Ways to relieve pain
Measures to help relieve pain in case of sinusitis:
- Washing. Saline solutions and decoctions are used. The nasal cavity is cleared of pus.
- Warming up. There is an increase in the outflow of secretions.
- Inhalations. Sea salt and herbs are used. The functions of the mucous membrane are restored, irrigation is restored, and swelling is relieved.
- Vasoconstrictors. Applicable in case of clearing the nasal cavity from pus. Effectively relieve congestion and reduce headaches.
In case of frequent nosebleeds, rinsing is contraindicated. Likewise, it is necessary to avoid warming the sinuses if the patient has a fever.
What can hurt with sinusitis?
According to the medical reference book of symptoms and syndromes: “Sinusitis is characterized by severe pain, in which the head, teeth, eyes and bones may ache. Depending on the localization of this unpleasant feeling, it differs in pathogenetic mechanism (mechanism of development and manifestation), etiological factors (in origin).” Also, depending on the location of the organ that hurts, it is possible to differentiate sinusitis from other types of sinusitis (since there are nine paranasal sinuses of the upper respiratory tract, lined with mucous membrane, there are a corresponding number of nosological units).
Most often, patients complain that their teeth hurt. There are two possible mechanisms – bottom-up and top-down. The first is considered if the teeth are the primary focus of the lesion, that is, the inflammatory or infectious process began in these organs. Further, it can spread to the maxillary sinuses (both on the right and left sides), since they have a direct connection with the cavity of the oropharynx.
The relationship between sinusitis and toothache
If we talk about a descending lesion, then the primary focus may not be the teeth, but the mucous membrane of the air pocket. This situation is described by clinicians much more often and is more predictable due to the typicality of the pathological process (catarrhal drainage of exudate and its accumulation in cavities that are anatomically located below - a feature characteristic not only of sinusitis).
For differentiation, the time period of symptom manifestation is used. If the tooth initially hurts, this speaks in favor of an ascending inflammatory process. Just like if your teeth hurt after characteristic rhinorrhea and nasal congestion, you can conclude that sinusitis is descending.
The following combination of symptoms is often encountered: “I constantly have a stuffy nose and pain in the bags under my eyes.” This, although indirectly, is also a sign of sinusitis, since under the eyes there is a “canine fossa” (anatomical formation, which is represented by a depression in the maxillary bone), into which the maxillary sinus is projected. Additional diagnostic evidence of the correct diagnosis can be increased intraocular pressure, since the edematous mucous membrane puts pressure on the excretory ducts of the chambers of the eye. In this case, in addition to compressive pain, there is redness of the visible sclera and pronounced swelling of the lower eyelids. A complaint such as “there are tears in my eyes” is considered pathognomic.
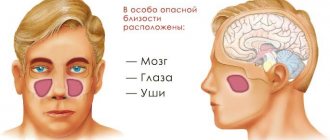
The maxillary sinuses are located in close proximity to the brain and are connected to the cavity of the cranium by a complex system of passages, therefore sinusitis may also be characterized by pain, which is classified as a headache. The mechanism of its appearance is similar to why the eyes hurt - it’s all due to pressure, although this time it’s intracranial. In connection with a new pathophysiological element, complaints such as “I have a feeling of fullness in my ears” or “I always feel as if I have dived under water” may be encountered. This description is quite common in the scientific works of practicing clinicians.
Complications
With odontogenic sinusitis, a chronic inflammatory process occurs. Dental microflora appears in the sinus, not typical for the upper respiratory tract, which can destroy bone tissue. Due to the fact that the paranasal sinuses have contact with the orbit and brain, odontogenic sinusitis can lead to severe complications:
- intraorbital (orbital phlegmon, ophthalmitis, optic nerve neuritis);
- intracranial (meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess).
Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of this disease, you should consult a doctor.
Why do teeth hurt with sinusitis?
