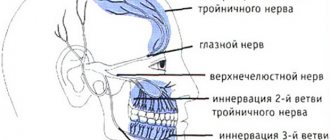
Trigeminal neuralgia is a pathology that is accompanied by sharp pain attacks with a burning character, in some cases piercing symptoms are felt. The pain appears suddenly and then disappears. To get rid of pain, Finlepsin is used for trigeminal neuralgia.
The main symptom of this pathology is pain in the area of the affected branch of the nerve.
About the composition and released form
The main component of the drug is Carbamazepine; in addition, the drug includes other components:
- Gelatin.
- Magnesium stearate.
- Cellulose.
Retard tablets include:
- Polymer methacrylate.
- Talc.
- Crospovidone.
The medicine is produced in the form of tablets that have a prolonged effect. Purchase is possible in different dosages of the active substance, namely 200 and 400 mg.
Finlepsin in factory packaging
Indications for use
Based on the instructions for the drug, you can determine the factors when Finlepsin is used:
- For epileptic seizures, which are accompanied by severe convulsions.
- When physical or mental disorders appear after quitting alcohol.
If you use the drug as a pain reliever, the indications for use will be as follows:
- Trigeminal neuralgia.
- Diabetic neuropathy, with severe pain.
- Phantom pain.
- Restless legs syndrome.
- Before a migraine attack.
Finlepsin can be used in the following cases:
- Affective or psychotic disorder.
- Depression.
- Extraneous noise in the ears.
- Somatic failures.
- Stopping certain medications or quitting drugs.
Medicines indicated for antidiuretic action:
- For diabetes insipidus.
- In the event of renal failures and disorders of the psychophysical development of children that are not caused by hormonal levels.
To avoid complications after taking the pills, it is necessary to exclude self-treatment. The drug must be prescribed by a doctor.
Finlepsin: instructions for use for trigeminal neuralgia, toothache
For patients suffering from trigeminal neuralgia, toothache, and convulsive conditions, the doctor may advise taking Finlepsin. The drug acts as an antipsychotic, is effective for epilepsy in people of all ages, and can be used as a pain reliever. Produced in tablet form by pharmaceutical companies in Germany and Israel.
Composition of the drug
The only active component of the drug is a substance called “Carbamazepine”, each tablet contains only 200 mg. In addition to Carbamazepine, the drug contains a number of additional components: magnesium stearate, croscarmellose sodium, gelatin and microcrystalline cellulose.
Finlepsin for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Both adults and children over one year of age can take this medication if trigeminal neuralgia has developed.
The drug has a noticeable analgesic effect, so doctors often recommend it for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve (we recommend reading: drug treatment for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve).
Adults are prescribed 0.5 - 1 tablet twice a day. The dosage is gradually increased to 2 - 4 tablets twice a day.
READ ALSO: how and where the trigeminal nerve is located on the face: photo
The course of treatment continues until the pain completely disappears. After this, treatment continues with a reduced maintenance dosage of 2 tablets per day, divided into two doses. On the recommendation of a doctor, the course can be supplemented with acupuncture.
For toothache
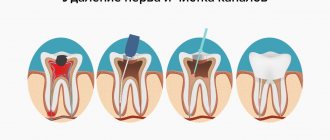
It is permissible to use the drug in question for toothache as prescribed by a doctor. Dental diseases are not listed among the direct indications, but the fact that the medicine is positioned as an analgesic allows it to be taken to relieve pain syndromes.
Many dentists recommend taking Finlepsin for a number of dental diseases, for example, for pain caused by pulpitis. The average dosage is 1 tablet three times a day. The product promotes some normalization of the condition and calms the nerve. It should be taken into account that taking these tablets slows down the reaction rate and drowsiness may occur.
