Removing a wisdom tooth, like any other fragment of the jaw row, is an ordinary dental procedure that does not involve the use of any modern technologies and equipment.
Its success directly depends on the qualifications and skills of the doctor. It is done under local anesthesia and is almost painless. Some discomfort is present only at the stage when the anesthesia wears off.
However, against the background of an abscess, the pain threshold is greater, so in the case of an impacted tooth, it is better not to take it to such an extreme, but to get rid of it immediately.
In modern practice, there are ways to preserve it, but you need to understand that, firstly, it is expensive, and secondly, it presupposes the presence of modern equipment in the clinic, which is not always available.
Reasons for appearance
Retention is a common pathology inherent in wisdom teeth. The third molars are the most sensitive teeth to this process.
The main reason for this phenomenon is that when they begin to cut (and this happens in adulthood), the jaw row is already fully formed and they simply do not have enough space for full development and growth.
Thus, lack of space is the main risk factor for the occurrence of this pathology, in which the tooth simply begins to grow into the bone tissue.
In addition, the causes of impaction of third molars are:
- hereditary predisposition - due to the genetic characteristics of the structure of the maxillofacial apparatus;
- neglect of orthodontic therapy when it is really necessary.
Kinds
Dystopia comes in several forms. Let's take a closer look at them.
Oral and vestibular
Oral dystopia is a position when teeth erupt on the upper jaw from the side of the palate (palatal position), or on the lower jaw, from the lingual side (lingual), in which they go deep into the oral cavity .
The most common lingual and palatal position occurs when teeth change; if they erupt incorrectly, adjacent lateral incisors and premolars suffer.
This type of dystopia most often occurs in childhood, when the milk line changes to permanent .
The causes of oral dystopia are:
- lack of space in a row;
- bad habits;
- underdevelopment of the alveolar process of the upper jaw in the anterior region;
- disruption of the process of changing dairy products to permanent ones.
Consider the vestibular position, in which there is a displacement outward from the dentition . Very often fangs are susceptible to this.
The causes of vestibular dystopia are:
- bias;
- lack of space for new growth;
- disruption of the development process, including eruption;
- narrowing of ranks;
- bad habits.
Mesial
In dentistry, there is a type of dystopia called mesial, in which the teeth move forward. They interfere with the teething of others, which in turn leads to the formation of an incorrect bite.
Also, due to their incorrect position, injury to the lips, tongue, and cheek tissue occurs. In addition, it is impossible to carry out normal oral hygiene procedures and remove plaque, which in turn leads to the development of caries.
In addition, such a tooth can cause a violation of chewing function, and a person’s speech is also impaired.
The causes of the mesial anomaly are: any disturbances during teething, their presence in excess of the norm, as well as the atypical position of the rudiments. All this is revealed at a dentist’s appointment when diagnosing the patient’s oral cavity.
Distal
Distal dystopia is usually understood as a phenomenon such as tooth displacement back along the arch . The causes of this disease are considered to be disturbances that occurred during eruption, the atypical position of the rudiments, as well as the presence of extra units.
Some patients can identify this disease themselves, especially when it is severe. In order to prescribe the necessary treatment, the patient must visit a dentist, namely an orthodontist.
Its task is to normalize the shape and size of the dentition. For this purpose, orthodontic removable and fixed structures are used.
Transposition and tortoposition
Such phenomena as tortoposition and transposition are less common in practice than other anomalies associated with teeth, but can lead to serious consequences associated with a person’s bite, as well as with health in general.
Let's take a closer look at this problem:
- tortoposition is a phenomenon in which there is a turn around its axis; both canines and incisors are susceptible to this.
This can even lead to tooth loss. By contacting a dentist with such a problem, the patient will receive appropriate treatment and save his teeth; - transposition this is an incorrect position in which a rearrangement occurs, for example, the incisors change places with the canines. The reason for this is the incorrect formation of tooth germs.
The choice of treatment method in this case depends on the degree of inclination, as well as displacement of the roots.This can be surgical intervention (removal of some teeth) or orthodontic intervention, using braces, mouthguards, and their restoration with artificial crowns or veneers is also possible.
Varieties
The most common types of impacted eights found in dental practice, complexity and specificity:
- normal - the organ grows correctly, without deviating to the side, but develops too slowly, causing discomfort and sometimes aching pain in its owner.
The situation is, in principle, controllable and, with timely medical care, does not pose a serious danger to neighboring teeth. The main thing is to install a special frame in time, which will speed up eruption and help the weak organ to finally develop; - transverse - the figure eight grows horizontally, rests on the adjacent tooth, negatively affects its condition, destroys enamel and hard tissue. Caries occurs, and a previously healthy organ is in danger of destruction. The case is difficult because the only way out is to remove it;
- on a slope - the organ grows at an oblique angle relative to the jaw row, and the deviation can be either towards the cheek or tongue, or interfere with its “neighbors”.
If there is no pressure on the adjacent jaw segments and the tooth does not cause any inconvenience to the patient, does not injure the soft tissue and mucous membranes, it can be left alone. And if it interferes, then the best solution is to get rid of it.
According to the level of eruption, they are divided into fully or partially submerged. In this situation, diagnosing the development of figure eight is extremely difficult and it is not always possible to identify the pathology in time.
The complexity of the case is that inside the soft gum tissue a favorable environment is created for the accumulation of bacteria that provoke caries and inflammation.
Treatment of dental dystopia
If a dystopic tooth does not pose a serious aesthetic and functional problem, but only causes chronic injury to the oral mucosa, you can limit yourself to grinding down the sharp cusps. If there is room for a dystopic tooth in the dental arch, orthodontic treatment is carried out. In other cases, the choice is made in favor of removing dystopic teeth.
To correct the position of teeth, removable and non-removable orthodontic devices of mechanical and functional action, and braces are used.
Removal of a dystopic tooth in surgical dentistry is classified as a complex operation. Absolute indications for the removal of dystopic teeth are jaw cysts, periostitis and osteomyelitis of the jaw, complete traumatic dystopia of the tooth; relative indications - periodontitis and pulpitis, difficulties in treating caries of 7 teeth or prosthetics, etc. Complications associated with the removal of a dystopic tooth may include dislocation of an adjacent tooth, dislocation and fracture of the lower jaw, trauma to the mandibular canal, bleeding from the tooth socket. Dystopic teeth located outside the alveolar process must be removed in a hospital setting.
In case of incomplete traumatic dystopia, under local or general anesthesia, the displaced tooth is repositioned and subsequently splinted using heliocomposite or wire ligatures. In most cases, dystopic teeth require combined hardware and surgical treatment.
Danger
A fully or partially submerged figure eight can cause its owner a lot of problems, and if the situation is complicated by the factors described above, then its presence threatens the following problems:
- rapidly growing caries ;
- developmental defects and improper eruption of neighboring units , their loosening (sometimes even spontaneous loss), change in the angle of growth;
- pulpitis of nearby adjacent roots;
- granuloma;
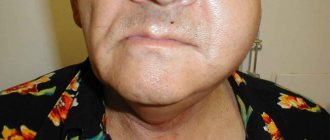
- external facial defects caused by gradually developing jaw asymmetry;
- swelling and inflammation of the gums.
Symptoms and consequences
The most common form of dystopia in adults is abnormal growth of wisdom teeth.
Often the presence of dystopia becomes a cause of aesthetic discomfort. However, the main negative side of this pathology is its functional disorders:
- The most advanced cases are when the dystopic tooth is located outside the alveolar process (the area of the jaw on which the teeth are located). So, it can be located in the body of the jaw. This in turn causes discomfort.
- Abnormal movement and tilt can cause injury to the cheek tissue. It is even possible that decubital ulcers may appear.
- Due to the incorrect alignment of teeth, it becomes more difficult to maintain oral hygiene, due to the difficulty of removing food debris and plaque. Due to this, caries may begin to form over time.
- Over time, a malocclusion develops.
- There are cases when gum pockets begin to appear above the abnormal parts, or more precisely, above the part that has not erupted. Over time, bacteria begin to accumulate in them, which leads to inflammation.
- In case of severe curvature, speech and chewing functions may be impaired.
Diagnostics
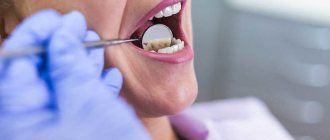
Before doing anything, the doctor must certainly conduct a thorough diagnosis, because cutting off any organ of the human body requires categorical arguments.
In dental practice, examination of such patients is carried out by probing and palpation. A specialist can obtain an accurate clinical picture using targeted radiography.
In order to have more accurate information, as well as in complex, non-standard cases, for example, in the presence of an atopic tooth, orthopedic tomograms are used as in-depth diagnostics.
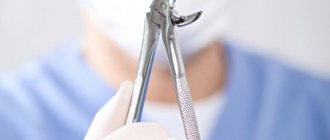
Removal of a tooth
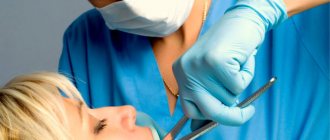
The surgical intervention takes about 10-15 minutes. It is recommended to eat a large meal before surgery. During the removal process, the patient does not feel anything, but is conscious. Read more useful information about whether it is worth removing a wisdom tooth in this material. The operation is carried out in several steps:
- An X-ray examination is performed to prevent difficulties during the operation.
- An injection is given into the gum with a painkiller (local anesthesia).
- After the anesthesia has taken effect, the doctor cuts the gum and separates its soft tissue from the bone. Sometimes they resort to sawing out bone tissue to get to the bones.
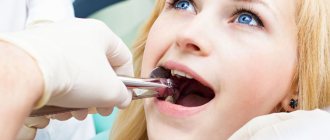
- The molar is removed with dental tweezers, or they resort to loosening if removal is difficult. In advanced cases, doctors remove the tooth in parts.
- Treatment of the hole with antiseptics.
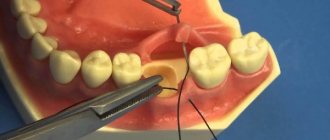
- Stitching.
- If there is pus, drainage is installed in the hole to pump it out.
- Stop bleeding with a gauze pad. Read more about how to stop bleeding after tooth extraction here.
- Applying ice to reduce swelling.
- At the end of the operation, the doctor gives recommendations, prescribes medications and schedules a follow-up appointment to monitor the patient’s condition.
Before using anesthesia, you should find out whether you are allergic to one or another component of the drug. This can be checked by donating blood for the desired allergen in any laboratory.
Operation
Wisdom tooth removal surgery is a procedure that requires a step-by-step approach. In addition, not every practicing surgeon performs such manipulations. This requires certain qualifications and training.
Preparation
The main point of this stage is the patient’s physical tolerance of the drugs that will be used as anesthesia.
In addition, if a person suffers from any chronic diseases, the surgeon should know about it. In some cases, consultation with specialized specialists may be required to avoid possible relapses and complications.
The patient should behave as he would when preparing for any other surgical procedure:
- Do not drink alcohol for 2 - 3 days before surgery ;
- do not eat food directly on the day of removal;
- pay more attention to your health , since even a minor cold that is ignored can lead to serious consequences.
Pros and cons of dental fluoridation in children and reviews from specialists. Read here whether stomatitis is contagious in adults.
Follow the link https://dr-zubov.ru/ortodontiya/apparaty/plastiny/dlya-vyravnivaniya.html to see photos of plates for straightening teeth in children.
Stages
Depending on the complexity, such manipulations take from one to three hours. All this time the patient is under general anesthesia, and his physical condition is constantly monitored.
The removal procedure includes the following steps:
- bringing the patient into a state of sleep by intravenous anesthesia;
- cutting the soft gum tissue is carried out with a scalpel, the skin is moved to the side, opening access to the bed;
- a hole is drilled in the hard tissue of the bone (if the organ has grown into the bone);
- if the tooth is in the gum, it is removed by dislocation ;
- an antiseptic drug is placed into the resulting void and, if necessary, iodine-based turunda is poured in;
- if the cut area is too wide, it is partially sutured with special surgical threads .
Dressings
Removal itself is not the final event. A few days later, a second visit to the dentist is indicated, and if there is a turunda inside the hole, this will have to be done repeatedly in order to permanently replace it.
These manipulations are absolutely painless, but require mandatory implementation, since they are an important condition for speedy healing and acceleration of the recovery process.
Difficulties
Such procedures are considered non-standard in medical practice, and not because of the abnormal location of the wisdom tooth.
During surgery, there is always a certain amount of risk associated with various difficulties that cannot be foreseen in advance:
- injuries to soft tissue and mucous membranes and, as a result, bleeding;
- partial chip of the ridge process;
- dislocation, displacement, and sometimes fracture of the jaw;
- damage to the maxillary passages and sinuses by root processes.
In the video, a specialist talks about the need to remove an impacted wisdom tooth.
When is it necessary to remove an impacted tooth?
Removal is indicated if:
- there is repeated acute, subacute or chronic pericoronitis;
- signs of progressive painful periostatitis, caries, periodontitis, pulpitis appeared on impacted or adjacent teeth and their surrounding tissues;
- destruction of the dentin tissue of the root occurs, resorption of the roots of neighboring teeth, which are under pressure from the impacted dental unit;
- neuralgic pain occurred as a result of a chronic inflammatory process;
- a follicular cyst has formed;
- a tumor (odontoma, ameloblastoma) has formed around an unerupted tooth;
- there is no place for it in the dentition;
- destruction of the tooth neck has occurred;
- necessary orthodontic treatment requires additional free space;
- a medial diastema developed as a result of a transversely impacted tooth.
Removal technique
The surgical operation to remove an impacted tooth lasts from 25 minutes. up to 3-4 hours. Main removal steps:
- organizational measures for local anesthesia of infiltration type or general anesthesia;
- a complete (extensive) incision or patchwork incision of the soft mucous tissues and periosteum, creating access to the coronal part of the tooth;
- peeling of mucous tissue, exposure of the bone bed;
- preparation and formation of the surface of an impacted tooth for removal. Using a special bur, in order to gain access to the roots of the tooth, a hole is drilled and sawed out in the bone tissue;
- direct tooth extraction, extraction. Can be done with elevators, simultaneously with pliers and elevators, or with a cutter with a straight tip. First, the upper part of the tooth is cut and removed, then its root and everything else. The release of all parts of the tooth and their extraction from the socket are performed by dislocation and at right angles. This makes it possible to break all periodontal bonds;
- The entire surface of the open wound and the resulting voids are well cleaned of bone tissue residues, and washed with antiseptic solutions. If the area of the affected area around the tooth was extensive and a strong inflammatory process was observed, then turunda soaked in iodoform is placed in the hole;
- suturing, suturing damaged tissue with suture material, catgut.
In case of partial retention, a mucosal incision is not necessary. The surgeon, using forceps, swings the crown part of the tooth in a pendulum-like motion, and then pulls it out. Impacted teeth located on the lower jaws are more difficult to remove.
The removal operation can also be performed with a laser beam (laser). This is a less traumatic and faster procedure. It takes place without drilling, the rehabilitation period is simple and short, the complications that arise are minimal, and the risk of wound infection is significantly reduced.
Contraindications
Surgery to remove an impacted tooth is contraindicated in the following cases:
- state of hypertensive crisis;
- acute stages of heart disease or diseases of the nervous system;
- existing viral or infectious diseases:
- existing diseases of the blood and hematopoietic system;
- in the last phase of menstruation in women;
- if less than 14 days have passed since the operation to terminate the pregnancy.
Complications
We are talking about complications both during the process and in the postoperative period. These include:
- severe pain accompanying the patient on the first day. They are relieved with local anesthetics (usually in the form of injections);
- swelling of the inflammation site and periodic bleeding. Sometimes - an increase in temperature, less often - inflammation of the lymphatic system, manifested by enlarged submandibular lymph nodes;
- alveolitis - acute pain, accumulation of purulent masses , severe swelling associated with infection;
- uncontrolled bleeding - occurs due to mechanical injury to the blood capillaries;
- dried out socket - caused by the absence of a characteristic blood clot that prevents the penetration of microbes. The complication is accompanied by a dull, incessant pain.
Dystopic wisdom tooth: what is it?
A dystopic tooth is one with an incorrect location relative to the entire dentition, which may extend beyond the border of the alveolar processes. As a rule, such an anomaly can be predicted in childhood and appropriate therapeutic or preventive measures can be taken. In the case of wisdom teeth, this is more difficult to do, since the rudiments of eights form much later than those of other teeth. Moreover, pathology can harm neighboring teeth, so when a specialist discovers a dystopic wisdom tooth, the question of its removal is almost always raised. Symptoms of a dystopic wisdom tooth usually manifest themselves in the form of inflammation and pain.
Rehabilitation
The rehabilitation period is a long undertaking, since wound healing requires at least a week even in the absence of complications.
We can talk about full restoration of health no earlier than after 3 to 4 weeks.
During this period, doctors recommend following the following rules that can help make the process more comfortable:
- in the first 24 hours you should apply cold - this will relieve swelling;
- do not neglect pain - take pain relief at the first signs of its manifestation;
- on the first day, observe the temperature regime for food intake , avoid alcohol, and do not smoke;
- for the entire recovery period, avoid activities that contribute to general overheating of the body (baths, saunas);
- To speed up wound healing, use special antiseptic and wound-healing solutions and sprays .
Watch a video about a clasp denture for the upper jaw and learn about its features. Find out the prices of teething gum gels in this article.
At this address https://dr-zubov.ru/krasota-i-uxod/sredstva/irrigatory/kakoj-luchshe-sovety-po-vyboru.html all about which is better to choose an irrigator for the oral cavity.
FAQ
Every person faced with the problem of an impacted wisdom tooth is interested in questions typical for this situation. Let's look at the main ones.
Is it possible not to delete it?
It is possible - but in very rare cases. Even if it doesn’t interfere, it’s like a time bomb - a complication can arise at any moment. If you don’t want to leave, regular visits to the dentist are a must.
As long as the tooth is sealed, nothing will happen to it
This is fundamentally wrong. The oral cavity is the most susceptible substance to infections in the human body.
A simple cold caused by general hypothermia can cause pathology. And beginning caries is generally enemy No. 1.
General anesthesia is required
Not necessary, sometimes local anesthesia is sufficient. It all depends on the complexity of the case.
It is worth noting that the drugs that are used for this are quite strong relief agents.
They'll hit you with a hammer
Such barbaric treatment of patients is a thing of the past. The level of development of modern domestic medicine requires the use of other instruments - a drill, a special cutter, which is undoubtedly more humane.
Rehabilitation period
Removing an impacted wisdom tooth is a complex manipulation, so superficial tissue restoration will take about a week, while complete regeneration of the deep layers will last a month. Pain and discomfort will accompany the patient only for the first seven days.
On this topic
- Wisdom teeth
Find out what to do if your wisdom tooth hurts
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 2, 2020
During the recovery period, it is important to follow some recommendations:
- To relieve swelling, you should apply a cold compress to your cheek on the first day after the procedure.
- For severe pain, analgesics will help.
- For three hours after removal, it is prohibited to smoke, drink alcoholic beverages, or eat cold or hot food.
- It is advisable not to visit the sauna.
- To speed up regeneration, it is necessary to use restorative drugs.
If there was purulent inflammation, then antibiotics and physical therapy in the hospital are prescribed. It is also useful to take baths with anti-inflammatory agents. During recovery, mouth rinsing is prohibited. If there is severe swelling or pain that does not go away after three days, you should consult a dentist.
Prices
It’s difficult to say for sure how much removal will cost, everything is individual. If we consider the trend as a whole, then the operation, depending on the level of complexity, region, and prestige of the clinic, varies in the range from 2000 to 4500 rubles.
For example, simple vertical retention is the most budget option and is unlikely to cost more than the lower limit.
If the operation is performed on a complicated tooth, with a horizontal position, when additional drugs are used, additional equipment is used, the price will be determined individually. The above prices for each specific service are taken into account here.