Often teeth hurt with sinusitis. What is this connected with? Often the cause of toothache is the neglected condition of the upper teeth, after which the nasal canals become clogged, a liquid substance is formed, and over time a purulent formation is released. What is sinusitis? This is an inflammatory disease of the paranasal sinuses, which appears as a result of improper treatment of the disease. According to statistics, people of all ages suffer from sinusitis (mainly in the autumn-winter period).
If you discover the first symptoms of the disease, you should not self-medicate. Immediately contact a specialist, namely an otolaryngologist, to diagnose and treat the disease.
In its advanced state, sinusitis can cause a number of serious infections, including damage to internal organs and sepsis.
And in 70-80% of cases, sepsis can lead to death.
Causes of sinusitis
The causes include previous infectious diseases such as influenza, scarlet fever, runny nose and others. There are several factors leading to this disease:
- caries of the upper teeth;
- past infectious diseases;
- curvature of the nasal septum in case of injury;
- weakened immunity.
Often, sinusitis occurs when attempting to self-treat previous infections, so it is extremely important to always pay attention to the condition of your body. Even with the slightest violation of your usual state, you must contact a medical facility. The main thing is to remember that it is much easier to cure a disease in the early stages than in the later stages, when the process often becomes irreversible and the risk of death increases.
The main thing is to remember that it is much easier to cure a disease in the early stages than in the later stages, when the process often becomes irreversible and the risk of death increases.
The main thing is to remember that it is much easier to cure a disease in the early stages than in the later stages, when the process often becomes irreversible and the risk of death increases.
Symptoms of the disease
Factors preceding the disease are quite varied (simple headache, swelling of the cheeks and eyelids). The most common symptoms are:
- Continuous headache.
- Swelling of the cheeks.
- Difficulty breathing through the nose.
- Fatigue.
- Body aches.
- Chills.
- Fever.
- Cough.
- Mucous discharge from the nose.
Therefore, if you notice initial signs of sinusitis, you should not delay or try to recover without going to the doctor at home. Do not forget that this disease is quite serious and disorders caused by improper treatment can often be irreversible.
Toothache with sinusitis
In most cases, the occurrence of odontogenic sinusitis is explained by the structural features of the human body. The maxillary sinus is located close to the apices of the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw. Inflammatory processes in this area can spread to the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus, causing a disease such as sinusitis. The course of the disease with lesions on the teeth is not much different from ordinary sinusitis.
There are two types of diseases in which teeth hurt: ascending and descending. In ascending sinusitis, the primary organ affected is the oral cavity, and in descending sinusitis, the primary organ affected is the mucous membrane of the airway.
The diagnosis of odontogenic sinusitis is based on diagnostic results, namely rhinoscopy and radiography. The disease may be accompanied by severe toothache.
Treatment of all types of odontogenic sinusitis occurs in the same way as for ordinary sinusitis, only a dentist will examine you. Recovery is facilitated by the use of medications, instillation of anti-inflammatory drops into the nose, and the use of steam baths. In addition to traditional treatment, doctors recommend that patients breathe steam over various herbal mixtures or propolis tincture.
Don’t forget to monitor your health, seek help from specialists in a timely manner and stay healthy.
Symptoms of tooth pain due to sinusitis
With the development of this disease, the patient may not experience any sensations at all. When pressing under the eyes, a slight discomfort, similar to pressure, may be felt. Sometimes the nose is very stuffy, but the discharge contains pus in certain cases mixed with blood. By nasal discharge, you can determine whether the patient is developing sinusitis or whether it is a common cold. Below we will consider what signs will indicate the development of a dangerous disease:
- The right sinus hurts, it radiates to the teeth.
- The pain is concentrated along the entire side of the skull.
- Discomfort in the area of the wings of the nose and forehead.
- The nose is very stuffy and radiates into the teeth.
- Aching pain in the upper jaw.
- Headache on one side.
- Severe weakness.
- Increased body temperature.
To answer the question of why a tooth hurts, an examination is necessary. One of the symptoms of sinusitis is intense, ongoing headaches. If the pain under the nose radiates to the tooth, a professional doctor will be able to determine the cause of the discomfort.
How to relieve pain after filling at home?
Post-filling pain can be relieved by rinsing with warm saline and soda solutions.
