Wounds on the roof of the mouth - causes and treatment features
The formation of wounds in the oral cavity, or more precisely, on the surface of the palate, can be caused by a number of infectious diseases, and not only.
The most common reasons include the development of any infectious diseases, as well as stress, leading to a decrease in the protective functions of the body. Palpation of inflamed areas of the mucous membrane can be accompanied by acute pain, and the affected areas themselves can complicate the process of chewing and swallowing food, as well as speech function.
Causes of sores in the mouth
The oral mucosa has increased sensitivity to adverse environmental factors. Wounds appear for the following reasons:
- Aphthous stomatitis refers to chronic diseases of the oral cavity. Manifests as ulcers, aphthae on the mucous membrane. With pathology, many ulcerative defects develop on the inner surface of the cheeks, tongue, and palate.
- Herpetic infection affects the skin, membranes, and internal organs. Herpetic stomatitis is manifested by numerous small ulcers, which are located in groups at the bottom of the oral cavity.
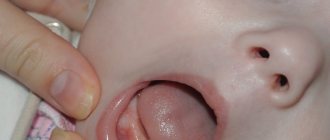
- The appearance of wounds on the mucous membranes of the mouth is caused by poor hygiene. Failure to comply with hygiene procedures is more common in children. Babies may suffer from Bernard's afte. They represent ulcerative defects that form on the hard palate from the mechanical impact of foreign objects.
- The wound appears from an accidental bite.
- A hard toothbrush, dentures, dentures, pointed crowns, the habit of biting the lips, and strong blows to the cheeks cause the defect.
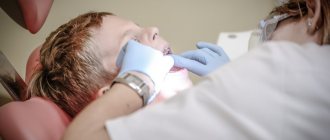
- During treatment and dental procedures, the patient may receive minor injuries to the gums, lips, and cheeks from instruments. Dental implantation can also lead to various types of damage to the oral cavity. This is why, among other things, it is so important to trust the installation of implants to qualified specialists.
- The proliferation of fungi on the inner surface of the oral cavity is manifested by ulcers with white cheesy deposits. The first symptoms of candidiasis.
- Lack of vitamins and strong feelings lead to a decrease in local immunity and the appearance of pathological lesions in the mouth.
- Necrotizing periadenitis is manifested by compactions in the submucosal layer, which over time degenerates into painful ulcers. Healing of defects takes a long time.
Why do wounds appear on the roof of the mouth?
Among the variety of causes that provoke the occurrence of wounds (ulcers) on the roof of the mouth, special attention should be paid to factors that can be divided into three categories.
Oral diseases
These common oral diseases include:
- Gingivostomatitis of necrotic type. The development of this disease is facilitated by oral injuries, weakened immunity, hypothermia, lack of vitamins, and the presence of allergic stomatitis. The gums, tonsils, palate, cheeks and tongue are affected. With this disease, the wounds may have a yellow or greenish coating, which causes an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity. Shallow wounds have uneven outlines. Very often, with this disease, the appearance of wounds is accompanied by minor bleeding. The treatment process must necessarily take place in a hospital setting and with the help of drug therapy.
- Herpetiform stomatitis. This disease is characterized by the appearance of sores very similar to herpes sores. In this case, damage to the palate and tongue occurs. The course of the disease usually takes no more than a few days. However, if the wounds do not heal on their own within seven days, you should definitely contact a specialist.
- Necrotizing periadenitis. The initial stage of this disease is characterized by the appearance of small compactions, which after some time become wounds (ulcers). The localization of the disease covers the lips, palate, cheeks and tongue. This causes difficulty while eating and talking.
- Recurrent stomatitis. The localization of wounds and ulcers in this disease covers the palate, the area around the lips, cheeks, and also the tongue. The disease is characterized by the presence of pain when eating, as well as a feeling of discomfort in the mouth. Treatment of this type of stomatitis must begin immediately when the first nonspecific symptoms appear.
- Oral tuberculosis. The course of this disease is characterized by the formation of ulcers (wounds) affecting the entire oral cavity, including the cheeks and surface of the tongue. There is no pain during the formation of such ulcers, but over time the ulcer can grow. During this type of tuberculosis, the wounds are not deep, but have a loose structure. Often the formation of wounds, as with necrotizing gingivostomatitis, is accompanied by bleeding. The wounds have uneven outlines. Treatment of this disease should take place exclusively in a hospital setting and under the close supervision of medical personnel.
Reasons for appearance
Conventionally, all types of oral ulcers can be combined into 2 broad groups:
- ulcers, the formation of which is associated with damage to the tissues of the oral mucosa;
- ulcers as symptoms of another disease .
It is important to correctly determine the cause of the formation of such a defect and begin treatment in order to exclude complications and the occurrence of a serious illness.
First, let's look at the causes of ulcers due to damage to the mucous membrane and tissues of the oral cavity. These include:
- Stomatitis – sores of an infectious nature;
- Injuries – ulcers of traumatic origin.
Stomatitis
The most common cause of mouth ulcers is infection - stomatitis. The following types are distinguished:
Aphthous
Aphthous stomatitis (recurrent) is a chronic disease and is inflammatory in nature.
Its peculiarity is the periodic appearance of aphthae (small ulcerations) in the oral cavity.
Such ulcerations may appear on the roof of the mouth, tongue, inner cheeks, or on the mucous surface of the lips. They are painful and may not go away for a long period if they are frequently damaged.
People with aphthous stomatitis regularly develop colitis . Typically, aphthae heal within a week or 10 days; in more complicated and advanced situations, when several aphthae appear at once, recovery takes from 2 to 4 weeks .
The prerequisites for the appearance of such ulcerations are: severe overexertion, trauma to the surface of the oral mucosa, or menstruation.
Herpetiformis
Stomatitis herpetiformis, characterized by the formation of small ulcers in large quantities .
Externally similar to herpes simplex sores. Women under 30 years of age are most susceptible to their appearance.
Areas of frequent localization are areas of the lower surface of the tongue and the floor of the mouth . They do not have a clearly defined shape, the base is gray. They heal within 10 days, leaving no scars.
This stomatitis, in a milder form, is also observed in children. During treatment, it is recommended to take vitamin C.
Afty Setton
Setton's aphthae is a more complex and painful type of stomatitis , the initial stage of development of which begins with the appearance of compaction.
Such compactions develop into painful ulcers with dense and raised edges.
An ulcer appears in the mouth with impurities of blood and lymph inside - as in the photo. Such inflammations most often form on the inner mucosa of the cheeks, lips and on the lateral surface of the tongue.
There is pain when eating (sometimes even when talking). This type of ulcer takes a very long time to heal – up to several months.
Afty Bednar
Bednar's aphthae are often called erosions - traumatic ulcerations. Such ulcers can only appear in the mouth of a child . The causes of formation are considered to be a strong and rough impact on the mucous membrane of the palate and poor oral hygiene.
Appear on the hard and soft palate. On top of such formations there is a yellowish coating .
Injuries
Ulcers of traumatic origin occur as a result of physical exposure. Possible reasons include:
- mucous membrane bite;
- injury from a toothbrush while brushing your teeth;
- complications of dental treatment - careless use of instruments by the dentist, too sharp crowns;
- damage to the prosthesis when their surface is too sharp or the dimensions are larger than necessary;
- exposure of the mucous membrane to various acids, alkalis or medications.
To minimize the possibility of ulcers, choose the right brush. Read more about this here.
Traumatic ulcers are characterized by the absence of severe pain . As a rule, they are small in size and go away on their own if contact with the traumatic factor is eliminated. It takes 1-2 weeks for the mucous membrane to recover.
Ulcers as a symptom of another disease
The formation of ulcers in the oral cavity can also be caused by serious internal diseases of the body. These include:
Tuberculosis
Bacteria and pathogens of this disease (Koch bacilli) penetrate the oral cavity and spread to the mucous membrane. Lumps characteristic of tuberculosis appear. Gradually they develop into large ulcers.
Their bottom is loose, they are shallow, their boundaries are unclear, and their structure is soft. They are characterized by severe pain . The superficial tissues of such ulcers may bleed. The patient experiences poor health, lack of appetite, plaque formation on the surface of the tongue, and elevated temperature.
Such ulcers of a tuberculosis nature are treated in anti-tuberculosis departments . Additionally, local treatment is carried out using antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agents.
Syphilis
chronic disease . Lasts 20-25 days. During this time, the patient experiences regular occurrence of ulcers in the mouth. Unlike tuberculosis, such ulcers are painless.
The shape is rounded, the bottom is covered with a coating and has a red color, the edges are raised . Most often localized in the sky. They go away quickly, but a scar may remain. With such ulcers, the presence of infiltrate is noted. Such ulcers are treated in venereology hospitals.
Endocrine disorders
Malfunctions of the endocrine system can lead to the formation of ulcers in the oral cavity. They are usually white , small in size and painless. They don’t go away for a long time; recovery takes a long time. This is due to weakened immunity.
To treat such ulcerations, it is necessary to establish the proper functioning of the endocrine system.
Also, the appearance of ulcers in the mouth can be a sign of diseases such as:
- improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- chronic renal failure;
- complications after chemotherapy.
Other reasons
Ulcerative rashes in the mouth can be a reaction of the body to various types of irritants . It could be:
- A side effect after taking medications, as some drugs interfere with saliva production, reducing salivation. For example, diuretics.
- Vitamin deficiency and malnutrition. It has been proven that a lack of vitamins B and A can cause ulcerations in the mouth.
- Allergic reaction of the body to various foods (cereals, citrus fruits, milk, eggs, chocolate and others).
- The use of toothpaste or mouth rinses containing a component such as sodium lauryl sulfate . This component dries out the oral mucosa.
- Hormonal surge , for example, during menstruation or menopause.
- Dehydration of the body.
- Genetic predisposition .
- Cigarettes and alcohol.
Traumatic factors
These include:
- Eating rough (scratching) foods - nuts, crackers, dried fish, etc. Such foods can lead to damage to the mucous membranes and epithelium, which, in turn, can cause wounds to appear.
- Thermal and chemical burns - too hot drinks and food, careless handling of various types of acids. The adult population is most susceptible to this factor.
- Rough or improper oral hygiene. The mucous membranes of the child’s oral cavity are most susceptible to this type of damage.
- Incorrectly installed braces, crowns or dentures.
- Teeth brushing performed inappropriately.
- Microcracks in soft tissues that occur after bites.
- Improperly performed oral sanitation.
The possibility of such irritation should be taken into account when choosing a particular medical product, food product or hygiene product intended for oral care (various rinses, toothpastes and powders, etc.).
Structure and functions of the hard and soft palate
The palate separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity and maxillary sinuses. Anatomically, the soft palate is part of the oropharynx. It consists of a mucous membrane with muscle fibers, small blood vessels, small salivary glands and lymphatic vessels. The mucous membrane of the palate is a dense multirow squamous epithelium. However, the submucosa has numerous small salivary glands, especially in the hard palate.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Inflammation of the lymph node in the neck and teeth
The periosteal covering of the hard palate becomes a relative barrier to the spread of cancer into the palatine bone. Neurovascular supply to the palate is provided by the palatine foramina located medial to the third molars.
Functionally, the soft palate serves to separate the oropharynx from the nasopharynx during swallowing and speech. The soft palate moves toward the back of the throat when swallowing to prevent regurgitation and allow air to escape through the nose.
How to treat wounds on the palate at home?
The most important thing to correctly determine the method of how to cure ulcers on the roof of your mouth is to determine the cause of this pathology. Only after identifying the root causes can you choose the most appropriate treatment. There are two types of treatment for this disease: medication and folk medicine. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Drug treatment
It should be noted here: the prescription of medications to eliminate ulcers in the oral cavity should be carried out exclusively by a dentist.
Since only a professional doctor is able to determine the exact etiology of the disease and, based on this, prescribe the necessary medications.
We propose to briefly familiarize yourself with some drugs and means that can eliminate both the disease itself and its consequences.
- Antibiotics. Most often, this class of medications is prescribed when the disease is severe. The duration of treatment and the type of such medications are selected strictly individually.
- Two percent gel Xikain. Reduces painful manifestations and successfully fights pathogenic and inflammatory microbes, which helps wounds and ulcers heal in the shortest possible time. The use of Xikain gel is strictly contraindicated for children under six years of age. The reason for this is the presence of components harmful to the child’s body in this medication.
- Medicinal ointments. A very well proven remedy is Benzocaine ointment. Having an anti-inflammatory effect, this ointment can quickly eliminate inflammation in the mouth. This product contains analgesic components, so it is recommended to use it in the presence of pronounced pain.
- Benzocaine can cause an allergic reaction, so it is not recommended for children to treat ulcers. For them, you can use, for example, an ointment like Kamistad.
- Analgesic injections. The only really significant advantage of this type of drugs over others is the speed of action on the affected areas of the oral cavity, which makes it possible to urgently eliminate pain syndromes, especially with open ulcers, when the pain is felt most acutely. However, injections are completely ineffective in eliminating the causes that provoked the appearance of wounds inside the oral cavity.
Read also: How to relieve toothache
Traditional methods
There has long been a great variety of folk methods for treating inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. Very often, such remedies are very, very effective and help make the healing process much shorter and more effective.
Let's look at a few examples of such effective remedies from the collection of folk wisdom.
- Rinsing the mouth with a salt-soda solution. It couldn’t be easier to prepare: one teaspoon of soda and salt are dissolved in two hundred grams of cold boiled water. Rinsing is done three times a day.
- Rinsing the mouth with a solution of pharmacy calendula tincture (two teaspoons per two hundred milliliters of warm boiled water). Rinse twice during the day.
- Gruel of finely grated potatoes. Applying such lotions very effectively relieves inflammation and accelerates the recovery and healing processes.
- Rinse your mouth 3-4 times during the day with freshly squeezed carrot juice, slightly diluted with boiled water.
- A very effective way to eliminate wounds on the palate and other parts of the mouth is to lubricate the affected surfaces with natural honey. This procedure will especially appeal to young children.
- Another very effective folk recipe for treating wounds on the roof of the mouth is the following remedy: mix one hundred grams of warm (preferably homemade) milk, one teaspoon of natural honey and one chicken egg yolk. Wipe the affected areas of the mouth with the resulting mixture three or four times a day. This is done using sterile gauze or a bandage wrapped around a finger and soaked in the above mixture. The course of such procedures should be carried out for at least three days.
When to contact a specialist
It is necessary, however, to note that, despite the apparent effectiveness of using traditional methods of treating wounds in the mouth, still at the first signs of the appearance of ulcers, wounds or other, even the most minor, foci of inflammation in the mouth, it is necessary to immediately contact a dentist in order to obtain a qualified consultation and effective, timely and professional treatment.
Advanced diseases that have become chronic can cause various kinds of complications and are much more difficult to eliminate than those detected in time.
Causes of mouth ulcers
The most common cause of inflammation of the oral mucosa with the appearance of ulcers is stomatitis. It can be aphthous, herpetiform, fungal (candida), allergic, traumatic. The disease occurs in acute and chronic forms.
- Aphthous stomatitis. This is an inflammatory disease of the oral cavity, which is characterized by the presence of painful aphthae - grayish-white ulcers with clear outlines.
- Aphthous recurrent stomatitis. Refers to diseases of a chronic nature with periods of exacerbations. With minor trauma, small lesions appear on the mucous membrane - aphthae.
- Stomatitis herpetiformis causes many small ulcers in the mouth that resemble herpes simplex. This disease usually occurs in women under 30 years of age.
- With fungal stomatitis, mouth ulcers are covered with a white coating and are caused by a fungal infection entering the oral cavity.
- Recurrent necrotizing periadenitis (Setton's aphthae) is characterized by the formation of a compaction in the submucosa, then painful ulcers with raised and compacted edges form in this place, as well as the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate
- Ulcerative stomatitis. The disease develops as a result of untreated simple, or catarrhal stomatitis.
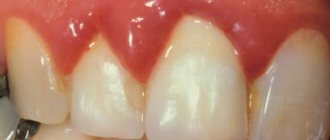
- Ulcerative gingivitis. The disease is characterized by the appearance of ulcerations in the area of the papillae between the teeth.
- Chemical and radiation injuries. Multiple red and painful rashes appear as a reaction to radiation therapy. Accidental or intentional entry of chemicals into the oral cavity causes a burn with ulcerative manifestations.
Traumatic ulcers are also a common cause of oral lesions. They may be a consequence of:
- injuries from rough food;
- biting cheeks, lips;
- excessive brushing of teeth;
- inaccurate dental intervention.
In a small child, ulcers on the roof of the mouth can form due to thumb sucking (so-called Bednar's aphthae). The ulcers are yellowish in color and are located on the mucous membrane of the palate.
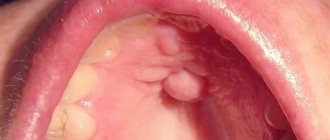
Ulcer on the roof of the mouth - what is it and why does it occur?
The oral mucosa is very sensitive; if it is injured, a person feels it almost immediately - burning and itching, pain, and a reaction to thermal, mechanical and chemical stimuli occur. Only a few go to the doctor: small abrasions and sores appear quite often in every person and, as a rule, with normal immunity, quickly heal on their own. This is explained by the high ability of the mucous membrane to regenerate.
But at the same time, the oral cavity constantly contains a huge number of microorganisms - both useful, necessary for digesting food and maintaining the necessary environment, and pathogenic. Sometimes the ulcer does not heal for a very long time, it may shrink and drag on, then it appears again and significantly poisons life. What is this and what is the reason?
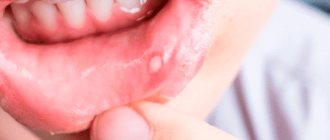
An ulcer or sore, as it is often called popularly, is any damage to the mucous membrane, usually red in color, with a white or yellowish coating, often accompanied by swelling and pain. The size and shape of the sore can be very different, as well as the causes.
Conventionally, they can be divided into two groups:
- traumatic - if the mucous membrane in the mouth is scratched, bitten, burned with hot food or chemicals, damaged when installing braces or dentures;
- pathological - when its formation is provoked by an infection that penetrated from the outside or from other internal organs.
If a white ulcer appears on the roof of your mouth, most often it is a disease such as stomatitis. In this case, very rarely white sores appear only on the palate; usually they are scattered throughout the mouth - on the inner surface of the cheeks, gums, and tongue. The sores are covered with a white, curd-like coating, usually round in shape with bright red edges.
If the plaque is scraped off, such a sore will begin to bleed. Stomatitis can be chronic - the ulcer can disappear, then form again, but in a new place. In children, the temperature often rises and the lymph nodes become enlarged. With extensive lesions of the mucous membrane, the patient cannot eat food from a spoon or fork, it hurts him to talk.
White ulcers on the palate can also be a symptom of an infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract - tonsillitis or scarlet fever. With some pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, ulcers also appear in the mouth.
Endocrine disorders and decreased immunity can cause painful white ulcers to form on the roof of the mouth.
Important: white sores in the mouth are one of the signs of syphilis. And sometimes it is a symptom of cancer.
If the patient can remember scratching the roof of their mouth or overdoing it, for example, with teeth whitening products, and then found white ulcers on the roof of their mouth, there is no particular cause for concern - it is important to start treating it immediately, avoiding infection and inflammation. Then the trouble will be forgotten in a few days.
If ulcers appear frequently and do not heal well, it is necessary to be examined by a doctor, determine the cause of their occurrence and treat the underlying disease first.
Ulcers as a symptom of a general disease
Some serious diseases include mouth ulcers in their arsenal of symptoms. Among the most common ailments are:
- Tuberculosis of the oral mucosa. The first sign is small mounds, in place of which a little later ulcers form, gradually growing. The ulcer is small, its bottom is formed by bleeding epithelial cells. The pain is acute. The patient loses weight, the tongue is coated, the work of the sweat glands increases, and the body temperature increases.
- Syphilis. This disease is characterized by round, painless, red ulcers covered with a dark gray coating.
- Gingivostomatitis in acute necrotic form is provoked by a viral infection. Usually the ulcers cover the cheeks, gums, soft palate, and tonsils.
- Cancer . In such a situation, the ulcers that appear are characterized by uneven, thickened edges. They don't hurt, but they take a very long time to heal.
Treatment for mouth ulcers can be quite lengthy if you use medications thoughtlessly. Remember that any disease has its own cause, which must be established without fail.
Read also: How to treat sores in the mouth
Causes of mouth ulcers
Often the formation of wounds in the mouth on the palate, leading to the occurrence of traumatic ulcers, is associated with damage to the lining of the oral cavity when eating rough food, brushing teeth with a brush with stiff bristles, or biting a tooth. Erosion, called Bednar's aphthae, is observed in young children who have the habit of putting a variety of objects into their mouths. In some cases, injury to the mucous membrane is a consequence of inaccurate dental treatment. Rashes on the palate also appear when the mucous membrane is exposed to chemically active substances or irradiation.
In children and adults, the appearance of ulcers can cause stomatitis. There are many types of this disease, occurring in acute or chronic form:
An ulcer on the roof of the mouth may indicate a serious systemic disease affecting the body. In this case, to eliminate the ulceration, it is necessary to treat the disease of which it is a symptom. These may be the following diseases:
- Damage to the oral mucosa by the tuberculosis process. Initially, small tubercles appear at the site of introduction of the tuberculosis causative agent - Koch's bacillus, then they turn into ulcers, increasing in size over time. Bleeding epithelium is visible at the bottom of the ulcers. The disease is accompanied by severe pain, increased sweating, loss of body weight, and elevated temperature.
- Syphilis. Painless, red, round ulcers appear, with a surface covered with a gray coating. After the wounds heal, retracted star-shaped scars remain.
- Disruption of the activity of endocrine organs. The appearance of ulcerations in the oral cavity occurs in cases of dysfunction of the pancreas and thyroid glands - nodular toxic goiter, diabetes mellitus.
- Necrotizing gingivostomatitis. Wounds with a necrotic crust form on the surface, bleeding gums and enlarged lymph nodes are noted.
- A malignant tumor may also be accompanied by the appearance of ulcers that do not heal for a long time. They are not painful and have thickened edges.
Read also: How to remove bad breath
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis
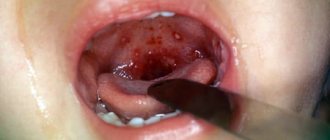
Canker sores usually appear on moving parts of the mouth, such as the tongue or the inside of the lips and cheeks, and at the base of the gums. The ulcers initially appear as small oval or round reddish swellings that usually appear within a day (see photo).
Ruptured ulcers are covered with a thin white or yellow membrane and are surrounded by a red circle around the edge. In general, the ulcers heal within two weeks without leaving scars. Fever is rare and ulcers are rarely associated with other diseases.
Usually a person develops one or more ulcers at a time.
Prevention
In order to prevent the treatment of ulcers on the oral mucosa from becoming a habit for you, you should follow some recommendations that will help minimize their occurrence:
- Treat your teeth in a timely manner, and choose a careful dentist.
- take vitamins and immunostimulating agents.
- Do not eat too hot food or drinks.
- avoid trauma to the oral cavity.
- Maintain good oral hygiene.
- avoid stress.
The appearance of ulcers on the oral mucosa is a common phenomenon and most have already encountered similar infections. It is a mistake to neglect the disease and wait for the ulcers to heal on their own; it is important to detect the ulcer in time and hurry with treatment, because sometimes an advanced disease can lead to tangible problems.
How to treat mouth ulcers at home
Traditional medicine has invented a huge number of recipes that allow you to treat mouth ulcers at home.
Here are some of them:
- Make a paste of baking soda by adding a small amount of water and apply it to the affected area. At the same time, you can mix some baking soda in water and rinse your mouth several times a day.
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth with a decoction of calendula flowers, horseradish juice diluted in half with water, a decoction of horse sorrel, carrot juice, and hydrogen peroxide. From the first day of illness you need to take multivitamin teas.
- Take 1 tbsp. calendula leaves, pour 250 ml of boiling water over it, then keep the mixture on the fire for 10 minutes. The broth will need to be filtered and used as a mouth rinse.
- For 2 cups of boiling water, 5 tablets of furatsilin, a teaspoon of soda and salt. Use for rinsing.
- Take the juice from the inside of aloe vera leaves and apply it directly to the ulcers. Do this several times a day.
- Lubricate the affected areas with sour cream with the addition of chopped garlic or onion, you can also use sea buckthorn oil.
- After using the tea bag, place the wet tea bag in the refrigerator for a few minutes. After some time, take a cooled, damp tea bag and gently place it on the sores for fifteen to twenty minutes.
If all of the above home recipes do not help, you can try other methods of treating mouth ulcers:
- Mix the contents of 2 ampoules of vitamin B12 and one ampule of dexamethasone, add 2 crushed nystatin tablets. Soak small cotton wool flagella in the medicine and apply them for 10 minutes three or four times a day.
