What is trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia (trigeminal neuralgia) is a lesion of one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve, characterized by paroxysmal pain.
In 65% of cases, women over 50 years of age are affected. The disease occurs in 2 forms: primary (isolated damage to the nerve itself) and secondary (as a consequence of another disease). The trigeminal nerve is part of 12 pairs of cranial nerves. Its purpose is to provide facial sensitivity. This nerve runs on both sides of the face (right and left), and in turn is divided into 3 bundles: the first (ophthalmic) innervates the eye, upper eyelid and forehead; second (maxillary) - lower eyelid, cheeks, nostrils, upper lip and gums; third (mandibular) - lower jaw, lips and gums.
The pathological process is triggered when a nerve is compressed, pinched or irritated at its exit from the brain. As a result, the nerve root is “exposed” (dimyelinated) and reacts to any impact, sending impulses to the brain. He, in turn, reacts with a portion of intense pain impulses.
Trigeminal neuralgia is a difficult pain for humans to bear. Due to frequent attacks, patients develop stress, depression, insomnia and even mental disorders.
Further treatment
It should be remembered that all home recipes aimed at eliminating toothache associated with nerve damage are temporary measures. They certainly alleviate the patient’s condition, but cannot cure the disease that provoked this phenomenon. That is why people suffering from severe pain due to nerve irritation need to consult a dentist the very next day after the onset of such a symptom. The doctor will determine the cause of the disease and prescribe qualified treatment. In some cases, it may even involve removing the nerve. Self-medication can lead to complications.
In general, relieving pain caused by an irritated nerve at home is not that difficult. To do this, it is enough to use a folk recipe or a pharmaceutical remedy, and you can get rid of the unpleasant sensations for the next few hours.
Read also: Wisdom tooth bad breath
Causes of trigeminal neuralgia
Still not known for sure. Scientists identify factors that trigger the pathological process:
- pinching of the nerve fiber by vessels at the point of its exit from the skull;
- cerebral aneurysms;
- pathological tortuosity of the cerebral arteries;
- Devic's neuromyelitis optica;
- disseminated encephalomyelitis;
- hypothermia;
- sinusitis;
- caries;
- brain tumors;
- multiple sclerosis;
- meningitis;
- herpetic infection;
- colds;
- facial injuries;
- gingivitis;
- pulpitis;
- osteomyelitis;
- pregnancy;
- traumatic tooth extraction;
- stress.
Reasons that provoke an attack of pain:
- touching the face;
- shaving;
- teeth cleaning;
- chewing and swallowing food;
- movement of the jaws when speaking;
- smile;
- wind;
- pungent odors (paint, ammonia);
- applying makeup.
Causes of inflammation of the dental nerve or pulpitis
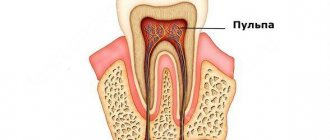
The main reason for the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the pulp is the entry of infections into the internal dental tissues, which in a closed state are absolutely sterile. How can bacteria get there?
Why can a nerve become inflamed?
- An advanced form of caries, when the destruction of dentin exposes the pulp. In this case, treatment is carried out in several stages, and depulpation is possible. Read more information about the technology for treating dentin caries here.
- Unprofessional dental care is the introduction of infection into the dental cavity during the treatment of caries.
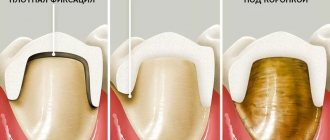
- Incorrect grinding of the abutment tooth when installing crowns or orthodontic structures.
- Mechanical damage, including fractures, breaks, chips, cracks in the teeth.
- The occurrence of retrograde infections, which can enter the tooth through a destroyed root, even if the integrity of the crown is preserved. Such an inflammatory process can be caused by an exacerbation of sinusitis, periodontitis, or the presence of osteomyelitis.
- Through the blood, if there is an infectious blood poisoning. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the pulp through the root or inflamed gum pocket, which provokes acute pain and the development of the disease.
Symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia
- sudden paroxysmal one-sided very intense (burning, shooting) pain along the nerve fiber;
- immobility of the patient;
- facial muscle spasm;
- attack duration is up to 3 minutes, in 7% of patients - up to 3 days;
- frequency of attacks 1-10 per day;
- the pain doesn’t go anywhere;
- excessive drooling and lacrimation;
- dilated pupils;
- decreased or increased sensitivity of facial skin;
- in 99% of cases the attack occurs during the day.