Baking soda and salt are used in folk medicine to solve many diseases. After all, they remove inflammation and have an antiseptic effect. Salt can draw out pus, so it is used simultaneously with soda even for.
Warm rinses with soda and salt should be used in the early stages of pain. So, the tooth is heated from the inside. At the same time, warming the cheek from the outside is strictly prohibited.
The solution is prepared from hot water (which the mouth can tolerate). Place one teaspoon of soda and salt in a glass of water. You need to rinse four to five times per hour until the pain completely disappears.
Sometimes a couple of drops of iodine are added to the saline-soda solution. But not all patients can use iodine (for example, in case of thyroid diseases it is better to exclude it).
Medicinal pain relievers will also help relieve pain. Baralgin, ketanov, ketorol, etc. are suitable.
Treatment of odontogenic sinusitis
Treatment of this disease will be effective only if it begins with eliminating the cause of infection of the maxillary sinuses, and then proceeding to cleanse them of purulent contents. If the cause of the disease is an infected tooth, it is removed. If the reason lies in the condition of the tissues, they are opened and foci of infection are removed or other effective therapy is carried out.
Often, in order to urgently drain serous fluid from the tissues of the maxillary sinuses, it is necessary to make an incision in the gums and remove it using a syringe. This measure allows you to remove almost completely the accumulated serousness and pus directly from the body, bypassing the nasal passages. But additional measures must also be taken to prevent the formation of new pus.
Traditional methods of treatment
For odontogenic sinusitis, traditional medicine recipes are very limited. In addition, they are aimed at suppressing symptoms rather than eliminating the underlying cause of the disease. But it is still possible to alleviate the patient’s condition using folk methods.
For the treatment of odontogenic sinusitis the following is used:
- rinsing the mouth with infusions or decoctions of medicinal plants (chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort, linden) - they have anti-inflammatory and disinfecting properties;
- rinsing the nasal passages with saline solution (1 tsp per 1 glass of water) or decoctions of sage, St. John's wort, eucalyptus - reduce swelling and improve breathing.
It is with such a disease as odontogenic (dental) sinusitis that traditional medicine recipes can be auxiliary, but the main emphasis should still be on conservative treatment - in this situation it will be more effective.
Drug therapy
The maxillary sinuses are washed with antiseptics (Miramistin, Furacilin, Dioxidin) and antibiotic solutions (Summamed, Ceftriaxone) to clean them of remnants of harmful microorganisms. Vasoconstrictor drugs (Nazivin, Otrivin, Sanorin) are instilled into the nasal passages - they relieve inflammation of the mucous membrane, reduce swelling and make breathing easier.
Also, in addition to local antibiotic therapy, general antibiotic therapy is almost always prescribed in order to completely suppress infecting bacteria in the body. After recovery, you need to take a course of lactobacilli to normalize the microflora.
To boost immunity, the doctor may prescribe vitamin complexes, and to suppress painful sensations, painkillers.
Operation
Surgery is not often required, but sometimes there will be no recovery without it. There are two reasons for this:
- violation of the integrity of the septum - in this case, it is restored surgically, after which diseases of the oral cavity will not spread to the maxillary sinuses;
- too much damage to the teeth, the presence of cysts or polyps in the upper jaw - in this case, the formation is completely removed and therapy is carried out aimed at speedy healing.
Surgery is prescribed only if recovery is impossible without it.
Sinusitis after tooth extraction
This development of events is also possible and occurs in several cases:
- The tooth to be removed was dangerously close to the maxillary sinus or its roots were located directly in it. In this case, when a tooth is removed, a fistula is formed, through which infectious agents penetrate into the maxillary sinus. Blood clots, small fragments of bone or roots are also pierced into it;
- An impacted tooth is removed (most often it is a wisdom tooth, although other teeth rarely remain impacted). Impacted is a dental organ that has not erupted fully or partially, hiding under the gum or bone. They usually don't bother people. Many people don't even know about their existence. But in case of complicated eruption, the presence of caries on the adjacent erupted tooth, in the presence of acute and chronic inflammation at the location of the impacted tooth, it should be removed. During this operation, unintentional destruction of the sinus wall, the entry of foreign bodies into it, and mechanical trauma are possible;
- Implant installation. When placing an implant on which an artificial crown will later be installed, the walls of the sinus may be damaged.
