Causes and mechanisms
The infraorbital region is formed by the upper jaw, zygomatic bone and lateral wall of the nose. Therefore, pain in this area can occur due to pathological processes localized in the immediate vicinity. We can talk about the following conditions:
- Acute sinusitis.
- Dacryocystitis.
- Traumatic injury.
- Osteomyelitis of the upper jaw.
- Trigeminal neuralgia.
Thus, pathology can cover various structures - paranasal sinuses, lacrimal ducts, bones, soft tissues, nerve fibers. As a rule, it is necessary to ascertain the inflammatory process, but there are also mechanical damages.
When conducting diagnostics, it is necessary to pay attention to the condition of the overlying eye. Even simple fatigue after prolonged work at the computer can provoke heaviness in the surrounding area, not to mention impaired visual acuity (myopia) or increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma). The probability of each condition is considered so as not to miss the cause of pain.
Only a doctor can determine the source of the disorder. Having carried out a full diagnosis, he will indicate the origin of the pain under the eyes.
Pain due to skin diseases
This disease can be classified in this way:
- allodynia of the tactile type, in which the skin of the face hurts when you touch it with your fingers;
- statistical allodynia (mechanical) - pain occurs when touching the face with a cotton swab or pad;
- mechanical or dynamic impact - pain develops during actions such as washing;
- Allodynia of the thermal type occurs during temperature changes, for example, if a person enters a warm room straight from the cold.
It is almost impossible to cure this disease on your own. Therefore, you should immediately consult a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease. The risk group includes people aged 20 to 30 years, although signs of the disease can also develop in a young person aged 18-19 years.
To alleviate the patient's situation, doctors may prescribe physical therapy. Some people find that using dry heat helps. Techniques such as reflexology and acupuncture have shown high effectiveness in combating the disease.
Some patients feel better after a psychotherapy session. The most modern method of combating the disease is the implantation of devices under the skin that control the passage of nerve impulses.
Test drive: a new product will get rid of wrinkles and puffiness under the eyes
But at the present stage of development, medicine cannot always help the patient, since when eliminating this disease, doctors often have to act almost blindly. In some cases, after achieving normal skin sensitivity, the patient's condition subsequently worsens. The reasons for this phenomenon have not yet been clarified. The use of therapeutic procedures in this case can greatly harm the patient.
The facial skin is very thin and sensitive. It is not surprising that it hurts even with minor pathological processes. Consider, skin soreness appears.
In case of mechanical damage, for example, from a fall, the delicate skin of the face suffers quite a lot. In addition to unpleasant sensations, unsightly abrasions and bruises are clearly visible.
Almost every person has moles on their face. In normal condition they do not cause any discomfort. However, a mole can develop into a malignant neoplasm. Therefore, you should be wary if the following signs appear:
- the mole hurts, usually the discomfort is one-sided; for example, if the mole is located on the left, pain is felt on the left side of the face;
- its outlines lost clarity;
- the color and dimensions of the nevus have changed;
- the mole is oozing or bleeding.
To avoid adverse health consequences, these signals should direct the person to an oncologist.
Acne on the face hurts
Acne is a normal occurrence for every teenager. However, with some ailments, such as gastrointestinal disorders, hormonal imbalances, acne can haunt a person even at an advanced age. Single superficial pimples go away easily and do not cause discomfort. It is more difficult to deal with deep-seated acne and wen.
Women often face situations where, after applying a cream or lotion, their face hurts or itches. However, pain is not the most unpleasant thing you can experience with allergies. Additionally, the following unpleasant symptoms may appear:
- rashes on the skin;
- swollen face;
- swelling of mucous tissues;
- copious nasal mucus;
- difficulty breathing.
We list the conditions that cause pain on the surface of the head and facial part:
- bad hairstyle, long-haired people often pull their hair into a bun, and also use hard, uncomfortable accessories, for example, headbands that squeeze the head;
- skin diseases such as eczema;
- various pathologies of the NS;
- VSD.
It is quite difficult to independently identify why your head and facial area hurt. Therefore, it is better to visit a health care facility.
In pathologies of the cardiovascular system, the tone of blood vessels is significantly impaired. This causes sudden changes in blood pressure, which generally makes you feel worse. However, there are some vascular pathologies in which the facial part aches. For example, temporal arteritis. The disease is formed during the active occurrence of inflammatory processes in the carotid and temporal arteries.
Symptoms
The cause of certain symptoms can be discussed based on the complete clinical picture. Painful sensations are a subjective sign, so they need maximum detail:
- Character (sharp or dull).
- Appearance (bursting, aching, shooting, pulsating).
- Intensity (strong, weak, moderate).
- Duration (short-term, long-term).
And when pain is described as occurring under the orbit, this does not mean that the pathology is localized there. After all, an impulse can come from neighboring areas along nerve fibers (irradiate). Factors that provoke pain are also taken into account, for example, tilting the head, touching, hitting, etc. All other symptoms are detailed in a similar way.
Acute sinusitis
The first thing you should think about if a patient has pain under the eye is acute sinusitis, in particular sinusitis. Inflammation of the maxillary sinus quite often manifests itself with a similar symptom. The pain can radiate to the temple or the entire half of the head, they acquire varying intensity (from a simple feeling of heaviness to moderately severe), intensifying when bending over or straining (exudate pressure increases). Local signs of sinusitis also include:
- Nasal congestion.
- Discharge (mucopurulent).
- Impaired sense of smell.
When palpating the infraorbital region, pain is determined. The soft tissues may be slightly swollen and reddened, but this symptom becomes most obvious with the development of complications of sinusitis - an abscess or phlegmon of the orbit. General symptoms of the inflammatory process in the maxillary sinus include fever (up to febrile levels), a disturbance in the general condition (malaise, loss of appetite, headaches).
Acute inflammation of the maxillary sinus is the main cause of pain in the infraorbital region in the practice of an ENT doctor.
Dacryocystitis
The nasal cavity is closely connected with the conjunctival sac through the lacrimal ducts. And they are also susceptible to inflammation. If the removal of tear fluid is impaired, it stagnates in the corresponding sac located at the inner wall of the orbit. This leads to the activation of microbes and provokes a disease called dacryocystitis.
Acute inflammation of the lacrimal sac is quite specific. Patients experience painful swelling and redness below the inner corner of the eye. They can spread to the bridge of the nose and cheek on the affected side. The eyelids are swollen, the palpebral fissure is narrowed. I am concerned about tugging pain in the corresponding area, which intensifies with palpation. The infectious process is accompanied by fever and intoxication.
After a few days, a softening forms at the site of the swelling, in the center of which a yellow clearing is visible. This indicates the development of an abscess that can break out or into the nasal cavity. In addition to this outcome, acute dacryocystitis in some cases becomes chronic. Prolonged inflammation is accompanied by lacrimation and discharge of pus from the inner corner of the eye. Other structures of the organ of vision (eyelids, conjunctiva, cornea) are often infected.
Traumatic injury
If pain under the eye begins to bother you, then you should find out if there was any injury (direct blow, fall). This symptom is the first to appear after mechanical damage. Then swelling increases, and a hematoma gradually forms. In case of extensive injuries, the eye may be damaged, in which hemorrhages are detected. If the bones of the facial skull are damaged, then the symptoms are more pronounced.
Osteomyelitis of the maxilla
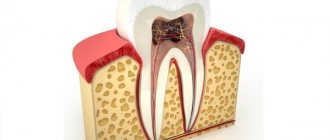
A purulent process in the upper jaw can occur due to inflammation of the teeth and gums, otitis media, injuries, and gunshot wounds. Acute osteomyelitis begins suddenly - the temperature rises sharply with chills, appetite and sleep worsen, weakness and fatigue increase. If the cause is a tooth, then pain is felt in this area, which spreads to the ear, temple and eye socket. An unpleasant odor comes from the mouth, and the gum pockets fill with pus.
With osteomyelitis, the soft tissues of the zygomatic and infraorbital areas swell and turn red. Inflammatory infiltration becomes diffuse. The sensitivity of the upper lip decreases, mouth opening may be impaired, and facial contours are distorted. A purulent process from the bone can move to the maxillary sinus (sinusitis), break into soft tissues (abscess and phlegmon), and become a source of lymphadenitis and thrombophlebitis.