Other diseases
The drug shows high effectiveness in relieving and preventing epilepsy attacks - both simple and complex. When taking medications containing carbamazepine, you should avoid drinking alcohol. It is also not recommended to drive before completing the therapeutic course due to the development of drowsiness and reduced reaction speed.
| Daily dosage | Psychosis | Convulsions | Diabetic neuropathy | Alcohol withdrawal | Note |
| Initial | 1 – 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | For psychosis, the daily dose of the drug is divided into 2 doses, for convulsions, neuropathy and withdrawal symptoms - into 3 doses. |
| Supportive | |||||
| Maximum | 4 | 6 | 6 |
The regimen for using the drug in the treatment of epilepsy will differ from the instructions for its use in the treatment of other pathologies. In this case, the direct influence on determining the quantity and frequency of taking tablets directly depends not only on the characteristics of the condition and course of the disease, but also on the age of the patient.
| Age, years | Dosage | Note | |
| Initial | Supportive | ||
| 1 — 5 | 0.5 pcs. 1–2 r. / day | 1 tab. 1 – 2 r. / day | The dosage can be reduced or discontinued only on the recommendation of the attending physician if seizures are completely free for 3 years. |
| 6 – 10 | 0.5 pcs. 1–2 r. / day | 1 tab. 3 r. / day | |
| 11 – 15 | 0.5 pcs. 1–2 r. / day | 1 tab. 3 - 5 rub. / day | |
| 16 and older | 1 PC. 1–2 r. / day | 1 - 2 tab. 2 r. / day |
Contraindications and side effects
Taking Finlepsin is contraindicated for patients suffering from disorders of bone marrow hematopoiesis, acute intermittent porphyria, and atrioventricular block.
This medicine cannot be recommended to patients with hypersensitivity to tricyclic antidepressants or components of the drug. It is not allowed to prescribe Finlepsin simultaneously with MAO inhibitors or lithium preparations.
With caution, under the supervision and control of the attending physician, Finlepsin can be prescribed in the following cases:
- prostatic hyperplasia,
- decompensated chronic heart failure,
- active alcoholism,
- dilution hyponatremia,
- liver or kidney failure,
- elderly age.
Taking this medication has a negative impact on the effectiveness of oral contraception; for this reason, patients of fertile age should use additional means and methods to prevent unwanted pregnancy until the end of therapy.
When deciding whether it is admissible to use Finlepsin to treat a woman during gestation, the doctor should be based on a comparison of possible complications and expected benefits.
If a woman takes this drug during the first 12 weeks of gestation, the risk that the fetus will develop NVD increases significantly.
A patient who is planning a pregnancy while taking Finlepsin should be informed about this, as well as in cases where conception occurred before the end of the course of treatment.
The possibility of undergoing antenatal diagnostics and the need for this study should also be explained by the attending physician.
The medicine provokes a deficiency of folic acid, therefore, before pregnancy and during pregnancy, additional use of medications containing this substance is recommended. In the final trimester, it is recommended to take vitamin K1 (it is often recommended for newborns) to prevent increased bleeding.
The development of side effects when taking Finlepsin is usually observed in case of irregular use of the medication (then the concentration of the active substance in the patient’s body undergoes sharp fluctuations) or when the recommended dosage is exceeded.
Disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, hematopoietic and endocrine systems may occur, and metabolism may also be disrupted.
There is a possibility of developing dysfunction of the sensory organs, musculoskeletal system, genitourinary and cardiovascular systems.
Analogs
Replacing the prescribed drug with an analogue is possible only with the agreement of the attending physician. If we consider matches by level 4 ATC code, then the main analogues of the drug in question include Carbamazepine and Tegretol. Carbamazepine is indicated for patients diagnosed with epilepsy; it also has a psychotropic effect.
Neuralgia of various etiologies is also one of the indications for taking the medicine. Tegretol is an anticonvulsant drug that has a neurotropic and psychotropic effect. Available in tablet form, it is indicated for trigeminal neuralgia. Also among the analogues of the drug are Actinerval, Zeptol, Storilat.
Loading…
Source: https://spacream.ru/stomatologiya/finlepsin-instrukcziya-po-primeneniyu-pri-zubnoj-boli-i-nevralgii-trojnichnogo-nerva
Instructions and dosage
For trigeminal neuralgia, Finlepsin can relieve a person from cramps, pain, and also has an effect on the general normalization of the body and improving the patient’s mood. The medicine is used not only to treat the underlying disease; it can be combined with other drugs.
Finlepsin can be used for both conventional treatment and complex treatment, which is supplemented by paroxysms. Symptoms such as anxiety and nervousness disappear in people after taking the pills.
The effect of the active substance is long-lasting and occurs several hours after consumption. In practice, cases have been recorded when the drug has an effect for 20-30 days.