Symptoms of this type of sinusitis appear within a few days after surgery. Swelling and pain appear in the sinus area, and the socket heals poorly after removal of a dental organ and causes pain. The cause of sinusitis becomes clear immediately.
Medications
Painful sensations in the dentition can be eliminated before going to a medical facility. To do this, you will need an anesthetic drug. For example Nurofen or Nise.
Ketanov is considered a highly effective medication against dental pain, but its use for more than 3 days in a row is unacceptable. Before taking pain medication, it is strongly recommended that you carefully read the instructions for use. The drug is able to eliminate the clinical sign of the pathology, but does not relieve the patient of the provoking factor.
"Dental" sinusitis
What dental problems can bring you to an ENT doctor and what are the features of their diagnosis and treatment?
Surely everyone has heard that you need to visit the dentist at least twice a year, otherwise fleeting preventive meetings with the dentist can turn into long and painful therapeutic appointments for both parties.
Moreover, often an otolaryngologist also joins this idyll. “What does he have to do with it?” - you ask. The answer is simple: an ENT doctor treats odontogenic or, more simply put, “dental” sinusitis, which quite often occurs as a complication of dental diseases.
How are bad teeth and sinusitis related?
And the connection here is purely anatomical. Sinusitis itself is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the air sinus, which is located in the thickness of the upper jaw. The bottom or lower wall of this sinus is a layer of bone that separates the sinus from the roots of the upper teeth (molars and premolars, sometimes canines).
The thickness of this layer varies from person to person - for some it is an impressive plate of bone substance, for others there is no layer at all, and the roots of the upper teeth are located directly in the sinus.
When a tooth starts to hurt, it becomes a source of infection. Bacteria that infect it can spread from the root of the tooth to the mucous membrane of the sinus (and this is all the easier the thinner the bone border between the teeth and the sinus) and contribute to the occurrence of “dental” sinusitis.
The main causes of odontogenic sinusitis:
- deep caries, pulpitis and periodontitis of molars and premolars of the upper jaw;
- periostitis and osteomyelitis of the upper jaw;
- suppurating cysts of molars and premolars of the upper jaw;
- damage to the sinus wall during dental treatment of molars and premolars;
- unsuccessful tooth extraction (sometimes after tooth extraction, a hole can form between the oral cavity and the sinus - a fistula, through which bacterial flora from the oral cavity easily penetrates into the sinus).
Please note that almost all causes can be prevented by maintaining oral hygiene and visiting the dentist on time
How does odontogenic sinusitis occur?
The symptoms of odontogenic sinusitis are in many ways no different from the symptoms of any other sinusitis:
- pain and swelling of the upper jaw in the sinus area;
- nasal congestion on the side of the “sick” sinus, mucopurulent or purulent discharge from the nose, decreased sense of smell;
- rise in body temperature to 38–39 degrees;
- headaches that get worse when you bend your head forward;
- general weakness.
Naturally, with these symptoms, patients first go to the ENT specialist, without even suspecting that they need a dentist. However, there are points that should make you think about the “dental” origin of sinusitis. For example, if you have:
- the molars and premolars of the upper jaw hurt;
- pain in these teeth intensifies when tapping on them or chewing food;
- most recently you visited the dentist and had molars and premolars of the upper jaw treated or removed;
- and, perhaps, the most characteristic symptom is that only one maxillary sinus is affected - the one associated with the causative tooth.
As a rule, without eliminating the cause - a diseased tooth - odontogenic stomatitis is quite difficult to treat and often recurs.
Diagnosis of the disease
Usually, a doctor can assume the presence of odontogenic sinusitis after a thorough questioning and examination of the patient. X-rays or CT scans of the paranasal sinuses and intraoral radiography will help confirm the diagnosis, which will allow one to assess the relative position of the roots of the teeth and the sinus wall, as well as the presence of inflammatory foci in the bone tissue and the degree of swelling of the sinus mucosa.