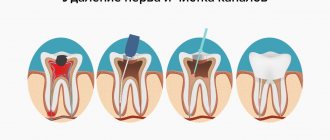
Trigeminal neuralgia
Damage to the middle branch of the trigeminal nerve is also accompanied by pain under the eye. In this case, it is paroxysmal (in the form of an attack), piercing and shooting. A characteristic sign will be the presence of “trigger” zones, the impact of which provokes pain. This is exactly what happens when brushing your teeth or pressing on the infraorbital area. The pain impulse spreads to neighboring and distant areas. And although the attack is usually short-lived, it has an extremely negative impact on the general condition of the patients, disrupting their usual lifestyle and reducing their ability to work.
An attack of pain with neuralgia of the middle branch of the trigeminal nerve covers not only the infraorbital region, but often spreads to the entire half of the head.
Why the bone under or above the eye may hurt - causes and treatment of the symptom
A sign of pathological disorders can be pain not only in the eyeballs, but also painful sensations around the organs of vision , including pain under and above the eye.
The causes of such sensations can be not only ophthalmological diseases, but also pathologies of the ENT organs .
Depending on the disease, tingling may vary in nature and intensity. Most often, such sensations are caused by the development of sinusitis in the acute stage.
In this case, the aches are felt even without pressure, and symptoms such as:
- redness of the area in which the pain is localized;
- swelling;
- phlegmon or abscess of the orbit (in advanced situations).
Pain without pressing on the infraorbital area can occur with injuries , when a person develops a hematoma.
are possible , which manifest themselves as redness of the conjunctiva.
Often, tingling under the eye can occur due to lesions of the trigeminal nerve , which is partly related to the visual system. In this situation, pain can manifest itself in the form of attacks and is of a “shooting” nature.
In certain pathologies, pain appears or intensifies only when pressure is applied to certain areas.
It happens that a painful sensation when pressing with a finger under the eye occurs with glaucoma, but the pain in this case is mild.
Possible reasons
Tingling under the eye may be a symptom of one of the following conditions::
- SinusitisThe pathology is an inflammation of the nasal sinuses, which communicate with the lacrimal canals. With this disease, the maxillary sinuses, which are located under the eye sockets, become clogged with purulent discharge.
The pathology in its advanced form can progress to the chronic stage, and inflammatory processes can spread to the upper respiratory tract.Treatment in this case is carried out by an otolaryngologist, who prescribes appropriate anti-inflammatory and, if necessary, antibacterial drugs.
- Osteomyelitis . A purulent-necrotic process in the bones, which can develop against the background of complications of dental diseases, when infectious processes from the teeth of the upper jaw spread to the infraorbital bones.
Treatment consists of taking immunostimulating and antibacterial drugs, vitamins, and in severe cases, blood plasma transfusion to detoxify the body. - Mechanical damage to the periocular area. Painful sensations in such cases require, first of all, symptomatic treatment and the use of painkillers.
And with concomitant damage to the eyeball and penetrating wounds, antibacterial treatment and surgical intervention are necessary. - Neuralgic pathologies. Such disorders are usually accompanied by a complex of symptoms, including disturbances in facial expressions, numbness of the facial, hypoglossal and pharyngeal nerves.
Often the patient experiences tingling sensations in the temples, shoulders or neck. - Disturbances in the activity of the vascular system of the organs of vision . In such cases, the patient may feel pain in the bone under the eye, but this syndrome only affects the blood vessels and soft tissues.
Only a specialist can determine what exactly causes such a symptom after conducting an appropriate examination.
Treatment is determined solely by the origin of the pathology and its severity.
Diagnostic methods
- donating blood for general and biochemical tests;
- rhinoscopy (examination of the nasal cavity);
- nasal swab to analyze the discharge for the presence of pathogenic microorganisms;
- CT scan;
- radiography of the upper jaw area;
- dacryocystography (examination of the tear ducts using x-rays);
- puncture of the maxillary sinus (if sinusitis is suspected).
Why might the bone above the eye hurt?
With certain diseases and disorders, pain appears in the bone above the eye, in the eyebrow area. This may occur in the following cases :
- Infectious or inflammatory ENT diseases leading to dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. The pain may radiate to the bone above the eye permanently or be temporary.
- Fractures of the nose or base of the skull. In such cases, in addition to acute pain, additional symptoms are observed in the form of swelling, bruises, redness, and in some cases, fluid may be discharged from the ears.
- Osteomyelitis . With this bone disease, pain can be localized in any part of the face, including in the eyebrow area, but this occurs less frequently than the development of pain under the eye.
- Some people with malocclusion may develop pain due to improperly distributed load on the muscles. And if this problem is not corrected, over the years, deformation occurs not only of the muscles, but also of the bones, to which the pain syndrome transfers.
From this video you will learn about the causes and treatment of pain above the eye:
Feelings of pain in the bone under the eye or in the eyebrow area always have serious causes.
In such cases, you cannot wait until the discomfort goes away on its own; you must undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist and begin treatment as early as possible .
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material and the author!
( 1 5.00
Source: https://zrenie1.com/bolezni/simptomy/kost-pod-gl-bol.html
Additional diagnostics
Additional methods can help identify and confirm the cause of suffering. Some of them are aimed at identifying the source of disorders, while others establish pathological disorders in the body. The diagnostic complex includes laboratory and instrumental methods:
- Complete blood count (leukocytes, ESR).
- Blood biochemistry (inflammatory markers, proteinogram).
- Nasal swab, analysis of discharge (cytology, culture).
- Rhinoscopy.
- X-ray of the upper jaw.
- CT scan.
- Dacryocystography.
- Puncture of the maxillary sinus.
Each case is individual and therefore requires its own approach. But there are certain standards regulating diagnostic measures for a particular pathology. The doctor adheres to them when prescribing an examination.
Symptoms
Nasal congestion can vary. For example, the following combination is common: the nose is clogged at night, and during the day it constantly flows. Or it is constantly stuffy, the sinuses are clogged, the person breathes through the mouth. Naturally, he lacks air, which results in a headache. Or simply - general weakness, stuffy nose, headache, mucus does not clear, no cough.
The nature of the headache can also vary depending on the disease, as well as the body’s immunity.
Pain sensations can be concentrated both in the temporal part and in the frontal part. The pain can be sharp (especially in the eye area), or it can be dull throughout the head. In people prone to migraines, severe pain can trigger an attack with deterioration in vision.
Most often, the pain intensifies in the morning. This occurs due to the fact that at night the outflow of mucus from the sinuses is less intense (due to sleep).
It happens that a runny nose causes nosebleeds. This is typical for both children and adults. Such bleeding occurs with sinusitis, rhinitis, and sinusitis. Crusts can form in the nasal cavity due to frequent but ineffective nose blowing. Later they scratch the mucous membrane, which leads to the release of a small amount of blood. Sometimes such a symptom indicates hypertension or circulatory disorders. Most often this occurs due to weak vessel walls due to vitamin deficiency, but only a doctor can accurately determine the cause.
The bone under the eye hurts: causes, diagnosis and treatment methods
When the bone under the eye hurts, this condition is called prosopalgia. Such a disorder can have neurological, vascular and symptomatic properties. Often pain occurs due to psychogenic factors. If a person feels that the bone under his eye hurts, such a symptom cannot be ignored.
Causes and symptoms
Pain can be caused by various reasons, which are characterized by certain symptoms:
- Osteomyelitis (according to ICD 10, M86). It is a consequence of advanced dental disease. This is, first of all, inflammation of the bone, which gives a high temperature. Osteomyelitis (according to ICD 10, M86) can spread to absolutely all elements of hard tissue, as well as to spongy and compact substance and even to the periosteum.
- Mechanical injury. It may be associated with bruises or a fracture of the facial bone. Upon palpation, a person feels severe pain. The site of injury becomes blue and swells.
- Neuralgia, which affects the nerves located in the facial area. We are talking about the trigeminal, glossopharyngeal, facial and hypoglossal nerves. A person’s facial expressions may be disturbed, facial asymmetry may arise, and, in addition, the bone on the cheek under the eye may hurt. Shooting along with twitching usually accompany trigeminal neuralgia. It can shoot at the neck, ears, shoulders and temples.
- Vascular eye disorder. It causes sharp pain around the eye sockets, pain and tearing are also possible. Weak and, in addition, damaged vessels supply blood to the eye area very poorly, which is why similar symptoms appear.
Inflammation of the paranasal sinus (development of sinusitis)
When the bone under the eye hurts, the pain is also caused by an inflammatory process caused by viruses and bacteria (that is, sinusitis).
