Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve or neuralgia develops suddenly against the background of complete well-being. The pain characteristic of this condition appears sharply and disappears unexpectedly. We will tell you more about what kind of disease this is, what symptoms it is accompanied by, as well as how to treat it with tablets and folk remedies at home.
Anatomy and functions of the trigeminal nerve of the face
Anatomy of the trigeminal nerve is the largest and most sensitive facial nerve. It received this name because it consists of three branches : ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular. It is classified as a mixed nerve because it simultaneously performs several functions.
The trigeminal nerve is paired : similar branched canals are located on both the right and left sides of the face.
Each pair emerges from the lateral part of the pons and divides into three branches. They activate the chewing muscles of the face, salivary glands, skin of the lower eyelid, eyeballs, and partly the lacrimal glands, since they ensure the transmission of impulses from the brain to individual facial muscles and vice versa.
The superior branch of the trigeminal nerve passes to the surface of the skin through the orbits, the small processes of which reach the skin of the forehead. Fragments of the central nerve extend to the cheekbones and wings of the nose. The lower part is the longest: it innervates the movable jaw, chin, and partly the cheeks, ears, temples and cheekbones.
If one of the branches of the nerve is damaged, the function of muscle innervation and sensitivity is impaired.
The inflammatory process, or neuralgia , is a chronic disease, the main manifestation of which is paroxysmal severe pain in the areas controlled by the affected branch of the trigeminal nerve.
As much detail as possible about the anatomy of the trigeminal nerve:
Causes of development of trigeminal neuritis
Despite the fact that the disease has been well studied, the exact causes of the disorder are not yet fully understood. According to current views, the most common culprit factors are the following:
Infectious processes at the local level
We are talking about a variety of violations. Including such common ones as caries or tonsillitis (throat infection by an infectious agent). Depending on the general level of immunity, the patient can endure the septic process for a long time without any particular reaction to it. But the line is fine. As soon as the body's defenses weaken, the disorder manifests itself and begins with severe symptoms.
Correction of trigeminal neuritis involves eliminating the root cause. It is necessary to sanitize the source of infection. It is also worth noting that infections of a distant nature, prone to dissemination and spread throughout the body, have the same danger. For example, syphilis and tuberculosis have such properties. The likelihood of expansion is high. A common culprit in the onset of the disorder is sinusitis. In particular - sinusitis. Especially with a long course without proper therapy.
Tumor processes
Cranial or facial localization. In this case, compression of nerve tissue occurs. Tumor and large non-tumor formations (such as cysts) cause a mass effect when they are of sufficient size and in a certain direction of growth. In this case, it is not difficult to identify the etiology of the disorder, given that the visual picture is informative. Treatment is very difficult due to the usually complex localization of neoplasia.
Multiple sclerosis
Demyelinating disease. Multiple sclerosis is characterized by damage to a special membrane that covers nerve fibers and is involved in the normal conduction of impulses. The myelin sheath is destroyed, in the early stages the symptoms are represented by pain, but as the disorder progresses, the discomfort disappears and turns into a persistent neurological deficit with paresis and other disorders. Treatment is systematic. Aimed at correcting demyelination itself.
Facial injuries
Damage up to fractures. The normal configuration and anatomical structure of bone structures changes. Even slight displacement or thickening of bones can cause compression of nerve fibers. Is it dangerous.
Recent surgeries
Trigeminal neuritis can develop even after tooth extraction or puncture of the maxillary sinus. Therefore, the advisability of radical assistance is determined separately, in each specific case, after a thorough diagnosis and assessment of the situation. This may also include more extensive interventions. Be it surgical interventions for tumors of the facial area, brain, and others.
Nonseptic autoimmune diseases
They are much less common. They are characterized by an inadequate immune response when the body’s own defenses begin to attack healthy cells. Recovery is possible only with a complex effect on inflammation and pain.
The causes of the development of trigeminal neuritis are determined in the system; all possible factors must be taken into account in order to obtain a complete picture of the pathological process.