- Take antihistamines (loratadine, tavegil, suprastin) or desensitizers (fenkarol) orally.
- Treat ulcers with lidocaine gels.
- Treat ulcers with dexamethasone gel.
- Rinse your mouth with antiseptics from the pharmacy.
- When ulcers appear on the red border of the lips, you can confidently diagnose herpes and use Acyclovir ointment.
To cauterize ulcers in the mouth, you can use hydrogen peroxide, furatsilin solution or ready-made chlorhexidine purchased at the pharmacy.
Causes
The formation of mouth ulcers on the palate occurs for various reasons. Most often their appearance is provoked by:
- consumption of foods that injure the oral mucosa: crackers, chips (also leads to the formation of ulcers);
- taking hot drinks, food;
- oral care rules
Other causes of ulcers on the palate:
- Incorrectly installed or poorly selected dentures .
- extraction and filling .
- Brushing your teeth with a paste that contains sodium sulfate: the mucous membrane becomes susceptible to bacteria and food acids.
- Genetic predisposition. If relatives experience frequent relapses of stomatitis, the likelihood of developing the disease increases several times.
- Malocclusion .
- Allergies to food (chocolate, citrus fruits), oral care products.
- Taking antibiotics, hormonal drugs.
- Eating unwashed fruits and vegetables.
- Fungal infections.
- Hormonal imbalance is one of the causes of ulcers on the palate in women during pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause.
- Alcohol abuse , tobacco addiction.
- Frequent stress.
- Low immunity.
- Diseases of the digestive system.
- Deficiency of fluid, vitamins and minerals in the body.
On this topic
- Sores
How to quickly cure sores on the inside of the lip
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 4, 2020
Sometimes sores on the palate are a sign of systemic diseases. The appearance of mouth ulcers may indicate:
- Tuberculosis.
- Syphilis.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas and thyroid gland (the appearance of wounds on the mucous membrane of the palate is observed in diabetes mellitus, toxic goiter).
- Necrotizing gingivostomatitis.
- Oncological disease. A malignant tumor may also be accompanied by the appearance of long-term non-healing ulcers on the palate, but they are rare.
It is difficult to independently determine what caused the wounds on the palate. But if you pay attention to the clinical signs of pathology, you can help the doctor quickly make a diagnosis and select effective treatment.
Ulcers on the roof of the mouth: causes, symptoms and treatment
The oral mucosa is capable of quickly regenerating, since it is lined with several layers of epithelium, which is constantly renewed. In addition, it is resistant to irritants of various origins and infections.
However, small ulcers often occur on the lining of the mouth, particularly the roof of the mouth, causing discomfort and pain.
Ulcers on the roof of the mouth appear due to:
- Eating crackers, nuts, fish. Products with sharp edges can scratch the epithelium, leading to the formation of ulcers.
- Chemical and thermal burns of the palate (hot food and drinks, careless handling of acids).
- In children, the mucous membrane can be damaged due to improper and rough oral hygiene.
Ulcers as a symptom of the following diseases:
- candidiasis;
- herpes;
- tuberculosis;
- stomatitis;
- syphilis;
- scarlet fever;
- endocrine disorders.
Ulcers, or in scientific terms aphthae, cause a lot of inconvenience, so they cannot be asymptomatic and a person will immediately understand that the mucous membrane of the palate is not in order:
- Due to the appearance of ulcers, the mucosal tissues swell, and this can make speech difficult.
- It is impossible to eat hot, spicy, sour and salty foods, as they will irritate the damaged surface of the palate.
- A person, even with his mouth closed at rest, may experience pain, and in advanced cases, the ulcers bleed.
Read also: A white sore appeared on the gum, how to treat it
Not all canker sores are harmless. Of course, if they were formed due to mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, they will go away on their own in the shortest possible time.
If the ulcers do not go away, you need to track the accompanying symptoms in time to begin treating systemic diseases:
- When the herpes virus enters the oral mucosa , a person’s condition generally worsens, body temperature may rise, lymph nodes enlarge, salivation increases, and then small wounds form on the palate.
- Often, with a decrease in immunity or long-term use of antibiotics, it is possible to develop a disease such as candidiasis or thrush of the oral mucosa. In this case, a burning sensation is felt, taste sensations are lost, and a characteristic white coating of a cheesy appearance forms on the entire mucous membrane; eventually, aphthae can form on the palate, which sometimes bleed.
- When infected with syphilis at the beginning in the oral cavity , a rash may occur, which then develops into ulcers on the soft tissue of the palate and cheeks.
- Aphthous stomatitis. A chronic disease characterized by inflammation of the oral mucosa and the appearance of ulcers on the palate. Besides. such stomatitis can be a symptom of generalized aphthosis, a disease that affects all mucous tissues in humans (gastrointestinal tract, genitals, eyes). Ulcers form gray-yellow in size from 2 to 10 mm, depending on the course and stage of the disease. They are quite deep, painful, do not heal for a long time and often recur.
- With pulmonary tuberculosis , initially small compactions in the form of reddened tubercles may form on the palate, which then transform into shallow round wounds.
Symptoms
Ulcers, or in scientific terms aphthae, cause a lot of inconvenience, so they cannot be asymptomatic and a person will immediately understand that the mucous membrane of the palate is not in order:
- Due to the appearance of ulcers, the mucosal tissues swell, and this can make speech difficult.
- It is impossible to eat hot, spicy, sour and salty foods, as they will irritate the damaged surface of the palate.
- A person, even with his mouth closed at rest, may experience pain, and in advanced cases, the ulcers bleed.
Not all canker sores are harmless.
Of course, if they were formed due to mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, they will go away on their own in the shortest possible time. If the ulcers do not go away, you need to track the accompanying symptoms in time to begin treating systemic diseases:
- When the herpes virus enters the oral mucosa , a person’s condition generally worsens, body temperature may rise, lymph nodes enlarge, salivation increases, and then small wounds form on the palate.
- Often, with a decrease in immunity or long-term use of antibiotics, it is possible to develop a disease such as candidiasis or thrush of the oral mucosa. In this case, a burning sensation is felt, taste sensations are lost, and a characteristic white coating of a cheesy appearance forms on the entire mucous membrane; eventually, aphthae can form on the palate, which sometimes bleed.
- When infected with syphilis at the beginning in the oral cavity , a rash may occur, which then develops into ulcers on the soft tissue of the palate and cheeks.
- Aphthous stomatitis. A chronic disease characterized by inflammation of the oral mucosa and the appearance of ulcers on the palate. Besides. such stomatitis can be a symptom of generalized aphthosis, a disease that affects all mucous tissues in humans (gastrointestinal tract, genitals, eyes). Ulcers form gray-yellow in size from 2 to 10 mm, depending on the course and stage of the disease. They are quite deep, painful, do not heal for a long time and often recur.
- With pulmonary tuberculosis , initially small compactions in the form of reddened tubercles may form on the palate, which then transform into shallow round wounds.
Diagnostics
If aphthae occurs on the roof of your mouth, you should contact your dentist.
The doctor will examine the oral mucosa and may ask the following clarifying questions:
- How long ago did the ulcers appear?
- How painful are they?
- Do they bleed?
- Does the patient smoke or not?
- What are the common chronic diseases, and what diseases were recently suffered?
- Do any of your relatives have similar ulcers?
If wounds on the palate appear as a result of mechanical damage, then no special measures should be taken.
The only thing is to eliminate the cause of their formation, that is, avoid foods with sharp edges, brush your teeth more carefully, take a break from eating sour, salty and hot foods. The epithelial tissues will renew themselves, and the palate will return to normal.
You can rinse your mouth with a collection of medicinal herbs such as chamomile, sage, calendula.
Treatment of aphthae caused by some diseases of the body must be carried out in three directions:
- Eliminating the cause of ulcers.
- Local treatment of ulcers, their permanent treatment.
- Relieving pain.
To eliminate the causes, you must first increase your overall immunity. The doctor may prescribe general health-improving medications and vitamin-mineral complexes.
To eliminate swelling, antihistamines are prescribed at the discretion of the specialist. If the wounds cause severe discomfort, painkillers containing paracetamol or ibuprofen are used. In case of acute pain, before contacting a specialist, it is possible to use lidocaine in a spray.
If the cause of aphthae on the palate is a disease such as candidiasis, the doctor will prescribe antifungal drugs, for example, Diflucan or Flucostat.
If the cause lies in herpes, antiviral drugs are used, for example, Zovirax or Acyclovir.
Ulcers caused by bacterial infections require more serious treatment with antibiotics of various groups.
Aphthae that appear against the background of tuberculosis, syphilis and other infections are treated with appropriate anti-tuberculosis, anti-syphilitic and antiviral drugs.
Diagnosis and symptoms of cancer of the palate (soft, hard, uvula)
Cancer of the palate is usually the first to be seen among other types of oral cancer because this area is most involved in speech and eating, just like the tongue.
Malignant tumors are often detected by dentists in their early stages. Melanoma appears as smooth black, brown, or brownish-gray lumps on the mucosa. And Kaposi's sarcoma usually looks like bluish lesions. This type of malignant tumor is often detected in patients with HIV infection. Sometimes tumor growths occur at the junction of the hard and soft palate; in this case, the diagnosis is made based on the territorially larger lesion on one side.
Most malignant neoplasms take the form of ulcers. In the early stages of development, ulcers are usually painless and do not bleed, but later become painful.
The main symptoms resulting from the formation of a malignant tumor or preceding its appearance:
- bleeding (the edges of the ulcer usually bleed or undergo necrosis);
- bad breath (may appear long before the tumor appears);
- loss of teeth, loosening of teeth, bleeding gums;
- softening of the gums, periodontitis;
- change in speech;
- difficulty swallowing food, saliva, water;
- trismus of the jaw (inability to open them);
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- swelling of the neck, mouth;
- pain that does not go away after taking painkillers.
Lymph nodes are also vulnerable to this type of cancer. About 30% of patients have metastases in the lymph nodes at the initial examination. The most affected are the submandibular nodes and the upper jugular lymph nodes. If the tumor affects the soft palate, the retropharyngeal lymph nodes may also be affected. Carcinoma of the soft palate is defined as cancer of the oropharynx according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with White lumps on the tonsils with an unpleasant odor: what is it?
With squamous cell carcinoma, in 70% of cases, the tumors extend beyond only one part of the hard or soft palate. Without treatment and surgical removal, they can grow to sizes of more than 5 cm. If the tumor occupies the entire soft palate or uvula, the patient's speech is impaired and the swallowing process is greatly affected.
The absence of a corneal reflex is an indicator of damage to the foramen ovale or orbital fissure. Dental numbness may indicate perineural invasion. In some cases, there is a disorder of the masticatory muscles. Trismus, malocclusion, and pain symptoms indicate invasion of the pterygoid muscles. Sometimes the swelling can spread to the gum tissue. The maxillary sinuses and maxillary bone are also affected.
Only a detailed examination will help to assess the degree of tumor development and the stage of cancer.
After discovering a suspicious lump on the roof of your mouth or an ulcer that does not go away for more than two weeks, you must consult a doctor to clarify the diagnosis. If the result is positive for cancer, the oncologist will conduct a detailed examination of the tumor. Palpation, computed tomography, and sometimes MRI or positron emission tomography are used. This is necessary to examine the entire body and determine the presence or absence of metastases. Sometimes it happens that a tumor on the roof of the mouth is secondary, that is, its cause lies in a cancerous tumor in other parts of the body. However, this rarely happens; most often, oral tumors are of primary origin.
Folk remedies for the treatment of ulcers on the palate
There are many traditional medicines that can relieve pain from wounds on the palate or help relieve inflammation:
- Dilute 1 teaspoon of salt and 1 teaspoon of soda in a glass of boiled warm water. Rinse your mouth with this solution 3 times a day.
- Dilute 2 teaspoons of calendula tincture in a glass of boiled water, rinse 2 times a day.
- Use freshly squeezed carrot juice diluted with water for rinsing 3-4 times a day.
- Grate raw potatoes on a fine grater and use the resulting pulp as a lotion for canker sores.
- Many people find that smearing ulcers with honey helps.
- One of the folk recipes suggests using the following option: you need to mix half a glass of milk with 1 egg yolk and a spoonful of honey. Mix the mixture well until smooth, then wrap your finger in a clean sterile cloth or bandage, dip it in the mixture and wipe the wounds. It is enough to wipe 3-4 times a day for 3 days.
It should be remembered that you should not get too carried away with folk remedies. With their help, you can relieve symptoms, relieve minor inflammation, or help the mucous membrane regenerate faster. The search for and treatment of the main cause of ulcers on the palate should be carried out by a specialist.
Treatment
If wounds on the palate appear as a result of mechanical damage, then no special measures should be taken.
The only thing is to eliminate the cause of their formation, that is, avoid foods with sharp edges, brush your teeth more carefully, take a break from eating sour, salty and hot foods. The epithelial tissues will renew themselves, and the palate will return to normal.
You can rinse your mouth with a collection of medicinal herbs such as chamomile, sage, calendula.
Treatment of aphthae caused by some diseases of the body must be carried out in three directions:
- Eliminating the cause of ulcers.
- Local treatment of ulcers, their permanent treatment.
- Relieving pain.
To eliminate the causes, you must first increase your overall immunity. The doctor may prescribe general health-improving medications and vitamin-mineral complexes.
To eliminate swelling, antihistamines are prescribed at the discretion of the specialist. If the wounds cause severe discomfort, painkillers containing paracetamol or ibuprofen are used. In case of acute pain, before contacting a specialist, it is possible to use lidocaine in a spray.
If the cause of aphthae on the palate is a disease such as candidiasis, the doctor will prescribe antifungal drugs, for example, Diflucan or Flucostat.
If the cause lies in herpes, antiviral drugs are used, for example, Zovirax or Acyclovir.
Ulcers caused by bacterial infections require more serious treatment with antibiotics of various groups.
Aphthae that appear against the background of tuberculosis, syphilis and other infections are treated with appropriate anti-tuberculosis, anti-syphilitic and antiviral drugs.
For local treatment of ulcers, doctors usually prescribe rinsing with antiseptic solutions (for example, chlorhexidine solution or miramistin). Rinsing with pharmaceutical herbs has also proven to work well. Levomekol can be used as an ointment.
Prevention
What to do and what not to do:
- It is necessary to strictly observe oral hygiene.
- Visit the dentist 2 times a year.
- It is advisable to minimize sour, spicy, salty foods in your diet, and try not to eat too hot food, which can burn the mucous membrane of the palate.
- It is necessary to determine whether there are any allergies to any food products, because they can cause ulcers to appear on the palate.
- It is recommended to take vitamin complexes, and also monitor the level of iron, zinc and folic acid in the body, because their lack provokes aphthae.
- Doctors also recommend strengthening the immune system and avoiding emotional stress.
If you follow preventive measures and start treatment at an early stage, you can avoid such troubles as ulcers on the palate.