Among bacteria, the most dangerous and common provocateurs are Staphylococcus aureus.
The disease can develop due to infection of the respiratory canals, as well as with advanced dental problems (due to deep caries and periodontitis). The following people are considered at risk:
- with a crooked nasal septum;
- with the presence of congenital defects in the structure of the nasal cavity;
- with nasal injuries.
And then we will look at the symptoms and treatment of sinusitis in children and adults.
Root Causes
When the bone under the eye hurts, it is necessary to look for the root causes of fluid stagnation in the paranasal area and nasal cavity.
It could be:
- Allergic reaction to dust, wool, chemical components, fluff and nutritional products containing irritants.
- Presence of sinus deformation due to trauma. In addition, the cause may be a curvature of the nasal septum along with a displacement of the jaw, an abnormal structure of the shells and improperly fused bones of the skull.
- Viruses that have entered the sinuses. They can provoke fluid secretion along with narrowing of the canals and swelling. If bacteria are also added to them, then improper therapy causes resistance to antibiotic drugs.
- The appearance of fungi settling in the sinuses, which cause mycosis. The severity of this disease depends on the type and aggressiveness of the fungus.
- Cold air. It can constrict blood vessels, and oxygen will not flow into the orbit of the eye in sufficient quantities, which sometimes provokes the feeling that the facial bone under the eyes hurts. In addition, the cause of discomfort is dust and air pollution.
- With vitamin deficiency, the immune system suffers. A weakened human body cannot resist attacks from pathogenic microorganisms, which is why a runny nose often develops, and then its complications.
- Hypothermia. With it, the body's protective functions weaken. The respiratory organs are the first to suffer infectious blows. If a person can hardly tolerate the cold, then in the autumn and winter he will suffer from rhinitis.
Symptoms and treatment of sinusitis in children and adults are interrelated.
Next, we will take a closer look at the pathologies occurring in the paranasal sinuses, which are classified as inflammatory processes.
Rhinitis
It is the body’s protective reaction to bacterial, viral, allergic and infectious irritants. The disease can provoke not only hypothermia with a cold, but also illiterate therapy with vasoconstrictor drops.
Sinusitis
A pathology such as sinusitis is an unpleasant disease caused by inflammation of the maxillary region. This disease develops due to rhinitis, fungal growth, colds, dental problems and allergies. The patient may be bothered not only by pain in the bridge of the nose, but also in the eye sockets, on the back of the head and in the temples.
Ethmoiditis
With ethmoiditis, inflammation affects the ethmoid cavity. This disease is an unpleasant consequence of rhinitis or sinusitis. If it is not treated, it will spread deeper into the frontal region and provoke frontal sinusitis.
Frontit
Frontitis is characterized by the process of inflammation in the mucous membrane of the frontal cavity. Among all sinusitis, it is considered the most dangerous disease, since if it develops, various serious complications are possible, for example, meningitis.
Sphenoiditis
The disease sphenoiditis is an inflammatory process occurring in the mucous wedge-shaped region. Its danger lies in physiology. The sphenoid cavity is usually located deep in the skull near the optic nerves and carotid artery. Since the disease is provoked by pathogenic microbes, in the case of intensive reproduction they can cause harm to these organs.
How diseases manifest themselves
Bone pain under the eye occurs in various pathologies, which are accompanied by certain symptoms:
- Rhinitis is accompanied by nasal congestion, from which clear fluid is released (and even flows at the height of the disease). A person's nasopharynx is sore, there is movement and itching. The eyes usually turn red. Tearing with sneezing is possible.
- Ethmoiditis is characterized by a condition where the bone under the eye hurts when you press on it. In the morning, phlegm may be coughed up, and viscous yellowish and green discharge from the nose is observed. They have an unpleasant putrid odor. Swelling in the eyelid area is possible. The sinuses under the eye also hurt. Patients suffer from dizziness, lacrimation, and, in addition, photophobia.
- With sinusitis, the bones of the face under the eyes hurt. People lose their sense of smell, purulent and sometimes bloody discharge appears from the nose, in addition, the voice becomes rougher and significantly deeper, and breathing, in turn, becomes difficult. If sinusitis develops, there may be a risk of inflammation in the cranial cavity. The chronic form serves as a source of infections, provoking relapses of osteomyelitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis and rhinitis, among others. Acute sinusitis sometimes affects the trigeminal nerve. In this case, people experience severe pain in the facial area.
- With frontal sinusitis, the eyes, forehead and temples hurt most often in the morning. Breathing may be difficult, and thick discharge (even crusty) may appear from the nose. The temperature increases, the eyelids swell, and, among other things, there is pain in the eyes.
- Sphenoiditis is characterized by prolonged pain in the area of the back of the head and crown. Even the use of analgesics does not relieve the painful symptom. It may hurt under the eye when pressed, and vision deteriorates somewhat. Patients feel weak and unwell. You may feel discomfort in the nasopharynx.
In acute forms of these diseases, people may develop a fever, and in addition, they often experience dull headaches and a stuffy nose. In chronic forms, the symptoms are not so pronounced, but getting rid of them is very difficult.
Next, we’ll talk about what kind of diagnosis and treatment is carried out when pain of this nature appears.
Carrying out diagnostics
When the bone under your eye hurts, you shouldn’t hesitate. In case of alarming symptoms, the patient should definitely contact a therapist or otolaryngologist. The specialist will certainly give a direction to do a nasal culture. In addition, certain studies are shown:
- Performing endoscopy of the paranasal sinus.
- Performing ultrasound diagnostics.
- Taking x-rays of the lateral and frontal areas of the face.
- Performing computed tomography.
- Carrying out magnetic resonance imaging.
Only immediately after receiving the result can the doctor understand why the bone under the eye hurts.
Doctors
The first specialist you should contact in case of the described symptoms is an otolaryngologist (ENT). He will make a diagnosis according to his profile and, if necessary, refer you for consultation to another specialist. For example, if a runny nose causes bouts of nosebleeds, you need to be examined by a neurologist, a therapist, and possibly a neurosurgeon if you suspect a brain disease. Or in the event of a migraine attack due to sinus congestion, again to a neurologist, who may prescribe a study of cerebral vessels or other tests.
It is possible that the otolaryngologist will not find any diseases in his field and will refer the patient to an allergist - if he suspects the allergic nature of the listed symptoms. You may need to consult an oncological surgeon to rule out or confirm the presence of tumors in the nasal cavity.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis will begin with an examination. An experienced doctor, based on the symptoms described, will rule out (or diagnose) the likelihood of one of the diseases. However, for a more accurate diagnosis, a number of studies may be required: radiography, ultrasound or even CT (computed tomography) of the sinuses.
Based on the results of the research, the presence or absence of inflammatory processes in the upper sinuses of the jaw, the frontal region, and the mucous membranes of the nose will be determined.
If the examinations did not reveal inflammation, the diagnosis will be continued by another specialist - an allergist, neurologist, or oncologist.
Diagnosis and treatment
The condition in which the cheekbone on the face hurts is a rare phenomenon. In most cases it is caused by trauma and direct blows, but sometimes it can appear as a result of quite serious inflammatory or neurological diseases. To get rid of the problem, it is advisable to visit a doctor and find out the reason that led to the pain.
When making a diagnosis, accompanying symptoms and location of pain play an important role. The cheekbone may hurt under the eye, closer to the temples near the ear, when opening the mouth or pressing. Often the pain is accompanied by jaw tightening, spasms when yawning or chewing food. You should tell your doctor about all these signs at your appointment.
If a person has pain in the cheekbones of his face, the reasons may be hidden in the following pathologies:
- inflammatory processes in the TMJ;
- diseases of the sinuses or eyeball (sinusitis, orbital cellulitis);
- mechanical damage (dislocation, bruise);
- dental diseases;
- ear pathologies (otitis media);
- vascular diseases (temporal arteritis);
- damage to the bones of the face.
Inflammation of the TMJ
Often, with pain in the cheekbones, the causes of discomfort are diseases of the TMJ (temporomandibular joint), which include:
- Arthritis is an inflammation of the joint, characterized by swelling, redness in the affected area, crunching when moving the jaw, pain when palpating or at rest, stiffness of the cheekbone, problems with chewing and speech.
- Arthrosis is an inflammatory process that leads to changes in the anatomical structure of the joint. A person feels a dull pain, which often intensifies when opening the mouth.
