Even scientists are still arguing about how the trigeminal nerve is treated.
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve (neuralgia) is a common disease that affects both sexes, but it mainly affects women over 50 years of age.
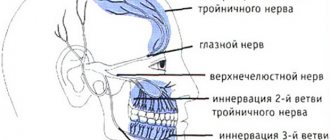
The trigeminal nerve is located on both sides of the face and has three branches.
- The first of them is responsible for the forehead, eyebrows and upper eyelid.
- the second - for the lower eyelid, nose, cheeks and upper jaw.
- the third branch, the very last - behind the bottom.
Thanks to the trigeminal nerve, a continuous connection with the central nervous system is ensured. Which is responsible for muscle movement, sensitivity of the skin and mucous membranes.
There are various drugs and traditional medicines.
You can find out which of them are more effective from our article.
Causes of nerve inflammation
The main reasons contributing to the development of inflammation are considered to be:
- Hypothermia of the face,
- Head injury,
- Nerve compression due to vascular diseases and tumors,
- Multiple sclerosis,
- Oral diseases, etc.
Inflammation can be primary, for example, as a result of hypothermia, and secondary, i.e. be a consequence of ENT diseases and brain diseases.
Healing tea against inflammation
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, treatment at home which is aimed at getting rid of the inflammatory process and maintaining a weakened immune system, can be treated with medicinal herbs. You need to mix 100 grams of lavender flowers and 150 grams of St. John's wort herb. The resulting mixture must be poured with boiling water (1 tbsp.
spoon per 1/2 liter of liquid), leave for 15-20 minutes, then filter. Take the resulting tea warmly twice a day, 200 ml, until the alarming symptoms disappear. In the home treatment of facial nerve disease, chamomile tea will also help, for the preparation of which one spoon of dry raw material needs to be brewed with boiling water in the amount of 1 cup.
It is necessary to take it into your mouth and hold it for a while without swallowing.
Symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is difficult to overlook. Its symptoms are pronounced and may not go away for a long time:
- Acute paroxysmal pain, localized on one side and reminiscent of toothache or electric shock, lasts 1-2 minutes.
- Facial hyperemia, impaired vision, hearing and taste.
- Paralysis of facial muscles.
- Increased salivation and lacrimation.
In the absence of timely help, attacks become longer and recur more often.
Attention! Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic disease.
A provoking factor in an exacerbation can be improper installation of dentures, treatment or removal of a tooth, and even laughter.
Complications of inflammation of the trigeminal facial nerve include further inflammation and swelling. Which can lead to:
- to pinching of the facial nerve;
- violations of movement coordination;
- hearing loss.
Causes of the disease
Before starting treatment for inflammation of the facial nerve, it is necessary to find out the cause of its occurrence. This will help you prescribe treatment as correctly as possible. Facial neuritis can occur as a result of inflammation of the middle ear. Sometimes the disease is the result of injuries to the base of the skull, ear or face. The presence of infectious diseases of the face and ear also leads to neuritis of the facial nerve.
The disease can occur as a result of intoxication, hypothermia, or improper actions of the dentist. If blood circulation is impaired, this disease also develops against the background of a cold. Diagnosis of facial nerve neuritis consists of identifying the causes to eliminate which treatment is directed.
Symptoms of the disease
The facial nerve is responsible for the activity of the facial muscles. When it becomes inflamed, a person experiences a feeling of stiffening of the face. The patient's appearance during this period deteriorates significantly. His face becomes distorted and the corners of his mouth droop on one or both sides. If the facial nerve is inflamed on one or both sides, then the eyelids of the corresponding eye open wide and the patient cannot close them.
The presence of the disease can be judged by the numbness of the face. A person loses the ability to control facial muscles. Some patients complain of increased sensitivity to loud sounds and changes in taste sensations. The presence of tinnitus and pain in this area are also a symptom of the disease. Patients complain of hearing loss. The disease can cause watery or dry eyes. Some patients with this disease experience scanty salivation, while others experience excessive salivation.
The appearance of these symptoms indicates the close location of the facial nerve to the intermediate and auditory nerves. With severe inflammation of the facial nerve, these nerves are also involved in the pathological process. During neuritis, a person experiences acute pain in the facial area. The pain is characterized by paroxysmal pain. It appears in the following areas of the face:
- lips;
- gum;
- jaws;
- language.
With neuritis of the facial nerve, pain can occur as a result of talking, brushing teeth, or strong emotions. When this disease appears, the patient cannot live a full life. The slightest movements of the facial muscles cause him discomfort.
During active treatment of facial nerve neuritis, as well as in severe forms of the disease, watching TV and the load on the facial muscles is better to reduce. This will help avoid excessive tearing, tension in the facial muscles and, accordingly, speed up the healing process.
Important! Only a doctor can establish an accurate diagnosis after a comprehensive examination.
Treatment of the trigeminal nerve with drugs
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using a visual examination. Sometimes a CT scan or MRI may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Self-prescription of drugs is strictly prohibited.
The peculiarity of therapy is to detect and eliminate the cause that caused neuralgia.
Most often, doctors prescribe anticonvulsants.
At the beginning of treatment, anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers and antispasmodics are used.
If necessary, sedatives may be needed.
When pain cannot be relieved with analgesics, a specialist may prescribe narcotics.