Treatment of vagus nerve damage
Treatment is prescribed only after confirmation of the diagnosis by a medical specialist. It is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease; Prednisolone, vitamins, antihistamines, anticholinesterase drugs are indicated; plasmapheresis. Differential diagnosis:
- Tumors and cerebrovascular disorders in the medulla oblongata.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
- Herpes zoster.
- Tumors of the lungs, thyroid gland, esophagus.
- Left atrial hypertrophy.
- Aneurysm of the aortic arch.
Essential drugs
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
- Prednisolone (systemic GCS). Dosage regimen: the average oral dose for adults is 5-60 mg/day. in 3-4 doses. The maximum daily dose is 200 mg.
- Milgamma (B complex of vitamins). Dosage regimen: therapy begins with 2 ml intramuscularly 1 time per day for 5-10 days. Maintenance therapy - 2 ml IM two or three times a week.
- Prozerin (inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase and pseudocholinesterase). Dosage regimen: orally for adults, 10-15 mg 2-3 times a day; subcutaneously - 1-2 mg 1-2 times a day.
- Diphenhydramine (antihistamine, sedative, hypnotic). Dosage regimen: 1–5 ml of 1% solution intramuscularly; orally 0.025–0.05 g 1-3 times a day. The course of treatment is 10-15 days.
Diagnosis of trigeminal neuralgia
A neurologist makes a diagnosis after examining and interviewing the patient. Carrying out MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) allows you to clarify the causes of the disease (neoplasms, areas of multiple sclerosis, etc.).
Additionally, electroneuromyography and radiography of the jaws are prescribed. Laboratory tests include a blood test for the presence of the herpes virus. The disease is differentiated from Ernst syndrome, occipital neuralgia, temporal tendonitis, and temporomandibular joint dysfunction.
How to relieve pain and relieve inflammation?
Inflammatory processes often lead to severe pain. You need to know how to quickly relieve pain and calm the dental nerve, if a person is at home.
Read also: Tooth rotting
There are several effective techniques that can quickly and for a long period of time calm the nerve and relieve acute pain.
First aid is limited to taking painkillers. Dental drops will most effectively cope with the task.
If they are not in your home medicine cabinet, you can use analgesics that will relieve or reduce the painful manifestations of inflammation.
If the cause of the pain is a mechanical impact, it is necessary to rinse your mouth with water to get rid of tooth fragments, carry out hygiene procedures to remove food debris, and consult a dentist.
If the cause of the disease is inflammation of the gums, then in addition to brushing your teeth, you should rinse your mouth with a warm decoction of sage and chamomile - this will help prevent the development of microorganisms.
Traditional methods for independent use
Most often, at home, people resort to traditional methods of dealing with pain. Among the most common and effective are the following types of assistance:
- using a lotion of water and hydrogen peroxide;
- vodka compress;
- warming (it can be used in the first stages of the disease, when there is no suppuration);
- infusion of onion peel.
Garlic is also effective in relieving pain. It must be crushed, mixed with salt and applied to the sore tooth.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
Typically, trigeminal neuralgia is treated at home.
The goal of drug therapy is to eliminate or reduce the number of pain attacks. For this purpose, anticonvulsants are prescribed with individual dose selection (Finlepsin, Tegretol), antidepressants (Amitriptyline), antispasmodics (Baclofen), local anesthetics (Lidocaine), injection blockades with ethanol, vitamin therapy (Milgamma).
Among the effective physiotherapeutic methods are ultraphonophoresis with hydrocortisone, dynamic currents, galvanization with novocaine, diadynamic therapy, and infrared laser therapy.
Neurologists recommend therapeutic exercises:
- rotating the head along and then counterclockwise for 3 minutes;
- tilt the head to the right and left for 2 minutes;
- stretch your lips into a smile, and then close them with a tube for 2 minutes;
- alternating between closing and opening the eyes for 1.5 minutes.
Traditional methods of treating trigeminal neuralgia are very effective: compresses made from geranium leaves, alcohol-based, birch buds. The site of the disease is also rubbed with “Star”, beet juice, and propolis tincture. Use soothing tinctures based on chamomile, mint, and motherwort.
