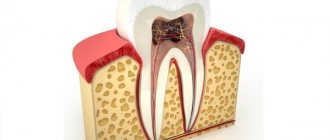
Reduced discomfort when pain occurs
For tension cephalgia, regular painkillers such as Aspirin and Ibuprofen will help. Migraine relief requires prescription medications, rest in a quiet, dark room, neck compresses, massage, or even a small amount of caffeine. Treatment for sinus pain includes inhaled oxygen through a mask or preventive medications.
But not everyone automatically tries to take the pill, especially if the child has a headache. There are also methods that can relieve pain without having to attack the nervous system:
- Add liquid. Hand on heart, answer how much water did you drink today? Did you know that approximately 2/3 of your total water intake should be drunk before lunch?
- Add minerals. In particular, magnesium. Its deficiency increases nervous irritation, any pain occurs more easily.
- Reduce tension. Many health problems are caused by stress, so try to either find ways to relax or reduce the effects of stress.
- Go for a walk. Active movement that accelerates blood circulation, relaxation, ideally in nature, are good methods for treating and preventing cephalalgia. Nature is not mentioned just out of habit, being surrounded by greenery has been proven to have an extremely positive relaxation effect on brain activity!
- Click the desired point. Press a point just below your nose or between your eyebrows. This method will help, regardless of whether the right eyebrow hurts or the left one - it will relieve discomfort throughout the head.
Types of inflammation of the sinuses
Sinusitis is divided into:
Acute sinusitis is divided into:
- Serous , when the sinus is filled with serous or watery discharge.
- Odontogenic , when the disease develops due to tooth pathology (tooth root abscess, granuloma), the pus with such a disease is foul-smelling.
Chronic sinusitis is classified into:
- Purulent . With chronic inflammation of the sinuses, distortion of the nasal septum can occur.
- Hyperplastic . There is rapid growth of cells in the nasal mucosa.
- Allergic . Frequent allergic reactions in the sinus mucosa lead to the formation of polyps (eosinophilic polyps).
One of the main symptoms is purulent discharge and slight pain. If the sinuses or nasal passages are wide and nothing prevents nasal secretions from flowing out, then such symptoms are considered minimal.
- If, due to swelling of the nasal mucosa, the sinus canals become narrow and pus accumulates in the sinuses, then the pain increases and can become unbearable, while the temperature rises, the forehead, cheeks and eyelids swell. As a result, pus cannot flow out of the nose.
- If sinusitis is localized in the maxillary sinus, the cheek, facial skin, lower eyelid swell, the cheek hurts, the pain radiates to the forehead.
- If the cells in the bones of the eyes are damaged, the root of the nose and both eyelids swell. There is pain in the root of the nose and the recesses of the eyes.
- If the location of the sinus is in the sphenoid sinuses, then the pain is localized deep in the recesses of the eyes and the back of the head.
- If sinusitis forms in the frontal sinuses, the skin of the forehead above the eyelid swells. The pain begins two to three hours after waking up and disappears in the evening. This condition repeats itself every day and leads to complications. Pain is felt when pressing on the forehead (above the eyelid), in the recesses of the eyes, under the eye near the root of the nose. When you lower your head, the pain spreads to your eyes and your forehead hurts a lot.
- heat;
- bad feeling;
- purulent nasal discharge;
- yellow or green mucus with a bad odor, maybe mixed with blood;
- dull pain in the forehead, root of the nose, eyes;
- swelling of the nasal mucosa;
- redness of the nasal mucosa;
- stuffy ears;
- labored breathing;
- neither taste nor smell is felt;
- swelling of the cheeks;
- cough;
- headache;
- bad breath.
What can cause the bridge of your nose to hurt?
When pain presses on the bridge of the nose, the reasons may be different, but first of all, doctors always rule out a prolonged runny nose and its complications. Unpleasant sensations can also occur due to:
- Poorly chosen glasses, the temple of which rubs the bridge of the nose.
- Lenses or glasses whose diopters are not suitable for the patient, which is why the person has to strain his vision.
- A subcutaneous wen that has jumped up on the nose.
- Herpes affecting the nasal mucosa.
The remaining provoking factors can be combined into the following groups.
In fact, every cold is accompanied by a runny nose (rhinitis). When there is a bacterial infection of the mucous membrane, clear mucus initially separates from the nose. If treatment is carried out correctly, over time the amount of mucus decreases and rhinitis stops.
Sinusitis, which provokes severe pain in the head, forehead, and bridge of the nose, can generally occur for the first time without the release of mucus. Possible signs of the disease are nasal congestion, swelling, and a feeling of pressure from the inside. In the absence of treatment, yellow, thick mucus begins to flow from the patient’s nose, and the temperature rises.
Sinusitis, an inflammation of one or both paranasal sinuses, can also cause nasal pain. A person develops swelling of the face, the nose turns red, becomes loose and large. The patient often has a headache, the bridge of the nose, and the area near the nose. The pain intensifies if you press on the bridge of your nose.
Remember, it is necessary to treat a runny nose! Lack of treatment leads to a deterioration of the condition; otitis media and frontal sinusitis may be added to sinusitis. A person’s temperature rises, and the pain becomes almost constant.
Ethmoiditis
A rather severe complication of a runny nose, in which pain develops in the bridge of the nose - ethmoiditis. Most often, this inflammatory process in the acute stage is diagnosed in children. In adults, ethmoiditis occurs less frequently, usually in a chronic form.
With this disease, inflammation of the nasal sinuses occurs, accompanied by damage to the ethmoid labyrinth. This inflammatory process affects the frontal sinuses, the maxillary sinuses, and the anterior cells of the ethmoid bone also become inflamed.
How does the disease progress? Inflammation develops deeply, the mucous membranes of the nose swell and swell, blocking the gaps of the ethmoid bone. The outflow of mucus worsens, as the ducts narrow or completely block. The inflammatory process can affect the bone and provoke the development of suppuration. Main symptoms:
- Reduced perception of odors.
- Pain in the bridge of the nose, extending to the corners of the eyes.
- Swelling of the nose.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Headache.
- Temperature increase.
Injury
Another common reason that a person has a sore bridge of the nose and a headache is a previous injury. Discomfort is caused by damage to the soft tissues of the nose, forehead, eyebrows, as well as complex injuries - fracture of the bridge of the nose, upper jaw, and skull bones.
Pain may occur immediately at the time of injury. In this case, unpleasant sensations bother the patient for a long period of time until the tissue is completely restored. There are also post-traumatic pains that occur a certain period after recovery. Pain may appear a year after a bruised nose or concussion.
If a person has fused bones incorrectly after an injury or has a deviated nasal septum, he may later develop chronic rhinitis, which will cause pain in the bridge of the nose.
The cause of intense headaches, as well as pain in the bridge of the nose, can be inflammation of the nerve ganglion. There are several types of pathology:
- As a complication of sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, neuralgia of the nasociliary nerve occurs. With this disease, the patient complains that his face hurts a lot, the pain presses on the nose and head when bending over. Touching the nose and eyes causes increased discomfort. Unpleasant sensations can last a long time, from a couple of hours to two to three days. Another sign is that herpetic rashes appear inside, in the nasal passages, on the skin of the nose and bridge of the nose.
- With inflammation of the ethmoid sinuses, the patient may develop ganglionitis of the pterygopalatine ganglion. The nature of the pain is intense, sharp, burning. Painful sensations occur in the palate, upper jaw, under the eyes, in the bridge of the nose. There are painful shootings in the eye, under the ear, under the lower jaw, even in the hand. At the same time, the person’s tears flow, mucus is released from the affected side of the nose, and the face turns red.
Damage to the nerve ganglion can be caused by the Zoster virus, a cold, or even a stressful situation.
Nasal septum hurts
Sensitivity of the nasal septum can lead to serious disorders. What causes the following violations:
- As a result of injury to the nasal cartilage, the internal septum shifts to the right/left, distorting the skin and internal mucous membrane of the organ. The subsequent formation of a hematoma and abscess threatens serious difficulties.
