A lump on a child’s gum is a problem that many parents have to deal with. Often its presence indicates that a purulent inflammatory process is occurring in the baby’s body. Since such a lump may not hurt or bother the baby too much, the disease may progress to an advanced stage if ignored. To minimize this likelihood, you should understand why a lump on a child’s gum may appear in the first place, and what needs to be done if it is detected.
A lump on a baby’s gum can appear for various reasons.
Causes
Having discovered that a lump has appeared on a child’s gum, the first thing parents should do is understand what exactly they are dealing with. Many years of medical practice show that this can be.
Hematoma
In this case, the ball on the gum will be blue. A hematoma is usually a direct consequence of the injury and does not cause much pain to the baby. The shape of the formation can be oval or round, its structure has an average density.
Purulent fistula
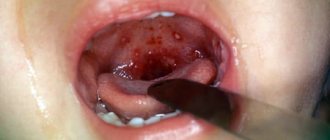
A purulent fistula has a rich red color. Usually the tumor is a sac with smooth, hyperemic edges. It contains pus. The ball is quite painful and appears against the background of one or another infection.
Important! The size of the fistula can reach 1 cm. If it is detected, the baby must be shown to a specialist.
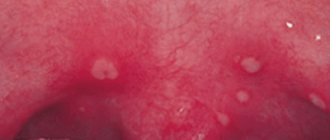
Cyst
A cyst is a dense ball that is white in color and begins to hurt when directly exposed to any irritant. Most often, such a lump appears on a child’s gum next to a tooth affected by caries.
Benign neoplasm
A benign tumor usually does not hurt, can be hard or soft, and its shape varies depending on the nature and cause of the disease. Despite the fact that such a formation most likely will not hurt, due to its tendency to grow, it is recommended to remove it surgically.
The baby's oral cavity should be carefully examined periodically.
Exostosis
Gingival exostosis is a bone overgrowth and most often occurs on the gum of the lower jaw. Being relatively small in size, such a lump does not cause virtually any discomfort to the child.
All possible prerequisites for the formation of cones can be divided into the following categories:
- fungal or bacterial infection;
- age-related changes inside the oral cavity;
- damage caused by external factors.
What type of spots can pose a danger to a newborn?
Not always spots on a baby’s gums can be caused by relatively harmless reasons. That is why it is important not to leave the problem unattended, even if there are no signs of concern.
If you notice a deviation from the usual appearance of children's gums, you should consult a doctor:
- Periodontitis appears as white or clear blisters. Due to the fact that the baby puts everything in his mouth, they can burst, and an infection will enter the fragile body, then a purulent pimple will appear, and the infection threatens to spread further.
- Thrush manifests itself in the form of a white coating on the gums and tongue, the wounds underneath cause significant discomfort, because of this the baby may completely refuse to eat. To avoid this, it is necessary to undergo antifungal therapy, give the baby water, and also walk in the fresh air.
- Due to infection in the body, cysts can form on the gums. It is quite difficult to diagnose; an accurate diagnosis can only be made on the basis of x-rays.
- Wen is a relatively harmless disease, but it causes discomfort to the child, so, as a rule, the doctor decides to remove it.
- A gum tumor with a white head looks like a lump or cyst, but there may be cancer lurking inside. Any tumor should be immediately examined by a specialist.
Read also: Fistula on a tooth
Symptoms of lump formation
Goose bumps in a child - possible causes
The specific symptoms of a lump on the gum largely depend on the cause of its appearance. There are some common signs that can help you determine if there is a problem:
- discomfort while eating;
- pain when pressed;
- bleeding;
- discharge of pus.
Since the infant’s body is still quite weak, the appearance of a lump is often accompanied by additional symptoms. The baby’s general health deteriorates, body temperature rises, appetite suffers, and apathy begins. Sometimes, in addition to the above, enlargement of the lymph nodes occurs.