If you take Finlepsin for neuralgia, patients indicate an improvement in their condition. Discomfort and pain disappear approximately 8 hours after taking the drug or 3 days after starting to use the medicine. The product also helps with injuries that cause pain and other symptoms.
The action of the tablets is long-lasting and maintains blood flow properties. In this regard, the dosage of Finlepsin for trigeminal neuralgia may be reduced, but the therapeutic effect will remain the same. You should take 1-2 tablets per day, depending on the severity of the disease. The exact dosage can be indicated by your attending physician.
You need to take 1-2 tablets a day
FINLEPSIN
Anticonvulsant
Release form, composition and packaging
Pills
white, round, chamfered, convex on one side and with a mark in the form of a wedge-shaped recess on the other.
| 1 tab. | |
| carbamazepine | 200 mg |
Excipients: microcrystalline cellulose – 60 mg, gelatin – 11 mg, croscarmellose sodium – 6 mg, magnesium stearate – 3 mg.
10 pieces. – blisters (5) – cardboard packs.
pharmachologic effect
An antiepileptic drug (dibenzazepine derivative), which also has antidepressant, antipsychotic and antidiuretic effects, has an analgesic effect in patients with neuralgia.
The mechanism of action is associated with the blockade of voltage-gated sodium channels, which leads to stabilization of the membrane of overexcited neurons, inhibition of the occurrence of serial neuronal discharges and a decrease in synaptic conduction of impulses.
Prevents the repeated formation of Na+-dependent action potentials in depolarized neurons. Reduces the release of the excitatory neurotransmitter amino acid glutamate, increases the reduced convulsive threshold of the central nervous system and, thus, reduces the risk of developing an epileptic attack.
Increases K+ conductivity, modulates voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, which may also contribute to the anticonvulsant effect of the drug.
Effective for focal (partial) epileptic seizures (simple and complex), accompanied or not accompanied by secondary generalization, for generalized tonic-clonic epileptic seizures, as well as for a combination of these types of seizures (usually ineffective for petit mal seizures, absence seizures and myoclonic seizures ). In patients with epilepsy (especially children and adolescents), a positive effect on symptoms of anxiety and depression, as well as a decrease in irritability and aggressiveness, was noted. The effect on cognitive function and psychomotor performance is dose dependent. The onset of the anticonvulsant effect varies from several hours to several days (sometimes up to 1 month due to autoinduction of metabolism).
In case of essential and secondary trigeminal neuralgia, carbamazepine in most cases prevents the occurrence of painful attacks. Pain relief from trigeminal neuralgia is observed after 8-72 hours.
In alcohol withdrawal syndrome, it increases the threshold of convulsive readiness, which in this condition is usually reduced and reduces the severity of the clinical manifestations of the syndrome (increased excitability, tremor, gait disturbances).
The antipsychotic (antimanic) effect develops after 7-10 days and may be due to inhibition of the metabolism of dopamine and norepinephrine.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
Absorption is slow but complete (food intake does not significantly affect the speed and extent of absorption). After a single dose of the tablet, Cmax is reached after 12 hours. The average Cmax value of the unchanged active substance after a single dose of carbamazepine at a dose of 400 mg is about 4.5 mcg/ml. The time to reach Cmax is 4-5 hours.
Distribution
Css of the drug in plasma are achieved in 1-2 weeks (the speed of achievement depends on the individual characteristics of metabolism: autoinduction of liver enzyme systems, heteroinduction by other simultaneously used drugs), as well as on the condition of the patient, the dose of the drug and the duration of treatment.
There are significant interindividual differences in Css values in the therapeutic range: in most patients these values range from 4 to 12 μg/ml (17-50 μmol/l). Concentrations of carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide (a pharmacologically active metabolite) are approximately 30% of those of carbamazepine.
Plasma protein binding in children is 55-59%, in adults – 70-80%. Apparent Vd – 0.8-1.9 l/kg. In the cerebrospinal fluid and saliva, concentrations are created in proportion to the amount of active substance not bound to proteins (20-30%). Penetrates through the placental barrier.
The concentration in breast milk is 25-60% of that in plasma.
Metabolism
Metabolized in the liver, mainly along the epoxide pathway with the formation of the main metabolites: active - carbamazepine-10.11-epoxide and inactive conjugate with glucuronic acid.