- A chronic disease - sinusitis - occurs with a painful sensation in the center of the septum, and the forehead hurts with a runny nose. The exact pain threshold cannot be determined, so the patient needs immediate medical examination followed by treatment to avoid prolonged remission.
- An inflammatory process that occurs as a result of an advanced form of a cold, accompanied by headaches. This is followed by a runny nose, which is a sign of chronic sinusitis.
- Prolonged stay in places with heavy dust accumulation, as well as response to climate change, lead to changes in the nasal turbinates. If treatment is not timely, symptoms of hypertrophic rhinitis appear.
- If the patient has a deviated septum and adenoids, then this disease is almost impossible to treat. Due to the proximity of febrile endings in the nasal cavity, pus is localized externally and internally.
- The nasal passage narrows, and even a small pimple can become very painful and later develop into furunculosis.
- Night attacks of the neuralgic form are especially painful when the nasociliary nerve is inflamed. In the place where the ethmoid bone of the skull connects to the nasal passage, the mucous membrane can become inflamed, provoking the disease ethmoiditis in a chronic form.
- Very rarely, nervous diseases occur - ganglionitis and ganglioneuritis, in which the painful shock spreads to all organs.
Even with the slightest pain, you should immediately go to the doctor. As practice shows, ailments that do not deserve close attention can be harbingers of serious consequences that are difficult to heal.
Therapy problems
You should consult a doctor if pain continues for more than two to three days. After examination and diagnosis, he will make an accurate diagnosis, which will make it possible to fight against the immediate cause of the feeling of discomfort. To temporarily improve the patient’s condition, vasoconstrictors can be used (Nazivin, Galazolin may be used). Such drugs can reduce the intensity of pain.
What to do if the bridge of your nose and head hurt? Nasal rinsing is highly effective. You can use a special rubber teapot, or, if you don’t have one, a syringe without a needle. The procedure should be carried out several times during the day. It is completely safe. For rinsing you can use:
Solutions based on sea salt. To prepare them, you need to dissolve a spoon (teaspoon) of salt in water. One glass of liquid will be enough. If possible, it is recommended to use sea salt. But cookware is also suitable for washing.
Solutions based on permanganic acid. An effective remedy against pain caused by inflammatory processes
But the product must be used with caution. It is necessary to ensure that all potassium permanganate crystals dissolve in the water, otherwise you can get a chemical burn to the nasal cavity.
Chamomile/sage infusions
These herbs have a calming effect on the nasal mucosa, which leads to a reduction in swelling. This circumstance allows you to reduce the intensity of pain.
Furacilin solution. Bactericidal agent. Can be used to treat pain due to sinusitis.
Today, pharmacies offer a large number of sea salt-based rinses. The patient can use “AquaMaris”, “Morenazal”, “Marimer”, “Aqualor” and other means for rinsing the nasal cavity.
If the cause of pain is neuralgia, rinsing will be ineffective. In this case, it is better to have a special massage. It will alleviate the patient’s condition and have a positive effect on pain relief. To carry it out, you need to pre-warm your hands and lubricate them with special massage oil.
After completing the preparations, you need to lightly press the place where the bridge of the nose meets the eyebrows and begin to make circular movements. There is no need to apply unnecessary pressure. If the patient's nose bridge hurts when pressed, the pressure should be eased. Next, you need to massage the area near the nostrils with your middle and index fingers. The massage should be performed at a slow pace. It is advisable to repeat the manipulations up to ten times. After this, you need to move to the area located behind the earlobes.
The methods described above allow you to get rid of pain. However, they remove the symptom without affecting the cause of the problem.
For correct therapy, you need to consult a doctor.
Sinusitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, ganglioneuritis and other diseases require different therapeutic approaches.
Antibiotics, antiseptic and antiviral drugs can be used in their treatment.
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary (for example, a puncture for sinusitis, or surgery to restore nasal tissue after injury).
Thus, if a patient has a headache in the area of the bridge of the nose, this may indicate the development of a serious pathology.
Neurological causes of facial pain in the periorbital region
Neuralgia of the first and second branches of the trigeminal nerve (trigeminal neuralgia)
The first, orbital branch of the trigeminal nerve is involved in the formation of the ciliary ganglion and innervates the skin of the forehead, upper eyelid and wing of the nose on the corresponding side. Neuralgia in this case is, as a rule, secondary in nature; the cause may be long-term inflammatory processes in the frontal sinus, injuries, tumors, and inflammatory eye diseases.
Location of branches of the trigeminal nerve
The second, maxillary branch is responsible not only for the sensitivity of the teeth and alveolar process of the upper jaw, but is also involved in the innervation of the inner wall of the maxillary sinus and the posterior parts of the nasal mucosa. With the secondary nature of neuralgia, the causes may be diseases of the upper teeth, long-term sinusitis, as well as injuries and neoplasms.
In both cases, the pain is paroxysmal in nature, its localization corresponds to the zone of innervation. For the first branch this is the forehead, upper eyelid, inner corner of the eye and wing of the nose, and for the second - the corner of the eye, the posterior part of the nasal mucosa (pain is felt in the depths), as well as the teeth of the upper jaw.
Ciliary knot syndrome (Hageman-Patchman)
The ciliary ganglion is located behind the eyeball and is adjacent to the lower bony wall of the orbit. Sensitive fibers in this formation innervate the deep structures of the eyeball. Hageman-Patchman syndrome is a secondary neuralgia that can be caused by inflammation in the paranasal sinuses, oral cavity and orbit, viral infections, and trauma. The pain in this case lasts from several days to two weeks, is localized in the depths of the orbit and nasal cavity, spreads to the entire half of the head and can intensify when pressing on the eyeball from front to back.
Sectional view of the ciliary node
Cluster headaches (Slader syndrome)
This disease is manifested by sharp, very severe pain in the orbit and forehead on one side, the pain can spread to the neck and back of the head. The attack is accompanied by redness of half the face, lacrimation and the discharge of a large amount of clear fluid from the nose. The reason has not been fully elucidated; the working version is considered to be a violation of vascular tone, mainly of the external cerebral artery. The frequency of occurrence of pain is characteristic: attacks follow one after another at intervals of several hours for several days, forming a so-called “bundle”. Then comes a light period, which can last up to a year.
Migraine is one of the types of primary headaches; the cause is considered to be a violation of the regulation of intracranial vascular tone. The pain is very intense and the person loses the ability to perform daily activities. Sounds, light and strong smells lead to increased pain, the attack lasts from several minutes to 2-3 days. The pain is usually unilateral, usually localized in the orbital area, forehead and temple. This disease requires serious treatment, both during an attack and in the inter-attack period.
A sign of pathological disorders can be pain not only in the eyeballs, but also painful sensations around the organs of vision , including pain under and above the eye.
The causes of such sensations can be not only ophthalmological diseases, but also pathologies of the ENT organs .
Main reasons
In order to understand why the forehead hurts and a runny nose appears, it is necessary to carry out timely diagnosis.
There is no need to ignore the initial symptoms and ailments, since the pain and the disease itself will progress, and the discomfort will become much stronger.
Very rarely, discomfort can go away on its own, but you shouldn’t count on it.
The main causes of pain in the forehead after a runny nose include the following diseases:
- Rhinitis.
- Intoxication.
- Inflammation.
- Sinusitis.
- Ethmoiditis.
- Frontit.
To identify and try to identify the disease yourself, you need to know the main symptoms and factors in the appearance of each disease.
When a person has rhinitis, a runny nose and mucus appear initially in the nasal cavity, after which the mucus appears in the paranasal sinuses.
After accumulation in this area, the forehead hurts even more. As a rule, discomfort occurs in the frontal region, as well as above the eyes.
If proper treatment is not provided, over time the pain becomes more intense, the patient may lose appetite and sleep deteriorates.