- Ankylosis is a pathological fusion of joint limbs caused by infection or injury. In addition to pain, the disease is accompanied by a feeling of shrinkage of the cheekbones.
The disease is characterized by damage to the eye tissue as a result of infection through the blood or from a diseased sinus. When it develops, a person’s eyes hurt when blinking, the eyelids turn red and swell. Sometimes the affected eye protrudes or completely stops seeing. When the infection spreads to nearby structures, the cheekbones and other affected areas hurt.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis covers the maxillary sinuses and is manifested by a prolonged runny nose. A person experiences a feeling of fullness in the bridge of the nose and pain that radiates to the cheekbones, forehead, and temples. Additional symptoms are:
- nasal congestion;
- frequent sneezing;
- deterioration of sense of smell;
- temperature increase;
- excessive tearing;
- swelling and pain in the eyelids.
Warm tea with honey and lemon and rosehip decoction will help ease the symptoms of the disease. A good way to get rid of congestion is inhalation and warm baths.
If there is pain under the eye even after drug therapy, the disease does not recede, but rather worsens, surgical intervention is used. For inflamed sinuses and severe narrowing that interferes with the removal of purulent secretions, a puncture is used.
Treatment
Needless to say, self-medication for these symptoms is fraught with the most unexpected consequences. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
The basis of treatment for infections of the ENT organs are systemic and local antibiotics. To improve drainage of the sinuses, vasoconstrictors and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. If it has become possible to talk about chronic inflammation, then it is treated using procedures that restore the integrity of tissues and increase immunity.
Respiratory infections are treated with antimicrobial and vasoconstrictor agents. They restore the natural drainage process in the nose and thereby normalize the outflow of mucus.
Allergic diseases are treated with antihistamines, as well as topical glucocorticosteroids. As for tumors, they are removed through surgery using an endoscope.
It is also possible to prescribe physiotherapeutic treatment if the patient has been treated as prescribed, but persistent nasal congestion does not go away.
These can be hardware procedures such as:
- electrophoresis – anti-inflammatory medications are injected into the tissues of the nasal cavity using direct current;
- ultrasound – the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx is exposed to ultrasonic waves;
- UHF – acts on foci of inflammation through high-frequency electromagnetic waves, due to which inflammation goes away and wounds heal.
If pus has accumulated in the paranasal sinuses, the patient is prescribed a puncture (minimally invasive operation) - insertion of a needle, with the help of which the purulent mass is removed from the inflamed cavity.
Causes of pain under the eye
The eyes are perhaps the most sensitive organ of our body. The state of this paired organ can be affected by a variety of pathological processes developing in our body: vegetative-vascular dystonia, arterial hypertension, neoplasms, colds and more. In all cases, pain under the eye is not the main process and therefore does not require treatment. The unpleasant symptom will go away on its own when the underlying pathology is eliminated.
Mechanical injury
Bruising in the area of the eye, nose and cheekbones causes severe pain, the occurrence of which can be reduced by cold. If you have an abrasion and bleeding, then you need to treat the wound surface with a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
A bruise is indicated by pain under the eye, which is accompanied by bruising and swelling of the tissue. When a swelling appears, it is not enough just to remove it, the presence of a fracture or crack in the facial bone should be excluded. In this case, radiography will help.
Osteomyelitis
Purulent inflammation of the bone can provoke aching pain under the eye, which radiates to the cheekbones and ear. Often, osteomyelitis is the result of untimely treatment of diseases of the teeth and gums. In this case, the treatment is carried out by the dentist.
Vascular disorders
What is accommodative asthenopia
If problems occur with the blood vessels around the eyes, pain can occur both under the eye and near the eyebrows. Patients may also complain of pain in the eyes. Painful sensations are provoked by poor supply of the eye with problematic blood vessels. In this case, patients are recommended to consult a cardiologist and ophthalmologist.
Severe pain can also be caused by glaucoma, which is caused by increased intraocular pressure. The disease causes discomfort around the eyes, around the eyeballs, and in the temporal or occipital part of the head. All this is accompanied by deterioration of vision. Patients also complain of nausea and general weakness. In this case, the eyeball is extremely sensitive and should be especially protected from various types of irritants.
Load on the eye muscles
Spending a long time at the computer, watching TV, reading books - all this can cause increased fatigue. Patients begin to complain of pain, cramping and fatigue.
If you spend a long time in front of the TV, pain in the eye area can become chronic.
In order to avoid increased fatigue, it is important to adhere to the rules of visual hygiene, which includes the following:
- If your job involves spending long periods of time at the computer, be sure to take breaks. The eyes should rest; to do this, sit for a while with your eyes closed, you can put your palms on top. It is also useful for training the eye muscles to alternately look at objects located near and far. With your eyes closed, try to draw a circle, a square, and various lines.
- A proper daily routine includes adequate sleep. You can’t stay up until midnight at work; your eyes get maximum rest at night.
- Sufficient lighting. Working in low light is very harmful to the eyes. Don't forget, the lighting from the computer is not enough. As for schoolchildren, when writing, right-handers should have the light source on the left, and left-handers should have the light source on the right.
Why does it hurt under the eye and what to do?
The feeling of unpleasant pain under the eyes can signal problems in the body. If the patient feels pain in the infraorbital cavity, in the facial bone, then this is a signal about the need to consult a specialist doctor: dentist, surgeon, neurologist, ENT specialist.
Various reasons cause pain under the eye. Depending on the nature of the pain, the illness is determined and accordingly it is decided what to do to eliminate the unpleasant sensations.
Mechanical damage
If the pain in the eye area was preceded by a blow to the surface, then the cause of the discomfort lies in mechanical damage as a result of contact of the face with a sharp or hard object.
In addition, external signs appear: hematoma, soft tissues swell. If the blow was strong, a bone fracture or crack is possible.
It is necessary to take an x-ray to have a complete picture of the nature of the damage.
To relieve swelling, it is advisable to apply ice or a cold object to the site of impact. If there is a bleeding abrasion, treat the area with hydrogen peroxide to prevent infection.
Load on the eye muscles
Sitting for a long time near the computer, watching TV or reading books leads to overstrain of the eye muscles. As a result, patients receive complaints about pain, pain in the eyes and a tired person.
To avoid eye injury or correct the current situation, it is necessary to follow the rules regarding visual hygiene:
- Spending a long time at the computer should be interrupted by a short rest. Sit for a few minutes with your eyes closed. Do gymnastics: move your gaze from a near object to a distant one. Closing your eyes, try to draw a circle, square, lines.
- Follow a daily routine - you need full sleep, since it is at night that the eyes receive maximum restoration.
- Sufficient lighting of the workplace. For schoolchildren, the light should fall from the left for right-handers and from the right for left-handers.
Patients who wear glasses or contact lenses are susceptible to eye pain. The reason is incorrectly selected products:
- Insufficient or excessive lens power.
- The lens material used is not suitable and causes irritation.
- The diameter of the product is not suitable.
- An allergy or infectious infection is accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Postoperative period
There is always discomfort after cataract surgery. The injured eye often hurts, there is tingling and itching. If the doctor’s recommendations are followed and the postoperative period passes without complications, then the symptoms will stop after 2-3 days.
Laser vision correction also does not come without consequences. But since the operation is performed under local anesthesia and with minimal damage to the mucous membrane, the discomfort goes away within 2-3 hours.
Diseases
Pain under the eye, in the facial bone - this means purulent inflammation or a problem with neuralgia. It all depends on the nature of the pain, its location and how it manifests itself: when pressed or simply exists.
Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses
The appearance of an inflammatory process in the sinuses provokes pain under the eyes. Inflammation is caused by bacteria and viruses. Staphylococcus aureus is especially dangerous. It develops when the respiratory tract becomes infected or the patient has advanced dental problems: deep caries, periodontitis.
Patients at risk may develop sinusitis:
- The nasal septum is bent.
- There are congenital defects in the structure of the nasal cavities.
- Nose injuries.
What can cause an inflammatory process in the nasal cavity:
- Allergy. A disease that affects more and more people every year. Allergens include: dust, wool, pollen, household chemicals, fluff, food.
- Deformed sinus. As a result of mechanical damage, a curvature of the nasal septum, displacement of the jaw, and improper fusion of the skull bones occur. Congenital abnormal structure of the nasal concha.
- Viruses. When viruses penetrate the nasal sinuses, fluid is released, the channels narrow, and swelling appears. The appearance of additional bacteria leads to non-response to antibiotic treatment.