The main isoenzyme that ensures the biotransformation of carbamazepine into carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide is cytochrome P450 (CYP3A4). As a result of metabolic reactions, a low-active metabolite 9-hydroxy-methyl-10-carbamoylacridan is also formed.
Can induce its own metabolism. The concentration of carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide is 30% of the concentration of carbamazepine.
Removal
T1/2 after taking a single oral dose is 25-65 hours (on average about 36 hours), after repeated doses, depending on the duration of treatment - 12-24 hours (due to autoinduction of the liver monooxygenase system).
In patients receiving additional anticonvulsants that are inducers of the monooxygenase system (phenytoin, phenobarbital), T1/2 averages 9-10 hours. After a single oral dose of carbamazepine, 72% of the dose taken is excreted in the urine and 28% in the feces.
About 2% of the dose is excreted in the urine as unchanged carbamazepine, about 1% as the 10,11-epoxide metabolite.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In children, due to accelerated elimination, relatively higher doses of the drug per kg of body weight may be required compared to adults.
There are no data on changes in the pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine in elderly patients.
Dosage
The drug is prescribed orally, during or after meals, with a sufficient amount of liquid.
Epilepsy
Where possible, Finlepsin should be prescribed as monotherapy.
The addition of Finlepsin to already ongoing antiepileptic therapy should be carried out gradually, with the doses of the drugs used adjusted if necessary.
If the patient forgot to take the next dose of the drug in a timely manner, the missed dose should be taken as soon as this omission became noticed, and a double dose of the drug should not be taken.
Adults
The initial dose is 200-400 mg (1-2 tablets)/day, then the dose is gradually increased until the optimal effect is achieved. Maintenance dose – 800-1200 mg/day, divided into 1-3 doses per day.
The maximum daily dose is 1.6-2 g.
Children
If the child is unable to swallow the tablet whole, it can be chewed, crushed, or shaken in a small amount of water.
Initial dose for children aged 1 to 5 years
– 100-200 mg/day, then the dose is gradually increased by 100 mg/day until the optimal effect is achieved;
for children from 6 to 10 years old
– 200 mg/day, then the dose is gradually increased by 100 mg/day until the optimal effect is achieved;
for children from 11 to 15 years old
– 100-300 mg/day, then the dose is gradually increased by 100 mg/day until the optimal effect is achieved.
Maintenance doses: for children aged 1-5 years
– 200-400 mg/day (in several doses),
6-10 years
– 400-600 mg/day (in 2-3 doses);
11-15 years
– 600-1000 mg/day (in 2-3 doses).
The recommended dosage regimen is presented in the table.
| Age | Initial dose | Maintenance dose |
| Adults | 1 tab. 1 time/day | 1-2 tab. 3 times/day |
| Children from 1 year to 5 years | 1/2 tab. 1-2 times a day | 1 tab. 1-2 times a day |
| Children from 6 to 10 years old | 1/2 tab. 2 times/day | 1 tab. 3 times/day |
| Children from 11 to 15 years old | 1/2 tab. 2-3 times/day | 1 tab. 3-5 times/day |
The duration of use depends on the indication and the patient’s individual response to the drug. The decision to transfer the patient to Finlepsin, the duration of its use and discontinuation of treatment is made by the doctor individually. The possibility of reducing the dose of the drug or stopping treatment is considered after a 2-3-year period of complete freedom from seizures.
Treatment is stopped, gradually reducing the dose of the drug over 1-2 years, under EEG monitoring. In children, when reducing the daily dose of the drug, the increase in body weight with age should be taken into account.
Trigeminal neuralgia, idiopathic glossopharyngeal neuralgia
The initial dose is 200-400 mg (1-2 tablets), which is increased to 400-800 mg (2-4 tablets) in 1-2 doses, until the pain completely disappears. In a certain proportion of patients, treatment can be continued with a lower maintenance dose of 200 mg (1 tablet) 2 times a day (corresponding to 400 mg/day).
Elderly patients
and for patients with hypersensitivity, Finlepsin is prescribed at an initial dose of 100 mg (1/2 tablet) 2 times a day (corresponding to 200 mg/day).
Treatment of alcohol withdrawal in a hospital setting
The average daily dose is 200 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day (corresponds to 600 mg/day). In severe cases, in the first days the dose can be increased to 400 mg (2 tablets) 3 times / day (corresponding to 1200 mg / day).