Treatment and prevention
The dentist and otolaryngologist should treat odontogenic sinusitis together. Let's repeat. that without eliminating the cause - the source of chronic infection in the oral cavity - it is unlikely that the disease will be completely cured.
That is why they first deal with the required tooth - treat it or remove it, and then begin treatment for sinusitis, which includes the mandatory prescription of antibiotics and rinsing the sinuses with antiseptic solutions. In order to alleviate the patient's condition, vasoconstrictor nasal drops, antipyretic and painkillers are used.
Odontogenic sinusitis is a disease that is much easier to prevent than to treat. Therefore, let's not forget about prevention - maintain oral hygiene and regularly visit the dentist. Be healthy!
Related products: toothbrush, toothpaste, dental floss
Under what circumstances can a tooth hurt?
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses is caused by various reasons. The disease is most often caused by dental problems. This is why you may be referred to an ENT specialist and a dentist at the same time regarding sinusitis.
Sinusitis due to a diseased tooth (odontogenic)
Odontogenic sinusitis is diagnosed when the cause of inflammation of the maxillary sinus is a diseased tooth. If the 4-8 tooth in the upper jaw becomes inflamed, then sinusitis is not far away. Inflammation of the roots easily spreads to the maxillary sinus.
Odontogenic sinusitis is difficult to treat. You can ideally wash the sinus and extinguish the inflammation, but since the real cause is not in the sinus itself, but in the oral cavity, an outbreak of odontogenic sinusitis will definitely return. That is why the ENT doctor must properly treat the maxillary sinus and then refer it to the dentist.
If it is possible to save the tooth, then it is treated , carious areas are removed, filled, depulped , if necessary, and preserved . If he is completely bad, then you need to say goodbye to him.
A striking sign of odontogenic sinusitis is an extremely unpleasant putrid odor. If you smell a smell from the nasal cavity or, during puncture of the maxillary sinus, the doctor notes a sharp, unpleasant stench, then the diagnosis is unambiguous.
Because of wisdom teeth
The roots of wisdom teeth are located almost in the cavity of the maxillary sinus and this is very bad. If you have had a CT scan or a regular x-ray of the paranasal sinuses, the image will show how the roots go directly into the maxillary sinus. Periodically, wisdom teeth will provoke odontogenic sinusitis.
For most people, they deteriorate immediately after being cut. Some patients experience inflammation of the gums above the wisdom tooth as it erupts. If the gum cap is too thick, it cannot break through, so the gum has to be cut. In this case, it often turns out that the enamel under this cap is already affected by the carious process.
Cause of toothache
Why do teeth hurt with sinusitis?
- The accumulated exudate (purulent contents) puts pressure on the walls of the maxillary sinuses, discomfort occurs in the upper jaw, and the pain can increase significantly when tapping, pressing on the molars or during eating (under load).
- With sinusitis, teeth hurt even if the inflammation has affected the trigeminal nerve. Patients experience lumbago radiating to the upper jaw, ear, forehead, and temples.
- Dental sinusitis led to inflammation of the bone tissue (osteomyelitis). Since the maxillary sinus is located directly above the upper jaw, it is also affected.
- There is also sinusitis from teeth; it develops as a result of dental problems affecting the upper teeth.
Toothache with sinusitis can have a different character. So, if it is dull, aching, and worsens when chewing, then most likely the inflammatory process has affected the trigeminal nerve. When the pain syndrome is severe, there are lumbagoes in the forehead, ear, upper jaw, and we are talking about acute odontogenic inflammation of the maxillary sinuses.
The inflammatory process (suppuration) in the maxillary sinuses can be a complication of dental diseases (caries, periodontitis, etc.)
Causes of odontogenic sinusitis:
- the disease can be triggered by foreign bodies entering the maxillary sinuses during dental treatment;
- cyst, granuloma at the root of the tooth, abscess. Any suppuration in the oral cavity can spread to the maxillary sinuses and provoke sinusitis due to a sore tooth;
- periostitis. The bone walls of the molars are quite thin; holes (fistulas) quickly appear in them, through which the maxillary sinus “receives” air, bacteria, even food particles and, accordingly, becomes inflamed.
Pain due to inflammation of the maxillary sinuses is one of the characteristic signs of the clinical picture of sinusitis (along with nasal congestion, fever, and a nasal voice). They can be localized in different places and indicate both the disease itself and its complications. The mechanism of pain with sinusitis is as follows.
At an early stage, soon after the onset of action of the pathogen, the cause of pain is the direct inflammatory process. With further development of the disease, the mucous membrane swells and partially or completely blocks the anastomosis of the accessory chambers, as a result of which the outflow of fluid worsens or stops completely.
Stagnation of mucus occurs, in which pathogenic bacteria develop, and pus is formed. As the amount of exudate accumulates, it increases, the pressure on the walls of the sinus increases, and the pain becomes more intense and widespread. A characteristic feature of sinusitis is increased pain in the upper jaw when tilting the head forward, this allows it to be differentiated from other sinusitis, such as frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis and sphenoiditis.
A very common situation is when teeth hurt due to sinusitis. This is not surprising, given that the oral cavity and maxillary sinuses are located next door, separated only by a thin partition. Often, due to the individual characteristics of the structure of the human skull, the roots of the upper teeth (apexes) protrude upward and actually end up inside the accessory chambers.
- Rising. In this case, the teeth are the initial source of damage; it is from them that the infection or inflammatory process rises into the sinuses. Depending on the location of the diseased teeth, sinusitis can be right-sided, left-sided or bilateral. At the same time, due to the reverse reaction from the maxillary pockets, the pain in the affected tooth becomes much more intense, and healthy teeth also hurt.
- Descending. The primary source of infection in this development of events is the maxillary sinus. Such situations are diagnosed much more often, they are more typical and predictable: exudate flows into the lower part of the cavities, which are anatomically located below the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw.
The causes of the development of unpleasant sensations are differentiated by time intervals. If first the tooth ached, and then the symptoms of sinusitis appeared, then the process is most likely ascending. If the initial symptom was congestion, runny nose and fever, then a descending process is evident.
How to treat
If, when pressed under the nose, it hits the tooth, headaches occur, or nasal discharge appears, then you need to see a doctor as soon as possible. If the cause of sinusitis is dental disease, then comprehensive treatment will be required. A course of antibiotics (maximum 7 days) can be prescribed by an ENT doctor after the diagnosis is confirmed - inflammation of the maxillary (maxillary) paranasal sinus. Antibacterial drugs are used in the form of drops and tablets. For therapy in complex cases, intramuscular injections may be required. In addition to antibiotics, the patient is prescribed painkillers (Ibuprofen). To eliminate acute intense pain, Ketanov and other potent drugs are prescribed. Toothache due to sinusitis is a fairly common phenomenon. It is very difficult to independently determine the cause of the disease. Therefore, at the first alarming symptoms, you should immediately contact both a dentist and an ENT doctor.
Surgery
It is not always possible to get rid of inflammation in the paranasal sinuses by washing, using antibiotics, or warming procedures. In case of purulent sinusitis, surgical intervention is used:
- in the absence of a positive result for 5 days;
- at high temperature;
- severe headache;
- with swelling of the connecting canal.
The procedure is carried out after anesthesia. The wall of the sinus is pierced with a thick needle. An antiseptic is injected with a syringe and the pus is removed.
After a sinus puncture, the person’s condition improves and the pain goes away. Treatment is continued with physiotherapeutic procedures and rinsing the nasal cavity with antiseptics.
Diagnostics
After collecting anamnesis, a dental examination is required. The specialist must assess the condition of the teeth of the lymph nodes under the upper jaw (presence of pain during palpation, enlargement of the nodes).
If odontogenic sinusitis is suspected, the patient is referred for radiography of the upper jaw. To determine the diagnosis, images are required in three projections:
- panoramic picture of the jaw;
- maxillary sinus;
- upper teeth.
