Ubistesin is a drug that has a local anesthetic effect. The drug is one of the most modern and effective representatives of the group of local anesthetics.
Ease of use, a small number of preservatives and adverse reactions allowed Ubistezin to become the option of choice in the presence of somatic pathologies in the patient. Dentists widely use anesthetic for conduction and infiltration anesthesia.
Components of anesthetic and features of carpules
The drug contains:
- articaine hydrochloride 40 mg;
- epinephrine hydrochloride or adrenaline;
- water for injections;
- sodium chloride;
- sodium sulfite.
The product is available in 2 versions: Ubistezin 1/200000 and Forte version 1/100000. They differ in the amount of vasoconstrictor substance. In the first case, the amount of epinephrine will be 5 µg/ml, and in the second - 10 µg/ml.
The anesthetic itself is produced in the form of 1.7 ml carpules. They are packaged in special tin cans with a soft surface on the inside.
Thanks to this, integrity is maintained during transportation, and further storage proceeds without any difficulties.
Moreover, each individual carpule has its own characteristics:
- Coating the inner surface with a special silicone layer . As a result, the injection becomes smooth and controlled, the piston moves more gently, and the amount of force applied is much less.
- All the necessary information is printed on the carpule with marking tape , which replaced printing on glass. Accordingly, the risk of damage from fragments in the event of its destruction has been reduced. This point is very important when performing intraligamentary anesthesia, since the pressure exerted in this case is very high.
Pharmacological properties
All properties of the drug are achieved due to the main active ingredients: articaine and epinephrine.
Articaine is an amide-type local anesthetic. Its effect occurs within 2-3 minutes after administration and lasts approximately 50-60 minutes. Compared to older substances, for example, novocaine or lidocaine, the effect of articaine is 2 times stronger.
It is also eliminated from the body faster, does not increase wound healing time and is less toxic. Therefore, Ubistezin can be used by elderly people, pregnant women and children over 5 years of age.
Epinephrine is responsible for blood vessels. It has a vasoconstrictor effect, which significantly increases the time of the anesthetic effect.
Thanks to this component, the drug has high penetrating ability and almost completely binds to blood plasma proteins. This ensures the safety of its use in the treatment of pregnant and lactating women. The medicine does not pass into breast milk and does not cross the placenta.
Scope of application and contraindications
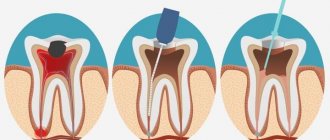
The anesthetic is used for intraligamentary, infiltration and conduction anesthesia during the following dental procedures:
- tooth extraction;
- treatment of superficial and medium caries;
- root canal cleaning;
- treatment of teeth for orthopedic structures;
- surgical interventions on the oral mucosa or bone;
- closing the communication between the maxillary sinus;
- cyst removal;
- installation of metal plates for jaw fractures.
Ubistezin and especially Ubistezin Forte cannot be used for:
- individual intolerance to the components of the drug;
- paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation;
- hyperthyroidism;
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- the use of non-selective beta-blockers;
- severe forms of liver failure;
- bronchial asthma;
- treatment with tricyclic antidepressants and drugs containing monoamine oxidase;
- cardiogenic shock;
- methemoglobinemia;
- B12 deficiency anemia.
Conditions in which the product should be used with caution:
- cholinesterase deficiency;
- kidney failure;
- diabetes;
- hypertonic disease;
- children under 4 years old.
Indications for use
Ubistezin injection solution is used as local anesthesia for a number of dental procedures:
- tooth extraction;
- root canal cleaning;
- preparation of carious cavities;
- preparation of the tooth stump before prosthetics;
- incisions and suturing in the palate.
- operations on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity or bones.
According to the instructions for use, the drug can be used for patients with somatic diseases, persons allergic to lidocaine, as well as those with a history of heart and vascular pathologies.
Contraindications
"Ubistezin" has a number of restrictions for use, which must be excluded from the patient's medical history before administering the anesthetic:
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- severe form of liver failure;
- hypertrichosis;
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- severe heart pathologies: unstable angina, post-infarction state, hypertensive crisis;
- bronchial asthma;
- intolerance to the composition;
- children under 4 years old;
- bleeding disorders;
- epilepsy;
- diabetes.
To exclude the presence of contraindications to the drug, the doctor may conduct a sensitivity test before administering it.
How is the medicine administered and in what dosages?
The method of administration and dosage of the anesthetic depends on the goals of the dentist:
- When treating uncomplicated caries of the upper jaw, the drug is injected into the transitional fold from the vestibular side. The injection volume is 1.7 ml. In some cases, the auxiliary use of an anesthetic from 1 to 1.7 ml is allowed to obtain the maximum anesthetic effect. Injections from the palate need not be performed. Using the same technique, anesthesia is used to remove teeth in the upper jaw.
- Injections from the palate are used to make incisions and sutures in the oral cavity . The optimal amount of anesthetic is 0.1 ml.
- If the manipulation is carried out on the lower jaw , then when treating and removing the frontal group of teeth and premolars, ordinary infiltration anesthesia with a volume of 1.7 ml is sufficient. If necessary, an additional injection of 1-1.7 ml is performed. If the desired effect is not achieved, then a full block of the nerve of the lower jaw is performed.
- When treating and removing lower molars, conduction anesthesia is always used. The optimal amount of administered substance is 1.7 ml. If necessary, the drug can also be injected into the transitional fold.
- Preparing a tooth for root canal filling or treating it for installation of orthopedic structures is carried out under infiltration anesthesia. The dose is 0.5-1.7 ml.
The maximum dosage is calculated from the ratio of 7 mg of articaine per 1 kg of body weight. One capsule contains 40 mg of anesthetic.
Characteristics and scope of use of "Ubistezin"
"Ubistezin" is a clear, colorless liquid. Packaged in disposable ampoules with a volume of 1.7 ml, the concentration of active ingredients in the ready-to-use solution is 4%. The amount of drug administered depends on the use scenario:
- Removal of one or two adjacent teeth on the upper jaw – 1.7 ml;
- Anesthesia for preparing the palate or suturing it – 0.1 ml;
- Extraction of premolars on the lower jaw – 1.7 ml by infiltration method;
- Treatment of premolars on the lower jaw – 1.7 ml by wire method;
- Preparation of carious cavities, grinding of the tooth stump for a crown – 0.5-1.7 ml through injections from the vestibular side;
- Mandibular anesthesia – 1.7 ml.
The indicated dosages are recommended; the dentist can independently change them depending on the complexity of the treatment and the sensitivity of the patients. For other cases, the standard volume of the drug is sufficient - 1.7 ml.
Some clinical cases of the use of "Ubistezin"
"Ubistezin", being a local anesthetic, is used for pain relief during almost all surgical operations in dentistry. Especially if they require preparation of dentin, carious cavities, soft tissues, as well as tooth extraction. When performing manipulations on the teeth of the lower and upper jaw, with the exception of premolars, infiltration anesthesia is used. This method anesthetizes tissue during extraction, treatment of caries, root canal treatment, and grinding of the stump for the installation of orthopedic structures. Infiltration anesthesia with the drug is also used for interventions in the soft tissues of the oral cavity - preparation, suturing, removal of cysts and other cases. Conduction anesthesia with “Ubistezin” is used for manipulations with premolars, since these teeth have increased sensitivity and are connected to nerve ganglia.
Pharmacological properties
The mechanism of action of the drug "Ubistezin" is due to the fact that it contains two active components - articaine hydrochloride 40 mg and epinephrine hydrochloride 0.006 mg, each of which has its own properties, but in combination, they have a persistent and long-lasting anesthetic effect:
- "Articaine" is an amide-type anesthetic from the thiaphene series, which allows blocking sodium channels and reduces the excitability of nerve fibers.
- “Epinephrine” is an adrenergic agonist that has the ability to constrict blood vessels in the area of administration, which complicates the absorption of articaine and provides a longer-lasting analgesic effect.
After using the drug, tissue regeneration occurs quite quickly, which significantly reduces the risks of complications. The low concentration of active components in the blood plasma allows the anesthetic to be used by people with diseases of the cardiovascular system, pregnant women and children.
Side effects
According to the instructions for the drug and medical observations, “Ubistezin” is well tolerated, but in some cases it causes side effects:
- headache;
- muscle tremors;
- breathing problems;
- nausea, urge to vomit;
- decrease or increase in blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- itchy skin, rashes;
- angioedema, anaphylactic shock.
The risk of side effects increases if the patient has a history of contraindications or if the recommended dose is exceeded. If any sign appears, you should exclude repeated administration of the drug and seek medical help. There is no antidote to this medicine, so side effects will be treated with symptomatic therapy.
special instructions
Intravenous administration is completely excluded. To prevent such situations from occurring, an aspiration test should be performed.
The drug should not be used in areas of pronounced inflammatory process. It is recommended to administer the product near the inflamed area.
To prevent the development of infections, needles and syringes must be changed during each withdrawal from a vial or ampoule. Opened carpules are not reused. The use of damaged cartridges is also excluded.
Possible adverse reactions and cases of overdose
Ubistezin can have the following inhibitory effects on body systems:
- Effect on the central nervous system . The patient may develop headache, loss of consciousness, breathing problems, and convulsions.
- Effect on the gastrointestinal tract . In some cases, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea occur.
- Changes in the functioning of the sensory organs are rarely observed . Sometimes, if the anesthesia technique is violated, diplopia or temporary impairment of visual acuity is possible.
- Effect on the heart and blood vessels . There is a possibility of a decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia or bradycardia, arrhythmia.
- Allergic reactions . The skin may become red and itchy. There is also a risk of developing allergic conjunctivitis and rhinitis. More serious complications include angioedema and anaphylactic shock.
- Local manifestations . Swelling or an inflammatory reaction may occur at the injection site. If the anesthesia technique is violated, ischemic zones appear and damage to the nerve trunk occurs.
Symptoms of excessive drug administration are:
- dizziness;
- change in consciousness;
- lowering blood pressure levels;
- tachy- or bradycardia.
What to do if unwanted reactions occur:
- immediate stop of drug administration;
- giving the patient a horizontal position;
- provision of oxygen;
- monitoring pulse and blood pressure;
- if breathing is impaired, the introduction of air ducts and artificial ventilation are recommended;
- if convulsions occur, barbiturates are used;
- circulatory disorders are corrected with electrolyte solutions;
- bradycardia is treated with intravenous administration of 0.1 mg of adrenaline;
- for tachycardia, selective beta-blockers are used;
- pressure is reduced by peripheral vasodilators.
Ubistesin forte - solution for injection in dentistry
Home \ Medicines \ Local dental anesthetics \ Ubistesin forte
Ubistezin forte, solution - infiltration and conduction anesthesia (including in dentistry - tooth extraction, filling a cavity, grinding teeth for crowns).
Compound:
Solution for injection 1 ml: articaine hydrochloride: 40 mg epinephrine (in the form of hydrochloride): 10 mcg 1.7 ml - cartridges (50) - tin cans.
Manufacturer ZM Deutschland, Germany
Ubistezin forte, solution d/in 40 mg + 10 μg/ml with epinephrine cartridge 1.7 ml cartridges No. 50, price: 2860.00 rub.
Ubistezin solution d/in 40 mg+5 μg/ml with epinephrine cartridge 1.7 ml, cartridges No. 50, price: RUB 2,390.00.
Analogues: ULTRACAINE D-S, solution ULTRACAINE D-S FORTE, solution ALFACAINE SP, solution ARTIFRIN FORTE, solution
Contraindications: - hypersensitivity; — B12-deficiency anemia; - methemoglobinemia; - paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia; - atrial fibrillation; - angle-closure glaucoma; - hypoxia; - intolerance to sulfo groups (especially in bronchial asthma). With caution: cholinesterase deficiency, renal failure, bronchial asthma, diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, arterial hypertension, children (up to 4 years - effectiveness and safety have not been determined).
When performing paracerebral blockade: preeclampsia, bleeding in the last trimester, amnionitis. Dosage Infiltration anesthesia: tonsillectomy (for each tonsil) - 5-10 ml; reduction of fractures - 5-20 ml; perineal seam - 5-15 ml. Conduction anesthesia: Oberst anesthesia - 2-4 ml, retrobulbar - 1-2 ml, intercostal - 2-4 ml (for each segment), paravertebral - 5-10 ml, peridural (epidural) - 10-30 ml, sacral - 10-30 ml, trigeminal nerve block - 1-5 ml, stellate ganglion block - 5-10 ml, brachial plexus block - 10-30 ml (supraclavicular or axillary access), blockade of the external genitalia - 7-10 ml (for each side), paracervical blockade - 6-10 ml (on each side). For uncomplicated extraction of maxillary teeth in the non-inflammatory stage, 1.7 ml per tooth is injected under the mucous membrane in the area of the transitional fold - vestibular depot, if necessary - an additional 1-1.7 ml; palatal incision or suture - palatal depot 0.1 ml. When removing premolars of the lower jaw (5-5) in an uncomplicated stage, infiltration anesthesia gives the effect of conduction anesthesia. When preparing cavities and grinding teeth for crowns, with the exception of molars of the lower jaw, a vestibular injection of 0.5-1.7 ml per tooth. The maximum dose is 7 mg/kg. Side effects From the central nervous system (depending on the dose applied): headache, impaired consciousness (up to loss of consciousness); breathing disorders (up to apnea); tremor, muscle twitching, convulsions. From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. From the senses: rarely - transient visual impairment (up to blindness), diplopia. From the cardiovascular system: decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, bradycardia, arrhythmia. Allergic reactions: hyperemia and itching of the skin, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, angioedema of varying severity (including swelling of the upper and/or lower lip and/or cheeks, glottis with difficulty swallowing, urticaria, difficulty breathing), anaphylactic shock. Local reactions: swelling or inflammation at the injection site, the appearance of ischemic zones at the injection site (up to the development of tissue necrosis - in case of accidental intravascular injection); nerve damage (up to the development of paralysis) - occurs only when the injection technique is violated. Overdose Symptoms: dizziness, motor agitation, loss of consciousness, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, bradycardia. Treatment: when the first signs of an overdose appear during injection, it is necessary to stop administering the drug, place the patient in a horizontal position, ensure an open airway, and monitor heart rate and blood pressure. For dyspnea, apnea - oxygen, endotracheal intubation, mechanical ventilation (central analeptics are contraindicated); for convulsions - slow intravenous short-acting barbiturates with simultaneous oxygen supply and hemodynamic control; in case of severe circulatory disorders and shock - intravenous infusion of solutions of electrolytes and plasma substitutes, corticosteroids, albumin; for vascular collapse and increasing bradycardia - epinephrine 0.1 mg slowly intravenously, then intravenously by drip under the control of heart rate and blood pressure; for severe tachycardia and tachyarrhythmia - IV beta-blockers (selective); with increased blood pressure - peripheral vasodilators. Oxygen therapy and monitoring of circulatory status are necessary in all cases. Drug interactions Tricyclic antidepressants and MAO inhibitors enhance the hypertensive effect. The local anesthetic effect of articaine is enhanced and prolonged by vasoconstrictors. Non-selective beta-blockers increase the risk of developing a hypertensive crisis and severe bradycardia. Special instructions Do not administer intravenously! To avoid intravascular injection, an aspiration test must be performed. Injection pressure should correspond to the sensitivity of the tissue. Do not inject into an inflamed area. Eating is possible only after sensitivity has been restored. To prevent infection (including viral hepatitis), it is necessary to always use new sterile syringes and needles each time a solution is taken from vials or ampoules. Opened cartridges must not be used again on other patients (risk of hepatitis). Do not use a damaged cartridge. The time of first collection of the solution should be noted on the label of the reusable bottle. Opened bottles should be stored according to instructions and used within 2 days. Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. The patient’s ability to drive vehicles or engage in activities that require a high mental and motor reaction is determined by the doctor. Pregnancy and lactation Does not have a harmful effect on the fetus (with the exception of possible bradycardia) with any technique of application and dosage. Use in children : With caution: children's age (up to 4 years - effectiveness and safety have not been determined). In case of impaired renal function With caution: renal failure.
ALSO BUY WITH THIS PRODUCT:
- Articaine INIBSA
- Articaine, Articaine with adrenaline, Articaine with adrenaline forte
- Brilocaine - adrenaline forte
- Cathejell with Lidocaine
- Dental injection kit AERS (disposable carpule syringe+carpule+needle)
- Disposable carpule syringe
- Orabloc®, injection solution
- Primacaine adrenaline
- Septanest with Adrenaline
- Scandinibsa® 3% (Scandinibsa 3%)
- Ultracain DS, Ultracain DS forte
- Ubistezin forte
- Carpule syringe
- Carpule needles
- Lidocaine