If necessary, Finlepsin can be combined with other substances used to treat alcohol withdrawal.
Treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome with Finlepsin is stopped, gradually reducing the dose over 7-10 days.
During treatment, it is necessary to regularly monitor the content of carbamazepine in the blood plasma.
Due to the possible development of adverse reactions from the central and autonomic nervous system, patients are closely monitored in a hospital setting.
Diabetic neuropathy pain
The average daily dose is 200 mg (1 tablet) 3 times/day (corresponds to 600 mg/day). In exceptional cases, Finlepsin can be prescribed 400 mg (2 tablets) 3 times a day (corresponding to 1200 mg/day).
Epileptiform seizures in multiple sclerosis
The average dose is 200 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day (corresponds to 600 mg/day).
Treatment and prevention of psychosis
The initial dose and maintenance dose are usually the same: 200-400 mg (1-2 tablets)/day. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 400 mg (2 tablets) 2 times / day (corresponds to 800 mg / day).
When assessing the frequency of occurrence of various adverse reactions, the following criteria were used: very often (≥10%), often (≥1%, but
How to use for pregnant and lactating women
Regarding the use of the medicine during pregnancy, it is not recommended to take Finlepsin in the first trimester, since the formation of the fetus is disrupted, a lack of folic acid appears, which leads to birth defects of the child.
In the second trimester, the use of tablets is possible only as prescribed by a doctor, based on the diagnosis of the pregnant woman, the condition of the fetus and mother.
If you are breastfeeding, it is not recommended to use the medicine, because the substances pass into the milk and children may develop a skin rash, lethargy and fatigue. It is recommended to transfer children to artificial feeding.
How to combine with different products
It is strictly forbidden to use Finlepsin with drugs that can inhibit monoamine oxidase. It is necessary to abandon such treatment a couple of weeks before starting to use Finlepsin, so that side effects and even death do not appear. With other drugs and substances the combination will be as follows:
- If you use hormonal drugs, their effect on the body will be significantly reduced.
- When using lithium drugs, liver destruction occurs.
- If you immediately take medications with tetracycline, the seizures may not stop.
- Paracetamol and similar drugs will increase the load on the liver as a result of its damage by toxins.
- The use of diuretics leads to a lack of sodium in the body, which causes a number of disorders.
Before prescribing Finlepsin for trigeminal neuralgia, the doctor should find out about all previously used medications.
Diagnostics
Before treating inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, it must be diagnosed and separated from other possible diseases. The symptoms of neuralgia are similar to frontal sinusitis, dental pathologies, otitis media and sinusitis.
To do this, during a consultation, a neurologist conducts an initial examination, listens to complaints and identifies possible symptoms. To determine the cause of the disease, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is performed. This allows you to see the structure of the nerves, existing vascular pathologies and tumors, and their localization if present.
Diagnostic methods include the following procedures:
- consultation with a dentist to identify possible dental diseases, poor-quality filling or removal, unsuccessful prosthetics;
- X-rays of the skull and teeth allow you to see the pinching of the facial nerve and the formations that caused it;
- to determine the nature of the passage of impulses along the nerve, electromyography is performed;
- To exclude viruses that cause the disease, the patient must undergo a blood test.
Side effects
After taking Finlepsin, some patients experience lethargy and drowsiness.
After using the tablets, people may experience side effects, including:
- Dizziness and headaches.
- Failures in coordination.
- Involuntary movements of the eyes and body.
- Lethargy, fatigue.
- Depression, hallucinations.
- Aggressive behavior.
- Malfunctions of taste buds.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Noise in ears.
- Stool disorders, such as diarrhea or constipation.
- The appearance of nausea followed by vomiting.
- Loss of appetite.
- Inflammation of the mucous membranes in the mouth and tongue.
- Development of heart pathologies.
- Malfunctions of the vascular system.
- Swelling of the extremities as a result of impaired fluid removal.
- Weight gain.
- Thyroid gland dysfunction.
- Kidney failure.
- Pneumonia.
- Rash and itching on the skin.
- Fever.
- Joint pain.
As you can see, there are a lot of side effects, which is why it is important to take the pills only with the doctor’s permission and in the dosage prescribed by him.