Types of inflammation
Depending on the mechanism of occurrence, primary (true) and secondary inflammation are distinguished:
- In the first case, the pathological process develops as a result of compression of the nerve roots or disruption of the blood supply in the absence of other pathologies, that is, an isolated lesion of the trigeminal nerve occurs. With primary inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, the pain is periodic and severe, piercing.
- In the second case, the nerve may become inflamed as a result of existing diseases or as a complication of the previous one. This type of pathology is expressed in constant, burning pain that occurs in any inflamed part of the face.
Treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
To eliminate the manifestations of neuralgia, an integrated approach is used; therapy includes taking medications, physiotherapeutic and manual methods, and traditional medicine can be used to enhance them.
Drug treatment
Therapy for facial neuralgia is aimed at eliminating painful sensations and the causes that caused the inflammatory process.
How to treat inflammation of the trigeminal nerve:
- novocaine intramuscular blockades to reduce the intensity of pain;
- antiviral drugs – Laferon, Gerpevir;
- antibiotic injections – Amoxiclav, Claforan;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Movalis, Nimesil;
- tablets to prevent the formation of cholesterol plaques - Atoris;
- glucocorticoids – Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone;
- muscle relaxants – Mydocalm, Mefedol;
- anticonvulsants - Rotaleptin, Finlepsin, Clonazepam;
- sedatives, antidepressants – Novo-passit, Amitriptyline.
The drug Mydocalm is used in the treatment of the trigeminal nerve
Lidocaine ointment relieves pain well - it is necessary to dry the oral mucosa with cotton pads, apply a thin layer of the product to the gums on the inflamed side. Unpleasant sensations disappear almost immediately, the product can be used 4-6 times a day.
Additionally, medications are prescribed to strengthen the immune system; B vitamins will help restore the functioning of the central nervous system.
Homeopathy to eliminate neuralgia
Homeopathic medicines activate the immune system - the body begins to fight inflammation more intensively, which leads to a rapid improvement in well-being.
Effective homeopathic remedies:
- Akonitum – quickly eliminates even severe attacks of pain;
- Agaricus - helps get rid of all the main manifestations of neuralgia;
- Argentum nitricum;
- Glonoin;
- Hepar sulfur;
- Silicea.
Glonoin is a homeopathic medicine
The best safe remedy for the treatment of neuralgia and neuritis is the drug Traumeel. It contains 14 herbal components and minerals; the medicine is produced in the form of drops, granules, solution for injections, and ointments.
How to relieve inflammation with folk remedies
Herbal medicines help reduce the manifestation of the inflammatory process in facial neuralgia and prolong the period of remission. But it is not advisable to use them as the main method of therapy; only in combination with medications will they help get rid of the pathology.
Alternative medicine recipes:
- Mix 200 ml of black radish juice with 10 ml of lavender oil, rub the inflamed area, cover your face with a warm cloth, lie down for half an hour.
- Brew 250 ml boiling water 1 tbsp. l. fresh red rose petals, leave for 30 minutes. Drink the entire portion of the medicine at once, repeat the procedure three times a day for 20–25 days.
- Pour 200 ml of vodka 4 tbsp. l fresh acacia inflorescences, leave in a dark place for a month, rub the affected area with the tincture in the morning and evening for 30 days.
- Brew 220 ml boiling water 1 tsp. chamomile inflorescences, strain after a quarter of an hour. The warm drink should be kept in the mouth for at least 20 minutes, the procedure should be carried out every 2-3 hours.
- Mix clay of any color with vinegar until a plastic, homogeneous mass is obtained, make thin plates, apply them to the inflamed area for half an hour before bedtime.
Tincture of acacia flowers helps in the treatment of the trigeminal nerve.
A permanent way to combat pain syndrome is to lubricate the inflamed areas 5-6 times a day with fir oil. Within 3 days, the skin will turn red and swell, but then all unpleasant symptoms will disappear.
Massage
Massage is an obligatory component of therapy in the treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve; the procedure can be performed during an exacerbation of the pathology, and in the stage of remission. It is better to consult with a specialist first so as not to increase the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
How to do a massage at home:
- Rubbing the cervical and shoulder region.