Fatigue appears quickly, as well as weakness in the body. Also, at the time of development of rhinitis, a person experiences severe intoxication of the body.
The forehead hurts due to stagnation of mucus and other fluids in the nasal cavity, and it begins to compress the lining of the brain.
The result is severe pain. Discomfort often occurs during intoxication.
A similar process infects the human body with toxins that appear due to a runny nose and bacteria that are in the mucus.
Once on the mucous membrane, the patient becomes inflamed, it is affected and cannot function normally, which provokes unpleasant sensations.
With inflammation of an infectious nature, patients also have pain in the forehead in the eyebrow area, and symptoms can also spread to the ears; in some cases, a runny nose does not allow breathing normally.
Inflammations should be diagnosed immediately during the examination of the patient.
There are certain symptoms that may indicate regular flu and other colds.
In this case, the person’s forehead hurts, but a runny nose does not appear. During colds, it is the pain that indicates the onset of the development of the disease, and if treatment is not carried out, the symptoms become stronger and more acute.
To understand that acute inflammation begins in the body, you can look at the characteristic symptoms:
- The condition worsens due to inflammation in about 2-3 days.
- A runny nose appears as a result of viruses entering the nasal cavity and pharynx.
- Possible addition of severe headaches.
- My headache gets worse when I go outside.
- In the morning, a person with a runny nose notices a large accumulation of mucus in the nose.
- If you do sudden lifting, you may experience shooting pain in the forehead.
- When turning or tilting the head, the discomfort intensifies and the forehead hurts more.
- If a cough begins, the person may feel worse, because the pain begins to become more intense.
If the described symptoms are present, then inflammation is actively developing and measures must be taken quickly to relieve the symptoms.
Otherwise, the disease will spread to other organs, leading to the formation of sinusitis and otitis media.
If sinusitis appears, then the reason for this is the transfer of mucus due to a runny nose into the maxillary sinuses, while a lot of mucus appears and they are viscous.
With this disease, pressing pain appears in the bridge of the nose, and if you touch it, you feel a sharp pain.
Patients have a stuffy nose, their cheekbones, forehead, and temples begin to ache, mucus and pus are released from the nasal cavity, so they acquire a characteristic green or yellow color, and may also have an unpleasant odor.
If the inflammation occurs in the ethmoid bone, then the person’s forehead hurts between the eyebrows and this indicates ethmoiditis.
During the examination of the patient, not only pain is detected, but also an increase in temperature, nasal congestion as a result of a runny nose, as well as pressure and a shooting sensation in the frontal part.
If it hurts in the frontal part, but the sensation does not occur between the eyebrows, then most likely the person has frontal sinusitis.
This disease is complemented by a severe runny nose with large mucus secretion, as well as an increase in temperature, possibly a febrile state and swelling of the mucous membrane and eyelids.
Frontal sinusitis must be treated at the earliest stages so that complications do not appear after it.
If treatment is done too late, the patient may lack oxygen. This makes the headache much worse.
Why do teeth hurt when you have a runny nose and can they be cured?
Colds and runny nose are unpleasant conditions of the body. A person feels general malaise, chills, and a headache begins due to nasal congestion. If at this moment completely healthy teeth begin to hurt, then the pain of the person who has caught a cold intensifies even more. In this case, the sensations can be so strong that all other cold symptoms fade into the background.
Main reasons
Colds or ARVI, acute respiratory infections are a common occurrence in the cold season, especially when the air temperature drops sharply. Common symptoms of infection are cough, runny nose, and sore throat and muscles.
To all these unpleasant sensations, toothache can be added. Her character is varied: from constant whining to shrill. It can be so strong that the patient stops noticing other signs of a cold.
If perfectly healthy teeth begin to bother you, this may be due to several reasons.
Inflammation of the ternary nerve
A common phenomenon caused by the penetration of harmful viruses into the human body. After treatment of the underlying disease, pain may persist for some time. In case of acute attacks, painkillers should be taken. Usually the ailment goes away on its own without the need for additional treatment.
Complications of a cold with the development of sinusitis, acute rhinitis or sinusitis
There is an accumulation of pus in the upper sinuses of the jaw. Inflammatory processes develop that affect the roots of the teeth. Further development of the process leads to an increase in the growth of pathogenic bacteria, since stagnant pus is an excellent environment for their habitat. Further, inflammatory processes on the gums may occur. All these phenomena cause severe toothache.
Cold
This disease is often accompanied by the formation of inflammatory processes in the throat and upper respiratory tract. Constant nasal discharge and swelling of the mucous membrane do not allow normal breathing. The maxillary sinuses accumulate mucus, pressure occurs on the jaws, resulting in unpleasant sensations.
Mouth breathing
Due to nasal congestion, normal breathing is disrupted. The patient begins to breathe through his mouth, the mucous membrane dries out. Lack of moisture leads to the accumulation of sugar, which turns into acid when interacting with bacteria. The gums begin to become inflamed, and increased sensitivity and pain appear in the teeth.
Increased sensitivity
This happens due to the use of medications and drinks containing ascorbic acid and sugar. Tooth enamel becomes thinner and more susceptible. Begins to react painfully to hot or cold drinks.
Each cause of toothache requires an individual approach. In some cases, more thorough oral hygiene and rinsing with soda solution after taking medications and food will be enough. Other cases will require immediate medical attention.
Main symptoms
Depending on the cause, toothache has different severity. The human body is a very complex system in which everything is interconnected - colds, inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, swelling of the mucous membrane affect the area of the nerve endings of the teeth, which leads to an increase in their sensitivity and the development of pain of varying strength.
Painful dental sensations can occur unexpectedly. The most severe symptoms occur with inflammation of the ternary nerve. The pain is acute, as if radiating to the head, and as a result, a migraine develops. Severe pain forces a person to take large amounts of painkillers.
If a person has had a cold of the ternary nerve at least once, then with any cold or inflammatory process it will immediately make itself felt with severe piercing pain. At the same time, it seems that the unpleasant sensations have engulfed the entire mouth.
In other cases, the unpleasant sensations can be described as short-term, shooting, slightly aching or pulsating.
Increased sensitivity of the dentition manifests itself in discomfort upon contact with warm, cold water or food. The pain is not very severe and quickly disappears after the irritant is removed. It is enough to restore the dental covering and the discomfort will cease to bother you.
Inflammatory processes of the gums are accompanied by constant aching symptoms. With sinusitis or sinusitis, a dull pain is felt in the area of the alveolar process of the upper jaw.
If the process enters an acute phase, then unpleasant sensations may affect the infraorbital area. A throbbing, stabbing, pressing pain can affect the entire upper row of teeth.
In addition, as a result of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, bad breath appears.
What to do
First of all, it is necessary to determine the cause of toothache. If the culprit is a cold, then you don’t have to plan a visit to the dentist. When the main provocateur disappears, the consequences will gradually disappear.
Experts do not recommend visiting the dentist’s office during the acute phases of an infectious disease. The body is weakened, it has to concentrate all its strength on fighting bacteria and microbes, so unnecessary stress is undesirable for it. Moreover, the patient can infect the doctor himself and his patients with the infection.
Before visiting a doctor, you can use the following treatment methods at home:
- Relieving severe pain with special medications.
- Rinse the mouth with a weak solution of baking soda. This will help slow down inflammatory processes in the gums, reduce the number of pathogenic bacteria and relieve discomfort.
- Application of dental drops. They are applied to a cotton swab and applied to the area of discomfort. The drug consists of camphor and mint, which have a calming effect.
- Using mint tablets . Slow resorption will relieve moderate pain within an hour.
- Application of propolis. It will not only reduce discomfort, but also prevent possible suppuration.
If a person suffers from unbearable toothache or discomfort remains after treatment of ARVI, it is necessary to seek help from a dentist. Perhaps pathological processes have begun to develop in the oral cavity that require specialist intervention.
