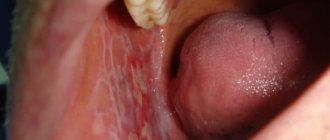
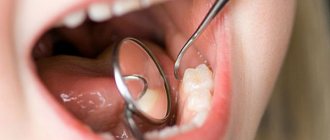
Caries is a fairly common dental disease that affects the structural integrity of the tooth. If neglected, it can lead to complete loss of the organ.
Pathology provokes the emergence of a number of more serious diagnoses and requires immediate treatment.
Unfortunately, most patients ignore this problem until the moment when it is no longer possible to do without the help of a specialist. At this stage, treatment is more drastic; sometimes the only solution is amputation of the damaged tooth.
General information
Cement caries is a partial damage to an organ, concentrated in the cement area of the tooth. It develops against the background of exposure of the root part and the appearance of a gum pocket, which is considered an abnormal phenomenon. Often the disease is diagnosed as root caries.
In this case, pathological bacteria and microorganisms affect the internal part of the organ, leaving the enamel and dentin intact.
This phenomenon is mainly observed in people of the older age group, in whom processes of atrophy of the gum bone tissue occur over time, which leads to partial exposure of the root.
Reasons for appearance
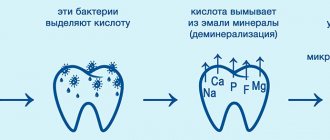
The main reason for the development of this type of disease is the negative impact of pathogenic microbes such as Lactobacillus and Streptococcus mutans on tooth tissue.
In turn, the following factors can provoke their occurrence in the oral cavity, as well as contribute to their active reproduction:
- Xerostomia - manifests itself in an abnormal decrease in the salivary mass washing the mucous membrane and jaw row, as well as in a violation of its qualitative composition.
These processes cause gradual demineralization of the surface layer of enamel. She, in turn, is no longer able to protect her teeth from the external influence of microbes. It is noteworthy that xerostomia can be caused by taking certain antihistamine medications, diuretics, sedatives and antidepressants. - Inadequate oral care – insufficiently thorough hygiene procedures are unable to properly clean the coronal part of the organ from plaque and stone deposits.
- The cervical type of caries is not eliminated in time; it actively spreads to the root area and affects its tissues.
- Incorrectly performed prosthetics - the artificial crown does not fit tightly enough to the gum, and microbes accumulate in the existing gap.
- Poor nutrition - a systematic lack of minerals and vitamins leads to demineralization of hard tissues, and in combination with an abundance of carbohydrates in the oral cavity, bacteria that cause caries begin to actively develop.
- Periodontal diseases.
- Oncology of the head during radiation therapy.
Types of mouthguards for bruxism, their action and rules of use for reliable protection of tooth enamel. This article contains all the most interesting things about the modern treatment of caries between the front teeth.
Follow the link https://dr-zubov.ru/ortopediya/semnye-protezy/pokryvnye/vosstanovlenie-ulybki-sendvich.html to get closer to the new generation Sandwich removable dentures.
A few words about prevention
As for prevention, the only correct solution is to strictly follow the rules of oral hygiene. However, this does not at all guarantee protection against the development of carious lesions. A specialist plays an important role in the matter of dental health, so choosing a doctor should also be approached with the utmost responsibility and care.
Video on the topic
1 According to the World Health Organization (WHO). 2 According to the classification of caries according to Black (Black).
Symptoms
Depending on the area of localization of the disease, a clinical picture characteristic of each case is observed. At the same time, it can be practically unexpressed if the pathology is hidden in the periodontal pocket.
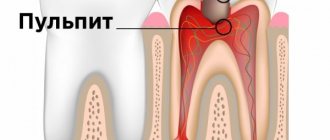
In such a situation, the anomaly is diagnosed, as a rule, already at an advanced stage, when acute pulpitis, visible to the naked eye, develops in the gum area.
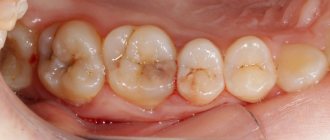
In the open form of cement pathology, the following symptoms appear:
- violation of external attractiveness - especially noticeable on the front part of the jaw row, when characteristic destructive manifestations of part of the outer surface of the tooth appear at the base of the organs;
- some pain during eating - when food fragments are ingested or under the influence of cold or hot foods, pain of varying degrees of intensity occurs.