- Stroking the back of the head closer to the base of the neck.
- Vibrating movements on the cheekbones.
- Lightly tap with your fingertips on the brow ridges, frontal area, and nasolabial fold area.
During the treatment it is necessary to massage the back of the head
Each movement should be performed easily, without much pressure, done 5-7 repetitions, the total duration of the procedure is 7-8 minutes. A massage course consists of 20–25 procedures, sessions should be carried out daily.
In advanced forms of neuralgia, massage is not only useless, but also dangerous.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures are prescribed after the manifestation of an acute inflammatory process has been eliminated; they help prolong the period of remission.
What physiotherapeutic methods are used in treatment:
- electrophoresis with calcium chloride, anti-inflammatory, analgesic drugs;
- phonophoresis with Hydrocortisone - the procedure is carried out even in the acute phase of neuralgia to reduce the frequency of attacks;
- magnetic therapy;
- heating with ultraviolet light;
- UHF;
- laser irradiation;
- acupuncture.
A course of physiotherapy helps restore blood circulation, promotes muscle relaxation, and improves their tone.
Phonophoresis with Hydrocortisone helps reduce the number of attacks
Operation
Surgical intervention is necessary if traditional methods of treatment do not bring a noticeable therapeutic effect, relapses of neuralgia become more frequent, and various complications develop.
Important!
To eliminate pathology, 2 main methods are used. Radiofrequency destruction - the affected area is treated with electric current, the roots of the trigeminal nerve are destroyed, improvement occurs after 1 procedure. Microvascular decompression - the posterior cranial fossa is opened, the trigeminal nerve is divided, and a special gasket is inserted between the roots.
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are several factors that can provoke trigeminal neuralgia.
These include:
- hypothermia. The development of a pathological process can be provoked by a cold wind, a draft, or an air conditioner turned on at full power;
- age over 50 years;
- head bruises, facial injuries;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- physical and mental stress;
- malnutrition of the trigeminal nerve associated with the deposition of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels;
- weakened immunity;
- metabolic disorders in the body caused by endocrine diseases, diabetes, gout;
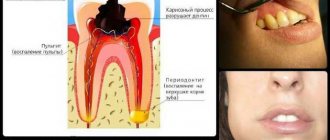
- diseases developing in the oral cavity – periodontitis, pulpitis;
- chronic stress, nervous exhaustion.
The sharp pain that accompanies the inflammatory process occurs due to injury to the nerve, swollen from swelling, against the walls of the canal. Experiencing pressure from surrounding tissues, the nerve becomes even more inflamed.
Important! Pressure on the nerve trunk can provoke pathological changes in nearby tissues - bone growths, enlarged blood vessels, tumor growths.
About pain with trigeminal neuralgia:
Inflammation of the trigeminal facial nerve as a symptom of serious pathology
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve may indicate serious pathological processes occurring in the body. This:
- tumor neoplasms;
- viral infections. In most cases, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve occurs when herpes viruses are activated;
- infectious diseases that provoke intoxication of the body and weakened immunity (tuberculosis, malaria);
- diseases of the hearing organs - otitis media, eustacheitis;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- multiple sclerosis;
- meningitis;
- encephalopathy;
- epilepsy;
- Cerebral palsy.
In the presence of provoking factors, damage to one or three branches of the trigeminal nerve may occur.
Symptoms of trigeminal nerve damage
The pain associated with damage to the trigeminal nerve is one of the most painful for a person. As a rule, the pain is in the lower face and jaw, so some may feel that the pain is localized in the teeth. Sometimes pain develops above the eyes or around the nose. With neuralgia, a person experiences pain that can be compared to an electric shock. This is explained by irritation of the trigeminal nerve, the branches of which diverge in the area of the cheeks, forehead, and jaw. Diagnosis of the disease may indicate one of the types of damage to the nervus trigeminus: neuralgia, herpes or pinching.
