Why is a cyst in the mouth on the palate dangerous?
The appearance of a formation in the oral cavity, including in the palate, seems to be a harmless phenomenon. Provided that it progresses slowly and does not cause serious discomfort. But even a seemingly harmless phenomenon, under certain circumstances, leads to serious consequences.
What is the main danger of cystic formation:
- It can develop into a cancerous tumor. Under certain circumstances, the cyst begins to grow rapidly and changes character. Atypical cells are formed in the tumor, it “turns” from benign to malignant.
- If the tumor is injured, the likelihood of infection increases, in which case the cyst turns into a formation filled with purulent contents. Intoxication of the body develops, and other symptoms appear.
- The cyst has a tendency to grow rapidly. Usually it slowly increases in size, but if the formation is frequently injured, it will begin to progress rapidly. This will lead to problems with articulation, the person will not be able to eat normally, and breathing problems will arise.
- If you bite through the cyst or cause serious damage to it, it will empty and the contents will come out. But then the neoplasm will appear again, and it will be larger in size than initially.
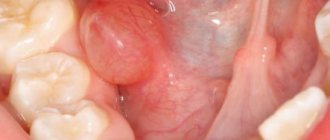
Oral cysts are common in dentistry; a similar diagnosis can be made to a child or an adult, regardless of gender. They are formed for the following reason:
- there is a blockage of the salivary duct;
- the secretion accumulates in its cavity, expanding the duct;
- the result of such a process is the formation of a cyst.
As a rule, the process proceeds without pronounced symptoms, nothing bothers the person and he leaves the appearance of a tubercle on the palate without due attention. Well, in vain, at this stage the problem can be solved without the help of a surgeon.
Treatment of oral pathology
Creams and ointments are ineffective in treating oral cysts, especially if the tumor progresses. The first thing you need to do is contact a specialist, because you won’t be able to do it without surgical intervention.
For children, the tumor is removed endoscopically. This method is more gentle and less traumatic. But when the growth size is more than 8 mm, a radical method is used. The operation is quick and done under local anesthesia. If there are no complications, the patient is allowed to go home on the first day after surgery. When a tumor forms on the palate, the inside of the lip or cheek, the tumor is cut out along with the affected tissues, while healthy areas are not touched. But in more severe cases - the formation of a cyst in the paired salivary gland or sublingual region, not only the cystic formation is removed, but also the submandibular salivary gland, which will prevent relapse of the disease.
It is important that the operation be under the guidance of an experienced specialist, since any incorrect action can contribute to damage to the facial nerves, which can lead to the development of paralysis of the facial muscles.
Prevention of complications after surgery
As mentioned, if there are no postoperative complications, the patient is allowed to leave the hospital on the day of surgery. But a prerequisite for independent home treatment is the prevention of complications. The patient is recommended to use ointments, creams and gels to treat the wound with a pronounced regenerative and anti-inflammatory effect, as well as rinse the mouth with an antiseptic after eating.
Read also: Oral thrush symptoms
Alternative medicine also helps speed up the wound healing process. Using folk remedies, it is permissible to use decoctions and infusions of herbal infusions. Honey, yarrow, nettle, and chamomile help restore the wound after surgery. It will be beneficial if you use herbal remedies at least once a day after each meal.
If you listen to your doctor’s recommendations, the recovery period will not take long. But if the patient notices that the wound has begun to bleed or fester, it is necessary to visit the dentist again to eliminate the development of complications.
Symptoms
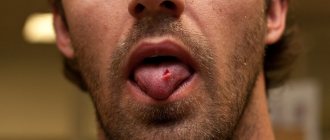
The signs are mild or absent altogether, but with due attention to your health, you can notice:
- That unpleasant sensations appeared, they bother you when eating or talking.
- On the palate, in the area of the cyst, a slight tingling sensation appears; the discomfort is present on an ongoing basis or bothers you periodically.
- When experiencing food, pain occurs.
- I am worried about the feeling that there is a foreign body in the oral cavity that I cannot get rid of.
Tinnitus - what is this symptom and how to get rid of it?
Less commonly, other symptoms are observed against the background of cyst formation:
- body temperature rises, but the phenomenon is temporary and does not reach serious indicators;
- Intoxication is a concern; it manifests itself in weakness, drowsiness, and decreased performance.
The tubercle rarely causes serious discomfort to a person; when it appears, there is no pain or other unpleasant sensations. It is unlikely that at this moment a person thinks that a cyst has formed in his oral cavity.