Not all symptoms of toothache with a runny nose can be dealt with independently; if there is inflammation of the ternary nerve, the development of sinusitis or acute sinusitis, then the patient will need the help of not only a dentist, but a neurologist and an ENT specialist.
Source: https://dentalblog.ru/zubnaya-bol/pri-nasmorke/
Why does your nose hurt when you have a runny nose?
Pain signals a problem, and if the pain is in the nose, then you need to take it seriously, because the brain is nearby. The infection can spread to him and lead to serious illness, even death. Therefore, in this case, you should consult a doctor. Nasal pain usually occurs with atrophic and hypertrophic rhinitis. With atrophic rhinitis, the nasal mucosa begins to dry out, cracks appear on it, and this causes pain in the nose. With hypertrophic rhinitis, the tissue of the nasal sinuses itself changes, growths appear inside the nose and this causes pain.
Why does the inside of the nose hurt from a runny nose?
A runny nose occurs not only with rhinitis, but also with sinusitis - acute inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. Sinusitis can be acute or chronic. Based on location, it is divided into:
- sinusitis, inflammation is localized in the maxillary region;
- ethmoiditis, inflammation of the ethmoid bone separating the nasal and cranial cavities;
- sphenoiditis, inflammation in the sphenoid sinus, located deep in the nasal cavity and bordering the carotid arteries, base of the skull, pituitary gland and optic nerves;
- Frontal sinusitis, inflammation of the frontal sinuses, is the most difficult to treat and the most dangerous, because the brain and eyes are nearby.
All these diseases cause pain inside the nose, which increases with pressure. Moreover, the localization of pain for different types of sinusitis is in different places. With sinusitis, pain is felt in the upper jaw and under the eye sockets and radiates to the teeth. In the evening the pain intensifies.
With ethmoiditis, a constant aching pain is felt in the area of the bridge of the nose. With sphenoiditis, the pain is felt in the back of the head and it intensifies in the morning. With frontal sinusitis, pain is felt in the forehead above the eyebrows, and it also intensifies in the morning.
Sinusitis cannot be started, because the following complications may occur: abscesses of the orbit or brain, meningitis, osteomyelitis, sinus thrombosis.
Why does it hurt under the nose from a runny nose?
The skin under the nose is thin and delicate, and when you have a runny nose, it becomes irritated by secretions and constant wiping of the nose. This does not pose any particular danger; you just need to avoid touching your nose with dirty hands to avoid infection. The runny nose will go away, the skin will heal and the pain will disappear. But you need to take into account that if the runny nose is allergic, then it is necessary to identify and eliminate the cause, otherwise you will have to wait a long time for the runny nose to disappear.
Why does the wings of the nose hurt from a runny nose?
The wings of the nose hurt with rhinitis due to irritation of the mucous membrane. In addition to inflammation in the nose, herpes can occur and also cause pain in this area. Everyone is accustomed to the fact that herpes occurs only on the lips; its appearance in the nose is confused with dermatitis and they begin to treat it on their own. This should not be done, because... the situation may get worse.
To avoid pain in the nose when you have a runny nose, you need to blow your nose less often and simply blot the nasal discharge. It is better to use napkins soaked in a special lotion for this. You also need to blow your nose correctly, try to release your nostrils one by one, slowly and carefully. You should try to make the discharge as liquid as possible using steam in a sauna or heated bathroom. You can also apply a compress with a warm, damp cloth to your nose.
Using a salt spray, sold at any pharmacy, helps a lot. If you don’t want to go to the pharmacy, you can prepare it yourself. To do this, dissolve half a teaspoon of non-iodized salt in a glass of warm water and rinse your nose with the resulting solution using a small enema.
Warm drinks also soften nasal discharge and should be drunk throughout the day. Tea with mint and cloves is good for clearing your nose. The use of hot spices when eating has the same effect.
As for medicines, it is enough to use drops to constrict blood vessels, not evil
consuming them, otherwise chronic rhinitis may occur. If nasal pain is caused by serious illnesses, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics; you should not use them yourself.
When your nose hurts due to inflammation of the maxillary sinuses
With sinusitis, the pain is constant. They are often accompanied by lacrimation. The nasal cavity narrows, chronic rhinitis appears, which is not amenable to therapeutic treatment. After pumping out the contents of the maxillary sinuses, the pain stops.
The concept of “nose,” used by most people in their daily lives, in most cases, does not fully reflect its anatomical essence. Since the formation that is located in the middle of the face is only part of it and is called the external nose. Under it, or on its inner side, there are structures hidden that are invisible to the naked eye. They are the internal nose and paranasal (
) sinuses.
- external nose;
- nasal cavity;
- paranasal sinuses (sinuses);
- mucous membrane;
- vessels;
- nerves.
External nose
The external nose is similar to a triangular pyramid. It contains two side faces, a base and a back face (
), which is essentially absent. The base of such a pyramid is represented by two nasal openings and a cartilaginous septum separating them. The lateral edges are formed due to the specific connection of bones and cartilage of the external nose. From above it is formed by two paired nasal bones and two paired frontal processes of the upper jaw.
and, in fact, it is the external nose. Under the layer of skin in the nasal area there are several facial muscles - the nasal muscle and the depressor septum muscle.
The highest point of contact of the side edges (
) of the external nose is called the root (
) nose. The lowest point of their junction is the tip of the nose, which seems to rise above the nasal openings. Slightly downward from the tip of the nose, the nasal wings are located, bending around the nasal openings. Between the bridge of the nose and the tip of the nose there is a long, narrow and somewhat convex part of the external nose - the dorsum. Everything that is on the inside of the nasal osteochondral skeleton belongs to the inner nose (
) and is only part of it.
The blood supply to the external nose is carried out through the branches of the external (
) and internal (
) carotid arteries. The outflow of venous blood is provided by the veins of the external nose, which flow further into the anterior facial veins or into the veins of the nasal cavity. Further branches of these veins flow into the internal jugular vein. The skin of the nasal cavity is innervated by branches of the trigeminal (
), infraorbital and supraorbital nerves.
Nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is formed by four walls - upper, lower, medial (
) and lateral (
- nasal bones (their inner surface);
- ethmoid bone (its cribriform plate);
- areas of the frontal bones;
- body of the sphenoid bone (its anterior surface).
The lower wall of the nasal cavity is the bony palate, which separates the oral cavity from the inner nose.
- vomer;
- parts of the ethmoid bone (its perpendicular plate);
- cartilage of the nasal septum.
The structure of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity is the most complex, since it is formed by the connection of numerous structures.
- areas of the upper jaw (its body and frontal process);
- ethmoid labyrinth;
- lacrimal bone;
- area of the palatine bone (perpendicular plate);
- part of the sphenoid bone (pterygoid process);
- alar and accessory cartilages (their inner surface).
On the inside, on the lateral walls, there are the so-called nasal turbinates - formations of irregular, rounded, oblong shape. There are three sinks on each wall (
). Under the corresponding shells are the nasal passages of the same name (
). Thus, the nasal turbinates cover these passages as a kind of canopy. In addition to the above-mentioned nasal passages, there is a common nasal passage in each half of the nasal cavity. It is localized in the free space between the nasal septum and the nasal turbinates (
), each of the lateral sides of the inner nose.
Following inward, the shells narrow and decrease in size, gradually moving into the nasopharynx. The nasopharynx is a narrow, rounded anatomical space located between the nasal cavity and the pharynx.
In addition to the nasal cavity itself, the inner nose includes additional paired formations located around its cavity. These formations in anatomy are called paranasal (
) sinuses or sinuses. They can be divided into anterior, located closer to the surface of the face, and posterior, located slightly behind the nasal cavity.
The anterior paranasal sinuses include the maxillary, frontal sinuses, as well as most of the ethmoid sinuses (
). The posterior paranasal sinuses are the sphenoid sinuses and the rest of the ethmoid sinuses are the posterior cells of the ethmoid bone.
The upper nasal passages communicate with the posterior sinuses, and the middle nasal passages communicate with the anterior sinuses.