- Fungi settle in the sinuses, causing them to become clogged. A disease occurs - mycosis. Different types of fungus cause different severity of the disease.
- Cold air. The reaction of blood vessels to a decrease in ambient temperature is narrowing. As a result, less oxygen reaches the eyes. There is pain under the eye. Airborne dust and gas particles cause pain around the eyes.
- Avitaminosis. A lack of vitamins in the body leads to a decrease in protective functions. This is why colds occur so often in winter and spring. The body cannot resist the infection, a runny nose occurs and, subsequently, complications.
- Hypothermia. Hypothermia leads to a decrease in protective function. Infections attack organs that cannot resist for long - breathing. With a constant cold, a person's nose becomes clogged and rhinitis occurs, which will worsen in the fall and winter, when it is cold.
Sinusitis (inflammation of the paranasal sinuses) is divided into several types, each with its own symptoms:
- Rhinitis. The nose is stuffy and clear fluid is leaking out. Soreness and itching in the nasopharynx. Eye redness, watery eyes and sneezing.
- Ethmoiditis. The disease is accompanied by pain in the bridge of the nose when pressed, discharge from the nose of a viscous yellowish-green liquid with an unpleasant smell of rot. The eyelids swell, pain appears under the eye. The patient feels dizzy and watery. Narrowed palpebral fissure, through which it is painful to look at the light.
- Frontit. Pain in the temples, eyes and forehead appears in the morning. The patient has difficulty breathing and thick fluid is released from the nose. The body temperature rises, the swelling of the eyelids increases and a stinging sensation is felt in the gases.
- Sphenoid. The patient is bothered by pain in the back of the head and crown. Taking painkillers does not help. It may hurt under the eye when pressed, and vision decreases. Weakness, malaise. Discomfort in the throat and nose.
Osteomyelitis
A disease associated with the development of a purulent process in the bone and bone marrow, affecting surrounding tissues. The causative agents of the disease are considered to be pyogenic bacteria that accumulate in the maxillary sinus area.
The patient notes the appearance of painful, aching unpleasant symptoms radiating to the cheekbone and area near the ear.
Advanced problems associated with an inflamed oral cavity: teeth and gums, inflammation of the dental nerve, dental caries of the upper jaw.
Osteomyelitis of the upper jaw is treated after consultation with a dentist and under his supervision.
Vascular disorders
Problems with the blood vessels around the eyes cause pain symptoms. They are concentrated not only under the eye, but also in the eyebrow area, and often complain of cutting pain. This is caused by a lack of normal supply of oxygen and nutrients to tissues.
Glaucoma occurs when intraocular pressure is increased. Feeling of pain in the eyes, discomfort near the organs of vision. The pain radiates to the occipital part and to the temporal part of the head. There are complaints of nausea, weakness and blurred vision. During this period, the sensitivity of the eyeball is increased, it is necessary to protect it from irritants.
Infectious processes
The human body is designed in such a way that all organs are interconnected. This applies to both the eyeballs and the paranasal sinuses.
Why does my eye hurt for no apparent reason? The inflammatory disease, once in the nasal cavity, has free access to the organs of vision, and shooting and pulsating pains appear.
If pathogenic microorganisms have penetrated to the back wall, it is painful to move your eyes. The reason for this is the presence of nerve endings in this area.
Phlegmonous dacryocystitis is an infectious disease manifested by pain in the inner corner of the eye. Accompanied by inflammation and swelling in the nose area. When pressing on the purulent focus, a sharp pain occurs. The tumor may move to the other eye. The patient experiences fever, cephalgia, and loss of appetite.
2-3 days are enough for pus to accumulate under the skin in one place and the skin becomes yellow. The abscess opens, the problem disappears. A scar or fistula remains.
Demodicosis
With demodicosis, the skin around the eyes suffers. The causative agent of the disease is the iron tick. It lives in hair follicles, sebaceous glands and meibomian glands located on the eyelids.
Trigeminal neuralgia
The patient complains of acute pain. Women over 40 years of age are more often affected. Discomfort may manifest as dental problems. Severe pain radiates to the upper and lower jaw.
Any movements: laughing, talking, brushing teeth - provoke attacks of pain.
Trigeminal neuralgia causes numbness in some muscles. There are disturbances in facial expressions, facial asymmetry occurs, and dryness and pain are felt in the visual organs. The upper eyelid swells.
The brow ridges contain a large number of blood vessels. Disturbance in the functioning of the arteries leads to pain above the eye. Migraine is a prime example of vascular problems. When the pain, starting in the forehead, gradually decreases to the eyebrows and reaches the eyes.
Temporal tendinitis
An inflammatory process that occurs in the tendons connecting the temporal bone and the lower jaw. Temporal tendonitis is characterized as a dull aching sensation and progresses to an acute one that cannot be tolerated.
Sinusitis and runny nose
Sinusitis - painful sensations are concentrated in the bridge of the nose and around the eyes. The patient's sense of smell disappears, pus is discharged from the nose, sometimes mixed with blood. If sinusitis is not treated, there is a danger of inflammatory processes flowing into the cavity of the cranium and may affect the brain.
Acute sinusitis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Headache;
- Sinuses and eyes hurt;
- Unpleasant sensation and pressure on the teeth;
- The pain radiates to the back of the head, creating a semblance of a migraine, intensifying in the evening;
- Nostrils become clogged and it’s hard to breathe;
- Increased temperature, swelling of the cheekbones, eyelids, weakness and fatigue.
Treatment
Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by a doctor. An attempt to independently combat pain in the eye area leads to a worsening of the condition and the emergence of complications or death.
To treat infectious diseases, doctors prescribe antibacterial solutions, antibiotics, ultra high-frequency therapy on the inflammation site, and blue light on the damaged area.
Eye pain caused by other reasons not related to diseases, for example, contact with a foreign object - here you can get by with improvised means.
Rinse the mucous membrane with clean water, and then instill medications in the form of drops with an antibacterial effect: Levomycetin, Albucid. Should I consult a GP? It is worth it if the patient cannot decide what exactly caused the pain.
Then the therapist will offer to take tests and undergo a general examination, after which he will say: “consult a specialist” and indicate a specific doctor.
Source: https://bolitgolova03.ru/head/eyes/bolit-pod-glazom.html
Why does pain occur above the eye?
In the area of the brow ridges there is a huge number of blood vessels. The expansion or, conversely, narrowing of blood vessels in this area can provoke painful sensations.
The main cause of pain above the eye is neurological disorders. During a migraine attack, the pain is first localized in the forehead and then moves down to the eyebrows and eyes. The condition is aggravated by nausea, vomiting, irritability and general weakness.
Infringement of the occipital nerve is another reason that provokes pain in the area of the superciliary arches. In this case, discomfort is felt in the area of the eyes, forehead, and temples. Stressful and depressive conditions can lead to pinching of the occipital nerve.
Pinching of the cervical vessels can also be a cause. Due to the narrowing of the vascular lumen, less blood enters the brain. As a result, oxygen starvation appears, manifested in the form of the following symptoms: pain above the eyebrows, in the forehead, deterioration of auditory and visual function, deterioration of thinking abilities and memory. Patients also complain of sleep problems and fainting.
Neurological pain is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- noise in ears;
- blurred vision;
- damage to the optic nerve;
- pathological changes in pupil movement;
- retinal hemorrhages.
A provoking factor can also be changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy or before critical days. The discomfort is similar to pain during the inflammatory process, only there is no runny nose.
Above the eyes may hurt due to alcohol intoxication
When intracranial pressure increases, pain is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- diplopia (split objects);
- bruises or circles under the eyes;
- severity of drowsiness;
- hypertension or hypotension.
Skin diseases are another provoking factor: molluscum contagiosum, boil, herpetic lesion. With barley and chalazion, pain is accompanied by hyperemia, the tissues of the eyelid swell. More often the process is localized under the lower eyelid.
Phlegmon of the orbit is a purulent inflammation of the orbit, in which, as a result of swelling and inflammation, vision can even be impaired. The pathological process poses a threat to life.
Pain can be triggered by traumatic brain injury, frontal sinusitis, and even frequent consumption of hot and spicy foods. What to do if pain occurs above the eye? First of all, you should understand the provoking factors. It’s simply wrong to take painkillers; treatment should be handled by an experienced specialist.
