809
A dental cyst is classified as a jaw pathology that combines a large number of forms and subtypes.
The disease can undergo several stages of its course - from latent, which practically does not manifest itself in any way, to the acute stage, the symptoms of which are quite pronounced and brightly colored.
One of the most current treatment methods is organ cystectomy.
The essence of the procedure
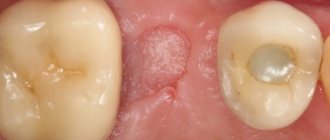
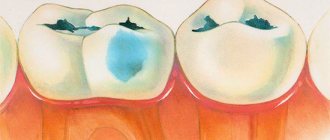
A dental cyst is a benign cavity formation filled with fluid, which consists of dead soft tissue cells, antibodies and dead bacteria.
Most often, this type of tumor is localized in the area of the roots of the teeth, and in the absence of treatment is characterized by a high growth rate and involvement of surrounding soft tissues in the pathological process.
Therapeutic treatment of a cyst is possible only in the initial stages of its development, when the capsule has not yet been formed, but an inflammatory process is present.
If the tumor has already become structured, getting rid of it is only possible through surgery, the optimal option for which is cystectomy.
Cystectomy is a tooth-preserving operation, the actions of which are aimed at removing the cystic formation and the mobile part of the root in whose area the tumor is localized.
The procedure allows you to completely excise and remove the cyst, which prevents the risk of its reoccurrence in the same place. Cystectomy is possible on both the upper and lower jaw.
Causes of cysts, their types and possible complications
A dental cyst is a pathological neoplasm that is formed as a result of the body’s protective reaction to infection or injury. It occurs when pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the bone tissue through the root canal, provoking an inflammatory process. Among the main causes and factors contributing to the appearance of neoplasms are:
- improper treatment of molars (for example, an incompletely sealed canal);
- the presence of infectious pathologies in the body, in which microbes are transferred into the gums through the bloodstream;
- untreated advanced form of carious lesions;
- abnormalities of jaw development.
At an early stage, the neoplasm is characterized by the absence of symptoms. Over time, you may experience discomfort when chewing food. During the period of exacerbation, a person suffers from acute pain. The reason for the transition of the disease to the acute stage is a weakening of the immune system, hypothermia, relapses of chronic pathologies, and infectious diseases. Often an exacerbation is accompanied by swelling of the face in the affected area, enlarged lymph nodes, a significant increase in temperature and general malaise. The following types of cysts are distinguished:
- Root. Appears from granuloma (is a continuation of pulpous necrosis).
- Follicular. It arises from the follicular sac, which affects each unerupted tooth. Characterized by rapid growth.
- Teething. Formed during teething.
- Residual. It can appear in the granuloma remaining after the removal of a molar.
- Primordial. It arises from developing tooth germs and is prone to relapse.
Dental cystectomy will help to cope with any type of cyst; the price of the technique is set on an individual basis. During the operation, it is completely enucleated and eliminated. The area where it was located is filled with material, thanks to which bone tissue is formed over time.
Despite the fact that a cyst is a benign neoplasm, it can lead to a number of problems, so a cystectomy with resection of the root apex should be performed in a timely manner. As the cyst progresses (increases in size), it can push back the canal of the inferior alveolar nerve and disrupt the external contours of the jaw bones, which will result in changes in the contours of the face.
There are cases when a cyst begins to involve neighboring tissues in the pathological process. This leads to the development of periodontitis. The growth of the tumor into the maxillary sinuses is accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membrane - the formation of sinusitis.
Indications
The cystectomy procedure is quite complex and time-consuming, therefore it requires high skill of the surgeon and is not performed in every clinical case .
However, experts note situations when this particular method of removing a cystic formation is indicated for the patient:
- the tumor is not too large, but affects several teeth;
- the cause of the neoplasm is disturbances in the odontogenic epithelium;
- the cyst is located on the lower jaw at the site of a missing tooth, and the structure of the jaw row allows the procedure to be carried out without complications;
- the tumor is localized in the area where the tooth is missing in the upper jaw, provided there is sufficient bone tissue.
Indications for periostotomy and details of the operation.
This material is dedicated to radicular dental cyst.
This link https://www.vash-dentist.ru/hirurgiya/udalenie-zubov/gemisektsiya-chto-eto.html offers a detailed description of the operation for hemisection of the tooth root.
Diagnosis of a dental cyst
The choice of treatment method for a dental cyst is based on a multifaceted diagnosis, which may include:
— examination of the patient; - “targeted” x-ray of the tooth, which the patient indicates as the causative tooth; - orthopantomogram (panoramic image of the jaw bones), which allows you to see pathologies and the most likely places of their development in the upper and lower jaws, in the maxillary sinuses, in the canals of the nerve trunks; - in some cases - a computed tomogram, which allows you to see the facial skeleton and skull bones, joints, maxillary sinuses in three projections (frontal, sagittal and horizontal) and in a three-dimensional volumetric image.