- frontal sinuses;
- maxillary sinuses;
- ethmoid sinuses (anterior, middle, posterior);
- sphenoid sinuses.
The frontal sinuses are located in the thickness of the frontal bone and are bony cavity structures. Each of the sinuses communicates with the nasal cavity through the frontonasal canal. The frontal sinus is surrounded by several walls. The anterior wall faces the face, the posterior wall faces the brain (
), lower – to the eye socket. The medial wall serves as a dividing wall between the frontal sinuses. Thus, it is common to both frontal sinuses.
The maxillary sinuses are cavity formations located inside the body of the upper jaw. They are almost parallel to the nasal septum, and their medial side serves as part of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. That is, each maxillary paranasal sinus is located on the side of the left or right turbinates. In the middle nasal passages, the nasal cavity communicates with the maxillary sinuses.
The paranasal ethmoid sinuses are located slightly posterior, outward and superior to the nasal cavity, between the frontal and sphenoid sinuses. The number of these sinuses is variable and on average varies from 8 to 10 pieces, located on each of the lateral sides of the inner nose. The ethmoid sinuses are formed by cells (
) ethmoid bone. Due to their location, cells are combined into groups (
). Cells of the anterior and middle groups (
) open into the middle nasal passages. The posterior group of ethmoidal paranasal sinuses communicates with the upper nasal passages.
Inside the body of the sphenoid bone are the sphenoid sinuses, separated from each other by a common septum. Each of the sinuses on the anterior wall contains an opening that connects this sinus with the nasal cavity (
). Some areas of the brain are adjacent to the body of the sphenoid bone (
). Below these sinuses is the nasal cavity and, thus, their lower walls participate in the formation of the arch of the internal nose (
). Near the lateral outer walls of the sphenoid sinuses pass the internal carotid arteries and a group of important nerves (
In the nasal cavity, the mucous membrane is continuous and smoothly passes into neighboring areas (
). It is located immediately on the periosteum or perichondrium and is firmly fused with them. Simply put, the nasal mucosa does not have a submucosal layer. The vessels and nerves of the mucous membrane are located in its thickness. In certain places of the inner nose, this membrane has some features.
- mucous membrane of the nasal vestibule;
- mucous membrane of the respiratory area;
- mucous membrane of the olfactory region.
The nasal vestibule is a small area of the mucous membrane of the inner nose, located directly under the cartilage of the nasal wings. The mucous membrane of the nasal vestibule, in essence, is a continuation of the skin of the external nose, which, smoothly bending around the nostrils, penetrates through the nasal openings into the nasal cavity. The epithelium here is multilayered, keratinized and contains many sebaceous glands and hair.
This area borders in front with the mucous membrane of the vestibule of the nose, and above with the mucous membrane of the olfactory region. It is represented by a cylindrical ciliated epithelium, which is built from several layers located on top of each other (
). In the lowest layer of this epithelium there are basal regenerating cells that constantly replenish the mucosa with new cells. In addition to basal cells, the mucous membrane contains goblet cells (
) and tubuloalveolar glands (
), which jointly participate in clearance (
) respiratory area, humidification of incoming air, as well as protection against microbes.
The mucous membrane of the olfactory region is a section of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity, located in the upper and, partially, in the middle nasal passages. On its surface there are special spindle-shaped olfactory cells that have sensitive endings. These cells are able to capture and perceive various odors. Between the olfactory cells is the ciliated epithelium, which cleans the entire olfactory area.
Vessels
Pain without runny nose
Severe pain in the upper part of the nose and head, without a runny nose, is caused by neurological diseases. They are considered the strongest and longest lasting. The reason for their occurrence may be:
- Neoplasms.
- Chronic rhinitis.
- Problems in dentistry.
- Congenital pathologies.
Before starting treatment, a diagnosis must be established. Diagnosis must be thorough and thoughtful. Treatment is prescribed by a specialist. Neuralgia is often confused with toothache; if the sinuses are affected, the pain radiates to the jaw.
Injuries
You can often get hit in the nose when falling. If it is swollen or bleeding appears, first aid must be provided. Depending on the impact, various consequences arise, including a broken bone, which must be treated surgically. First aid involves applying a cold compress to the injury site. In case of bleeding, stop the bleeding. Swelling, pain in the bridge of the nose, and dizziness will immediately appear. After a strong blow, you need to see a doctor and get an x-ray. If the septum and nasal passages are severely damaged, surgical assistance will be required.
Causes of pain in the sinuses
The most common cause of pain in the paranasal cavities is an inflammatory process. It can be caused by viruses (ARVI) and bacteria. Among the bacterial flora, staphylococcus is the most common. The disease can occur against the background of an infectious infection of the respiratory tract, as well as in the presence of processes in the oral cavity that are not cured in a timely manner (usually caries). A characteristic feature of inflammation in the sinuses of the nose is that it very rarely affects one of them; as a rule, the infection spreads to all the cavities.
Factors that predispose to inflammation of the paranasal sinuses are:
- curvature of the septum and nasal concha;
- congenital abnormal structure of the nasal cavities;
- injuries in the area of the paranasal sinuses.
Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses is called sinusitis. Among them are:
- sinusitis (inflammation of the maxillary sinuses);
- ethmoiditis (the ethmoid cavity is involved in the process);
- frontal sinusitis (forehead area);
- sphenoiditis (sphenoid sinus).
Causes
The cause of unpleasant sensations in the nose when pressed can be trauma, allergies, neurological pathology or infectious inflammation of the epithelial and cartilaginous structures in the nasopharynx. Conventionally, all causes of pain in the nasal cavity can be divided into two categories:
- internal – neuritis, fractures, inflammation;
- external – burns, frostbite, bruises, boils.
According to practical observations, pain in the nasopharynx during palpation of the wings of the nose and bridge of the nose can be caused by:
Rhinitis
To eliminate pain inside the nasopharynx, it is necessary to reduce inflammation in the mucous membrane and restore the outflow of viscous secretions from the nasal passages and paranasal sinuses. As a rule, nasal drops with antiseptic and vasoconstrictor effects are used for this. Inadequate treatment leads to the development of atrophic or hypertrophic runny nose, in which discomfort in the nose appears even without physical pressure on the wings of the nose or the bridge of the nose.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is inflammation of one or more paranasal sinuses. In most cases, the disease develops against the background of an infectious runny nose, allergic rhinitis and colds. Pathological changes in tissues are caused by pathogenic microbes and viruses.
Delayed treatment of sinusitis is fraught with the involvement of all paranasal sinuses in the inflammatory process and, as a consequence, the development of pansinusitis.
The main sign of the development of sinusitis is pain, which, when pressed on the tip of the nose, can radiate to the bridge of the nose, the orbital area of the face, the back of the head, etc. Clinical manifestations of sinusitis depend on the location of the lesions. With sinusitis, discomfort occurs at the level of the wings of the nose on the right and left side, with frontal sinusitis - in the bridge of the nose, with ethmoiditis - under the eyes, with sphenoiditis - inside the skull at the level of the nasal septum.
Herpes
Quite often, nasal pain occurs due to the development of herpes in the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx. As a rule, herpetic blisters form on the inner surface of the nasal canals, so when pressing on the wings of the nose, burning, itching and pain occur. The disease manifests itself in the event of a sharp decrease in the body’s immune defense, so the most likely causes of the formation of a rash in the nose include:
- hypothermia;
- hypovitaminosis;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- iron deficiency anemia;
- injuries to the nasal mucosa.
Untimely relief of inflammatory processes is fraught with the spread of infection to the conjunctiva of the eyes.
Neurological diseases
A fairly rare cause of pain inside the nasal cavity is neurological disorders. Inflammation of individual nerves (neuritis) and nerve nodes (ganglionitis) is accompanied by paroxysmal pain, which can disturb the patient for from several minutes to days. The nature of the discomfort depends on the location of the inflammation. With neuritis, pain can radiate to:
- eye area;
- eyebrows; bridge of the nose;
- back of the head;
- gum;
- temple;
- forearm.