Clinical signs
Depending on the location of the carious lesion under the gum, the clinic characteristic of cement caries is determined. Thus, when caries is localized in the periodontal pocket, when the inflamed gum closes the root from external irritants, we are talking about a closed location. In such cases, the clinic of root cement caries is not bright. As a rule, a person does not have any painful sensations or they are mild.
When cement caries is open, in addition to the root, the cervical region is also involved in the destruction process. Depending on the depth of the carious lesion, there may be complaints about:
- violation of aesthetics (especially on the front teeth)
- feeling of discomfort when eating
- the occurrence of pain from chemical (sweet, sour), thermal (cold and hot) and mechanical (when food penetrates under the gum) irritants.
Diagnostic methods
Professional methods for differential diagnosis of root cement pathology include the following complex manipulations using modern hardware and instrumental options:
- Thorough cleaning of teeth from plaque and hard deposits, since they are the main provocateurs of the development of the disease. During the cleaning process, curettes, scalers, ultrasonic caps, and the Air Flow hardware cleaning device are used.
- Separation of the diagnosed root fragment from the salivary fluid using the rubber dam technique.
- Direct probing of the root surface - a special pointed probe instantly detects lesions along the rough structure of the tissue surface.
- General X-ray - reveals the presence of pockets at a suspicious crown; caries inside the root looks like a darkened area on the X-ray. To diagnose a hidden type of pathology, a visograph is used - an ideal solution for visually examining an anomaly in various projections.
- Thermal diagnostics – as accurately as possible, states the staged degree of organ damage. In this case, the diseased tooth is exposed to too hot or, on the contrary, very cold water - if the pain syndrome is episodic and short-lived - this is the initial threshold of the disease, if the pain is impulsive and does not go away - this is a clear sign of the presence of pulpal formations.
- Electroondotometry is a point effect on the pulp area of electrical impulses of varying degrees of intensity. The more tingling in the affected area, the more advanced and pronounced the diagnosis.
Clinic and diagnosis of enamel caries
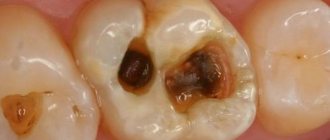
The difficulty in diagnosing initial enamel caries in the spot stage is that the patient does not experience any discomfort - the tooth reacts normally to changes in temperature, sweet, sour and salty foods and only in rare cases, for example, if enamel caries develops in the area of the sensitive neck of the tooth, mild discomfort is possible. Visually, enamel caries can appear as a white spot or a small cavity. The tooth surface in the affected area may become slightly rough.
One of the most insidious clinical cases of enamel caries is lesions in the interdental spaces. Since this area is hidden from view, pathology can often only be detected at a later stage.
What complicates the diagnosis of enamel caries is that damage to tooth enamel is not always caries. Fluorosis, erosion, abrasion of enamel and hypoplasia have similar symptoms. For example, both fluorosis and hypoplasia are accompanied by white spots or roughness on the enamel.
Types of diagnostics
- Visual examination
in the clinic using drying - this allows you to detect a rough surface on smooth enamel. - Diagnosis
of caries on tooth enamel using dyes: a quick and easy way to determine whether a patient is developing caries - or if it is just pigmentation. The fact is that with initial caries, tissue softening occurs in the enamel, and if the lesion is carious in nature, the dye will easily penetrate into the affected tissue and color it. With fluorosis or hypoplasia, staining will not occur. - Fluorescent diagnostics:
exposure of teeth to special ultraviolet lamps, during which healthy tissue begins to glow with a bluish or greenish light, but in the area affected by carious bacteria there is no similar effect. The method is quite accurate, but expensive.
Treatment
Therapy for cement pathology, depending on the degree of damage to the organ, involves two options for eliminating the problem:
- conservative;
- surgical.
The first is advisable at the stage when the processes of irreversible tooth destruction have not yet started. The second is carried out when pockets appear, when canal filling is the only solution.
What diagnostic measures are carried out to identify osteomyelitis of the jaw, and treatment used in modern dental clinics. Read here reviews about Invisalign aligners, their advantages and disadvantages in comparison with analogues from other manufacturers.
At this address https://dr-zubov.ru/ortopediya/nesemnye-protezy/koronki/sovremennye-raznovidnosti-zolotyx.html we suggest finding out how to clean gold crowns from tooth debris.
Conservative
Features of filling cavities for root caries require the following manipulations:
- professional cleaning of the jaw row – removal of stone deposits and plaque;
- elimination of their provoking factors - measures to correct prosthetic structures, complex therapy of periodontal disease and other inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- impact on the coronal part of the organ with remineralizing components - this technique involves the use of fluorine-containing compounds and antiseptic substances. For more effective processing, copper ions and calcium crystals are added to them.
Operational
The technique involves a surgical option to eliminate the problem of gum tissue and the crown of the tooth.
The technology involves the implementation of the following set of measures:
- local anesthesia - is provided by direct exposure of the narcotic to the affected area. The injection area is pre-wetted with a pain-relieving gel or spray;
- since it is quite difficult to secure the treated area using a cofferdam, the doctor performs a partial dissection of the gum area using diathermocoagulation;
- the next stage is corrective tightening of the marginal surface of the soft tissues of the gums with special hemostatic threads;
- then, the doctor removes the affected dentin fragments, forming a treated cavity. To diagnose the cleansing zone, a special composition is used - a caries marker;
- for medical reasons, the dentist amputates the nerve and performs a complex filling of the canals;
- the final stage - the entire oral cavity is subjected to complete disinfection with antiseptic drugs.
The choice of filling agents is determined by the anatomy of the cavity, the general clinical picture of the condition of the gum tissue, and the location of the affected fragment of the jaw row.
In this case, it is advisable to use the following components for canal filling:
- Amalgams are used extremely rarely, since their use requires the complete absence of a moist environment in the oral cavity, and this is almost impossible to achieve. In addition, the material contains mercury; individual protection is required for mixing it.
- Compomers provide a fairly strong and strong filling that can withstand high mechanical pressure from the outside. Indicated for use in small cavities. The disadvantage of the material is that the fixation is not very strong.
- Glass ionomers are an ideal option for the restoration of large areas affected by pathology. The product adheres well, does not react to moisture, and contains remineralizing components that regenerate the structure of the organ.
In the video, watch the stages of tooth root treatment.
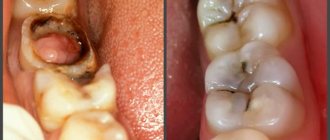
Treatment of cement caries: main stages
With root caries, the most difficult task is to gain access to the affected area, especially if the carious lesion is located under the gum. Traditionally, treatment of root caries takes place in several stages:
- Retraction. First, the dentist artificially exposes the neck of the tooth and part of the root, lowering the gums with special devices.
- Coagulation of the gums. It is carried out if indicated using laser exposure to gum tissue. The essence of the manipulation is to remove overgrown tissue.
- Direct treatment of caries. The choice of tactics depends on the degree and depth of the lesion. If caries is in the initial stage of the stain, then remineralizing therapy will be sufficient - restoring the mineral composition of tissues with the help of fluoride preparations. If the doctor reveals more extensive and deep caries with the formation of a cavity, then surgical treatment with preparation and filling will be required.
- Installation of an inlay or crown if the volume of destroyed tissue is more than 50%.
It is necessary to treat cement caries only in a trusted clinic with a reliable specialist, since violation of treatment technology and the use of low-quality materials can cause secondary caries, provoke the development of infection and inflammation of the gums, and lead to tooth loss.
Possible complications
Pathologies resulting from dental cement caries have been identified:
- pulpitis – focal inflammation of the pulp of an organ. It has acute and chronic forms. It is treated through comprehensive cleaning of the root canals and their further filling with high-quality composites;
- periodontitis is a pathology of the internal tissues of apical periodontitis, accompanied by severe pain;
- maxillary periostitis is a consequence of the diagnosis described above with its persistent neglect. Manifests itself as acute inflammation of the periosteum tissue. Accompanied by fever, pain, general weakness;
- osteomyelitis – accompanied by purulent foci. The patient complains of jaw pain, swelling of the cheek, fatigue;
- abscesses are a complex inflammation that occurs acutely, with severe symptoms. Differs in odontogenic nature. In its advanced stage it is very dangerous and poses a threat to life.