A reliable diagnosis can be made using the following diagnostic methods:
- Endoscopy. The specialist inserts the endoscope into the outlet of the maxillary sinus. With this tool you can evaluate the condition of your sinus.
- Cone beam tomogram.
- Multislice CT.
In addition, laboratory tests are required: blood, urine, and nasal discharge.
How and with what to treat bilateral sinusitis?
When the diagnosis is confirmed, urgent treatment of the pathological process is necessary.
Ways to relieve pain
In case of inflammation of the maxillary sinuses, which is accompanied by toothache, using various therapeutic measures, the unpleasant symptoms of maxillary sinusitis are eliminated, and all possible foci of infection are eliminated in the oral cavity. Antibacterial agents must be included in the treatment regimen. NSAIDs are widely used to relieve pain and eliminate inflammation.
In case of odontogenic sinusitis, the affected tooth is often extracted from the dental alveolus, the purulent fistula is closed, and only then conservative treatment is started:
- rinsing the maxillary sinuses;
- anti-inflammatory therapy;
- physiotherapy.
Having understood the cause of the toothache, the medical institution gives the patient a vasodilator, and then, using a special suction, creates negative pressure in the nasal cavity and accelerates the circulation of the saline solution, which is injected into the adjacent nostril.
Before the procedure, light anesthesia is performed. A catheter, which consists of a body and a cuff, is inserted along the lower part of the nasal canal. This device allows you to create a vacuum inside the nose, which opens the maxillary sinuses.
Surgery
Not in all clinical cases, sinusitis associated with toothache can be eliminated with the help of rinsing, the use of antibacterial agents or physiotherapeutic procedures. If purulent sinusitis develops from a diseased tooth, then surgical intervention is indicated. It is usually prescribed in the following cases:
- lack of positive dynamics for 5 days;
- the patient is in a feverish state;
- there are severe headaches that are not relieved by painkillers;
- The connecting channel swells.
Before starting the procedure, local anesthesia is used. Then the walls of the sinus are pierced with a thick needle. The cavity is filled with an antiseptic and the pus is sucked out. After puncturing the maxillary sinus, the person’s condition noticeably improves and pain is eliminated.
How can you get rid of pain
Sinusitis has characteristic symptoms, so comprehensive treatment must be carried out to improve the patient’s condition. Treatment should be aimed not only at eliminating local symptoms, but also at alleviating the general condition of the patient. Doctors identify three types of therapy that can be used to treat this disease:
- etiological.
- symptomatic.
- preventive.
Etiological therapy is aimed at sanitizing the diseased organ, which, in turn, has a positive effect on the root cause of the disease. The most common treatment is medication, which can be taken either orally or by injection. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often used in the treatment of sinusitis . The doctor may prescribe Ibuprofen, Diclofenac or Aspirin. Nasal rinsing using special devices, for example, a Yamik catheter, helps a lot.
When conservative methods are ineffective, surgical intervention is resorted to. In this case, the maxillary sinus is pierced, the purulent contents are pumped out and the cavity is washed with an antiseptic solution. After such manipulation, the patient’s general condition improves and the pain goes away.
Symptomatic therapy is used when you need to quickly relieve pain. For this purpose, strong analgesics are most often used. The doctor may prescribe Analgin, Tempalgin, Ibuprofen and Nise. If your teeth hurt very badly, Ketanov may be prescribed. The frequency of taking medications depends on the intensity of the toothache. If your teeth hurt slightly, then taking the medicine just once is enough, otherwise you can take painkillers up to 3 times a day.
Rinsing with hot water with salt and soda is good for toothache. For a glass of water, take half a teaspoon of soda and salt.
Preventative therapy is aimed at preventing the disease. It is necessary to carefully care for the nasal and oral cavities, and promptly treat all infectious diseases and dental diseases. Strengthening the immune system and proper nutrition play an important role.
During an outbreak of respiratory diseases, doctors recommend taking vitamin complexes to increase the body's defenses.