You should not warm up your nose if neuritis develops, because this will only increase the pain.
The basis of treatment for neuritis is antiepileptic drugs. If the drugs are ineffective, so-called intraosseous blockades are used. In the most severe cases, surgeons remove the nerves, but this is fraught with changes in facial expression and other side effects.
Other inflammatory processes
There are many causes of pain inside the nasal cavity, but most of them are associated with inflammation of the soft tissues. Often discomfort in the nose appears due to the development of furunculosis or streptoderma. Ulcers (boils) occur due to inflammation of the hair follicles in the nasal canals. The provocateurs of undesirable processes are bacteria, in particular Staphylococcus aureus.
If streptoderma develops, a pustule (blister) filled with turbid liquid forms in the nasopharyngeal mucosa. Over time, it bursts, causing an open wound to form in the nasal cavity, which causes pain. It should be understood that the treatment of inflammation in the respiratory tract is the prerogative of a specialist. Inadequate and untimely drug therapy is fraught with deterioration of health and dire consequences.
The gums under the nose hurt when pressed: causes and treatment
When focusing on dental health, people forget about their gums, which is where inflammatory processes most often occur. If your front tooth hurts, and your gums are inflamed and red, you urgently need to run to the dentist. Otherwise, the tooth may be lost. Let's look at the causes of inflammation and find out how to cure them.
Causes of gum pain
Dentists note several causes of tissue pain:
- Gingivitis.
- Periodontitis.
- Periodontitis.
- Poor quality treatment.
All diseases, if left untreated, lead to inflammation and organ loss.
Gingivitis occurs due to poor oral care. The edge of the gum becomes inflamed, swollen and bleeds. The fabric turns pale pink.
Periodontitis appears due to untimely treatment of gingivitis; this is the second stage of the process. The necks become exposed, become mobile, and the tissue festers. If treatment is not started, the organs will fall out and inflammation will spread to the entire oral cavity.
The cause of these diseases is poor oral hygiene. Plaque, which is usually removed by brushing, hardens. Microbes found in plaque provoke inflammation. When pressed, the tooth becomes painful and loose.
Periodontitis occurs when an abscess appears near the root tissue. This disease appears due to untreated caries. When pressure is applied to the tooth, the root moves, affecting the abscess and causing pain.
Poor quality treatment. If the root canal is not completely filled, free space remains. Pathogenic bacteria multiply in it, causing pain when pressed. For this reason, an abscess appears on the root. There is another reason for tissue pain, uneven application of the filling to the edges of the tooth. When hardened, the filling injures the adjacent gums, causing pain.
How to get rid of pain?
The first thing you need to do when inflammation appears is to contact your dentist for help. He will determine the cause of the disease and, if necessary, carry out the necessary manipulations. Before visiting the dentist, you can relieve pain using available means:
- First you need to thoroughly clean the cavity using toothpaste. If the pain does not subside, you can use auxiliary medications.
- Take a pain reliever. It will not cure gums, but will only temporarily relieve pain, so when it subsides, you should not neglect a trip to the dental clinic.
- Rinse your mouth. The cheapest means for cleaning the oral cavity are solutions of soda or salt. To prepare, you need to add a teaspoon of soda or salt to boiled warm water (200 grams or a glass of water) and mix thoroughly. Rinse your mouth every two to three hours for five minutes.
- You can rinse your mouth with herbal infusions - chamomile is best, it has an antibacterial effect, or vodka. Alcohol perfectly disinfects the oral cavity.
- Place a few drops of clove oil on the sore spot. You can find out where it hurts by pressing on your upper lip.
If there is inflammation or suspected purulent periodontitis, it is forbidden to heat the localized area. Bacteria spread faster when heated, causing inflammation in neighboring areas. In this way, the oral cavity is effectively disinfected and the sensations fade away.
Medicinal solutions for rinsing
If the listed remedies are ineffective and do not help get rid of pain, pharmacies offer antiseptic solutions for mouth rinses for acute inflammation:
- Chlorhexidine - used after gum surgery. It disinfects the wound after treatment. Before rinsing, you need to clean the cavity with a toothbrush and rinse with water. Then take a tablespoon of liquid and rinse for 20-30 seconds. Repeat the procedure 3 times a day for at least 5 days.
- Hydrogen peroxide is a local antiseptic; a 3% solution is used to rinse the cavity. Dilute 15 milliliters of peroxide with 100 milliliters of boiled water and rinse the cavity 4 times a day. The duration of treatment reaches 5 days.
- A solution of potassium permanganate is also an excellent antiseptic. To prepare, you need to add a few granules to boiled water and mix. You should get a pale pink solution. Rinse the entire mouth 3-5 times a day.
Prevention of gum pain
To avoid excruciating pain, cleansing procedures should not be neglected. The main indicator of healthy teeth and gums is daily oral hygiene. It includes:
- Brushing your teeth with toothpaste and brush.
- Cleaning between teeth using a special floss.
- Daily rinsing of the mouth with special solutions. They are sold in all hypermarkets and pharmacies.
- Regular visits to the dentist to identify inflammatory processes and treat the oral cavity.
- Eating food rich in vitamins and microelements beneficial to the body. With a healthy body, problems rarely arise in individual areas.
Maintaining good hygiene will relieve your gums from pain when you press under your nose and keep your teeth healthy.
Yulia Kalashnik
520
Source: https://VipLor.ru/vopros-otvet/bolit-desna-pri-nazhatii
How to treat the disease frontal sinus sinusitis. Medicines and folk remedies
You can alleviate your condition before visiting a doctor using folk remedies:
- inhalations;
- compresses;
- vegetable drops from the juice of vegetables or indoor plants.
For nasal problems, treatment with essential oils helps temporarily relieve pain. You need to have essential oils at home. Inhalations with them are convenient and effective. You can use any oil from the list:
- cedar;
- eucalyptus;
- sage;
- lavender.
If there is a pot of aloe on the windowsill, then the juice of this plant can be used instead of nasal drops. Throughout the day you can drip 4 times 2 drops. Garlic compresses help with nasal congestion and pain in the nasal area. The compress is applied 4 times a day. To do this, garlic is crushed and diluted with vodka.
Frontal sinusitis is one of the varieties of such a dangerous disease as sinusitis, in which the pathological inflammatory process is localized in the sinuses located in the superciliary region, in other words, above the eyes.
Like almost all other diseases, it can occur in acute and chronic forms. It is on this that depends how to treat the disease frontal sinusitis, the choice of therapy that will be the most effective and will lead to a speedy recovery.
If the development of sinusitis is only supposedly associated with atmospheric pollution, then this relationship has been proven in the occurrence of frontal sinusitis. After all, the diagnosis of frontal sinusitis is most often made to people living in the area of industrial enterprises.
Frontal sinusitis is characterized by not only local, but also general symptoms. This:
- elevated temperature (up to 40°C), which is a consequence of poisoning of the body;
- diffuse headache that appears as a result of liquor-dynamic disturbance and blood circulation;
- terrible weakness;
- pathological sensitivity to light;
- pain in the ears and teeth;
- difficulty in nasal breathing;
- blurred vision;
- headache concentrated in one place;
- lacrimation;
- dizziness;
- swelling of the eyelids and skin above the bridge of the nose;
- snot of various colors, but usually it is yellow or green;
- hyposmia/anosmia, etc.
If at least some of these signs appear, you must immediately contact an otolaryngologist, since the inflammatory process can spread to nearby organs and cause meningitis and other equally dangerous pathologies.
With a unilateral acute process - from the side of the inflamed sinus, with a bilateral one - in the entire area, and with a chronic process it is diffuse. The mechanism of its appearance is quite complex, since the trigeminal nerve is involved.
Other reasons for a headache, especially in the morning, are:
- decreased pressure in the inflamed sinus due to oxygen resorption;
- dilation of the arteries and the resulting painful pulsation;
- increased pressure due to the accumulation of pus in the sinus;
- exposure to metabolic products of microorganisms.
