Description
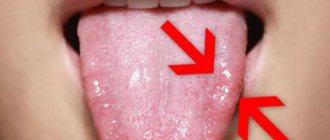
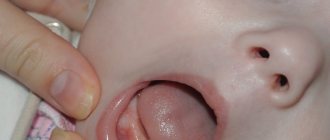
White sores in the mouth cause discomfort and constantly remind you of themselves. Because of the tiny wound, it is impossible to talk, eat, drink or smile without pain.
Unpleasant sensations in the mouth, the appearance of sores, require close attention due to the proximity of the brain.
They are most often located:
- On the inner side of the lower lip.
- Under the tongue.
- On the cheek.
- Found on the palatine process.
- In the throat.
- On the mucous membrane of the gums.
- In the corners of the mouth.
- On the lip line.
If a sore occurs, you should not put off visiting the dentist for too long; he will prescribe treatment or refer you to another specialist.
Lichen planus
Lichen planus has many forms.
One of them appears as white lacy spots in the mouth. Sometimes painful ulcers are added to these spots. The disease occurs when the patient's own immune system begins to attack the cells of the mucous membranes and skin. Why this happens is unclear. But there is evidence that hepatitis C, certain chemicals, heavy metals and medications (for example, ibuprofen, naproxen or medications for the treatment of arthritis) can lead to malfunctions of the immune system.
Like leukoplakia, lichen planus is associated with an increased risk of oral cancer. Therefore, patients with it are also referred for a biopsy. Anti-inflammatory and immune drugs are prescribed for treatment.
Causes
The causes of mouth ulcers can be:
- injuries;
- gum disease;
- dental problems;
- a chronic source of inflammation in the body.
Injuries
Injuries to the oral mucosa occur under the influence of irritants:
- mechanical;
- caustic chemicals;
- thermal.
A person can cause mechanical injury to himself through negligence when brushing his teeth or biting. The wound can also appear during dental treatment or surgical procedures. Mechanical damage also occurs with prolonged irritation from incorrectly placed crowns and dentures.
In infants, careless feeding can lead to injury to the mucous membrane of the palate and the formation of Bednar's aphthae inside the mouth. This phenomenon also occurs in older children if they have the habit of holding a pencil or pen in their mouth.
Similar damage to the palate also occurs in adults, but the cause is much more serious. Ulcers on the palate in adults are a sign of syphilis or tuberculosis.
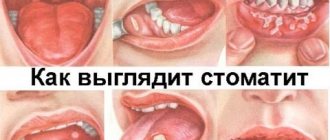
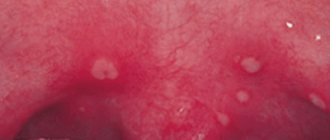
Stomatitis
Acute aphthous stomatitis is accompanied by symptoms:
- Burning pain when eating.
- Elevated temperature.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
The acute form without appropriate treatment takes a chronic course, relapsing with weakened immunity. A lack of vitamin C, B, and folic acid can provoke a chronic course of the disease.
Vitamin deficiency, gum disease (gingivitis), deep caries, periodontitis weaken the local immunity of the mucous membrane, predisposing to herpes infection.
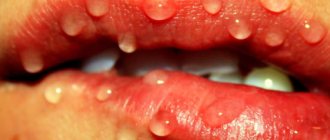
Herpes
The herpes virus is extremely common. In infected people, it is constantly present in the body in latent (inactive) or active form.
Its activity provokes a decrease in immunity and is manifested by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of ulcers on the lips and in the oral cavity;
- increased temperature;
- weakness;
- pain in muscles, joints.
Signs of a herpes infection vary from person to person, and sometimes even doctors do not immediately manage to find out why a white sore appears if a person feels completely healthy. The clinical picture of the disease may become more complicated and may include nausea, sleep disturbance, swelling of the eyes, and a runny nose.
Sores, not limited to the oral cavity, spread to the ears, face and hands. But they are more often found on the lips, tongue, gums and the inside of the cheeks. The bubbles may be single, small in size and not cause concern.
But when the disease is severe, small blisters filled with liquid merge and then burst, leaving behind a deep ulcer that does not heal for a long time, which is difficult to treat.
As a rule, the patient’s suffering ends safely after 7-14 days, the erosion heals, and the virus goes into a latent form and remains in the body.
Gum inflammation
The appearance of white spots on the gums occurs with leukoplakia. With this disease, the gum mucosa becomes keratinized under the influence of constantly acting factors:
- mechanical - an incorrectly placed filling, a tooth destroyed by caries;
- thermal - hot food;
- chemical - smoking.
The white plaque of the keratinizing epithelium can have a wide variety of properties and shapes. She can:
- rise above the gum and have rough edges;
- be at the level of the gums, not felt by the tongue;
- have clear or blurred boundaries;
- be completely painless or, on the contrary, be a constant source of discomfort.
In smokers, leukoplakia plaques create a feeling of dryness and burning of the gums.
The cause of white plaque on the gum mucosa can be candidal stomatitis. This fungal disease, also called thrush, occurs when the immune system is weakened.
Thrush often develops after long-term treatment with antibiotics in response to the destruction of beneficial oral microflora. It is useless to treat oral candidiasis with conventional antiseptics. If you suspect a fungal disease, you should definitely visit a doctor and get the right prescription.
A sign of fungal infection is the easy removal of the stain by scraping at the onset of the disease. Over time, it becomes more difficult to scrape off plaque; it seems to be soldered into the gums, tongue, and surface of the cheek.
There are a lot of causes and signs of inflammation of the gums near the tooth; we even have a separate article on this subject on our website. Read more here.
Avitaminosis
A white sore in the mouth may also appear due to a lack of vitamins in the diet. It occurs when there is a lack of vitamins B6, B2, C, A, P.
You can compensate for them by adjusting your diet and only if you adhere to proper nutrition.
Infectious diseases
They can also be the result of an infection, which manifests itself as ulceration of the oral mucosa. Such diseases include:
- diphtheria;
- chickenpox;
- syphilis;
- oral tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis of the mouth develops secondarily, as a complication of tuberculosis of the lungs and bones. A tuberculous ulcer (chancre) occurs on the mucous, red border of the lips. First, small, painless, flat, yellowish-red bumps about 3 mm in diameter appear.
Over time, each tubercle, growing along the edges, connects with neighboring ones, forming a plaque. An ulcer with a corroded edge, covered with a yellowish coating, forms in the center.
You can become infected through dental instruments if sterilization rules are violated, as well as through blood during medical procedures. With oral syphilis, one chancre usually develops.
This formation is located on the tongue, tonsils, palate, red border of the lips, and gums. Chancre can take different forms, but more often it is a round ulcer with raised edges, covered with a grayish coating.
Cancer
Compared to other cancers, oral cancer is rare and is diagnosed more often in people who use tobacco by any means:
- smoking cigarettes, cigarettes, pipes, hookahs;
- chewing nasvay, using chewing tobacco;
- with passive smoking.
Oral cancer is a deadly disease, and smokers are the main risk group. There is a high risk of developing oral cancer in individuals:
- alcohol abusers;
- those who eat irrationally.
With this disease, it is important to identify the tumor as early as possible and begin treatment. At an early stage, the cancer appears as a small ulcer, usually on the inside of the cheek, at the lip line, in the corners of the mouth, on the inside of the lower jaw behind the 3rd molar.
At this time, the compaction does not cause discomfort or pain. But as the tumor increases in size, salivation increases, and difficulties with swallowing and chewing appear.
Treatment of concomitant diseases
It is important to understand why mouth ulcers form: the reasons for their appearance are different and treatment can be much more complex than with ordinary stomatitis. In the presence of systemic, sexually transmitted, oncological diseases and complex infectious processes, it is not enough to simply spread medicinal products on the wounds.
Without eliminating the cause of mouth ulcers, it is impossible to get rid of the disease completely. After the abscess heals, it will soon appear again. This is why it is important to see a doctor even if home treatment seems to help with the ulcers.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to cure acute diffuse pulpitis: features of diagnosis and therapy
After diagnosing diseases more complex and dangerous than stomatitis, you need to be prepared for long-term treatment. It cannot be interrupted at your own discretion or the medications changed. Severe infections of bacterial origin require systematic use of antibiotics; folk remedies cannot be cured.
How to treat white sore?
When a white sore appears in the mouth, you need to find out the reason for its formation and find out what to do to get cured from a doctor, and not from a neighbor who “had it too.”
Before visiting a doctor, you can try to cope with the disease on your own. But you should not put off visiting a doctor for a long time if improvement does not occur within 2-3 days.
Medication method
Antiseptic mouth rinse:
- Chlorhexidine - a 0.05% solution is used;
- Miramistin – 0.01% solution;
- Furacilin – ready-made pharmaceutical solution without dilution;
When choosing a rinse solution, you must pay attention to the concentration of the active substance. If the indicator is high, you can get a burn to the oral mucosa and worsen the condition of the ulcer.
Chlorhexidine is considered the No. 1 antiseptic. Preparations with this compound are effective against most pathogenic bacteria, tubercle bacilli and herpes viruses.
For herpes, in addition to rinsing with chlorhexidine, you can use ointments and tablets with acyclovir (Zovirax, Acyclovir).
Anti-inflammatory drugs used:
- Chlorophyllipt – alcohol infusion of eucalyptus leaves;
- Stomatophyte – alcohol infusion of medicinal plants;
- Tantum Verde - contains benzydamine hydrochloride, alcohol.
Mouth ulcers can be treated with dental gels; Cholisal is recommended for children. The gel, thanks to its water base, is well absorbed and adheres to the gums, providing pain relief, eliminating bleeding and itching.
Metrogyl dental gel also helps, but it cannot be used for a long time due to the risk of oral dysbacteriosis. The fact is that the gel contains chlorhexidine, a strong antiseptic with anti-inflammatory properties.
Solcoseryl gel, a dialysate prepared from the blood of calves, will help speed up the healing of sores. The gel has regenerating properties, improvement occurs after just 3 procedures.
Rinsing with decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants has a positive effect during treatment. These products can be used for a short time and always remember the danger of an allergic reaction, especially in children.
Traditional methods
Common folk recipes that are easy to prepare at home include the use of decoctions, infusions of calendula, chamomile, sage, and oak bark. All these medicinal herbs have an anti-inflammatory, aseptic effect and soothe discomfort in the mouth.
Decoctions of these herbs can be used as an additional treatment, unless the doctor prohibits it. It is dangerous to independently diagnose yourself and choose a treatment - the brain is too close to the oral cavity.
The child has
A white sore in a baby’s mouth may be a manifestation of measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria, chickenpox, or Bednar’s aphthae.
The intention to independently cope with the diagnosis and treatment of the baby is a risk of complications and a waste of time.
Diet
You must include in your diet:
- vegetables – cauliflower, tomatoes;
- greens - spinach, parsley, onion;
- cereals – barley, wheat, oatmeal;
- fruits - apples, citrus fruits, grapes, plums;
- berries - rose hips, currants;
- legumes – beans, peas;
- walnuts, hazelnuts, almonds, peanuts;
- lean chicken, liver, beef, eggs;
- Champignon;
- fish - mackerel, salmon.
Video: why do sores appear in the mouth?
How to get rid of an old encapsulated wound on the mucous membrane
An encapsulated wound on the oral mucosa indicates that the pathological process is ancient. If after 3-4 weeks of intensive therapy no positive dynamics are observed, the question of radical treatment is raised.
Old, non-healing wounds are treated with a minor operation performed by a surgeon. After removing the capsule, antimicrobial ointments are prescribed. They speed up recovery and prevent the development of complications.
Timely seeking medical help, early diagnosis of the cause of the pathology, and compliance with medical recommendations will help prevent the formation of an old lesion in the mouth.
Article verified
by the editors
Mouth ulcers are a common ailment that mainly affects young people, as well as those who have psychological problems and are regularly under nervous tension or stress.
It is known that almost 1/3 of the world's population encounters this problem every year.
Quite often, people do not pay any attention to wounds in the mouth and do not treat them, because they often heal in a short period of time. This process is explained by the rapid regeneration of cells in the oral mucosa.
In some cases, such wounds can cause discomfort and pain. In such situations, immediate medical attention is needed. Because otherwise, other concomitant diseases may appear, which in turn will aggravate the person’s well-being.
Prevention
A sore in the mouth may not appear if you adhere to preventive measures. This is not difficult to do if they are caused by poor oral hygiene, an allergy to toothpaste, or a deficiency of vitamins. In this case, it is enough to balance your diet and pay attention to the composition of your usual toothpaste.
If the paste contains sodium lauryl sulfate, then it is possible that it is under the influence of the paste that the mucous membrane dries out, which reduces its immunity and leads to aphthous stomatitis and the appearance of white ulcers.
It is more difficult to protect yourself from infection with the herpes virus, since the appearance of this infection occurs mainly through saliva. Parents need to follow hygiene rules and not share utensils with their child.
Local treatment
How to treat mouth ulcers to achieve analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects? For this purpose, there are a number of drugs that have minimal systemic effect:
- Sprays for treating the oral cavity - Hexoral, Vinilin, Kameton, Yox, Ingalipt. These agents effectively anesthetize the oral mucosa, reduce the level of inflammation, disinfect the epithelium, and help eliminate the infectious agent.
- Kamistad is a gel used in dental practice, which contains chamomile extract and lidocaine. It is applied to the affected areas for an antiseptic and anesthetic effect.
- Cholisal is a gel with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and anesthetic effects. It is used to lubricate the ulcerated mucous tissues of the mouth several times a day.
- Metrogyl Denta is a product based on metronidazole, a substance that actively fights a wide range of bacteria and viruses. Prescribed for all forms of stomatitis, applied to the mucous membranes affected by the disease.
- Actovegin is a gel that is used to treat the initial form of ulcerative lesions.
Solcoseryl gel helps to heal the inflamed mucous membrane; it should be applied to irritated areas covered with ulcers and bleeding wounds. This way the epithelium will heal and recover faster. To speed up treatment and tissue regeneration, Proposol spray, Shostakovsky balm (Vinilin), Karotolin oil solution and sea buckthorn etherol are also used.
The following agents are used to treat the mucous membrane: boric acid, a light pink solution of potassium permanganate, Kalanchoe juice diluted with boiled water, Lugol’s solution. Many patients ask whether it is possible to treat the oral cavity with hydrogen peroxide, is it dangerous? This product has a powerful antiseptic effect, stops the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, acts on a wide range of bacteria and viruses, but when affecting mucous membranes it must be diluted with warm water in a 1:1 ratio.