In the absence of effect from drug treatment, with an increase in the frequency and intensity of pain attacks, surgical treatment is resorted to: blockade of the Gasser node (puncture radiofrequency coagulation of the node), retrogasseral transection of the node, vascular decompression of the root, removal of the trigeminal nerve, blockade of individual branches of the trigeminal nerve, radiosurgery using gamma knife and cyber knife, glycerin injections, percutaneous balloon compression, radiofrequency destruction of the trigeminal nerve root.
Approaches to treating an inflamed dental nerve
There are two of them: conservative and surgical.
Conservative treatment is possible only at an early stage of the disease, as well as with traumatic pulpitis. At the same time, it is possible to keep the pulp alive.
The doctor uses antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as special formulations containing calcium ions. In this case, the tissues of the dental nerve are sanitized and the normal alkaline-acid reaction is restored. An important step is the installation of a temporary filling (for 7-10 days) to completely relieve inflammation, which is then changed to a permanent one. When treating traumatic pulpitis, it is sufficient to apply antiseptics and calcium-containing preparations with further restoration of the coronal part of the tooth.
Periodic x-ray monitoring of the healed tooth is recommended.
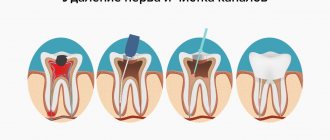
Surgical treatment of pulpitis involves removal of the affected pulp, i.e. killing of a tooth. The dental nerve is removed using vital and devital extirpation methods.
Vital extirpation involves extracting the pulp with dental hooks. The root canals and dental chamber are thoroughly cleaned and filled. On average, this process takes 1.5-2 hours. Local anesthesia is used.
Devital extirpation is a kind of “killing” of the inflamed nerve with special drugs. They are a temporary filling that is installed for up to two weeks. During this time, the pulp dies. When drilled, it is removed along with the filling material. In conclusion, a full treatment of the tooth is carried out with sealing of the canals.
Let us note that after treatment with both surgical and conservative methods, pain is noted that disappears within a few days. To relieve them, you can take an analgesic.
Prevention of trigeminal neuralgia
To prevent relapses of the disease, we recommend:
- promptly treat inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- regularly sanitize the oral cavity;
- strengthen immunity;
- harden;
- do not overcool;
- avoid drafts;
- perform regular physical activity;
- limit alcohol intake, quit smoking;
- avoid nervous tension;
- Conduct vitamin therapy courses 2 times a year.
Symptoms
| Occurrence (how often a symptom occurs in a given disease) | |
| Nasal tone of voice (nasal voice) | 90% |
| Choking on liquid and solid food | 90% |
| Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia, difficulty swallowing, swallowing disorder) | 80% |
| Difficulty speaking (speech disorder, speech disorder, speech problems) | 70% |
| Liquid food comes out through the nose | 60% |
| Hoarse voice | 50% |
Which doctor should I contact?
To avoid repeated attacks of trigeminal neuralgia, consult a neurologist. If differential diagnosis is necessary, consult a dentist or cardiologist. Contact the doctors of the Botkin.pro medical video consultation service. See how our doctors answer patient questions. service doctors for free, without leaving this page, or here. Consult your favorite doctor.
How to relieve pain before visiting a doctor?
Most often it is caused by caries. Other reasons:
- Gum disease.
- Injury.
- Infection after extraction.
- Bite correction.
- Plaque.
- Sinusitis.
- Neuralgia.
- Cracks.
Tooth decay
Decay destroys the tooth by dissolving its structures. When only the enamel layer is affected, it is painless. Enamel without innervation.
However, when the decay spreads to the sensitive dentin, the nerves begin to react to hot, cold, and sweet foods and drinks.
As the decay goes deeper, the pain increases in intensity.
It varies and is described as:
- intermittent, constant;
- soft, dull, aching, throbbing, sharp, intense, stabbing and even painful!
Gum diseases
Inflammation of the gums leads to toothache in the following sequence of events:
- Inflammation leads to weakening of contact between the edges of the gums and the tooth and the formation of a gap between them.
- Food and bacteria accumulate in the space between the gum and tooth.
- A periodontal pocket is formed.
- A deep, infected pocket leads to an abscess. This is called flux.
- The pain becomes very severe and prolonged.