The picture shows how the skin around the eyes is swollen due to phlegmon
Pain in the face (facial pain)
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Pain in the face (facial pain) – causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods. Facial pain belongs to the category of pain syndromes, the diagnosis of which is most difficult. Facial pain can be based on diseases of various organs or systems or occur due to damage to nerve fibers (primarily cranial nerves). Separately from these two groups, pain is considered, the clear cause of which sometimes cannot be identified. They are called persistent idiopathic, or atypical, pain.
Facial pain caused by damage to the branches of the cranial nerves (neurogenic) and pain caused by diseases of organs or systems (somatogenic) are diagnosed.
Trigeminal neuralgia,
in which the branches of the trigeminal nerve are affected, it is characterized by burning pain, which is paroxysmal in nature and intensifies with any movements of the mouth (chewing, opening), tension of facial muscles (smile, grimace). Most often it is concentrated at the exit points of the branches of the trigeminal nerve (in the area of the eyebrows and wings of the nose) and can be accompanied by tic. Increased lacrimation is often observed. In the area of the painful point there is a feeling of burning, swelling, the skin turns red or turns pale. An attack can be provoked by pressing on certain points. Sometimes areas of increased or decreased sensitivity are identified on the face.
It is believed that most often such pain occurs due to compression of the branches of the trigeminal nerve in the narrow bony canals of the skull by vessels that form loops around the nerve. In some cases, compression of the nerve in the small bone canals of the upper jaw occurs due to swelling of the surrounding tissues due to frequent rhinitis or chronic inflammation in the tooth area. The nerve may be compressed by a growing tumor. Sometimes pain syndrome develops against the background of a herpetic lesion. Diagnostics and examinations
When the nerve is compressed in the area of the infraorbital canal, pain can occur in the area of the eye sockets and eyebrows. When the maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve is compressed, the tooth is considered to be the culprit of painful attacks. This can be confirmed or ruled out using a panoramic photograph of the upper and lower jaws. To exclude the tumor nature of the pain syndrome, MRI of the brain or MR angiography is prescribed.
Which doctors should I contact?
The variety of symptoms accompanying trigeminal neuralgia makes its diagnosis difficult.
Consultations required:
- dentist;
- an otorhinolaryngologist, especially in the case of frequent rhinitis;
- neurologist.
What should you do if symptoms appear?
As a rule, patients intuitively exclude factors that can provoke a painful attack. They try to avoid eating and do not wash their faces for fear of affecting pain trigger points.
Treatment
Success in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia can only be achieved with an integrated approach.
After a thorough examination, the doctor may prescribe vitamins, antispasmodics, antidepressants and, in some cases, antiepileptic drugs.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are recommended: laser therapy, acupuncture, ultraionophoresis, electrophoresis, diadynamic currents, paraffin baths.
If it is not possible to achieve positive results with drug therapy, surgery may be necessary. Microvascular decompression allows the nerve root to be freed. The essence of this operation is to isolate the nerve and the vessel that compresses it. Radiofrequency destruction of the affected branch of the trigeminal nerve is effective.
Somatogenic facial pain
Pain in the face and head can be a manifestation of a disease of any organ or system, in which case they are called somatogenic. These pains may not be as sharp and intense as in the case of damage to the trigeminal nerve, but their persistence significantly worsens the person’s condition.
Possible reasons
The simplest and most quickly identified cause of facial pain is an affected tooth. With advanced caries or periodontitis, the pain is localized not only in the area of the diseased tooth, but also radiates to the jaw, temple and ear.
Significant suffering is caused to a person by disruption of the masticatory apparatus (dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint).
In addition to intra-articular changes (arthrosis, underdevelopment of the articular head), malocclusion can lead to pain, for example, due to the loss of a group of teeth or an incorrectly selected prosthesis, or prolonged spasm of the masticatory muscles.
Inflammatory processes in the area of the paranasal and frontal sinuses can also cause pain. Depending on the location of the pathological process, pain may be felt in different areas of the face.
So, with frontal sinusitis (inflammation of the frontal sinuses), pain can occur in the frontal region and radiate upward. Sinusitis (inflammation of the maxillary (maxillary) sinuses) is characterized by pain in the infraorbital region, radiating to the upper jaw.
With ethmoiditis (inflammation of the mucous cells of the ethmoid bone) - between the eyes with a return to the temporal region.
Diseases of the eyes (eyes) can lead to pain.
Sometimes facial pain is a symptom of angle-closure glaucoma (increased intraocular pressure), which requires immediate treatment, as the disease can lead to vision loss.
Diagnostics and examinations
To find out the source of pain, it is necessary to undergo a series of examinations.
The dentist will prescribe panoramic photographs of the upper and lower jaw. They allow you to identify a diseased tooth and sanitize the source of inflammation.
If pathological processes in the area of the nasal sinuses are suspected, it is advisable to conduct radiography or computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses (primarily the maxillary and frontal sinuses).
Much less frequently, the cause of facial pain is sought in dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint.
The articular nature of facial pain can be confirmed using radiography of the temporomandibular joint.
The radiologist will help identify changes in the articular surfaces and deformation of the joint space.
Clinical manifestations of temporomandibular joint dysfunction are characterized by:
– pain and crunching in the joint area when opening the mouth and chewing;
– inability to open the mouth smoothly and completely;
– swelling and pain in the joint area (between the cheek and ear;
– asymmetrical mouth opening;
– uneven wear of teeth on the right and left sides.
The “ocular” nature of the occurrence of facial pain has a number of signs.
The pain is always clearly localized on one side. There is pain when moving and pressing on the eyeball. Only an ophthalmologist can definitively make a diagnosis after measuring intraocular pressure and examining visual function.
Which doctors should I contact?
The presence of an extensive list of possible causes of facial pain often requires visiting doctors of various specialties: a dentist to exclude pain associated with dental damage, an otolaryngologist and an ophthalmologist if there is a suspicion of diseases of the ENT organs or eyes.
If studies do not confirm the somatogenic (that is, due to organ damage) nature of the pain, then a neurologist should continue further diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment in the case of somatogenic pain should be aimed at eliminating the disease of the “causal” organ.
If there are inflammatory phenomena in the area of the facial sinuses, the otolaryngologist will prescribe complex therapy, including antibacterial drugs, vasoconstrictor sprays, antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs. Sometimes a positive treatment result can be achieved by rinsing the sinuses using the YAMIK catheter.
If the cause of the pain is an eye disease, then further treatment is carried out by an ophthalmologist. As a rule, when the diagnosis of angle-closure glaucoma is confirmed, a complex of medications is prescribed, which includes pilocarpine and timolol, as well as diuretics. If there is no improvement, the ophthalmologist may recommend laser or surgical treatment
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Source: https://www.invitro.ru/library/simptomy/13234/
Pain when blinking
If the pain is accompanied by tearing, then the presence of a foreign object can be suspected. Usually, all excess comes out along with the tear fluid, but there are also cases when the body needs help. In this case, it is better to consult an ophthalmologist.
If pain occurs when you blink, this may also indicate a cold. At the same time, a runny nose, aches throughout the body, and lacrimation appear. The problem is resolved after eliminating the virus.
With conjunctivitis, the eye may also hurt when blinking. In this case, the whites are red, and purulent secretion is released from the eye. Cutting pain when blinking is a harbinger of stye!
Crohn's disease is the most unlikely cause, but perhaps the most dangerous, and should also be kept in mind. This is a chronic disease of the gastrointestinal tract. The disease is accompanied by various symptoms, among which conjunctivitis can be noted. Antibacterial therapy is carried out. In severe cases, surgery may be required.
Causes of nasal congestion with headache
Nasal congestion, which develops in combination with headache, is a polyetiological pathological manifestation. This means that the syndrome develops due to the presence of several diseases, which include:
- inflammatory processes localized in the paranasal sinuses;
- furunculosis;
- allergic rhinoconjunctivitis;
- formation of neoplasms in the nasal cavity.
Groups of diseases in which the nose is stuffy, there is a headache, there is no fever, although they are united by the same symptoms, they have different approaches to effective treatment.
Root Causes
When the bone under the eye hurts, it is necessary to look for the root causes of fluid stagnation in the paranasal area and nasal cavity.
It could be:
- Allergic reaction to dust, wool, chemical components, fluff and nutritional products containing irritants.
- Presence of sinus deformation due to trauma. In addition, the cause may be a curvature of the nasal septum along with a displacement of the jaw, an abnormal structure of the shells and improperly fused bones of the skull.
- Viruses that have entered the sinuses. They can provoke fluid secretion along with narrowing of the canals and swelling. If bacteria are also added to them, then improper therapy causes resistance to antibiotic drugs.
- The appearance of fungi settling in the sinuses, which cause mycosis. The severity of this disease depends on the type and aggressiveness of the fungus.
- Cold air. It can constrict blood vessels, and oxygen will not flow into the orbit of the eye in sufficient quantities, which sometimes provokes the feeling that the facial bone under the eyes hurts. In addition, the cause of discomfort is dust and air pollution.
- With vitamin deficiency, the immune system suffers. A weakened human body cannot resist attacks from pathogenic microorganisms, which is why a runny nose often develops, and then its complications.
- Hypothermia. With it, the body's protective functions weaken. The respiratory organs are the first to suffer infectious blows. If a person can hardly tolerate the cold, then in the autumn and winter he will suffer from rhinitis.
Symptoms and treatment of sinusitis in children and adults are interrelated.
Next, we will take a closer look at the pathologies occurring in the paranasal sinuses, which are classified as inflammatory processes.
Inflammatory processes in the sinuses
Anatomically, the paranasal sinuses are cavity formations of the bones of the facial skull that connect to the nasal cavity. These include the maxillary, frontal, sphenoid sinuses or sinuses.
In diseases of the nasal mucosa, the inflammatory process spreads to the paranasal sinuses. This process is combined with the term sinusitis. Quite often, an isolated pathological process is identified in the maxillary (sinusitis), sphenoid (sphenoiditis) and frontal (frontal) sinuses.
There are several known most common causes of inflammation of the paranasal sinuses:
- acute respiratory viral infection, which develops catarrhal inflammation of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, including any paranasal sinuses;
- bacterial infection (staphylococci, streptococci, intestinal, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella, Proteus), characterized by a more severe course with frequent development of a purulent process (pus accumulates in the cavity of the frontal, maxillary or sphenoid sinus);
- non-infectious causes of the inflammatory process in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, the most common of which is an allergic reaction with swelling of the mucous membrane.
Combined inflammation of several sinuses at once has a more severe course and can be accompanied by intoxication of the body. In this case, nasal congestion and headache are accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
Sinusitis
The inflammatory process localized in the maxillary sinuses (paranasal sinuses of the upper jaw) is called sinusitis. The main condition that promotes the spread of infection from the nasal cavity to the maxillary sinus is the development of a runny nose. Nasal congestion is the result of swelling of the mucous membrane, in which the outflow of secretions from the cavity of the maxillary sinus worsens, contributing to the development of the inflammatory process.
Why do teeth hurt with sinusitis?
The maxillary sinus becomes inflamed, accompanied by various symptoms. Patients suffer from severe headaches, high fever and nasal congestion. Such symptoms are characteristic not only of sinusitis. But toothache can occur with this pathology.
Causes of the disease:
- There is pressure from the accumulated exudate on the walls. The upper jaw is located under the sinus, on which pressure is applied, which is why the patient suffers from discomfort and may have toothache. Chewing food increases painful sensations, and tapping performed by a doctor during diagnosis has a similar effect.
- The upper molars are inflamed.
- The disease of a chronic nature lasted a long time, due to which the inflammatory process affected more than one mucous membrane. Bone tissues have undergone pathological processes. Due to the location of the maxillary sinus, the inflammatory process affected it.
- The inflammation affected the trigeminal nerve. Painful sensations of the shooting type radiate to the teeth and ears.
Pain in the teeth with sinusitis manifests itself in different ways. In the case of dull pain that intensifies when the patient chews food, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is often diagnosed. If the patient is sick with an acute odontogenic disease, the pain is sharp and severe.
Toothache with sinusitis: connection
If the inflammatory process affects the maxillary sinuses, pain is the main symptom of the disease. The spread of inflammation directly affects localization. The first stage of the disease is characterized by painful sensations due to the inflammatory process itself and the action of pathogens on the body.
Swelling of the mucous membrane appears later, causing nasal congestion. Discharge begins to accumulate in the nose, creating a favorable environment for harmful organisms. Bacteria actively begin to multiply, forming purulent exudate. The walls of the sinus are under pressure due to accumulated pus, causing the patient to experience pain.
Painful sensations in the teeth appear due to the fact that the maxillary sinuses are located close to the oral cavity. There is a small partition between them. It is also possible that the upper teeth have grown into the accessory chambers with their roots, being located in close proximity. The accumulation of pus puts pressure on the teeth. Depending on the pressure, the pain has different intensity.
If toothache occurs and it is difficult to identify the cause when visiting a dentist, consultation with an otolaryngologist is necessary.
Toothache develops when a disease occurs through two mechanisms:
- Rising. Sinusitis occurs due to a diseased tooth, which is the root cause of the disease. In case of infection of the sinuses, the pain increases due to the response. The remaining areas are covered, the intensity of painful sensations increases.
- Descending. The reason lies in the maxillary sinuses, which serve as a source of inflammation. There is pressure on the lower jaw from mucous and purulent discharge coming through the pockets. Acute toothache is a response.
If pain in the teeth appeared first, when the symptoms of the disease were not yet pronounced, an ascending mechanism of development is diagnosed, then the origin of sinusitis is from the tooth. When the clinical picture has formed first, the temperature rises, acute pain appears, and a downward runny nose occurs.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pathology aims to timely identify dental sinusitis and the diseased tooth that has become the root cause of development. Diagnosis occurs using X-rays, computed tomography, and endoscopy.
Sinusitis of an odontogenic nature is dangerous due to the development of complications, which is why treatment occurs in a hospital. First, an examination by a dentist is performed, thanks to which it is possible to get rid of the inflammatory process in the oral cavity.
Dental treatment involves removing the cause of the pathology. It is possible to remove a tooth, place a filling, or remove foreign particles that caused inflammation. The nasal cavity is rinsed.
Sinusitis after tooth extraction is cured with complex therapy, which replaces treatment at the dentist.
Symptoms and treatment of frontal sinusitis in adults at home
How can you get rid of pain
In the case of an inflammatory process affecting the paranasal sinuses, therapy is aimed at getting rid of the symptoms of the disease and therapeutic and preventive measures.
Odontogenic sinusitis is often the reason for the removal of the affected tooth and closure of the fistula. Later, conservative therapy is used, including:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Washing.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
Therapy is aimed primarily at removing the inflammatory process in the oral cavity. Treatment includes:
- Tooth extraction at the dentist's office or removal of foreign particles from the nose.
- Sanitation of the patient's mouth.
- The otolaryngologist rinses the sinuses through a puncture and administers medications.
Local anesthesia is used for the operation. If the complications are severe, it is necessary to use general anesthesia and carry out a full-fledged surgical intervention carried out in a hospital setting. Following the procedure, medications are prescribed in the form of vasoconstrictor drops. If a complication occurs, it becomes necessary to take antibacterial drugs.
The chronic form of dental sinusitis is treated in a similar way. A surgical operation is necessary in order to remove tumors that appear in the cavity and close the passages. Using an incision in the oral cavity, self-removal occurs, then the sinuses are washed out.
Surgery requires a specific medication regimen afterwards. Complex therapy is prescribed by a specialist and includes the following medications:
- Antibacterial drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Immunomodulators.
- Antihistamines.
Oral sanitation involves therapy including:
- Etiological treatment. The causes of pathology are eliminated.
- Symptomatic treatment. Relief of symptoms of sinusitis.
- Pathogenetic treatment. The disease progresses easier for the patient.
Puncture is resorted to when conservative therapy fails to achieve an effect in the fight against the disease. The puncture is made with a special needle, by creating a fistula, which helps get rid of purulent formations from the nasal cavity. Head pain goes away after the procedure.
Traditional methods for eliminating toothache
You can relieve pain at home using the following methods:
- Rinsing the mouth with saline solutions and soda. It is possible to add iodine.
- Using sea buckthorn oil and alcohol for lotions. The sore spot is treated with a cotton pad soaked in solution or oil. To eliminate the possibility of burns, propolis tincture is diluted in a one-to-one ratio with water.
- Rinsing the mouth with medicinal herbal decoctions. They use oak bark and chamomile for this. Efficiency increases when preparing a decoction from the collection.
Ways to relieve pain
Measures to help relieve pain in case of sinusitis:
- Washing. Saline solutions and decoctions are used. The nasal cavity is cleared of pus.
