorhexidine is more effective. Miramistin also destroys bacteria well, but also has a negative effect on the herpes virus. Therefore, the remedy is preferable for viral stomatitis.
Chlorhexidine has a pronounced bitter taste, which Miramistin does not have. The latter remedy is preferable to use in pediatric practice, including because viral stomatitis is more common in children.
Chlorhexidine is also chosen for its affordable price - the solution costs about 30 rubles, and the spray costs 60-70 rubles. The cost of Miramistin reaches 200-300 rubles. At the same time, the antimicrobial effect of both drugs is almost the same; moreover, cheap Chlorhexidine is even more effective against bacterial forms of stomatitis.
Gel Cholisal
Cholisal dental gel is also suitable for treating stomatitis at home. It has a complex effect, destroys microbes, suppresses the inflammatory process and anesthetizes the mucous membrane. Cholisal can be used to treat stomatitis in adults and children.
The gel can be used for common diseases in dental practice, as part of the complex treatment of ENT diseases. Cholisal is prescribed not only for stomatitis, but also for periodontitis, gingivitis, inflammation of the hood over the wisdom tooth and painful teething in children.
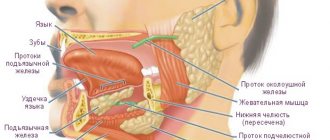
Classification of tumors and tumor-like formations of the salivary glands
The disease is classified according to the degree of activity of the process and the depth of the lesion.
The course of the disease is chronic, slowly progressive. There is an alternation between periods of exacerbation and stabilization.
According to Maksimovsky, stages of damage are distinguished depending on the level of destruction of hard dental tissues:
- initial, when the surface layers of enamel are affected by demineralization;
- transitional, in which the destruction is deep, reaching the enamel-dentin border;
- pathological, characterized by destruction of dentin.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Dentist-therapist | What diseases does it treat and when should you contact a dentist? | Competently about health on iLive
The pathological stage is divided into 3 degrees of damage. At grade 1, erosion spreads over 1/3 of the surface of the crown, at grade 2 it covers up to 2/3 of the area, and grade 3 is characterized by damage to more than 2/3 of the tooth.
| Tumors | Tumor-like formations | ||
| Benign | Malignant | ||
| Adenoma Adenolymphoma Polymorphic adenoma (mixed tumor) | Mucoepidermoid tumor Cylinder Cancer | Retention cyst of the minor salivary gland Retention cyst of the sublingual salivary gland (ranula) | |