Neuralgia
Inflammation usually occurs due to contact of a vein or artery with the nervus trigeminus near the base of the skull. Trigeminal neuralgia can also be a consequence of compression of the nerve by a tumor, which is guaranteed to lead to deformation and destruction of the myelin nerve sheath. Often the appearance of neuralgia in young people is associated with the development of multiple sclerosis. Symptoms of the pathology are:
- “shooting” pain in the face;
- increased or decreased sensitivity of the face;
- attacks of pain begin after chewing, touching the face or oral mucosa, facial movements;
- in extreme cases, paresis occurs (incomplete paralysis of the facial muscles);
- As a rule, pain appears on one side of the face (depending on the affected part of the nerve).
Pinching
If neuralgia develops due to a pinched nerve, attacks of pain occur suddenly and last from 2-3 seconds to several hours. The disease is provoked by contraction of the facial muscles or exposure to cold. A common cause of neuropathy is plastic surgery or damage caused by dentures. For this reason, pinched nervus trigeminus is confused with dental pain if it is provoked by damage to the second and third branches of the nerve. The symptoms of this pathology are:
- intense pain in the lower jaw;
- soreness above the eye and at the edge of the nose.
Herpes
Trigeminal neuropathy can occur not only due to mechanical damage, but also due to the development of herpes. The disease develops due to damage to the nervus trigeminus by a special virus - varicella-zoster (zoster, shingles). It is capable of affecting the skin and mucous membranes of the human body, causing complications in the central nervous system. Signs of neuralgia due to zoster are:
- herpetic rash on the skin of the face, neck or ear;
- the skin has a reddish color, characteristic swelling is noticeable;
- bubbles with clear and later cloudy liquid form on the face;
- The post-herpetic condition is characterized by drying out wounds that heal within 8-10 days.
Clinical picture
The pathological process is expressed in the following characteristic manifestations:
- suddenly appearing intense pain with sharp shootings. Pain is observed in one part of the face. The location of the painful manifestations depends on which branch of the nerve was affected: when the first branch is inflamed, pain appears in the forehead, temples and eyes, the second - in the area of the cheekbones and nasolabial triangle, the third - in the area of the cheeks, chin, and lower jaw. The area begins to hurt sharply, and the sensation lasts 3-5 seconds. Several dozen such attacks can be observed per day;
- change in skin sensitivity in the area of nerve damage. It can either decrease until complete numbness or increase. In the latter case, this manifests itself in the fact that pain can be triggered by chewing, shaving, applying cosmetics, and even pronouncing words;
- tic-like or spasmodic muscle contractions. This can cause severe facial asymmetry;
- watery eyes or excessive salivation;
- violation of taste perception;
- feeling of dryness in the nasopharynx;
- change in the patient's psychological state. Pain and involuntary muscle contractions make him irritable, nervous and can cause stress.
Note! As the disease progresses, trophic disorders occur: the masticatory muscles atrophy, persistent facial asymmetry occurs, teeth, eyelashes and eyebrows fall out.
Symptoms of pathology:
Which specialist will help?
If symptoms indicating trigeminal neuralgia are detected, you should consult a neurologist who prescribes diagnostic measures and monitors the treatment process.
After examining the patient, the specialist, if necessary , will prescribe a visit to an ENT doctor, ophthalmologist and dentist in order to differentiate inflammation of the trigeminal nerve from diseases of the teeth and gums, glaucoma, sinusitis, otitis media, and sinusitis.
If neoplasms are detected during the diagnosis, the patient will need to consult an oncologist .
Neuralgia is also treated by a physiotherapist who carries out therapeutic procedures and a neurosurgeon who performs surgical interventions.
Cost and analogues
The cost of the device can be about 9850 rubles . This device is quite suitable for use both within the walls of a medical institution and in a home environment.
Anyone can purchase Almag in medical equipment stores or pharmacies and use it themselves.
Among the analogues of the Almag device, one can highlight the Mag and Magofon-01 devices . Both devices are quickly used in the treatment of neuralgia, and also enhance the effect of drugs.