- Because the area around the tooth is swollen and infected, chewing becomes painful.
- Temporary relief occurs, but exacerbation will recur.
- The problem can only be cured by a dentist.
- Opening, drainage and antibiotics are necessary.
- If this is not an isolated case, the help of a periodontist is required.
The trigeminal nerve is large. Its branches run along the face and jaws. All teeth are connected by branches of this nerve. The pain can be felt from above, and the cause is inflammation of the tooth in the lower jaw. When it is caused by decay that has spread over the area around the tooth, it is easier to find it. An abscess is an example of such a situation.
A thorough examination by a dentist can determine which tooth is causing the problem.
There is no innervation in the enamel layer, but there is innervation at the base of the dentin. When dentin undergoes decay, the nerve begins to react to hot, cold, sweet foods and drinks. The pain is mild and goes away immediately after the cause is eliminated. The dentin layer is affected in the early stages of the decay process.
Causes:
- Abrasion. This is the wear and tear of the enamel by brushing too vigorously at the edges of the gums. The thin coating of dentin on the root also wears off easily.
- Erosion. Occurs when acids from the stomach enter the mouth, corroding and destroying enamel and dentin.
- Wear. Occurs by grinding. It is normal to experience signs of tooth decay as we age. But teeth grinding during bruxism is abnormal.
Sensitivity problems in the early stages can be managed with desensitizing toothpaste and dental treatment.
Sensitivity caused by decay is treated by cleaning the tooth from the inside out.
When the nerves and blood vessels of the tooth are initially affected, pain occurs in response to contact with hot, cold food and drinks. As the decay progresses further into the tissue, the dental nerve becomes inflamed, the pain becomes very severe, throbbing and constant. Attacks occur from time to time with aggravated circumstances, in a lying position.
It is usually caused by an abscess. This happens both at the early stage of decay and at the advanced stage:
- Pain indicates that the pulp has been destroyed during decay.
- Dead tissue produces gases that react strongly to hot foods and drinks.
- An abscess also forms at the end of the root, and the gum tissue becomes inflamed and swollen.
- This causes fever and poor health.
Treatment of the condition involves opening the tooth and removing the pus. Pain relief is immediate, but the tooth will still be sensitive and the area around the root end infected.
The remedy is drug treatment and cleaning of the root canal, followed by filling it with a filling or replacing the crown.
This combination of symptoms indicates that the abscess is spreading into the mouth. The sour taste and bad breath is caused by pus. The tooth is sensitive and very painful to chew. Pain and swelling decrease after getting rid of the pus, but treatment is still necessary.
The hole may have become infected. This condition is called "dry socket". Infection in the wound results in more severe pain than before the tooth was removed. It is continuous, stabbing and difficult to control with analgesics. This is a dental emergency and treatment should not be delayed.
A tooth may remain sensitive for a week or more after it has been filled. The cause is decay that has extended close to the pulp. The dentin near the pulp chamber is very sensitive.
It takes time for a protective layer of dentin to form after filling. This will provide insulation from temperature changes and reduce sensitivity.
Ideally, the teeth should be in close contact with their neighbors. This prevents food from getting stuck between them, as well as in the gum pockets when chewing. When this normal pattern is disrupted, small spaces are formed. Food inevitably gets trapped in them. The result is irritation and inflammation of the gums. They become swollen, red and painful. The inflammation spreads to other areas around the tooth and leads to a reaction to chewing.
Brushing and using dental floss, interdental sticks and brushes will help control the problem. This must be corrected by a dentist.
Food in the gum pockets causes inflammation around the crown of the tooth. The wisdom tooth causes pain by putting pressure on the nerves around it or on the tooth blocking its exit.
There are voids or sinuses in the bone above the upper teeth. The roots of some of these teeth are very close to the sinuses. In the teeth, jaws and most of the face there are branches of the same trigeminal nerve. The sinuses often become infected during a runny nose or sinusitis, and inflammation of the nerve occurs. This leads to pain felt in the upper teeth. When the sinusitis goes away, the condition returns to normal.
Accidents lead to damage to teeth, especially the front teeth. The intensity of pain depends on the nature and extent of the damage.
If most of the tooth is broken, nerves and blood vessels are exposed. This is very painful. Root treatment followed by tooth repair is necessary.