- Warming up. There is an increase in the outflow of secretions.
- Inhalations. Sea salt and herbs are used. The functions of the mucous membrane are restored, irrigation is restored, and swelling is relieved.
- Vasoconstrictors. Applicable in case of clearing the nasal cavity from pus. Effectively relieve congestion and reduce headaches.
Allergic rhinoconjunctivitis
A fairly common reason for a stuffy nose without fever and a headache is the development of a specific allergic inflammatory reaction affecting the mucous membrane of the nose and conjunctiva of the eye, as well as allergic rhinoconjunctivitis.
Allergy is a pathological process with a hypersensitization reaction (increased sensitivity) of the human body to certain foreign compounds, usually of protein origin.
When an allergen comes into contact with the mucous membrane of the nose or eye, histamine is released (this hormone is designed to raise alarm in the body). In response to such a signal, hundreds of chemical reactions occur, which manifest themselves in a number of characteristic clinical signs:
- nasal congestion with the appearance of mucous transparent discharge;
- a feeling of discomfort in the nasal area in the form of itching;
- burning in the eyes, lacrimation, sometimes photophobia;
- headache, which is a reaction to the spread of allergies to the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses.
The main feature of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis is that the inflammatory reaction is not accompanied by an increase in body temperature and intoxication.
How diseases manifest themselves
Dental diseases can cause severe pain in the facial part of the head. Let's take a closer look at oral ailments.
People often have severe headaches in the absence of timely treatment for inflammatory processes occurring in dental tissues. Such as caries, periodontitis, granuloma, periostitis.
In addition to pain in the mouth and face, patients experience an increase in body temperature. The condition is aggravated by eating hot or cold food.
If your face hurts for several days after the dentist pulled out a tooth, there is no reason to worry. It's quite normal. However, if the pain does not go away for several days, and its intensity only increases, the cause may be:
- poorly performed surgery;
- the presence of dental tissue remains inside the gums;
- the occurrence of infectious or inflammatory processes at the site of the extracted tooth.
To eliminate pathological symptoms, you will need to make an appointment with a dentist.
Soreness often occurs with ophthalmic disorders. A condition where the face hurts and the head can appear with:
- working at a computer for long periods of time or watching television for many hours;
- glaucoma;
- pterygium;
- blepharitis;
- conjunctivitis.
In such cases, it is necessary to consult an ophthalmologist.
Whatever the reasons for the condition when your face hurts, you cannot ignore it. Only under the supervision of an experienced specialist can pathological symptoms be eliminated and health maintained.
Allodynia often occurs suddenly. The main symptom of the disease is pain caused by touching the face. Soreness may be localized. Some patients experience pain that develops on the facial surface on the left or right. The pain itself can be acute or minor.
If pain appears on one side with fever, you must first find out what comes first—pain or fever. If the inflammatory process is caused by an infectious lesion, then the sweat glands try to remove toxins from the body. This causes inflammation of the nerve endings.
If a pain syndrome localized on one side of the face first developed, and then the temperature rose, then perhaps this is the appearance of a boil or erysipelas. With allodynia, a person experiences insomnia and nervousness. In many patients, the appearance of the disease causes a burning sensation on the skin, itching, and sharp tingling sensations.
Bone pain under the eye occurs in various pathologies, which are accompanied by certain symptoms:
- Rhinitis is accompanied by nasal congestion, from which clear fluid is released (and even flows at the height of the disease). A person's nasopharynx is sore, there is movement and itching. The eyes usually turn red. Tearing with sneezing is possible.
- Ethmoiditis is characterized by a condition where the bone under the eye hurts when you press on it. In the morning, phlegm may be coughed up, and viscous yellowish and green discharge from the nose is observed. They have an unpleasant putrid odor. Swelling in the eyelid area is possible. The sinuses under the eye also hurt. Patients suffer from dizziness, lacrimation, and, in addition, photophobia.
- With sinusitis, the bones of the face under the eyes hurt. People lose their sense of smell, purulent and sometimes bloody discharge appears from the nose, in addition, the voice becomes rougher and significantly deeper, and breathing, in turn, becomes difficult. If sinusitis develops, there may be a risk of inflammation in the cranial cavity. The chronic form serves as a source of infections, provoking relapses of osteomyelitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis and rhinitis, among others. Acute sinusitis sometimes affects the trigeminal nerve. In this case, people experience severe pain in the facial area.
- With frontal sinusitis, the eyes, forehead and temples hurt most often in the morning. Breathing may be difficult, and thick discharge (even crusty) may appear from the nose. The temperature increases, the eyelids swell, and, among other things, there is pain in the eyes.
- Sphenoiditis is characterized by prolonged pain in the area of the back of the head and crown. Even the use of analgesics does not relieve the painful symptom. It may hurt under the eye when pressed, and vision deteriorates somewhat. Patients feel weak and unwell. You may feel discomfort in the nasopharynx.
In acute forms of these diseases, people may develop a fever, and in addition, they often experience dull headaches and a stuffy nose. In chronic forms, the symptoms are not so pronounced, but getting rid of them is very difficult.
Next, we’ll talk about what kind of diagnosis and treatment is carried out when pain of this nature appears.
Neoplasms of the nasal cavity
In the nasal cavity, nasopharynx, in the area of the canals communicating with the paranasal bone sinuses, voluminous tumor formations can form.
The most common of them are benign tumors, which are called polyps. Their development is not accompanied by intoxication of the body, they do not spread to other tissues and organs (metastasis).
Despite their benign course, polyps of the nasal mucosa always lead to a deterioration in the passage of air during breathing and block the outflow of secretions from the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses.
This leads to the gradual development of congestion with headache and nasal congestion.
Stagnation of nasal mucus is an excellent environment for the proliferation of bacteria, and in the absence of adequate treatment, extensive bacterial damage begins. Usually it is accompanied by a deterioration in the person’s condition, the development of intoxication, in which not only the nose is stuffy and the head hurts, but also the body temperature rises.
Drug therapy for inflammation of the paranasal sinuses
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to undergo a diagnosis in the office of an otolaryngologist. Only by identifying the root cause of the symptoms can effective therapy be prescribed. If you act independently, there is a high chance of making a mistake and starting to treat something that is not needed. Drug treatment of inflammation of the paranasal sinuses is always complex and includes several areas.
Etiotropic therapy
It is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease - the causative agents of the inflammatory reaction, in most cases, are various pathogenic (disease-causing) and opportunistic bacteria, and their destruction is carried out using antibacterial agents.
For this purpose, antibiotics with a wide spectrum of activity (cephalosporins and semisynthetic penicillins) are used. The final list of drugs and the choice of specific names is determined by the doctor, and depends on the type of pathogen identified, as well as how long ago the disease developed.
Pathogenetic treatment
It is primarily aimed at improving the passage of air through the nasal canals, as well as the outflow of secretions from the paranasal sinuses. It includes the use of vasoconstrictor drops, which reduce swelling of the nasal mucosa and sinus canals. Drugs of choice: Galazolin, Nazol, Xylene, Rhinorus.
- In the case of an inflammatory reaction of viral origin, there is a need to use antiviral and immunomodulating agents of the Interferon group (Recombinant alpha/gamma interferons), the group of Neuraminidase Inhibitors (Relenza, Tamiflu, Peramivir).
- Symptomatic treatment is also indicated for stuffy nose and headache. It involves the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Paracetamol, Nimesil).
Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is not recommended, as this can adversely affect liver tissue.
During complex therapy, air humidification is always used (it is better to use household humidifiers), which is especially important during the heating season.
It is also advisable to rinse your nose with saline solution. Moisturizing the mucous membrane and improving its functional state is achieved using aerosols based on sea water.
The independent use of antibiotics is excluded; they can only be used after a doctor’s prescription.
Therapy for sinusitis
Treatment of sinusitis includes the main directions and principles of treatment of inflammatory pathology of the paranasal sinuses.
You cannot warm the nose and upper jaw area during an acute pathological process, as this can provoke the formation of pus.
The main treatment includes antibiotic therapy, the use of vasoconstrictor drops and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory components. The duration of therapeutic measures in the acute course of the disease is at least 5 days.
Treatment of allergic manifestations
Treatment of allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis has fundamental differences from the treatment of inflammation.
It includes the prevention of repeated contact of the human body with the allergen (a preliminary diagnosis is carried out to identify the compounds to which an allergy develops), as well as the use of antihistamines that help reduce the severity of the allergic reaction.