The drug "Almag" is not a panacea for all diseases. But one way or another, it has already proven its effectiveness in treating not only neurological disorders, but also diseases of other human organ systems.
Diagnostic measures
To make a diagnosis of “Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve,” the following measures are taken:
- CT and MRI. These imaging methods will help identify brain tumors, pathologically altered blood vessels, and signs of multiple sclerosis;
- electroencephalography (EEG). Using this method, the localization of structures in areas of which impulse disturbance occurs, as well as epileptic foci, is determined;
- electromyography. The procedure demonstrates disturbances in the neuromuscular part.
In addition to instrumental methods, studies are required to determine the presence of reflexes in the patient. This:
- brow reflex. The specialist strikes the edge of the brow ridge with a hammer. Under normal conditions, the orbicularis oculi muscle contracts;
- periosteal reflex. To check it, the doctor places a finger on the chin and lightly taps it. The normal reaction is to pull the jaw up;
- corneal reflex. It is checked using a strip of paper.
After receiving the results, the specialist determines which treatment methods will be most effective - conservative or surgical.
Video about diagnosing neuralgia:
Treatment approaches
Depending on the degree of the pathological process, the specialist prescribes the patient to take medications and undergo physiotherapeutic procedures or surgery.
How to treat inflammation with medications
For trigeminal neuralgia, medications are prescribed that can directly combat the cause that provoked the development of the pathological process, and drugs that eliminate pain.
At the initial stage of therapy, the patient is prescribed anticonvulsants , which reduce the severity of pathological impulses. This:
Carbamazepine
Gabapentin
Finlepsin
Clonazepam
Anticonvulsants reduce the activity of nerve fibers, thereby limiting the propagation of electrical signals in them. Thanks to such tablets, the severity of pain is reduced.
Important! Anticonvulsants should be taken instead of analgesics, since the latter are not effective enough to block the electrical impulses coming from neurons.
In addition, the following medications are used in the treatment of neuralgia:
- antidepressants that reduce pain and protect the patient from stress (Amitriptyline);
- tranquilizers to alleviate the general condition (Diazepam);
- antispasmodics and muscle relaxants that relieve pain and muscle spasms (Baklosan, Lamotrigine).
Amitriptyline
Diazepam
Baklosan
Lamotrigine
Movalis, Baralgin, and Ibuprofen are prescribed as painkillers and anti-inflammatory
Movalis Baralgin Ibuprofen
If medications do not reduce the severity of pain, alcohol blockades are used. It is produced at the exit points of the nerve. The analgesic effect is provided by a solution consisting of ethyl alcohol and novocaine, as well as distilled water. With the help of this manipulation, a section of the peripheral nerve is frozen. The disadvantages of the blockade are the short duration of action and the likelihood of complications.
Neurologist about symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of pathology:
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures complement drug treatment.
They are especially effective during the acute period of illness or during an attack. For trigeminal neuralgia, the following are useful:
- electrophoresis with the introduction of an injection of Novocaine or Diphenhydramine to relax muscles and reduce pain intensity;
- ultraviolet irradiation (UVR), which relieves pain;
- laser therapy, which can be used to relieve pain;
- acupuncture. During the procedure, certain points are affected and pain is relieved;
- UHF (ultra high frequencies). The procedure involves heating the affected areas, which reduces swelling and pain.
Another important effect of physiotherapy is improved nutrition and blood supply to the affected area, due to which the nerve is restored.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia is required if conservative treatment methods have not improved the patient’s condition, or if the pathological process is rapidly progressing.
The patient is prescribed one of the surgical treatment options:
- microvascular decompression . In this case, trepanation of the posterior fossa of the skull is performed in order to restore the correct position of the nerve roots relative to the arteries. Compression is eliminated by separating the nerve processes with special gaskets that prevent blood vessels from pressing on the roots;
- radiofrequency destruction . This method is more gentle. During the manipulation, which is carried out under local anesthesia, the pathologically changed roots are exposed to radio frequencies, after which they are removed.