When it remains intact but the jaw is damaged, the nerves and blood vessels at the tip of the root are damaged. In this case, the following symptoms occur. The tooth becomes very sensitive to the slightest pressure.
The dentist conducts a thorough examination, assesses the extent of the damage and decides on appropriate treatment.
Small scratches or cracks may become larger. When this reaches the pulp chamber, there is pain when chewing and a reaction to hot and cold.
Often the cause of the symptoms of inflammation of the dental nerve is difficult to find. If this problem occurs, the tooth may need to be removed.
This kind of neuralgia is pain of varying intensity affecting the face. Since the face and teeth are pierced by the same nerves, this neuralgia leads to toothache. The cause of the problem is not always easy to detect. This condition, fortunately, does not happen often.
Analgesics, or painkillers as they are commonly called, are used to reduce or eliminate pain. These are various substances used alone or in combination: aspirin, ibuprofen, acetaminophen (paracetamol), codeine and morphine.
We invite you to read: OCI solution instructions for use
A number of analgesics are available only by prescription, but many can be purchased at pharmacies. This group of drugs has analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory properties.
There are several ways to independently remove pain associated with inflammation of nerve endings. The main goal of home methods is to reduce the sensitivity of the rotted nerve.
- Alcohol. It cannot completely kill the nerve, but it can reduce the activity of pathogenic flora in the carious cavity. It works well as a mouth rinse and reduces the intensity of pain for a while.
- Powder. A small amount of a substance is placed into the affected area, which effectively relieves pain. It is important not to overdo the dosage of gunpowder, since intoxication of the body is possible. We do not recommend using this method, as it is very dangerous.
- Vinegar. The product is pre-mixed with water in a 1:1 ratio, since pure vinegar causes burns to the mucous membranes of the mouth. A cotton swab is moistened in the solution and applied to the carious cavity for 15 minutes.
- Pepper. Preference is given to spices with peas. The product is crushed and placed on the diseased tooth.
One of the most dangerous ways to remove a dental nerve at home is to use arsenic.
For arsenic to work, it must be placed in previously cleaned dental canals. If even a small dose of the substance enters the intestines, it will be fatal.
All of the above measures are emergency. Even in the absence of re-exacerbation of signs of pulpitis, you should consult a doctor. An infection inside a tooth cannot be destroyed on its own.
To relieve pain, you can use not only folk remedies, but also pharmaceutical preparations intended for dental procedures.
Can a tooth hurt after nerve removal?
- Cresofen. The main active ingredient of the product is dexamezone. The drug is available in the form of drops and has a gentle effect on the mucous membranes of the mouth. The product is used only after pre-treatment of the carious cavity with antiseptics at home. To improve the therapeutic effect, Crezofen is recommended to be used in combination with antibiotics. After using the drug, rinse the mouth with plenty of water.
- Kaustinev Rapid. Consists of 1/3 arsenic solution. The remaining components in the product are considered auxiliary. The duration and frequency of use of the drug depends on how deep the exposed dental nerve is located. If the pulp is located close to the carious cavity, then it is possible to relieve pain symptoms with one application of the solution.
- Davis ARS. Arsenic is also an active component of the drug. The advantage of the medication is the quick and effective elimination of toothaches. The effect of using the product is observed after 1-2 days. The drug is available in the form of syringes or liquid with a universal dosage.
- Devin - P. The drug is available in the form of a paste, which includes analgesic and antiseptic substances: menthol, chlorophenol, camphor oil. This drug is used to relieve the symptoms of pulpitis if medications with arsenic are prohibited for use. Due to the absence of arsenic in the composition, the paste is approved for dental treatment even for children.
Medicinal treatments
With inflammation of the dental nerve, symptoms and treatment directly depend on each other. Measures need to be taken as early as possible, while the pathological process is localized and nearby tissues are not affected by inflammation.
What to do if the dental nerve has caught a cold? Where to go for medical help? If your health worsens, especially in the case of a cold nerve, it is necessary to consult a specialist as soon as possible. There is no need to try to deal with the problem on your own. Only the attending physician can judge how severely the tooth nerve is cold. The development of an appropriate therapeutic regimen is also within his competence. When pulpitis is diagnosed, the patient will undergo dental treatment. If trigeminal neuralgia occurs from hypothermia, a person should definitely consult a neurologist who will prescribe complex therapy.