Cyst symptoms
Each type of education has characteristic features:
At first, the child may not experience any clinical manifestations other than the formation itself. There is no pain, so the child does not pay any attention to it and does not tell his parents about its appearance. For this reason, most of these formations are discovered only during an examination by a dentist.
Read also: My gums bleed heavily, what to do?
After some time, the cyst begins to increase in size. Painful sensations appear, which intensify during chewing.
Since the child’s body very actively responds to any inflammatory processes in the body, the temperature immediately rises, weakness and loss of appetite appear. In especially severe cases, swelling of the soft tissues of the face develops in the area of the inflamed tooth.
Such a gum cyst in an infant will manifest itself as a complete absence of any pain. In its cavity, such a cyst contains a clear liquid.
Need to know! After the tooth erupts, all manifestations disappear. An autopsy is required in very rare cases.
These neoplasms look like white lesions. Over time, they do not change their size. Therefore, they are sometimes mistaken for teething teeth. Such cysts can be localized on any surface of the alveolar ridge.
Help at home
Blood in the urine of a child - possible causes in infants
To ensure that the treatment of the lump does not cause harm to the health of the baby, who is barely a month old, only non-toxic and safe substances and preparations are allowed for therapy. The first thing you should do after discovering a lump on the gum above a child’s tooth is to show the baby to the dentist. He will check the condition of the teeth, make sure that their eruption occurs without pathologies, and will be able to determine exactly why a tubercle appeared on the gum.
Sometimes it is very difficult to understand whether something hurts your baby
Home treatment methods should be aimed at alleviating the baby’s condition before going to a specialist. Therapy on your own may consist of the following actions:
- Feed your baby food at room temperature.
- Significantly increase the amount of water your baby consumes.
- Brush your baby’s teeth (if teething has already been completed) with the utmost care.
- Rinse your mouth with infusion of chamomile or oak bark.
- Every 4 hours, give the child oral baths using an aqueous solution of chlorhexidine.
Important! When the baby is several months old, or barely a year old, doing something on your own is very problematic. It is imperative to contact your doctor or dentist for advice.
What not to do
If a lump on the gum begins to fester, the pathology should be treated immediately. Everything necessary should be done exclusively in accordance with the recommendations issued by the doctor. Under no circumstances is it permitted:
- heat the infected area;
- open the lump yourself;
- give your child aspirin;
- offer your baby hot or cold food;
- try to squeeze out the abscess.
Prevention and more prevention
To prevent diseases, teeth and gums must be kept clean. Hippocrates, the famous physician, once said: “Your food should be your medicine.” Watch your food: more vegetables and fruits. To maintain health, a toothless baby should be given a piece of apple to suck. Take your child to the dentist for examination regularly - once every three months. You can’t wait until the small white bumps double in size and turn red: as soon as a white sore appears, take your child to the dentist.
Read also: Gum cyst symptoms
Complications of untimely treatment
Red dots around the eyes of a child - possible causes of the rash
If a child has a red lump on his gum, you should not expect the problem to disappear on its own, even if the growth does not cause any discomfort. The consequences of delayed or ill-conducted therapy can be the most undesirable. With purulent bumps, we can talk about tooth loss, the development of osteomyelitis, periostitis.
Even a minor pathology, if left untreated, can in the foreseeable future affect not only the formation of the bite, but also the functioning of individual internal organs and systems. Thus, the lump should be treated as quickly as possible.
Causes of white spots
A change in the color of the mucous membrane may indicate one of the following diseases:
However, there may be other reasons for its appearance:
- development of the wen;
- fibrinous plaque after tooth extraction.
Its appearance and structure will help to more accurately determine the cause of the appearance of the spot.
If the stain is formed by a layer of dense plaque that cannot be removed, most likely it is stomatitis - inflammation of the oral mucosa . The mechanism of stomatitis has not yet been reliably determined, but the most common hypothesis considers stomatitis to be a specific immune reaction to irritants affecting the oral mucosa.
Stomatitis on the gum
Lymphocytes attack unidentified particles, which leads to the appearance of areas in the mouth first covered with a white coating, and then painful ulcers in their place. Along with this, swelling of the mucous membrane, hyperthermia, and pain are noted.
There are several factors that provoke the immune system to such a reaction:
- bacterial or viral infection;
- mechanical damage to the mucous membrane;
- avitaminosis;
- poor quality or poorly installed dentures.
Stomatitis can also be triggered by a decrease in salivation - as a result of general dehydration, taking certain specific medications, and even excessive oral hygiene.
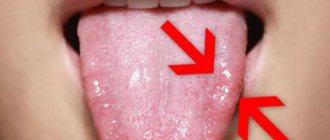
If the spot is formed by a whitish coating that can be easily removed with a cotton swab, but after some time forms again, this is a sign of candidiasis. Candidiasis or thrush is damage to the mucous membrane by fungi of the genus Candida .
Candidal stomatitis in a child
Fungal microorganisms of this genus are part of the normal microflora of the oral cavity, so the disease does not occur when they get on the mucous membrane (they are already there), but when they multiply excessively. This usually occurs against the background of reduced immunity and dysbacteriosis. The reasons that provoke pathological proliferation of fungi can be:
- decreased immunity due to severe diseases, especially infectious ones;
- avitaminosis;
- iron deficiency;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity.
Also, the development of candidiasis is facilitated by a decrease in salivation and an increase in the acidity of saliva (this condition is observed in many gastrointestinal diseases).
Leukoplakia
If the spot looks like a dense milky plaque or a cluster of small scales, this is a sign of oral leukoplakia. Leukoplakia is not an independent disease; it is a specific syndrome in which the epithelium of the mucous membrane thickens and becomes keratinized.
Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia can occur as a reaction to external aggressive stimuli, such as:
- injury to the mucous membrane from sharp edges of teeth or incorrectly installed dentures;
- frequent, prolonged consumption of hot or spicy foods;
- smoking;
- prolonged exposure to harmful chemicals on the body (for example, when working in chemical production).
This syndrome can also occur due to a lack of vitamin A.
The main danger of leukoplakia is that if left untreated, it can develop into cancer. The first sign of leukoplakia turning into a malignant tumor is graying and clouding of the surface of the white spot.
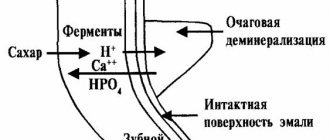
The cyst is not always visible on the surface, but sometimes it can be seen as a small whitish spot under the crown of the tooth. A cyst is a special formation in soft tissues, essentially a cavity right inside the gums, the walls of which are formed by modified cells.
Often this cavity is filled with pus. Dental cysts are formed as a result of infection of soft tissues and their pathological growth.
Wen, or lipoma, looks like a small spot of cloudy white or yellowish color, soft to the touch. It is a collection of adipose tissue surrounded by mucous walls. Such neoplasms usually do not cause inconvenience, do not hurt, and in most cases are harmless .
However, if the size is too large, the wen can interfere with the normal process of chewing or articulation. The most common cause of wen is frequent mechanical injuries, for example, biting the cheek or rubbing the mucous membrane with a brace or denture.
Fibrinous plaque
After a tooth is removed, after some time, a white coating may appear near the hole. However, this is practically the only case when white spots do not indicate illness, but, on the contrary, the healing process of a postoperative wound.
Fibrinous plaque after tooth extraction
These spots are the so-called fibrinous plaque. It represents dead epithelial cells covering a new growing layer. There is no need to treat fibrinous plaque ; during the healing process it goes away on its own without any consequences.
Methods for getting rid of white spots on gums depend on the reasons for their appearance.
- For stomatitis , no specific treatment is required - it is enough to maintain oral hygiene and adhere to a gentle diet (excluding too hot, spicy and rough foods). When irritants that can provoke an immune reaction are eliminated, stomatitis goes away within a week.
- Candidiasis requires longer and more thorough therapy. First of all, it is necessary to sanitize the oral cavity and carefully observe hygiene. It is also necessary to reduce the acidity of the oral cavity - for this purpose, rinsing with solutions of baking soda, boric acid, and clotrimazole is used. It is necessary to take antimycotic drugs orally, such as fluconazole, terbinafine ketoconazole, amphotericin B, levorin. Physiotherapy procedures are recommended - electrophoresis, ultraviolet irradiation, laser therapy.
- Leukoplakia also requires serious treatment. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the factor that irritates the mucous membrane and causes it to change. You should stop smoking, adjust dentures, sharpen the edges of the teeth, and minimize contact with harmful substances. You should also carry out thorough sanitation of the oral cavity and use applications with special preparations (retinol, cigerol, etc.) that promote the healing of damaged mucous membranes. If treatment fails, surgery is necessary.
- Cysts and fatty deposits also need to be removed surgically. The danger of these formations is that the cystic cavities are often filled with pus, which provokes an abscess and, in the worst case, inflammation of the bone. Wen tumors can eventually degenerate into malignant tumors. Therefore, both must be removed - conservative treatment in these cases is useless.
- Fibrinous plaque , as mentioned above, is not a disease; accordingly, it does not need to be treated. Moreover, it should not be touched at all - you can damage the layer of young epithelium growing underneath it.
Read also: Food got under the gum
Can a lump not hurt?
A lump on the gum can be caused by many reasons: an accidental blow, a cutting upper tooth, infection, etc. Not in every case the neoplasm will define itself as a pain syndrome. Painless pathologies include the following:
- fistula;
- epulis;
- exostasis;
- periodontitis;
- hematoma (the area near the bump may hurt).
Important! If your baby has bumps and doesn’t show any discomfort, this is not a reason to ignore the problem. Parents must observe one very important condition: when the child is several months or years old, any neoplasm on his body or mucous membrane should be a reason to consult a doctor.
Secrets of treatment
Having discovered the cause, the doctor will prescribe treatment. It is strictly not recommended to treat white pimples on the gums on your own, especially in infants. Those folk recipes that an adult body can withstand are not suitable for the delicate and vulnerable body of a newborn. During the appointment, the doctor will examine the child and, if he deems it necessary, take an x-ray.
- Wen disappears on its own and is usually not treated, but the baby will need regular doctor's examinations. Every day look at the wen – have they changed color? Size? The doctor sometimes prescribes surgical removal of the wen: this means that it is located in an area of the body where it poses a danger to the child.
- Herpes is treated with antiseptic solutions, antiviral drugs and similar drugs. The doctor will recommend medications suitable for the baby, but you should carefully read the instructions on the solutions yourself and monitor the child’s reaction to them. A newborn baby has a weak immune system: a medicine that is described as having a gentle effect can harm his health. Various ointments, solutions and preparations are also prescribed for stomatitis.
- Antiseptics and other medications are prescribed for white purulent pimples, but this is not always enough. The doctor sometimes has to remove the white sore surgically. The cyst is surgically removed. A white cyst is removed by several methods, depending on the reason that led to its appearance, but the first step is the same - remove the pus and cyst.
Chlorophyllipt - antiseptic rinse solution
Diagnostic methods
About half of the parents of small children notice a lump on the child’s gum already at a fairly late stage in the development of the disease. This is due to the fact that at the initial stages the toddler’s discomfort from the appearance of the lump is minimal, the lump itself is almost invisible.
Diagnosis must be carried out by a specialist
Diagnosis by a specialist is carried out in several ways:
- palpation;
- examination of the oral cavity;
- biopsy of material for histological examination;
- X-ray;
- oral questioning of the patient (if the child can already speak).
Treatment is prescribed after determining the nature of the lump based on diagnostic examinations.
Causes of white pimples on the gums of infants
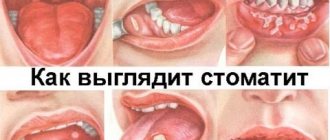
Whitish or red pimples are a fairly common occurrence in children of the first year of life; they can be of various shapes (flat and convex, like balls, oval and round), different to the touch (hard or soft), multiple or single. In any case, if any pathology is detected in the child’s mouth, you should consult a specialist.
The reasons for the appearance of pimples are completely varied, both dangerous and harmless:
- Stomatitis is the appearance of groups of white dots on the gums due to infection both in the child’s body and directly on the oral mucosa. It occurs due to trauma to the connective tissue of the epithelium. There are several types of stomatitis, which are caused by various viruses: Herpes (caused by the herpes virus) - the appearance of white-yellow erosions that cause itching and burst. The picture becomes clearer with accompanying symptoms (enlarged lymph nodes, tearfulness, fever and refusal to eat).
- Aphthous (several causative agents - bacteria, lack of vitamins, damage to the mucous membrane, allergies). First, swelling and redness appear on the gum - inflammation, after which several white dots become visible, they are called aphthae. Additional symptoms include increased salivation, crying, strong breath, fever and lack of appetite.
- Candidiasis (caused by candida fungi). Characterized by the appearance of painful and itchy white spots. Additional symptoms are bleeding gums, unpleasant odor, burning sensation, crying.
- Cysts are white spots filled with pus, around which there is swelling. They arise as a result of infection entering the dental canals: in the presence of stomatitis or other damage to the mucous membrane in the oral cavity. Cysts often require surgical removal, but they can burst on their own, after which ulcers and fistulas form in their place.
- Calcium deficiency can also cause white spots on the gums. In the event that the child is breastfed, and the mother’s milk does not have enough of this mineral due to poor unbalanced nutrition, or the baby has entered the stage of introducing complementary foods, but does not receive enough dairy products (milk, cottage cheese and kefir).
- Wen (soft white pimple). If it does not increase, then it does not require treatment and may disappear on its own. If it grows, it requires surgical removal.
- Epstein's pearls (these are peculiar cysts that form from the epithelium). Outwardly, they look like micro pearls, which is why they got their name. They do not require treatment and resolve on their own.
Read also: Swollen tooth, what to do at home
Stomatitis in a child
In addition to white pimples, a child may be bothered by the appearance of white plaque on the gums. This alarm bell should not be ignored, but diagnosis and treatment should begin.
Professional help
Professional medical assistance when a lump grows on the gum of a small child is mandatory. Specific therapeutic procedures will vary depending on the nature, location and characteristics of the development of the neoplasm:
- For a fistula, the doctor often prescribes treatment with soda solution.
- In case of periodontitis, inflamed tooth pockets are washed with a medicinal solution.
- Epulis requires curettage.
- In case of purulent formations, surgical intervention and cleaning of residual pus are required.
- In some cases, the lump is removed through surgery.
At the first suspicion of pathology, the baby should be shown to a doctor
Despite the fact that in most cases, a lump on a child’s gum can be cured quite easily, it is not strongly recommended to delay contacting a medical facility. The sooner the problem is identified and a diagnosis is made, the less negative impressions the baby will have from the treatment.
Treatment of cysts
The method of treating cysts will depend on both the cause and the tooth on which it formed.
Treatment of purulent cysts
The treatment method for cysts in primary teeth is quite simple. They are always removed.
All other methods are used only for permanent ones:
The first thing the doctor always tries is conservative treatment methods:
- Endodontic treatment of root canals according to generally accepted methods.
- Physiotherapy in the form of depophoresis. During the treatment, pus is pumped out of the root, which is then replaced with nitrous oxide. As a result, all pathogenic microorganisms die.
- Using a transchannel laser. In children, preference is given to this method, since there are no unpleasant sensations. The laser effectively destroys bacteria and promotes postoperative tissue restoration.
Important! Even the best conservative treatment method may not give a 100% result and you will have to resort to surgery.
Most often, 4 types of operations are used: cystostomy, cystectomy, hemisection, amputation and resection of the apex of the tooth root.
In the first case, the anterior wall of the jaw is removed, which leads to the formation of a communication between the oral cavity and the cyst. Gradually its size will decrease, and the defect in the bone tissue will be restored. The video in this article demonstrates the progress of the intervention.
A cystectomy is an operation to completely remove a cyst from the jaw. Most often it is combined with resection of the apex of the tooth root, especially that part of it that enters the changed area. Most often, this method is used to treat the upper front teeth. In the photo below you can see the diagram.
Hemisection is used only for multi-rooted teeth. Its use is indicated only in case of damage to one of the roots with a cyst located between them. In this case, the doctor divides the tooth into several parts and removes the changed one. At the same time, all cystic tissue is removed.
Amputation is also performed only on teeth with several roots. Its difference will be the removal of only one of them with complete preservation of the crown. For large cysts, tooth extraction is recommended.
Treatment of eruption cysts
In most cases, they do not require any intervention. If the formation begins to bother you, then the cyst is opened and the fluid accumulated in it is released.
Treatment of cysts in newborns
No special treatment is required for these tumors. They rupture on their own after exposure to friction during breastfeeding.
Prevention
The main means of preventing oral diseases is careful control over hygiene. In relation to diseases of the gums and other soft tissues of the oral cavity, attention should be paid not only to brushing the teeth, but also to the personal hygiene of the child:
- Regularly disinfect toys that your baby puts into his mouth and thoroughly wash and sterilize/steam feeding accessories.
- The baby should be given a few drops of water after each breastfeeding or formula feeding to “wash away” the remaining milk or formula and prevent the formation of a breeding ground for microbes.
- Monitor your child's general health - a strong immune system protects against many diseases, not just dental ones.
Symptoms of the problem
It is not difficult to notice early signs of thrush in a newborn's mouth. Already at the earliest stage, the disease manifests itself as characteristic white dots (visually reminiscent of semolina crumbs) on the gums, tongue, and cheeks.
Good to know!
It is quite simple to distinguish food plaque in the mouth of a baby from thrush - just take a clean napkin and wipe the problem area of the oral mucosa with it. Food plaque can be achieved without much difficulty, but the curdled waste products of the fungi Candida albicans are not so easy to wipe off. But even if this can be done, a characteristic red spot remains on the mucous membrane in the problem area.
In addition to visual symptoms, there are also common ones:
- Excessive anxiety;
- Constant crying;
- Decreased appetite.
Having discovered these signs, you should not postpone visiting the pediatrician, because in the very early stages of the disease they do not even use medications for treatment; they only manage to normalize the conditions for the baby to stay indoors.
Treatment
The main instruction for mothers who discover any obvious pathology in the gum area of their child is to visit a pediatrician or dentist as soon as possible, even if the cause of this disease is extremely clear.
When a child’s gums, in addition to white spots, dots and pimples, exhibit swelling, then we can safely judge that there is some kind of mechanical damage to the soft tissues. For example, after careless use of a toothpick or toothbrush, damage to soft tissues by the sharp edge of the tooth. In such cases, you can use special pharmaceutical solutions for rinsing the mouth. These medications will reduce the inflammatory process and accelerate the process of gum tissue regeneration. The exception to this treatment is symptoms that do not go away for a long time. In this case, you need to visit a doctor as soon as possible in order to reduce suppuration and prevent further suppuration of the soft tissues.
If the white formation in the form of a dot or a hard ball is a wen, there is no need to be particularly afraid, since these manifestations do not pose any threat to the child’s life. However, the only caution is the pathological growth of the wen, since if its size increases uncontrollably, surgical removal may be required. The formation of such wen on the gums can be observed not only in childhood.
Also, whitish formations on the gums may indicate the development of cancer, so this manifestation should not be taken lightly. It is necessary to go to the hospital for qualified assistance. Since, as soon as possible, it is necessary to take a piece of the affected tissue for a biopsy to confirm or refute the alleged diagnosis.