Note! After vascular decompression, complications may develop: hearing loss, stroke, facial numbness.
After radiosurgical treatment, a long rehabilitation period is not required. The risk of complications is minimal.
Neurosurgeon about the disease:
Physiotherapy
Another method that can become part of a complex of treatment measures for trigeminal neuralgia is therapeutic exercises.
Before starting classes, you should consult your doctor to prevent complications. When performing the complex you need to do the following:
- slowly tilt your head forward and back. Repeat 8 times;
- close your lips, fold them into a tube and stretch them into a smile. Repeat 8 times;
- take air into your cheeks and slowly exhale it through the narrow gap in your lips. Repeat 4 times;
- press your hand to your forehead, raise your eyebrows. Repeat 6 times;
- open and close your eyes with force. Repeat until you feel tired.
It is necessary to perform all exercises from the complex of therapeutic gymnastics in front of a mirror in order to control the process, in a sitting position.
Before performing each exercise, you need to completely relax your muscles.
Massage
For trigeminal neuralgia, massage sessions of the back of the head, collar area and face are indicated.
To perform the procedure, use the “point” method. In this case the following are shown:
- stroking and rubbing the back of the head, as well as the side and back surfaces of the neck with fingertips;
- tapping the chin area, supraorbital and infraorbital foramina with fingertips;
- circular stroking of the forehead area.
Note! For a massage session, you can use a vibration massager, but only with the permission of a doctor.
The duration of each massage session is from 3 to 7 minutes .
The course of treatment is from 7 to 12 procedures . They are held either daily or every other day.
Massage procedures are effective only in the early stages of the pathological process
Surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia - surgery
When the possibilities of conservative therapy have been exhausted, and the patient continues to suffer from attacks of severe pain, surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia is recommended. This still occurs in about 30% of patients. Therefore, for them, surgery is the only way a person can get rid of severe pain.
There are several methods of surgical treatment of neuralgia. All of them are aimed at eliminating the irritating effect on the nerve, provided that its source is known, or destroying the nerve.
The methods differ not only in the degree of effectiveness and safety, but also in price. For each patient, the surgeon individually selects the most appropriate method of performing the operation, based on the level and degree of damage to the trigeminal nerve, the clinical picture and existing concomitant diseases.
Today in the arsenal of neurosurgeons there are:
- microvascular or microvascular decompression;
- radiofrequency ablation;
- rhizotomy with glycerol;
- microcompression with a balloon;
- stereotactic radiosurgery.
In the absence of age-related and somatic contraindications, when diagnosing a neurovascular conflict, preference is usually given to microvascular decompression, since it is one of the reconstructive operations and does not lead to loss of sensitivity in one or another area of the face. But when concomitant diseases are detected in a patient, minimally invasive techniques are usually chosen, in particular radiofrequency ablation. It is also indicated for most elderly patients.
But when preparing for surgery, patients should understand that surgical intervention on the nerves requires the highest possible qualifications from a neurosurgeon. The slightest careless movement in such situations can lead to irreversible consequences, including complete loss of facial sensitivity. Therefore, it is important to approach the choice of a clinic and specialist extremely responsibly.
By contacting the SL Clinic, you minimize the risks of the operation, since we employ some of the best neurosurgeons who have considerable practical experience and are scrupulous about the problem of each patient. The clinic has modern equipment, which further increases the chances of success of the operation and reduces the likelihood of postoperative complications. Don’t waste time searching for a suitable medical center, entrust your health to the professionals at SL Clinic and you are guaranteed to receive top-level medical services. The cost of treatment for each method is given in the clinic’s price list.
Microvascular decompression
The Jannette procedure, or microvascular decompression, is often used for facial neuralgia. Its main advantage is the preservation of the nerve, while all other operations are destructive. Therefore, after microvascular decompression there is no risk of numbness of part of the face.
But it can only be used in situations where the trigeminal nerve is compressed by a nearby passing blood vessel, from which pulsation is transmitted to the nerve fiber, which provokes pain.
Microvascular decompression is performed openly through an incision behind the ear. The surgeon enters the cranial cavity after trephination of the posterior cranial fossa and revises the position of the trigeminal nerve root, the superior and inferior anterior cerebellar arteries, as well as the superior petrosal vein. After identifying the compression site, he separates the pathologically dilated vessels and introduces a special Teflon separating gasket. It will protect the nerve from mechanical irritation by the pulsating vessel, which will ensure pain relief.
In the vast majority of cases, the method leads to final recovery. Relapses are extremely rare. But microvascular decompression is an open surgical procedure and is associated with high morbidity and intraoperative risks. Therefore, performing the operation requires highly qualified surgeons.
After microvascular destruction, patients must remain in the hospital for up to 10 days. During this time and afterwards, they may experience pain caused by post-operative muscle spasms. To relieve them, taking antispasmodics or NSAIDs is usually sufficient. As the body recovers, the intensity of the pain decreases and soon disappears completely.
Rehabilitation involves taking a number of medications, undergoing a course of physiotherapeutic treatment, and subsequently massage sessions. Such a set of measures will contribute to a speedy recovery and consolidation of the results achieved through surgery.
Radiofrequency ablation
The method is one of the percutaneous operations and is considered the most effective and safe in the treatment of a large number of different diseases, including trigeminal neuralgia.
With the help of an image intensifier, the surgeon is able to precisely control his every movement and the time of exposure to radio waves. Other advantages of the method include:
- no risks associated with general anesthesia;
- extremely short and easy rehabilitation;
- possibility of early activation of patients.
Radiofrequency ablation does not require large incisions and significant tissue trauma. The destruction of the pain-provoking branch, its peripheral node or root is carried out through thermal energy released when ultra-high frequency currents pass through biological tissues.
It is carried out using special equipment consisting of a generator and two electrodes: damaging and indifferent. Ablation of the nerve fiber is performed around the bare end of the damaging electrode. It is introduced into the patient’s body to the selected point of destruction using a hollow guide needle. The length of such a cannula is 100 mm. It is installed under the control of the image intensifier to avoid accidental injury to healthy nerves.
A current with a frequency of 100 Hz is used to destroy sensory fibers, and 2 Hz for motor fibers. Radiofrequency ablation is performed under local anesthesia, so the patient remains conscious throughout the operation. He may feel a slight tingling sensation as the needle gets closer to the affected nerve. To accurately determine the desired branch of the nerve, it is stimulated with current.
After identifying the damaged branch, the electrode heating mode is turned on. It can heat up to 70°C, then the exposure time is only one and a half minutes. But it is preferable to use the pulsed ablation mode, which involves heating the tip of the active electrode only to 42°C. This completely eliminates the possibility of burns to surrounding tissues, but complete ablation requires 2 minutes.
In general, the entire procedure takes no more than 40 minutes. In 90% of cases, it leads to complete recovery, and the pain syndrome either disappears immediately after its completion, or a gradual increase in effect is observed over 6–8 weeks.
After radiofrequency ablation, the patient does not require complex rehabilitation or long-term bed rest. He can leave the clinic the same day.
Percutaneous selective rhizotomy with alcohol
The method involves performing an injection of the drug under MRI or CT control. A thin needle is inserted into the area of the affected nerve root, after which the solution is injected in small portions. The destruction of part of the nerve fiber occurs 3–4 hours after the injection, as a result of which the possibility of conducting a pain impulse is eliminated.
The technique is very old and was used before when there were no other more modern methods of treating neuralgia. This does not exclude the possibility of a relapse, but is not associated with a high risk of loss of sensitivity in the area of innervation of the affected branch of the trigeminal nerve.
Microcompression with a balloon
The operation involves the insertion of a special needle equipped with a small empty balloon. It is brought directly to the affected trigeminal nerve root and inflated until a persistent compression effect is obtained. Pressure has a destructive effect on the nerve fiber and leads to the elimination of pain.