Attention! A typical headache may disappear, but this is not always a sign of final recovery, since it can disappear only when the outflow of pus improves. In addition, an extraordinary heaviness appears, felt as if behind the eyes.
In addition, an extraordinary heaviness appears, felt as if behind the eyes.
Patients feel worst in the morning, which is due to the complete filling of the affected sinus with mucus/pus and a decrease in outflow from it.
In people diagnosed with chronic frontal sinusitis, during periods of remission, the severity of pain is significantly reduced, but they are still constantly present and have a clear localization. It is dull, pressing, sometimes pulsating, intensifies in the evenings, after prolonged tilting of the head or physical stress.
Ophthalmic causes
Headaches and facial pains have a wide variety of manifestations, and the causes that cause them are no less diverse. In particular, pain in the forehead, nose and eyes on one or both sides can accompany pathology of the eye or paranasal sinuses, and can also be a consequence of neurological disorders.
Acute attack of glaucoma
Glaucoma is a disease in which the normal circulation of intraocular fluid is disrupted. This leads to an increase in intraocular pressure and damage to various structures of the eyeball. In 90% of cases, the disease is painless, vision deteriorates gradually, so the patient does not notice any inconvenience for a long time.
The photo shows typical glaucoma
In some cases, the path through which the intraocular fluid circulates is completely blocked, which leads to a sharp increase in pressure. In addition to visual disturbances, a sharp pain occurs in the area of the eyeball, which radiates to the forehead and back of the head on the corresponding side - this is an acute attack of glaucoma. If pain in the forehead, eyes and nose began suddenly, and was preceded by visual disturbances in the form of red circles or spots of light in front of the eyes, you should urgently consult an ophthalmologist.
Inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct
The nasolacrimal duct connects the orbit with the lower nasal passage; normally, fluid flows through it from the lacrimal sac into the nasal cavity. With inflammation, the lumen of the canal decreases due to swelling of the mucous membrane, and the outflow of tears becomes difficult. This is accompanied by lacrimation and pain in the area of the inner corner of the eye and the base of the nose. Often inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct is accompanied by inflammation of the lacrimal sac and conjunctiva. Treatment is carried out by an ophthalmologist.
Farsightedness and incorrect vision correction
We see clear images of objects at different distances thanks to the eye's ability to automatically change the refractive power of the lens. When viewing close objects, as a result of contraction of the ciliary muscle, it becomes more convex, the focal length is reduced and the image is projected onto the retina.
A vision correction session is not as harmless a procedure as it might seem at first glance
With farsightedness or incorrectly selected means of vision correction, the ciliary muscle is forced to perform additional workload to “adjust” the visual apparatus, which causes fatigue, which is manifested by pain in the eye and forehead.
Pain in the nasal cavity
According to medical experts, if a patient has pain in the nasal passage, this can be caused by the following factors:
- Chronic sinusitis. With this disease, the nose begins to hurt in case of physical exertion, overwork, or during an exacerbation of the pathological process. The appearance of pain is caused by swelling of the mucous membranes of the nasal membranes. In addition to pain localized in the nasal area, characteristic symptoms such as increased body temperature, general weakness, and increased fatigue may be observed. To combat this disease, patients are prescribed a comprehensive therapeutic course, which is based on the use of antibiotics.
- Sinusitis. Painful sensations during sinusitis are caused by swelling of the mucous membranes, as a result of which the processes of normal outflow of nasal secretions are disrupted. Mucus and purulent discharge penetrate into the maxillary sinuses. An active inflammatory process causes pain localized in the maxillary sinuses. At the same time, depending on the characteristics of a particular clinical case, pain can be localized on one side or on both. There is a tendency for pain to increase when pressed, as well as at night and in the morning. Sinusitis in most cases is accompanied by general malaise, increased body temperature, difficulty in nasal breathing, and a feeling of heaviness in the head, jaw and paranasal sinuses. Treatment of sinusitis involves a course of antibiotic therapy and systematic rinsing of the paranasal sinuses from accumulated purulent-serous discharge. In some, especially complex and advanced cases, there may be a need for surgical intervention.
- Pain inside the nose can also occur in acute forms of rhinitis, which is associated with inflammatory damage to the mucous membranes of the nasal membranes. When you have a runny nose, a person suffers from difficulty in nasal breathing and copious nasal discharge of a mucous nature. In the case of a cold, infectious, viral or bacterial runny nose, pain in the nasal area may be accompanied by clinical signs such as headaches, muscle and joint pain, cough syndrome, fever, and general malaise. Treatment involves rinsing the nasal cavity, using antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and anti-cold medications, inhalations, warming and other physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Allergic rhinitis is also accompanied by pain localized inside the nasal cavity. Pain occurs due to frequent sneezing and copious mucus discharge. If allergic reactions are present, the patient suffers from lacrimation, blockage of nasal breathing, cough, sore throat and skin rashes affecting the skin area. The fight against allergic rhinitis begins with the elimination of allergens that provoke a runny nose. After a thorough diagnosis, patients are prescribed a therapeutic course using antihistamines and hormonal therapy.
- Hypertrophic rhinitis is a pathological change in the nasal tissues, which can be triggered by factors such as the presence of adenoids, oncological processes, excessively dry and dirty air, and temperature changes. The presence of hypertrophic rhinitis is indicated by clinical signs such as nosebleeds, impaired olfactory function, difficulty in blowing the nose and a feeling of dryness in the oral cavity.
Pain in teeth due to cold. Toothache during a cold: treatment and causes
During the development of acute respiratory viral infections and colds, many people not only develop painful sensations in the throat and muscles, but also begin to have toothache.
Such problems most often arise against the background of hypothermia due to wearing wet shoes, prolonged swimming in cool water, etc. When teeth hurt due to colds and acute respiratory viral infections, there is no need to specifically treat them.
The discomfort will go away on its own immediately after recovery. But if the pain intensifies and it becomes unbearable to endure, symptomatic treatment will come to the rescue.
Causes of toothache development
Can teeth hurt when you have a cold? Definitely yes, among the people this phenomenon has acquired the term “dental cold”, and although doctors do not make such a diagnosis, the phenomenon does occur.
There may be several reasons why teeth hurt during a cold; they are directly related to the disease itself or act as a consequence of infection.
So, the main factors suggesting the development of toothache during a viral or bacterial infection.
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
If a person is sick with a viral infection, inflammation of the jaw joint may begin when an enemy agent enters the body. It is accompanied by aching in the jaw and acute pain on the side where the inflammatory process predominates; swelling and swelling of the facial tissues are also pronounced.
When chewing food, trying to yawn, open your mouth wide, or laugh, severe discomfort occurs. Not only a viral infection can cause acute pain in the jaw; nerve damage can also occur if a person’s limbs and facial tissues freeze in the cold.
Sinusitis
If the first signs of a cold and runny nose are ignored by a person, sinusitis develops as a result of the layering of a secondary bacterial infection - inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. Against the background of this disease, the patient’s teeth ache along the entire length of the jawbone, and purulent bags may form on the gums. They weigh down the roots of the teeth, causing severe pain.
Respiratory infection
When a person’s feet are very cold or he has spent a long time in frosty, windy conditions, a cold will not be long in coming, especially if the immune system is weakened.
At this time, the airways and paranasal sinuses become inflamed. The mucous epithelium becomes covered with sputum, which is difficult to remove.
It interferes with normal breathing and creates increased pressure in the sinuses, resulting in a person's jaw pain.
Dry mouth
During a cold, a severe runny nose begins, which is not so easy to stop.
The nose is clogged, the patient has to breathe through his mouth, the situation is aggravated by coughing - the mucous tissue of the oral cavity dries out.
For this reason, sugar and acids intensively settle on the surface of the teeth, damaging the enamel layer; the process is accompanied by severe discomfort and aching pain in the jaw area.
Jaw pain after dental treatment
Signs of poisoning
Another reason why teeth can hurt is a severe case of influenza. A viral infection often causes nausea and vomiting, upset stomach, and diarrhea. The stomach intensively produces acid, which is thrown out during vomiting, and its remains actively corrode the enamel layer of the teeth.
What to do if your teeth hurt due to a cold? The most important thing is to establish the root cause of the phenomenon and deal directly with it
To reduce unpleasant symptoms, you should rinse your mouth more often with saline or soda solution, potassium permanganate or Furacilin. This way, you can at least remove acid residues from the surface of the teeth and wash away bacterial plaque from the mucous membrane.
Additional negative factors
Pain in the teeth during a cold does not always occur for physiological reasons - due to increased acidity in the stomach or a viral infection. In some situations, the person himself provokes the problem, which further aggravates the course of the disease; discomfort in the jaw develops here for the following reasons:
How to take Analgin for toothache?
- Inadequate oral care. When a person is sick, he does not have the desire and strength to carry out hygiene procedures with the same zeal; this can be explained by fatigue, fever, and drowsiness. Most of the time the patient lies in bed, ignoring brushing his teeth, believing that it recedes into the background. But after a week of lack of dental care, food debris accumulates in the gaps, and bacteria multiply, destroying the enamel. All this is aggravated by the remnants of vomit and other factors discussed above; if the teeth were previously affected by the initial stage of caries, it begins to progress rapidly.
- Eating acidic foods. Everyone knows that when you have a runny nose or a cold, it is useful to drink tea with lemon and raspberries; the drink removes toxins, copes with infections and reduces fever. However, a large amount of acid entering the body and settling on the teeth corrodes the enamel layer, causing discomfort and pain. Sensitivity increases, there is an acute reaction to sweets, hot and cold.
- Periodontitis. This is an inflammation of the gums and tooth root, which does not occur just like that; it develops as a consequence of untreated caries. During a cold, due to inadequate oral care, the carious process worsens, which is fraught not only with acute pain, but also with the development of dangerous complications (autoimmune reactions, pathologies of the heart, kidneys, joints).
- Granuloma. So, it is called a capsule filled with purulent contents, located deep in the gums, at the root of the tooth. The formation of a granuloma is accompanied by aching and bursting pain in the gums, swelling of the surrounding mucous tissues and an increase in temperature. Pathology can occur either independently or against the background of a viral infection, but is aggravated by caries and bleeding gums (and these problems come to the fore with a severe cold).
Possible complications
It happens that the pain during pulpitis subsides on its own (after 3-7 painful days). This doesn't mean everything is fine. The source of infection has not gone away, and the disease can take a chronic form.
In this case, toxins will constantly penetrate into the blood, causing poisoning of the body and inflammation of internal organs.
In the absence of dental care, pulpitis can quickly turn into periodontitis and spread beyond the tooth root.
In this situation, breathing may be difficult, so tracheostomy (surgery to install a temporary opening between the trachea and the environment) cannot be ruled out. Often a cold nerve causes periostitis, which also has to be treated surgically.
How can this be unpleasant and dangerous?
If the respiratory process is accompanied by painful aching sensations in the gums and teeth, this may indicate the emergence of health-hazardous conditions. They may be:
- Inflammatory process in the area of the trigeminal nerve process , as it can easily become affected by a cold infection. Bacteria are capable of enveloping nerve endings through the plexus of blood vessels and affecting the trigeminal nerve. In addition to cold symptoms, toothache begins to be felt, starting from the temples and ending with the jaw.
- Inflammation of the maxillary sinuses . The development of sinusitis increases pressure on the anterior bone of the upper jaw. Due to this, aching pain appears. It is because of sinusitis that teeth hurt most often when there is a runny nose. The pain goes away after completion of the therapy process.
- Common cold process . It happens that the very appearance of aching toothache indicates an acute respiratory viral infection. This is explained by non-standard physiological characteristics. Teeth begin to ache even before the appearance of fever, runny nose, chills, cough and other cold symptoms.
- Hidden dental pathologies . A person without the help of a dentist may not feel their presence for a long period. They can manifest themselves when the body is weakened by a cold infection. Diseases such as pulpitis, periodontitis or gingivitis are just waiting for the body’s immunity to weaken in order to manifest itself in all its glory.
To identify the exact cause, you need to seek help from specialists. In such cases, you cannot self-medicate at home. This can lead to serious consequences. Sinusitis, for example, can progress to a stage where surgical intervention is indispensable.
Disease prevention
Very often, the cause of hypothermia of the dental nerve is untreated caries. This is due to the fact that any impact on the nerve, including cold, can only cause harm if the tooth is already damaged.
articles
Many people are familiar with the symptoms of a dental cold - aching or throbbing pain in one tooth, or more often in several adjacent teeth. Sometimes a person who has a cold in his teeth has pain in his entire upper or lower jaw.
But how to distinguish the symptoms of a dental nerve cold from dental problems - caries, periodontitis, etc.? What to do if you have a cold in your teeth? What treatment is required for a cold dental nerve? In this article we will give answers to all your questions.
What to do to relieve pain
The cause of the disease will help determine the treatment method. Oral pain can be relieved in the following ways:
In case of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, treatment is prescribed only by a specialist. In some situations, surgery is necessary.
- To get rid of pain, it is possible to use an antiseptic liquid in the absence of proper care.
- Rinsing your mouth or drinking a glass of clean water will help relieve pain when eating foods that are high in acid.
- Rinsing your mouth with a saline solution will help with indigestion.
Toothpastes and gels
For increased enamel sensitivity, toothpastes are used. When your teeth hurt, your dentist selects toothpaste based on the symptoms of the disease. If it is not possible to contact a specialist, it is recommended to use toothpastes for sensitive teeth.
Anesthetic gels will help you get rid of severe pain. By acting externally, they are able to alleviate the inflammatory process for a long time. The most common and effective gels are Dentol and Metrogyl Denta.
Preventive measures
To prevent toothaches from bothering a person during colds, he needs to constantly take preventive measures, which include:
- a ban on the use of toothpastes and other oral care products containing sodium lauryl sulfate;
- eating large quantities of fresh vegetables and fruits, especially in winter;
- hardening of the body;
- regular visits to the dentist.
Also, do not alternate hot food with cold food and eat a lot of fruits with a high acid content. Such measures will help maintain dental health for many years.
Treatment methods
To get rid of a toothache, the patient must find out the cause of its formation. When determining the factors causing the disease, you should follow some recommendations.
Painful sensations in the teeth during a cold indicate an insufficient amount of vitamin C. Therefore, if the question arises, what to do if your teeth hurt from a runny nose, first of all, take care of your oral hygiene and take vitamin complexes.
Vitamin C is found in large quantities in ascorbic acid.
During treatment, avoid taking aggressive liquids, including sour and sweet drinks. In addition, the patient should not eat foods that are too cold or too hot.
Source: https://PlastikaPlus.ru/rot/lomit-zuby-pri-prostude.html
Causes and symptoms
Pain can be caused by various reasons, characterized by certain symptoms:
- Osteomyelitis , which is a consequence of advanced dental diseases. This is a purulent inflammation of the bone that gives high fever.
- Mechanical injury associated with bruises or fractures of the facial bone. On palpation, the victim feels severe pain. The site of injury becomes bluish and swells.
- Neuralgia , which affects the nerves located in the face - trigeminal nerve, glossopharyngeal, facial, sublingual. A person’s facial expressions are disturbed, facial asymmetry occurs, and there is pain under the eye. Shooting and twitching accompany trigeminal neuralgia. It can shoot in the ears, neck, shoulders, temples.
- Vascular eye disorders cause acute pain around the eye sockets, pain, and lacrimation. Weak, damaged vessels poorly supply blood to the eye organs, which is why similar symptoms occur.
Useful video
First aid for eye injury. Algorithm of actions before contacting a specialist.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.