Contraindications
Like all procedures involving surgery, cystectomy has some contraindications.
The main points among them are the following:
- signs of an inflammatory process on the oral mucosa, which threatens infection of the soft tissues when making an incision in the gums;
- immersion of the tooth root by more than a third into the cystic formation - there is a possibility of tooth loosening with subsequent loss;
- high degree of destruction of the crown part of the tooth;
- a small volume of bone tissue, resulting in a risk of damage;
- malignant tumors with an unpredictable growth rate;
- diseases that reduce the degree of blood clotting, which can lead to severe bleeding during surgery;
- regular increase in blood sugar levels;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels, for which any surgical interventions are prohibited;
- periods of exacerbation of infectious and chronic diseases.
Some dentists also consider pregnancy as a contraindication, during which procedures involving the administration of anesthesia are undesirable, as well as the habit of smoking, which worsens the recovery period.
Preparatory procedures
Before proceeding with the operation, the dentist performs a thorough examination of the patient’s oral cavity in order to identify existing pathologies.
Teeth adjacent to the element at the root of which the cyst is located are examined for electrical excitability and treated if there is no reaction to the current.
Open root canals are treated with an antiseptic and sealed. Using radiography, a specialist examines the location of the roots of the teeth and the localization of the tumor relative to them.
A specific method of preparation for surgical intervention, characteristic of cystectomy, is depulpation of teeth, the root system of which is located in the area where the cyst is located.
Often the reason for performing this procedure is damage or necrosis of the neurovascular bundle.
What is gingivectomy and the reasons for the operation.
Read the following material about methods of treating dental granuloma.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/hirurgiya/rezektsiya/verhushki-kornya-zuba-a-chto-posle-operatsii.html useful recommendations for the period after surgery for resection of the apex of the tooth root.
Removal of a dental cyst. Historically significant and modern methods of surgery for removing dental cysts
Initially, the most common method of treating cysts was their removal. For this purpose, 2 fundamentally different methods were used: cystotomy and cystectomy.
Cystotomy (or the PARCH-I method) has historical significance in the development and establishment of medicine. Today this method is practically not used, but previously it was indispensable for removing large cysts. To avoid complications and its severe consequences, a wide channel was created between the cyst cavity and the vestibule of the oral cavity by suturing the edges of the cyst shell with the oral mucosa.
Cystectomy (or PARCH-II method) involves complete excision/removal of the cyst. This surgical intervention is often simultaneously accompanied by the removal of the root apex, the source of the formation of the cyst containing infected apical deltas. Today this method is the most popular.
The main goal of cystectomy is complete sanitation of the cyst cavity, which is not possible without resection of the root apex. The fact is that the root pulp in its apical third has an apical delta with an unclear structure and very fine branching of the canals, even in single-rooted teeth. If such canals can be cleaned during tooth treatment, then during retreatment this is almost impossible, especially considering the narrowness of the lateral deltas. Removing the root apex, in addition, allows you to most effectively clean the cyst cavity behind the root. This is especially true for teeth 12 and 22, which have a more curved root system. The operation is carried out as follows: using a small incision on the gum, the surgeon very carefully reaches the surface of the bone located above the cystic cavity, removes the wall with a trephine or bur, making sure that the neighboring teeth are not damaged, and then removes the cyst shell and performs a resection of the root apex . Next, sanitation of the cystic cavity is carried out and its subsequent revision for residual cyst particles. After this, in some cases, retrograde filling is performed. The final step in the operation to remove cystic formations is filling the resulting cavity with osteoplastic material and suturing the wound.
In the case of the formation of a large cyst, amputation of the apex of the tooth root can be performed, or half of the tooth and damaged root can be removed (hemessection), and in the case of an interradicular cyst, this can be done by corono-radicular separation.
Technique
Cystectomy is a radical operation and is therefore performed under general anesthesia. Conduction and infiltration anesthesia helps not only to anesthetize the treated area, but also to bleed the surgical field.
After administering the anesthetic, the specialist performs the following activities:
- Exposing the bone. Incisions are made on the gum tissue to separate the periosteal mucous flap from the bone tissue in the area of the alveolar process.
The detached flap is fixed on special blunt hooks or ligatures. - Providing access to the cyst. In the exposed bone tissue, using a special tool, small holes are drilled around the perimeter of the cystic neoplasm.
Using a bur, the resulting holes are connected, allowing the plate of bone tissue to be removed, allowing access to the tooth roots and tumor. Using a milling cutter or other dental instrument, the hole is expanded to the required diameter. - Cyst removal. The shell of the cystic neoplasm is peeled off from the bone tissue using an elevator.
When a cyst combines with the root system of the teeth, a resection of the apex of the affected root is performed, after which the sawed-off area is removed along with the tumor attached to it. The remnants of the cyst shell are carefully scraped out to prevent recurrence of the pathology in the future. - Treatment of the root system. The root stump is inspected for the presence of cement in its canal, after which the canals are filled to prevent infection from entering the tooth.
- Treatment of the bone cavity. After filling the canals, the cavity formed in the bone after removal of the cyst is inspected for the presence of dental cement residues.
Then it is treated with antibacterial drugs and filled with synthetic bone material or a substance based on human blood plasma. - Stitching. The periosteal mucosal flap, detached at the beginning of the operation, is placed in its original place and fixed with suture material.
To avoid the formation of a postoperative hematoma, a pressure bandage is applied to the corresponding area of the cheek or lip, which is removed after 5-7 days.
The duration of cystectomy does not exceed 1-1.5 hours. Upon completion, the dentist prescribes painkillers, anti-inflammatory and antiallergic drugs to the patient, which will help facilitate the rehabilitation period.
In the video, watch the procedure for performing a cisectomy of a dental cyst.
Preparing for surgery
Not only its course, but also postoperative recovery depends on the patient’s level of preparation for surgery. It is for these reasons that it is necessary to especially carefully examine the analyzes and examinations of other specialists who examined the patient for this pathology.
More on the topic: How is surgical treatment of urinary incontinence in women performed?
A month before the planned intervention, it is necessary to exclude coffee, tea, alcohol and tobacco. Within a week, many people need to take antibiotics and other anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate pathology in the microflora of the bladder. Some people should stop taking thrombolytics (Cardiomagnyl, Cardiasc).
Three days before surgery, the diet is switched to a semi-liquid form with fiber. Before the operation, you are allowed to drink only water. As a rule, the doctor knows the intervention scheme, and he must write recommendations to the patient on daily routine and nutrition. Only after studying and receiving these tips can you sign a consent.
If during the operation passages will be formed to drain urine into the intestines, part of the intestine will be isolated for organ plastic surgery, and it is also planned to create fistula entrances, then the intestines need to be properly prepared. To do this, a siphon-type enema is performed for three days to completely cleanse, and infusions are also taken to slow down the motility of the intestinal tract.
Bifidobacteria and lactobacilli have proven themselves to be excellent for prevention. The night before, the hair of the perineum, above the pubis and around the genitals is shaved. At night and during the morning, liquid intake is not allowed.
General anesthesia is required, so an examination by an anesthesiologist is important, who checks ECG data, measures blood pressure and finds out about drug allergies. If there are dentures in the mouth, they must be removed.
Advantages
According to experts in the field of jaw surgery, cystectomy, despite the complexity of its implementation, has a number of advantages compared to other methods of cyst removal.
The main advantages of the procedure are the following:
- the ability to preserve the integrity and functionality of a tooth located in the area of projection of the cystic formation;
- no likelihood of tumor regrowth if it is removed properly;
- complete restoration of the integrity and functionality of the bone tissue formed at the site of tumor removal.
Possible complications
The radical nature of the operation entails high morbidity, which often manifests itself in the occurrence of some complications during the rehabilitation period.
The difficulties that dentists may encounter as a result of the procedure include the following:
- pain and bleeding of the operated area of the oral cavity, which is eliminated by taking medications prescribed by the dentist;
- fracture of the base of the jaw with insufficient bone tissue;
- recurrence of the disease due to insufficient cleaning of the cavity from the remains of the cystic formation - in the future the operation will have to be repeated;
- damage to the facial nerve , leading to numbness in areas of the face and pain, often the situation normalizes after 5-7 months;
- wound infection due to unprofessional actions of the dentist or failure of the patient to comply with hygiene rules.
The occurrence of complications as a result of cystectomy is quite rare, however, if severe pain or any discomfort occurs, you should contact your doctor to identify the causes and determine a plan for eliminating the pathology.
Recovery period and care
The duration of the rehabilitation period after cystectomy often does not exceed two months. At the same time, it may take 5-6 months to restore the integrity and functionality of your own bone tissue in the cavity.
Compliance with the recommendations given by the dentist is of great importance for the duration of the recovery period.
It is very important to follow these rules during this period:
- brush your teeth with great care to avoid damaging the suture material;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- eat soft, not too spicy and salty foods at a temperature comfortable for the oral cavity;
- Take vitamin complexes prescribed by your doctor and use recommended rinses.
Progress of the operation
Cystectomy is carried out in a strictly verified sequence:
- place a catheter in the bladder;
- the skin is cut above the pubis in the form of an anchor or an arc, which allows you to quickly ligate the arteries in the iliac region to eliminate bleeding;
- part of the peritoneum is peeled off or removed, the bladder is opened and examined, the vessels are ligated;
- the rear and side walls are isolated, while in men the seminal vesicles and prostate gland are freed from tissue;
- The ureter is cut 3 cm above the tumor and held in place with clamps. Catheters are placed inside the tubes;
- the seminal ducts are ligated, as is the bladder, which is moved back;
- in the pubic part of the muscles, the prostatic and bladder parts are intersected, as are the ligaments on both sides, part of the urethra is removed near the prostate;
- remove the bladder.
More on the topic: What anti-inflammatory drugs can be used for the genitourinary system?
Bleeding in the peritoneum is stopped by ligating the vessels, and the peritoneal defect is sutured. Sutures are applied to the skin and muscles in layers. Catheters for urine drainage are brought to the surface, drainage is placed in the pelvis and in the peritoneal cavity for examination after surgery. Antibiotics are administered.
Experts' opinions
Most dentists are inclined to believe that cystectomy is the most effective way to remove cystic formation. It helps prevent relapse of the disease and preserve the integrity of the tooth adjacent to the tumor.
Experts also note that before deciding on the choice of treatment method, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination of the oral cavity, which will identify factors that impede the implementation of a particular procedure.
Another important point is the choice of clinic and attending physician, whose professionalism determines the quality of the surgical intervention and the risk of complications.
Quality criteria for dental cyst removal
Despite the fact that cystectomy is a surgical intervention, the main indicator of the quality of treatment will be the sanitation of the root canals, including retrograde filling. Currently, in addition to eliminating the cyst shell itself, the unspoken rule has become the filling of its cavity with one or another osteoplastic materials, because this completely eliminates the possibility of blood clot suppuration, promotes rapid healing of the bone defect and improves the mechanical stability of the tooth.
Price
The average cost of cystectomy in clinics in Moscow and the region is 8-15 thousand rubles. Please note that some procedures may require additional payment:
| Procedure name | Price |
| Consultation, drawing up a treatment plan | 300—500 |
| X-ray | 200—400 |
| Infiltration anesthesia | 250—400 |
| Root apex resection | 1500—2000 |
| Surgical debridement with suturing | 1000—1900 |
| Filling the socket with bone material | 400—600 |
Cystectomy of a dental cyst: specifics of the procedure
The most common method of eliminating a tumor is cystectomy; its price depends on the complexity of the clinical case. Radical cystectomy is performed together with resection of the apex of the root near which it is located. This surgical intervention is necessary when conservative therapy has not led to the desired results. It is possible to perform cystectomy of the jaw, both upper and lower.
During the initial examination, the dentist conducts a visual examination of the oral cavity and sends the patient for an instrumental examination to obtain an image of the damaged area of the jaw. Preparatory measures are carried out 4-5 days before surgery. They consist of filling the root canal to 2/3 of its length. The methodology itself includes the following steps:
- administration of an anesthetic (possibly conduction or infiltration anesthesia);
- performing a surgical incision of soft tissues with subsequent detachment;
- elimination of thinned cortical plate (manipulation is carried out using a drill);
- peeling off the tumor using a surgical spoon;
- performing resection of the root apex. This allows you to eliminate the source of inflammation, prevent relapse of the tumor and save the tooth;
- performing filling (taking into account the absence of cement in the root canal). Thanks to filling, it is possible to prevent the development of the inflammatory process (due to infection entering the wound from the root canal);
- cleaning the cavity of the formation from the contents. This is a particularly important event, since if fragments of the tumor remain in the bone tissue, then there is a high probability of relapse;
- filling the resulting cavity with bone-forming substance. This must be done so that soft tissues cannot germinate. Gradually the tissue is restored in the area of the operation;
- suturing the wound.
Reviews
Despite being highly traumatic, cystectomy is the best option for cyst removal, allowing the functionality of intact teeth to be preserved.
However, the procedure is not indicated for all patients, so before performing it, it is necessary to consult with a dentist and clarify the possibility and advisability of its implementation.
If you had to experience the removal of a cyst using cystectomy, share the features and advantages of this operation in the comments section of the article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: dental cyst, operations in dentistry, dental cystectomy
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
What does simple tooth extraction mean, and in what cases is it performed?
Next article
What is tooth lengthening and who needs the procedure