Stereotactic radiosurgery
For more than 50 years, the treatment of neuralgic disorders has been carried out using the so-called Gamma Knife or CyberKnife. This completely bloodless technique does not require any incisions. The effect is carried out through precisely directed ionizing radiation to the affected area of the trigeminal nerve. Guidance is carried out using anatomical landmarks and a computer.
The rays formed by several hundred sources penetrate tissue without damaging them and are precisely focused at the point of impact, creating the required concentration of radiation. The operation, including preparation, takes one day and the patient can leave the clinic immediately after it. When performed correctly, there is absolutely no risk of side effects and complications.
Gamma Knife affects the nerve root located at the point where the brainstem exits the brain. The operation leads to a lasting recovery in 80–90% of cases. Only 7% of patients experience a temporary decrease in facial sensitivity after it.
The method is used to help all patients in whom conservative therapy has failed or was accompanied by severe side effects. In addition, it can be used to treat patients who have previously undergone microvascular decompression and other surgical interventions without obtaining positive changes. But the cost of stereotactic radiosurgery is significantly higher than other methods of surgical treatment of the disease
Methods for treating neuralgia at home
There are a number of traditional medicine recipes that can be used to supplement the process of the main treatment of trigeminal neuralgia.
| What to use | How to use |
| Fir oil | It is recommended to rub natural oil into the places where the pain is localized for a month, before going to bed. |
| Buckwheat | You need to take 2 handfuls of buckwheat, heat it on a baking sheet, pour it into a cloth bag. It must be applied to the sore spot and held until the cereal cools down. This procedure should not be repeated too often. |
| Black radish | Squeeze the juice from the root vegetable and lubricate the skin over the affected area with it several times a day. |
| Chamomile | Prepare a decoction based on this plant by pouring a teaspoon of fresh or dry raw material into a glass of boiling water. Allow the liquid to cool. During attacks of pain, take a small amount of chamomile infusion into your mouth and hold until the pain subsides. |
| Althea | A compress is prepared from the roots of this plant. 4 teaspoons of crushed marshmallow root are poured into a glass of boiled water and left for 8 hours. Next, a woven napkin is soaked in the liquid and applied to the sore spot. It is recommended to repeat this procedure daily for a week. |
| Ice | Rub an ice cube over your entire face and neck. Then you need to massage the skin, pinching it with your fingertips. Repeat the procedure 2 more times. |
| Eggs | Boil the egg hard, peel, cut in half. Apply one half, without cooling, to the sore spot, and leave until the pain disappears. |
| Dates | 3-4 fruits are crushed using a blender or meat grinder. The resulting mixture should be eaten 3 times a day, 3 teaspoons. |
| Clay | Take a few tablespoons of clay, mix it with vinegar, and knead until thick. Thin cakes are prepared from the mass and applied to the affected area. This should be done every evening for a week. |
| Malina | An alcohol infusion is prepared on the leaves of this berry: 100 g of fresh raw material is poured with 300 ml of vodka. Infuse the composition for 9 days. Drink the prepared liquid daily, before meals, a tablespoon. |
Before using any of these methods, you should consult your doctor.
Video about traditional methods of treatment:
Folk remedies
Before using “old-fashioned methods,” people should consult their physicians. This is due to the fact that an allergic reaction may occur to many components included in folk recipes.
If the patient does not have any contraindications, then he can use herbal infusions and decoctions in parallel with the drug course of therapy.
To eliminate inflammation, you should use the following recipes:
- Chamomile grass and marshmallow rhizome are crushed, after which the raw materials (4 tsp each) are placed in a separate container and poured with boiling water (400 ml). The contents of the dish must be boiled and left overnight. After waking up, the patient should filter the mixture, and put the strained infusion into his mouth and not spit it out for five minutes. The healing liquid can be used for compresses, which should be applied to places where painful sensations are localized.
- Fir oil should be dripped onto a piece of gauze or onto a cotton pad. After this, the compress should be applied to the areas of pain at least five times a day. People should not worry if their skin becomes red or swollen. Within a few days, the unpleasant symptoms will disappear on their own.