Causes
Modern medicine has no idea why such changes begin to occur in the human body. But doctors were able to identify a number of factors contributing to the development of cysts in the oral cavity, we list them:
| Cork. | When the salivary duct is blocked, the secretion cannot come out; it accumulates, stretches the cavity and forms a cyst. |
| Inflammation. | A similar process that occurs in the oral cavity, under certain circumstances, leads to similar complications. |
| Trauma or surgery. | As a result of exposure, tissue scarring occurs, which disrupts the functionality of the mucous membrane and increases the risk of cyst formation. |
| Inflammation of the salivary gland. | It is often observed with a disease such as salmonellosis and is chronic. |
Unsuccessful dental procedures can also lead to similar problems. As well as surgical interventions associated with suturing.
Autoimmune diseases, stomatitis, and metabolic disorders in the body can also lead to similar consequences.
Recommended video:
Myxoma as a cause of the development of cones
Another cause of hard white sores in the mouth is myxoma. In this case, the growths have a lumpy surface and appear in the area of the sky. The disease can be determined using hypoxia, which is prescribed by a specialist. X-ray examination helps not only to find out the exact size, but also to identify the structure of the formation.
Puncture is also an effective method for diagnosing myxoma. Analysis of the contents of the vial helps to more accurately determine the nature of the disease.
The only effective treatment for this disease is surgery. Under local anesthesia, the bubble is removed with a small capture of the tissue underneath it. This helps prevent myxoma from recurring.
Drug treatment
If a cyst appears on the palate, you can try to eliminate it using conservative methods, but such therapy is not always successful.
What the doctor prescribes:
| Absorbable medications. | A number of agents that prevent fluid accumulation are selected on an individual basis. Medicines are taken in courses, but if there is no result, then the question of surgical intervention is raised. |
| Antibiotics. | The action of drugs is aimed at stopping the inflammatory process in tissues; they are prescribed if the infectious nature of the formation is suspected. After a course of antibiotics, surgery is performed. If the cavity is already filled with pus, then antibacterial drugs will have to be taken even after the completion of the surgical operation. |
| Antiseptic solutions. | They are used for rinsing, they are prescribed before surgery, and used after. In order to speed up recovery. |
Causes and treatment methods for severe cough
Treatment can be complex; medications are selected on an individual basis. But the effectiveness of therapy directly depends on the speed at which the patient turns to doctors for help.
Some dentists argue that conservative therapy is ineffective; it is easier to immediately remove the formation, which will help save money and get results faster.
Pemphigus and its symptoms
Small, white, hard blisters may also occur due to epidermolysis or pemphigus. The disease is congenital and often develops in childhood. These lumps can occur on the roof of the mouth, as well as on the lips, inner cheeks and gums. In addition to small nodules, the disease is accompanied by increased development of caries.
Usually blisters due to epidermolysis
reach a certain size and then burst. After this, erosions may appear, which often develop into ulcers.
If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, the patient may experience indigestion, water and protein imbalance.
To diagnose pemphigus correctly, doctors examine the patient for Nikolsky syndrome, the main symptom of which is a disruption of the connections of epithelial cells. With free exfoliation of epithelial cells, erosion can occur, and then an ulcer.
When treating pemphigus, a course of antibiotics is prescribed: Cortisone or Prednisolone. Typically these drugs only have temporary effects. Enriching the patient’s diet with protein foods, as well as avoiding salt, will help increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Pemphigus true (acantholytic)
Local treatment of pemphigus should be accompanied by rinsing the mouth with special solutions that stop the development of erosion.
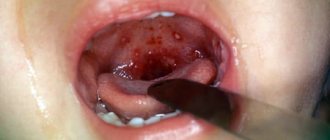
Surgical removal
The operation is associated with certain risks and in some cases, it is impossible to carry out for the following reasons:
- The patient has contraindications to the intervention.
- An acute inflammatory process occurs in the body.
- There are metabolic disorders and diseases of infectious, autoimmune or other origin.
| Advantages of the operation: | Disadvantages of surgery: |
| It will help solve existing problems in a short time, avoid tumor degeneration and eliminate the likelihood of developing such severe complications as: abscess, fistula, sepsis. | Involves suturing; the tissue scarring process can lead to recurrence of the formation. Applying sutures to the mucous membrane causes discomfort; in addition, you will have to regularly treat the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions. After surgery, antibiotics are often prescribed to speed up recovery. |
Blood loss and a long recovery period are the main disadvantages of the operation, but provided that it is carried out in a standard way, using a scalpel.
But you can remove the cyst using another method, a minimally invasive one, using:
| Laser beams. | Which helps reduce existing risks, reduce blood loss and avoid long recovery. Under the influence of high temperatures, the vessels are sealed, tissue regeneration occurs faster, and the risk of complications is reduced. |
| Cryodestruction. | Exposure to liquid nitrogen is used less frequently for several reasons, mainly due to the likelihood of not completely removing the formation. After all, you have to control the temperature and duration of the procedure yourself. Low temperatures lead to tissue necrosis, as a result of which the formation undergoes necrotic changes. |
The effectiveness of surgical intervention is compared with possible risks and the likelihood of complications. If the patient has contraindications, the operation is refused. They monitor the dynamics and prescribe medications.
Treatment methods
Having discovered a cystic formation in the mouth, you need to start treatment as soon as possible. If the pathology becomes advanced, it can provoke serious functional complications in the body. Do not self-medicate. The optimal effective treatment therapy should be prescribed by the attending physician, having determined the root cause of this pathology after conducting a comprehensive diagnosis.
Advice! In the early stages, cystic formations respond very well to treatment. The prognosis is favorable. Relapses are possible only if the cyst shell has not been completely removed.
Treatment of cystic formations is carried out surgically under local anesthesia. Conservative treatment methods for the presence of cystic growths in the mouth are ineffective. The operation, which lasts no more than half an hour, is performed by a dental surgeon, otolaryngologist. The sutures dissolve in five to seven days.
If the cysts are located on the palate, cheek, lower lip, or in the sublingual region, resection of the growth is carried out within tissues that are not affected by the pathological process. That is, healthy tissues and mucous membranes are not affected. When a benign formation is localized under the tongue, in the submandibular salivary gland, it is removed along with the affected gland to avoid relapses of the disease. Patients may be prescribed anti-inflammatory, decongestant, and restorative medications. If a cyst in the oral cavity in adults or children is caused by an infection, the attending physician prescribes a course of antibiotic therapy. Antibacterial, antiviral drugs, and systemic broad-spectrum antibiotics are used in treatment. The dosage, effective pharmacological agents, and frequency of medication administration are prescribed only by the attending physician. To strengthen the immune system, immunomodulators, complex mineral and vitamin complexes, homeopathic medicines, and alternative medicine are prescribed. Recently, laser therapy has been used in medical practice for cysts in the mouth. The advantage of this technique is the absence of complications, bleeding, minimal trauma to the mucous membranes and salivary glands. The treatment method is completely painless and does not take much time. The rehabilitation period is minimal.
Possible consequences and complications
If we talk about the consequences of the appearance of a cyst, they are as follows:
| The rebirth of education. | Cysts have this ability; a tumor, benign in nature, can “turn” into cancer. In this case, it will begin to increase in size faster, and pain will appear. To prevent the pathological process, the formation should be removed in a timely manner. |
| Secondary infection. | The addition of a secondary infection is observed with frequent trauma to the tumor; the process may be associated with attempts to independently remove the cyst, as well as with incorrectly performed surgical intervention. |
| Hemorrhage. | Occurs when a person tries to get rid of a tumor on his own. In the process of carrying out such manipulations, it can cause serious damage to blood vessels, which will lead to extensive blood loss. |
What is the main cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck?
If the cyst has festered, then when it is opened, severe bleeding may occur; biological fluid, along with purulent contents, will enter the throat and lungs, thereby complicating the breathing process. In such a situation there is a risk of being overwhelmed by the masses.
The cyst grows slowly and this has already been discussed earlier, but under certain circumstances it can begin to develop rapidly. In this case, a situation arises in which it is difficult for a person to breathe, take food and liquid.
Bruises in the throat
Due to various diseases and mechanical damage, manifestations such as bruising in the throat may occur. They usually frighten the patient and often require contacting a doctor.
An irritating factor (any of the above) comes into contact with the mucous layer of the pharynx. We mentioned above that it is incredibly rich in capillaries, therefore, viruses or bacteria quickly enter the bloodstream and lead to inflammation and dilation of local blood vessels.
The following table shows the “classic” signs of any inflammation, “translated” into symptoms of pharyngitis.
| Sign of inflammation | Symptoms of pharyngitis |
| "tickle" |
| "red throat" |
| sore throat that gets worse when swallowing |
| |
| Without clinical relationships, in case of pharyngitis |
Some differences are revealed in the picture of pharyngitis, the cause of which is group A streptococcus. This bacterium is also called hemolytic streptococcus. Literally translated from Latin, it means “destroying/dissolving” blood.
Once in the bloodstream, it destroys red cells in the capillaries of the larynx. Clinically, this manifests itself as small bruises on the pharynx, soft palate, and sometimes on the tonsils.
With the Coxsackie and herpes viruses, the connections between the cells of the mucous membrane are destroyed, and they “fusion” occurs. Clinically, it appears as fluid-filled blisters.
Prevention
There is no specific prophylaxis to prevent the appearance of formation. But dentists recommend, in order to prevent such problems from occurring, to do the following:
- carefully monitor oral hygiene, brush your teeth regularly, at least 2 times a day;
- stop smoking, since nicotine increases the risk of cyst formation, as well as their degeneration into cancerous tumors;
- visit the dentist regularly, even if nothing bothers you, at least once a year; treat caries in a timely manner;
- carry out adequate therapy for oral diseases with the participation of a doctor;
- avoid frequent trauma to the mucous surface of the palate, which can lead to blockage of the duct and cause the formation of a cyst;
- strengthen the immune system, lead a healthy lifestyle, take vitamins;
- After surgery, strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Recommended video:
The appearance of a cystic formation on the palate is a common occurrence, but you should not try to solve such a problem on your own. Unsuccessful attempts will lead to severe complications or cause the tumor to increase in size. It is better to seek help from a doctor, especially since at the initial stage of development, you can get rid of the cyst without surgical intervention.
Comments (5)
Yana
07/06/2019 at 23:24 |
I already know what a cyst is from my own experience. I think that even if the formation is small, it is better to remove it and not wait for it to progress; it’s easy to reach the cyst. Is not it?Answer
Expert Marina Rusetskaya
07/09/2019 at 10:21 |
Yana, you are right - any formation in the oral cavity or on another part of the body must be removed.
The reason for this is to prevent the risk of developing a malignant tumor.
The cyst should be removed as soon as you find it or learn about it. Some formations may progress and increase in size.
The only exception to the rule: a pituitary cyst that does not increase in size.
Regarding what you write “it’s easy to get a cyst” - this is not always the case. The formation may have a stalk that needs to be isolated.
In addition, the cyst can be fused with surrounding tissues, from which it must be carefully separated so as not to damage either the cyst itself or neighboring tissues.
You cannot remove any formation, even the most accessible and small one at first glance, on your own.
After all, the bed of the formation may begin to bleed heavily or become infected.
Also, the formation must be submitted for histological examination.
Answer
Julia
07/17/2019 at 23:25 |
Why are some doctors not particularly willing to remove such small formations in the throat, but say that it is necessary to observe? Why leave such a cyst, even if it is very small?
Answer
Christina
08/12/2019 at 06:17 |
Just different opinions on the same pathology. Some specialists are for removal, others are for observation. Who is generally responsible for the patient’s health then? As always, on the patient himself, probably? It’s just that you can easily detect a cyst in the oral cavity in the early stages and therefore try to remove it using conservative methods, which the doctor will advise. The main thing is not to let it go, otherwise you will only have to get rid of it surgically.
Answer
Expert Marina Rusetskaya
08/16/2019 at 22:25 |
Christina, there are many different approaches and opinions in medicine, but regarding all formations, regardless of their nature (benign or malignant), there is a general rule - any formation must be removed.
This is due to the fact that it (benign formation) can degenerate into a malignant tumor. And the size of the tumor has nothing to do with it.
The only contraindication to the removal of such formations may be the patient’s condition (decompensation of chronic diseases) or a disruption of the blood coagulation system.
In the first case, patients have more serious health problems and there is no need to urgently remove the formation.
In the second case, the patient may experience uncontrolled bleeding, which will lead to the death of the patient.
Only for these reasons can a doctor recommend monitoring the formation. In all other cases, indications for planned surgical treatment are given.
Answer
Anatomy of the larynx
- The pharynx is the beginning, but at the same time it is the “crossroads” of two systems – the respiratory and the alimentary. That is, any irritant, be it a virus, bacteria or food allergen, comes into contact with this area.
- Consequently, this is where a whole “army” of protective organs is located - the lymphatic pharyngeal ring. It consists of three paired and two unpaired formations (tonsils):
- Palatal
- Pipe
- pharyngeal
- lingual
- as well as lymphoid granules and lateral lymphoid ridges on the posterior wall of the pharynx.
- The pharynx is a muscular, hollow organ, and its structure is not particularly remarkable. It consists of four layers. The first is mucous, then fibrous (dense connective tissue). Next is the muscular and final layer that gives the pharynx mobility - adventitia (loose connective tissue).
With pharyngitis, the inner mucous layer suffers, since it is very rich in capillaries located close to the surface.
- In terms of location, the pharynx can be divided into three parts - the nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx. That is why, with pharyngitis, neighboring organs are often “affected” - the nose (rhinopharyngitis), tonsils (pharyngo-amygdalitis or tonsillitis) and the larynx (pharyngo-laryngitis). Also, this explains the abundance of symptoms of pharyngitis. Be patient - we'll talk about this a little further.
- The pharynx is the “entrance” to the pharynx from the oral cavity. Anatomically, it is located between the soft palate, the root of the tongue and the palatine arches. It is the changes in this area that the doctor is interested in when diagnosing pharyngitis: “Show me your throat.”