It can be treated conservatively and surgically. This depends on the stage of the disease, the age of the patient and the presence of chronic pathologies. In this case, teeth should be treated conservatively under local anesthesia. The doctor will remove the affected tissue to healthy ones and apply a special paste that has an antiseptic effect. With its help, you can prevent the reactivation of the inflammatory process, even if the nerve is well cold. This will speed up healing. If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner, the entire neurovascular bundle can be saved.
Pulp extirpation
However, in most cases the doctor does partial or complete
In case of severe inflammation, this is the only method of removing all pathogenic microorganisms from the tooth cavity. This must be done in order to limit the infection to the dental nerve and prevent further spread to the gums.
Larisa Kopylova
Dentist-therapist
If the dental nerve is cold, then you should visit several specialists at once. When neuralgia is a complication, the disease is treated by a dentist and a neurologist together. This requires an integrated approach to achieve complete recovery of the patient.
How to treat inflammation? Pain relief comes to the fore in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. This can only be done with the help of Carbamazepine, which has the ability to stop paroxysmal activity in the nerves. We treat the disease for a long time; it takes about 1.5–2 months to achieve a lasting positive result from the therapy. The appropriate dosage, frequency of use and course duration are determined by the doctor individually for each patient, since this necessarily takes into account how cold the nerve is.
Despite the fact that Carbamazepine is highly effective, it is prescribed with great caution. This is due to the fact that the drug is characterized by a significant number of side effects and complications. If a pregnant woman has a cold on her nerve, she is strictly forbidden to use Carbamazepine to relieve pain. The drug has a pronounced teratogenic effect, which can have an adverse effect on the growth and development of the fetus, especially in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. In this case, it is advisable to use other anticonvulsants: Phenibut, Pantogam, Baclofen, etc.
Phenibut
Pantogam
Baclofen
Antihistamines - Diphenhydramine, Pipolfen, etc. - will help enhance the effect of these drugs. To eliminate the pain syndrome of a cold trigeminal nerve, in some situations the prescription of tranquilizers and antipsychotics is indicated.
Diphenhydramine
Pipolfen
In the video, Elena Malysheva talks about the treatment of pulpitis:
Signs and symptoms of the problem
If the nerve in the tooth is inflamed, the main symptom of this condition is pain. The unpleasant sensations are acute, but diffuse in nature. It is almost impossible to establish the correct location of an inflamed tooth; the patient cannot indicate the exact location. The pain tends to intensify with any jaw movement, be it eating or even talking. With a diseased nerve, tooth enamel becomes unusually sensitive and reacts sharply to temperature stimuli - cold, heat. Other external factors also have an adverse effect - sour, salty, etc.
Other symptoms include severe swelling of the gums. If the pulp becomes inflamed, the dental nerves are compressed even more because they are in a confined space. This further enhances the signs of the inflammatory process, which leads to a significant deterioration in the patient’s well-being. The intensity of the discomfort depends on the time of day and the person’s position. The pain intensifies when the patient goes to bed, especially at night.
If deep tissues are inflamed, it is possible that bad breath may appear, since pulpitis is accompanied by rotting processes.
Larisa Kopylova
Dentist-therapist
If not treated in a timely manner, the infection gradually spreads to nearby tissues, which contributes to damage and inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, resulting in the development of trigeminal neuralgia. This leads to a rapid deterioration in the patient’s well-being. A similar complication occurs after a person has caught a nerve cold. To do this, just spend some time in an air-conditioned room.
Trigeminal neuralgia affects the trigeminal nerve
Neuralgia is characterized by unilateral localization. A cold nerve is manifested by severe pain, which has a paroxysmal character. In the area of innervation, isolated twitches of the facial muscles are noted. In severe cases, a nervous tic develops. It is possible that there is a violation of facial expressions and a distortion of the face on one side. If a person has a cold on a nerve, neuralgic signs often appear, manifested in the form of impaired sensitivity on one side of the head.
With neuralgia, pain provokes mental and physical exhaustion of the body. A person cannot get enough sleep and rest fully; weakness, severe fatigue, and severe irritability gradually develop. Not only the tooth or jaw hurts, but also the head.
A cold nerve provokes a slight increase in body temperature, which is due to the body’s general reaction to trigeminal neuralgia.
The video simulates the process of development of the disease and methods of its treatment: