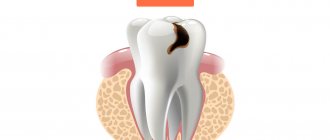
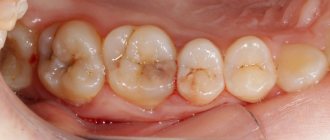
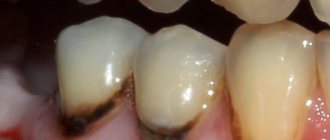
The decompensated form of caries is, in fact, an intensively developing caries, a pathological process that occurs very actively in the hard tissues of the tooth and leads to their rapid destruction. Often, carious cavities in this form of the disease are multiple and are present in many teeth at once.
In dentistry, there are several classifications of caries. When classified according to the severity of the process, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- compensated;
- subcompensated;
- decompensated.
Decompensated (acute, blooming) caries is the most dangerous form, since it develops much faster than in compensated and subcompensated forms. Acute caries can lead to tooth loss in just a few weeks. In this case, enamel and dentin are destroyed very quickly, and the transition from the initial stage to the deep stage occurs many times faster than in the chronic course of the disease.
On a note
The very name “decompensated form” means that the development of the carious process is in no way compensated by the body’s responses. It is in the absence of any obstacles that the process proceeds especially quickly and with very serious consequences.
The reasons for the development of pathology in the decompensated form are reduced bactericidal properties of saliva, lack of oral hygiene, unfavorable diet and hereditary factors, and unhealthy lifestyle. Sometimes acute caries develops due to weakened immunity.
Diagnosis of decompensated form of caries
Acute caries is most dangerous when the tooth is not treated. But unlike other forms, it is easily detected. The main symptoms that signal the development of a serious problem are the following:
- multiple noticeable external manifestations of caries on the surface of tooth enamel;
- acute prolonged pain in the teeth;
- strong reaction to cold, chemical, mechanical irritants.
If such sensations occur in the oral cavity, you should immediately contact your dentist.
Important:
If the carious lesion on the surface is very small, but the described symptoms are present, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor. Under a small entrance there may be a large carious cavity. An additional clue will be the loss of shine of the enamel, its grayish or chalky tint.
A dentist can easily diagnose a decompensated form of caries based on the following signs:
- wide base of carious form;
- narrow entrance;
- a large amount of softened dentin;
- sharp pain during probing.
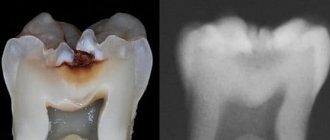
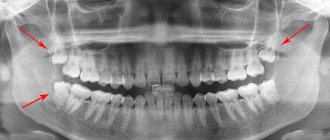
A probe and a dental mirror are usually sufficient for diagnosis. But if a carious cavity in a separate tooth is hidden from view, an X-ray is taken or transillumination is used (a method of “highlighting” hidden carious areas with a bright light flux from lamps). Also, in the decompensated form, fissurotomy is often used (this is a method of diagnostic search for hidden caries using prophylactic excision of “darkened” pits and enamel depressions on chewing teeth).
Who is at risk
The decompensated form of caries develops the faster, the lower the body's resistance. Therefore, the acute form is most often observed in people with weakened immune systems.
There are several groups of patients who are most at risk of developing this pathology:
- children with baby teeth;
- people who have recently had infectious diseases;
- people with metabolic disorders;
- elderly people with weakened immune systems.
It is also useful to read: What caries on teeth can look like: photographs
To avoid the development of acute caries, it is recommended to undergo routine sanitation of the oral cavity 1-3 times a year.
Causes and risk groups
The decompensated form of caries starts when nothing prevents the proliferation of pathogenic microbes in the mouth.
The main causes of the disease are a decrease in the bactericidal properties of saliva (or decreased salivation), as well as errors in oral hygiene.
Other provoking factors include deficiency of vitamins and minerals, metabolic disorders, and bad habits.
The lesions are indicated by arrows
Blooming caries can develop both primarily, due to the progression of the moderate form of the disease, and secondarily, on a filled tooth. Causes caries process bacteria (streptococci).
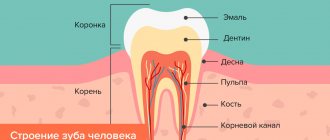
During the fermentation of food in the oral cavity, lactic acid is formed, which damages the enamel, allowing bacteria access to the inside of the tooth. They penetrate the dentin, causing the removal of calcium salts. This leads to softening and destruction of hard tooth tissues.
Cariogenic bacteria multiply in dental plaque. If it is not removed, the disease begins to progress rapidly. The main causes of acute caries are:
- persistent immune system disorders;
- poor diet with a lack of microelements;
- serious lack of calcium and fluoride in the body;
- vitamin deficiency of varying degrees;
- decreased bactericidal properties of saliva;
- disruption of the body's metabolic processes;
- presence of chronic diseases.
Improper oral care (lack of hygiene) and bad habits can provoke an exacerbation, accelerating the disease process. Children are more often exposed to the most acute form of the disease, especially during the period of growth of baby teeth. Also at risk may be:
- teenagers, during the period of hormonal changes in the body;
- children suffering from tuberculosis or other serious infectious diseases;
- patients with impaired absorption of microelements, especially calcium;
- patients with HIV infection who have reduced immunity;
- elderly people with various chronic diseases.
Patients who are at risk need to undergo examinations on time.
The danger of decompensated form
Acute caries is dangerous for many reasons. The advanced form of the disease often leads to the following problems:
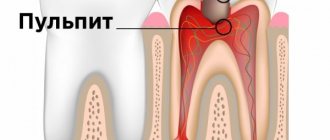
- development of pulpitis and periodontitis;
- development of periodontitis;
- tooth splitting;
- tooth loss.
In addition, the decompensated form is a signal of a disruption in the functioning of the entire organism. Untreated caries is often a consequence of decreased saliva production and a decrease in its bactericidal properties, which affects the general condition of the oral cavity as a whole. In pregnant women, this can affect the general physical condition of the expectant mother and the health of the fetus.
Types of disease
Acute caries has two forms:
- medium spicy;
- deep spicy.
The difference between medium and deep acute forms lies in the size of the carious cavity. With moderate acute caries, there is no need to remove the nerve, and the tooth can be treated and restored. In case of deep acute caries, depulpation is usually required, and in case of severe tooth decay it is necessary to remove it.
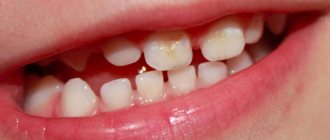
Since in the acute form of the pathology the destruction of tooth tissue occurs very quickly, and children are most susceptible to the disease, in pediatric dentistry the following grouping is accepted:
- Compensated form (I group);
- Subcompensated (group II);
- Decompensated (group III).
Groups have been created to carry out clinical observation.
Pediatric dentist T. F. Vinogradova identified several dispensary groups:
- practically healthy teeth;
- compensated form;
- subcompensated form;
- decompensated form.
Children with a compensated form are examined once a year, with a subcompensated form - 2 times, with a decompensated form - 3 times. Planned sanitation reduces the risk of complications in the development of caries, the number of fillings and extracted teeth decreases. The need for treatment is also reduced by almost half, and the number of annual scheduled examinations is reduced.
Monitoring risk groups allows you to keep records based on a number of criteria:
- general prevalence of caries;
- anamnesis of life;
- health status;
- severity of the disease.
Planned sanitation and timely diagnosis of caries in adults and children make it possible not only to cure it in the initial stages, but also to prevent the development of blooming caries.
What is subcompensated tonsillitis?
The subcompensated form of tonsillitis is one of the types of tonsillitis that has a chronic course and manifests itself with typical symptoms.
Nominally, tonsillitis is usually classified based on its 3 main forms:
- Compensated.
- Subcompensated
- Decompensated.
If we talk about the second form of the disease, it is characterized by the occurrence of certain processes in the body that provoke the appearance of unpleasant symptoms:
- a sore throat;
- intoxication of the body;
- increase in body temperature.
A characteristic sign of chronic tonsillitis, regardless of its form, is considered to be plugs on the tonsils. Purulent formations fill the organ cavities, indicating that an inflammatory process is underway in the body.
Attention! Inflammation is a consequence of the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria inside the tissues of the body. When inflammation becomes chronic, the body does not react so actively to the processes, the immune system is suppressed, weakness, malaise, and decreased performance are disturbed.
It is believed that the chronic inflammatory process of tonsillitis is not fraught with danger, but this is not so. Pathological processes lead to serious complications - brain abscess, meningitis and others.
In addition to the characteristic symptoms, a person is worried about an allergic reaction. The body reacts sharply to substances, so eating or drinking can trigger a sore throat.
It is not necessary to be hypothermic or have a cold; it is enough to simply eat something wrong to provoke another attack of tonsillitis.
Compensated chronic tonsillitis is an infectious-allergic disease with predominant damage to the lymphatic tissue of the palatine tonsils. These organs are responsible for local immunity and serve as a natural barrier to viruses and bacteria. The disease is usually diagnosed in children. The peak incidence occurs at 12 years of age.
According to official statistics, chronic tonsillitis of the compensated form accounts for about 25% of all pathologies of the ENT organs. However, recently there has been an increase in the number of such diseases.
WHO instructions require immediate treatment of chronic tonsillitis, which prevents the development of complications from the cardiovascular system and kidneys.
How is blooming caries treated?
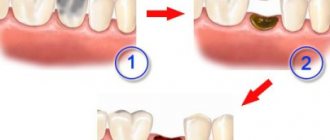
Treatment of decompensated forms of caries can be divided into three stages:
- removal of all tooth tissue affected by caries;
- removal of the nerve (if necessary);
- tooth restoration.
Since blooming caries causes severe pain, all stages of treatment are carried out under local anesthesia or general anesthesia (less frequently). This means that the procedures are painless for the patient. Modern anesthetics are absolutely safe and hypoallergenic, so this treatment is available even for pregnant women.
Removal of affected tissue is mainly carried out using a drill. But this is not the only possibility. There are also more modern methods: washing out with dental sandblasting, evaporation with a dental laser. Unfortunately, these modern methods do not yet have a good evidence base for their effectiveness for the treatment of serious carious lesions, and are not widely used in our country.
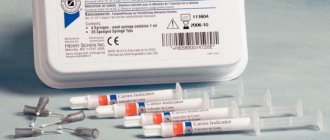
It is also useful to read: The use of caries markers (indicators) in dentistry
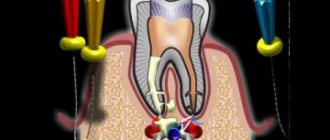
At the next stage of treatment (if necessary), the dental nerve is removed using special equipment. Then the dental canals are cleaned and filled.
Restoration is the last stage of treatment. Using filling materials, the dentist restores the original shape of the tooth.
Treatment of acute caries is a complex and lengthy process. Most often it takes place in two visits. During the first, the affected tissue is removed and medicinal treatment is carried out. During the second visit, the tooth is restored.
Briefly about terminology
Considering the wide extent and area of damage resulting from the action of pathogenic microorganisms, acute caries is classified as a deep-type disease, which, depending on the rate of its development, can take place in three forms:
- chronic;
- sharp and acute;
- paused.
The disease progresses quickly, depending on the degree and speed of tooth decay, it can be as follows:
- Compensated. In this variant, the disease develops at a low speed, without exacerbations or symptoms. In addition, compensated caries differs in that the enamel is affected in a weak form.
- Subcompensated. Weak symptoms and absence of manifestations of the disease at the initial stage.
- Decompensated. It has a high rate of spread, can affect up to several teeth at the same time and is characterized by severe pain.
Important! During the treatment of acute caries, a high degree of visualization of the work process is very important. Modern doctors achieve it using a dental microscope, which magnifies the affected area several tens of times. This allows you to carefully plan treatment, sterilely process root canals and detect their branches, if any. Not all patients know that the device makes it possible to achieve high aesthetics of the treated and restored tooth, since only affected tissues are removed, while healthy ones are preserved.
There are many options for classifying the typology of caries and its types; the differences relate to the intensity of the disease, its course and the area of damage. For example, the World Health Organization relies on the following classification of this disease:
- enamel caries;
- cement caries;
- dentin caries;
- unspecified;
- suspended;
- odontoclasia;
- other cases.
Prevention of decompensated form of the disease
Everyone can prevent the development of acute caries. Even with a hereditary predisposition, dental problems arise due to poor oral hygiene and poor nutrition.
Prevention of the decompensated form of the disease is quite simple. To carry it out you need:
- brush your teeth morning and evening;
- use toothpaste with fluoride;
- clean interdental spaces with dental floss;
- do not consume too cold or hot food or drinks;
- limit the amount of soft and sweet foods, since after eating them, plaque forms on the teeth, which contributes to the demineralization of the enamel;
- Visit the dentist 1-3 times a year.
Planned sanitation of the oral cavity makes it possible to identify caries at the earliest stages and prevent it from developing into an acute form. Regular visits to the doctor allow you to timely detect weaknesses in the care of your teeth and gums, make adjustments and stop their diseases. Therefore, visiting a dental clinic to check the condition of your teeth should become a rule for everyone who cares about their health.