Hidden caries is unnoticed tooth decay. This term does not appear in the medical literature, but recently practicing dentists are using it more and more often.
The disease can only be detected using special diagnostic methods. Difficult caries can develop in those parts of the tooth where food debris accumulates all the time, for example in the interdental space.
The insidious feature of the latent form of caries is that a person may not be aware of the development of this disease.
Definition and types of disease
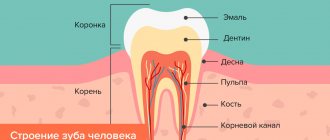
Hidden or internal caries is damage to hard tissues that does not affect the enamel. A bad tooth often does not cause discomfort. Pain and inflammation appear at the stage when it begins to crumble. In the early stages, it can be detected using modern diagnostic methods and cured.
Most often, the hidden form of the disease forms on hard-to-reach parts of the tooth.
The main types of hidden caries:
- fissure (occurs in fissures, that is, anatomical depressions). Read more about the forms and elimination of fissure caries here;
- contact (develops in the interdental spaces, does not manifest itself externally until pain or sensitivity to cold or hot food appears);
- caries of the roots of the tooth (the infection initially affects the roots, but not the upper hard tissues, enamel);
- secondary (develops under a filling if damaged tissue remains in the cavity during treatment).
During preventive visits to the dentist, tartar cleaning is recommended. This allows the doctor to evaluate the natural appearance and color of the enamel and identify the problem in time.
The fissure appearance can only be seen in excellent lighting. At the initial stage, it appears as a dark spot under the enamel. The root lesion develops from the bottom up, and not as a result of damage to the enamel. The contact form (caries between teeth), especially in the early stages, can only be detected during a dental examination.
Symptoms
During the first period of development of the pathology, there are no signs of the disease. There is no pain, the surface has no changes.
Symptoms begin to appear only when the tooth is already sufficiently damaged and the damage has affected nearby nerve endings.
Often the disease leads to the destruction of crowns or a previously placed filling falls out .
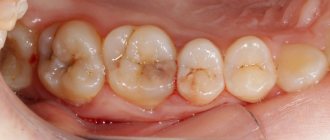
Darkening of the tooth surface is an alarming signal; you should contact your dentist.
If the disease progresses, it manifests itself in the fact that when eating foods that contrast in temperature, discomfort and sometimes pain occurs .
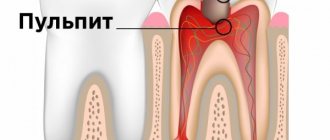
If pain occurs without an obvious irritant, we can say that carious damage has led to pulpitis .
Pain also occurs when chewing food . Its particles get into the formed recesses, which causes significant discomfort, which disappears only after cleaning.
The most important negative factor of hidden carious lesions is their invisibility in the early stages, which is expressed in the absence of symptoms . Only with the development of pathology do visible manifestations appear.
In general, they can be grouped, taking into account the above:
- Darkening of the surface of the teeth;
- Painful sensations of varying strength;
- Discomfort when eating foods that contrast in temperature, pain when chewing;
- Fillings and crowns are destroyed.
Causes
The latent form has similar causes to other types:
- improper or insufficient brushing (less than 2 minutes, or less than 2 times a day);
- violations of oral hygiene (incorrectly selected toothpaste or brush, failure to use dental floss);
- irregular visits to the dentist (less than 2 times a year for adults or 4 times a year for children);
- an abundance of soft foods rich in carbohydrates (sweets, drinks with high sugar content);
- lack of fluoride in drinking water;
- chronic oral infections that damage healthy teeth from the inside.
If you ignore dental floss, there is a high risk of damage to not one, but several teeth at once.
Sometimes a tooth located between two already damaged ones appears healthy. But an experienced dentist can suspect a problem. Another common cause is chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Find out more about what causes tooth decay here.
The constant presence of food particles in the interdental space is a breeding ground for bacteria. Over time, it leads to the development of caries.
Causes
The main factor that provokes hidden caries is ignoring the rules of oral hygiene. Secondary are called:
- sweet tooth;
- avitaminosis;
- deficiency of microelements (mainly phosphorus and calcium);
- chronic diseases of the digestive system;
- weak immunity;
- improper growth of teeth.
In the latter case, the problem arises due to the fact that the patient is unable to fully cleanse.
Is it possible to detect the disease at home?
The main problem, as previously noted, is the complete absence of any symptoms in the first stages. A simple visual examination of the oral cavity usually does not reveal the disease.
The first signals begin to arrive only when the carious cavity becomes large enough, and sometimes extends to a good half of the tooth. At this stage, the patient is already suffering from quite severe pain.
The development of a secondary disease is usually indicated by the loss of an old filling or its mobility. With such a problem, you need to immediately go to the dentist.
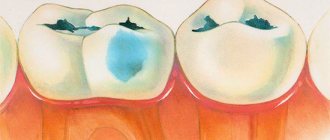
- even the slightest darkened areas visible under the enamel;
- suddenly increased sensitivity to cold and equally hot foods and drinks;
- aching pain after eating sweets.
Short-term discomfort that appears under the influence of one or another irritant does not cause many people to worry, which is unfortunate, because it is at this stage that treatment is easiest to organize. Pain that persists constantly clearly indicates the presence of advanced caries. By this point, the disease usually spreads to the pulp. Subsequently, the inflammation spreads to the gums and bone tissue.
Symptoms and clinical manifestations
The main danger of hidden caries is the absence of external symptoms. The first visible manifestations, pain and discomfort appear in the later stages. The following signs will help you suspect it in the early stages of development:
- the appearance of dark, barely noticeable spots on the enamel (requires immediate treatment of caries at the initial stage);
- pain of varying intensity;
- sensitivity to hot or cold food, mechanical stress (goes away immediately after eating);
- filling falling out.
With the development of secondary caries, the filling may sag or partially collapse. Even if the filling has not fallen out completely, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
If pain occurs randomly, for no apparent reason, this is a possible sign of pulpitis. The tooth is deeply damaged from the inside, although it looks healthy on the outside.
Pain during hidden caries occurs only under the influence of certain factors. It is worth informing your doctor about them, this will facilitate diagnosis.
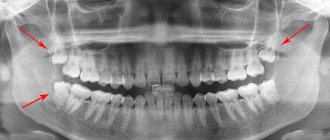
Detection of carious signs from an image
Since an x-ray does not provide a clear picture of pulpitis, it is determined by the type of carious lesion and its location.
Important! Using X-rays, you can only detect caries that has affected at least a third of the hard tissues of the tooth.
Depending on the form, caries appears differently on an x-ray:
- Average caries. There is a darkening localized strictly within the dentin.
- Deep carious lesions. The dark areas on the x-ray communicate with the pulp chamber. Sometimes a slight darkening of the cavity of the neurovascular bundle is visible.
- Secondary caries. X-rays show defects with uneven contours. Light areas are visible next to them. Sometimes the border between the filling and the cavity seems to be “undermined” - this indicates pathological changes in the tissues.
- Wedge-shaped changes. A gap is visible near the neck of the tooth - a wedge-shaped white stripe.
Radiography is necessary to monitor each stage of pulpitis treatment.
Important! Radiography does not detect cervical, fissure, approximal and caries in the spot stage. These types of pathology are not characterized by significant damage to tooth tissue.
Lesions on the occlusal (chewing) surface are best visible on x-rays. At a certain stage they take on a V-shape.
Diagnostics
The following comprehensive diagnostic methods will help to identify internal caries in a timely manner:
- examination using a mirror (primary examination);
- transillumination (inspection using a photopolymer lamp);
- X-ray (allows us to identify the causes and nature of internal damage);
- laser diagnostics (hidden damage is detected using a laser beam).
This allows you to identify hidden areas of caries in a timely manner and begin treatment.
If a stain on the enamel or other damage is detected, the tooth cavity must be opened. This will allow internal damage to be identified in time.
Diagnostic criteria
Today, to determine the latent form of caries, various diagnostic methods are used, which help to identify the exact location and form of the disease.
In this case, an important factor is to identify the presence of a carious process. This is very difficult to do, since external signs are not always present.
To determine pathology, the following activities are carried out:
- laser research. It is considered the most informative and reliable. For this purpose, a special device is used - Diagnodent. The method is based on the reflection of the affected area from a laser beam, which produces a characteristic sound;
- X-rays help detect defects in hard-to-reach areas. The disadvantage of this method is that radiography cannot detect the initial stages of the disease;
- using a dental mirror . This type of research is carried out first, the dentist identifies potential carious areas, and subsequently uses other diagnostic methods;
- The use of a special photopolymerization lamp , with the help of which darkened areas are revealed, they are the ones that indicate the presence of pathological changes. This method is called trans luminescence.
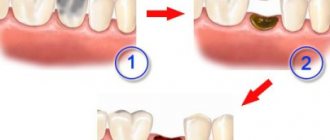
Treatment
In general, the treatment of hidden caries is no different from the treatment of its other forms. The strategy and methods of intervention depend on the stage of the disease. Let's consider the main ones:
- At an early stage, the tooth cavity is opened. Damaged tissue is cleaned out using a drill and then sealed. Restoration of damaged enamel is carried out using remineralization with fluoride and calcium preparations.
- For fissure caries, drilling and filling are often not required;
- In case of secondary caries, you will need to remove the filling and clean the tooth cavity again. After this, disinfection and further sealing are carried out.
- Radical caries is the most difficult to treat. This will require cleaning damaged tooth tissues and dental canals. After this, disinfection is carried out, sequential filling of the tooth canals, and then external filling. In severe stages, tooth extraction and implant installation will be required.
In moderate to severe stages, tissue reconstruction is performed, and then a crown is installed.
Treatment methods for hidden caries
Since latent caries is diagnosed already in the presence of a carious cavity, the treatment of such pathology is exclusively surgical. In such cases, therapy is carried out in the following order:
Complications
If the identified problem is not treated, the following complications develop:
- acute diffuse pulpitis;
- periostitis;
- various inflammatory reactions;
- purulent abscess;
- phlegmon.
Pulpitis is a deeper lesion that leads to complete or partial removal of the pulp.
Complete destruction of a tooth from the inside leads to infection of neighboring teeth. This leads to the risk of root caries of adjacent teeth.
Hidden caries provokes the development of chronic infection in the oral cavity. This increases the risk of tonsillitis and other chronic infections.
X-ray as one of the methods for diagnosing pulpitis
X-ray examination is an examination using x-rays. They are passed through the tooth and reflected on a special film. The resulting image shows dark and light areas. They correspond to soft and hard tissues.
Important! Most dentists use visiographs - X-ray machines that project images directly onto a computer monitor.
X-ray is used only as an accompanying method.
The development of pulpitis cannot be detected on x-rays. Rays are reflected only from hard tissues. In fact, radiography is an additional diagnostic method. Indirectly, you can only determine the depth of the carious cavity and its connection with the pulp chamber.
The exception is acute purulent and chronic gangrenous forms of the disease. Its development leads to the death of soft tissues and pathological changes in bone tissue. They are reflected in the photographs.
Therefore, x-rays are used only as an accompanying method. At the same time, a visual examination, electroodontodiagnostics (EDD) and thermometry are carried out.
Important! Although it is impossible to diagnose pulpitis using X-ray photos, examination is used to exclude other diseases with similar symptoms: periodontitis, granulomas, cysts.
The final diagnosis is made by opening the carious cavity and probing its bottom.
Prevention
The development of hidden caries can be prevented by simple prevention:
- Regular visits to the dentist. For adults this is once every 6 months. Children will need a dental check-up every 4 months as baby teeth are at higher risk of caries.
- Rules of oral hygiene. Includes regular cleaning and use after rinse aid. It is important to floss after every meal.
- Introduce as much solid food into your diet as possible. Vegetables and fruits clean teeth well and are a source of essential vitamins and minerals.
- Drinking water rich in fluoride. Prevents enamel damage and promotes its natural remineralization.
- Avoid eating food at different temperatures. This leads to damage to the enamel, including interdental areas. In the future, this causes destruction of dental tissue. More details on how to protect teeth from caries below.
At the first signs of caries (pain, discomfort while eating, the appearance of spots or black spots on the enamel), you should consult a dentist.
How is pulpitis determined from an image?
Pulpitis in the image can be identified by:
- Inflammation of soft tissue - darkening will be visible on x-ray.
- The depth of the carious cavity: if the destruction extends beyond the dentin, it can be argued that pulpitis is developing.
- The presence of granulomas - appear as light areas.
- Dental formation – wall cavities formed from dentin tissue.
X-rays can only detect dental caries.
Important! Denticles are formed as a result of mineralization of the pulp - its coronal or root part. They are considered one of the key signs of the disease. The x-ray shows round, multiple or single, dense darkened areas.