Physiotherapy can help reduce pain: ultraviolet irradiation, UHF, electrophoresis, laser therapy.
If conservative therapy fails, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Important! Prescription of drugs and duration of administration should only be carried out by a specialist, taking into account the characteristics of the body.
Medicinal alcohol tincture
Treatment of the trigeminal nerve of the face at home is a set of measures, including drug therapy, massage and heating, aimed at relieving inflammation and normalizing the sensitivity of the facial apparatus. Self-therapy should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor after an accurate diagnosis of the disease and initial treatment in a medical institution.
Treatment of the facial trigeminal nerve at home is effective through the use of massage, which must be done very carefully, since touching sensitive points can cause a wave of unbearable pain. It is recommended to massage the neck in a circular motion on the painful side, starting from the shoulders and moving towards the chin.
With mild and moderate forms of trigeminal neuritis (that is, with not very acute symptoms), the face can be massaged from the center to the outer part - along classic massage lines. To obtain a more effective result, it is recommended to use massage oil. You can prepare it yourself using bay leaves.
100 grams of fresh or dried product must be filled with 0.5 liters of any vegetable oil, left for a week, strained and used as directed. If it is not possible to massage, it is recommended to lubricate the skin in the area where the trigeminal nerve is located with this product. Treatment at home, reviews of which are positive, is possible only after consultation with a doctor, which is necessary to avoid possible complications.
In older people, as we have already said, the trigeminal nerve becomes inflamed quite often. Treatment at home, according to patients, ensures a quick recovery. In particular, rubbing alcohol helps a lot. You need to take 50 grams of dried plantain raw material, pour it into a glass container and pour a glass of vodka.
Close the jar and leave the healing agent in a dark place for 7 days. The prepared solution should be rubbed onto the painful area. It is recommended to perform these steps before going to bed. Then you should tie a warm down scarf around your head, while trying to carefully wrap your face, and sleep in it until the morning. According to reviews from patients who have used this method, the facial nerve will restore its functions after approximately 6-10 treatment sessions.
Treatment of the trigeminal nerve with folk remedies
The opinion that inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can be cured only with the help of folk remedies is fundamentally wrong.
Trigeminal neuralgia is a dangerous disease that can be caused by brain tumors and vascular diseases.
Traditional medicine can only be an addition aimed at alleviating symptoms, to the main therapy or as a preventive measure.
Treatment at home should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
If it is not possible to quickly consult a doctor, the following recipes can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation:
- Warm chamomile tea . A packet of chamomile is brewed in a glass of boiling water and cooled to 30-40°. Keep the infusion in your mouth without swallowing until it cools completely.
- You can relieve pain with warm dry compresses ; an egg is great for this purpose. A warm egg is applied to the sore spots through gauze or a scarf. You can replace it with dry buckwheat heated in a frying pan.
- Fir oil . A tampon soaked in fir oil is applied to the painful area or rubbed in; the procedure should be carried out during the period of exacerbation of pain 5-6 times a day.
- Geranium leaves . They are applied to the areas where the pain has become active, tied with a scarf and left for 2-3 hours, then the leaves are changed. If you don’t have geranium leaves on hand, you can replace them with cabbage leaves.
- Lubricate the site of inflammation of the ternary nerve with “Golden Star” (“Star”) ointment.
- Garlic oil is an effective homeopathic remedy, sold in pharmacies. It is rubbed into the affected areas.
- Black radish juice must be rubbed into the area where the nerve is located.
Treatment is medicinal
Drug treatment of facial nerve neuritis is carried out according to a specific scheme. Depending on the cause of the disease and its period, different remedies are effective:
- glucocorticoids – Prednisolone, which has a strong anti-inflammatory effect;
- antiviral drugs;
- B vitamins – help improve the functioning of nerve fibers;
- vasodilators - Nicotinic acid, Complamin - improve blood circulation;
- decongestants – Furosemide, Triampur – to reduce edema and prevent the progression of pathological changes;
- painkillers – Indomethacin;
- anticholinesterase drugs - Prozerin, Galantamine - to improve the conductivity of nerve fibers;
- medications that stimulate metabolic processes - Nerobol.
Prozerin
Prozerin is an anticholinesterase drug. It helps improve signal conduction along nerve fibers to muscles, which increases their tone and restores the functions of the affected nerve. Prozerin is prescribed from the second week of treatment, one tablet 1-2 times a day, thirty minutes before meals. The course is a month and a half. If contracture of the facial muscles appears, the drug is discontinued.
A nicotinic acid
Nicotinic acid is a vasodilator vitamin. Prescribed to improve blood circulation in the area of the inflamed nerve. Nicotinic acid also regulates metabolic processes. The drug is prescribed in the form of tablets or injections. Orally – 0.025–0.05 grams 2–3 times a day after meals for a month. Intramuscularly administer 0.002–0.003 g per 1 kg of body weight once a day.
Antibiotics for neuritis
Antibiotics for the treatment of facial neuritis are prescribed in case of bacterial infection. The best effect will be with intramuscular administration of antibiotics, since oral administration reduces and slows down the effect of the drug. In such cases, Amoxiclav or Claforan are prescribed. The need to use antibiotics in each individual case is determined by the attending physician after identifying the cause of neuritis.