Smoking and drinking alcohol after anesthesia
For general or local anesthesia, anesthetic drugs are used.
All medications have a number of side effects. To reduce the risk of complications, it is important to adhere to the rules recommended by the anesthesiologist. Nicotine and alcohol are incompatible with anesthetics. They can affect the course of anesthesia in different ways. In some cases, the anesthetic medicine will have a weak effect on the body, but may enhance the effect of anesthesia.
After surgery, some patients do not know whether it is possible to smoke (ordinary cigarettes or electronic cigarettes, hookah), drink alcohol (beer, wine, etc.)? And how soon can I use it?
You should talk to your doctor about your lifestyle after surgery.
Medicines are eliminated from the body after a certain time. During the first day - the main part of the medicine, and over the next days or weeks the residual concentration of the anesthetic substance. The elimination period depends on the type of anesthetic and dosage, as well as the condition of the body. Therefore, drinking alcohol within a short period of time after anesthesia or local anesthesia is not recommended.
Beer contains an average of 5% alcohol, but is also a product that causes fermentation, which complicates the healing of postoperative wounds. Even low-alcohol drinks have a stronger effect on the body after anesthesia, since low concentrations of alcohol adversely affect the weakened body during rehabilitation. Therefore, it is not recommended to drink beer while the body is recovering after surgery.
Under the influence of alcohol, blood has low coagulability. This causes bleeding that is difficult to stop. In some cases, bleeding is fatal.
During the postoperative period, alcohol is strictly prohibited!
After surgery, the attending physician most often prescribes antibiotics to the patient. Alcohol should not be drunk during antibiotic therapy for a certain group of drugs, as it can cause a disulfiram-like reaction.
Such patients exhibit symptoms such as:
- severe headache
- spasms of the upper and lower extremities,
- tachycardia,
- feelings of heat in the chest, face and neck,
- nausea,
- heavy and intermittent breathing.
You should ask your doctor about when you can drink alcohol after surgery. After all, everyone’s recovery time is different.
The concentration of alcohol in the blood when drinking beer and wine depends on the amount drunk. But it is worth remembering that even a small dose of alcohol can increase the risk of complications after anesthesia (local, general) or increase the recovery time for an operated patient.
Laparoscopy is a diagnostic surgical procedure used for diseases of the abdomen and pelvis. It is prescribed when it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis.
Despite the apparent simplicity of laparoscopic surgery, it is performed under general anesthesia using endotracheal anesthesia. Therefore, all rules regarding alcohol consumption apply both before and after laparoscopy.
When is alcohol consumption allowed before and after surgery?
An approximate list of operations after which you should limit alcohol consumption:
- during abdominal surgery, drinking alcohol is allowed no earlier than a month later;
- For those who have had their gallbladder removed, drinking alcohol is prohibited for the rest of their lives;
- after surgery to remove appendicitis, you will also need about a week of sobriety;
- during eye operations, alcoholic beverages can only be consumed after months;
- After plastic and cosmetic surgical interventions performed under general anesthesia, alcohol should be avoided for at least 3 weeks.
The duration of abstinence from alcohol varies from person to person. Therefore, it is necessary to consult with your doctor before discharge and do this in as much detail as possible, asking all your questions, clarifying the types of alcohol and its amount allowed for the body after the rehabilitation period.
Why you can’t drink after surgery is understandable, but what about the period of sobriety before it? How long before it can you drink alcohol? The timing is individual and depends on the complexity of the upcoming intervention and the drugs used for anesthesia. A minimum of 3 days must pass before surgery after drinking alcohol; in some cases, this period is regulated by the doctor and can last for a month.
Fact! None of the anesthesiologists will be able to predict the effect of the substances used if less than a day has passed since the last binge with alcohol.
What can you eat after anesthesia?
A special postoperative diet is established even after minor surgery, and this is a prerequisite for the recovery period. 1.5-2 hours after surgery (except for surgery of the digestive system), the patient is given a few sips of water. After this (with normal fluid tolerance), drinking is indicated every half hour with a gradual increase in volume. In the absence of negative signs, the first light meal is carried out 5-5.5 hours after surgery. For these purposes, only liquid food is suitable: broth, pureed soup.
Liquid nutrition is maintained for 3-4 days, while a frequent (up to 6 times a day) but fractional regimen is provided. If it is impossible to eat food on your own, it must be administered artificially through a tube or by drip. It is strictly prohibited to consume the following products within 1-2 days after anesthesia is removed: whole milk, carbonated drinks, plant fiber, sugar syrups.
After 3-4 days, you can switch to semi-liquid food with a predominance of pureed foods. During this period you can eat: chicken and turkey broths, pureed soups without fat, jellies, low-fat yoghurts, mousses, boiled rice porridge. The duration of maintaining a strict diet is determined by the attending physician, based on the complexity of the operation and the course of the recovery period.
Solid food is introduced gradually already 6-7 days after surgery. The dose is set within 35-45 g per day with a gradual increase in the absence of complications. After general anesthesia, it is recommended to refrain from eating fried, salty, and canned foods for a month. Important nutritional conditions are fresh preparation and optimal temperature of the dish.
Everything you need to know about anesthesia!
Smoking is one of the bad habits that has a detrimental effect on the human body. Inhalation of tobacco smoke shortens life and is considered one of the main causes of the development of dangerous diseases, most often incurable.
Smokers are often interested in questions regarding the relationship between their habit and various medical procedures that they have undergone or are about to undergo. It has been proven that nicotine use can cause many times more harm during anesthesia or during tooth extraction than in a normal case.
Smoking after surgery increases the risk of complications
The heart of smokers uses more oxygen during its work than the heart of a non-smoker. Because of this, they often experience pathological symptoms: rapid pulse, arrhythmia and frequent uneven breathing, and in addition, high blood pressure.
As one might think at first glance, the smoker should, on the contrary, receive increased portions of oxygen in the blood, but this is far from the case, because oxygen useful for cells is blocked by carbon monoxide, which enters the body along with cigarette smoke. Against this background, one conclusion suggests itself - the smoker’s heart is exposed to an acute oxygen deficiency.
This condition can result in negative consequences during surgery, which involves the use of anesthesia. In other words, a person has a high chance of developing cardiovascular diseases - coronary heart disease, bradycardia, which can result in cardiac arrest.
Tobacco smoke contains a large amount of tars and toxins that can accumulate in the body. At first glance, this has nothing to do with anesthesia, but precisely because of this effect, smoking often causes an unpredictable reaction of the body to anesthesia drugs, due to disruption of the body's enzyme systems.
When performing an operation using deep anesthesia, the patient undergoes tracheal intubation. For people leading a healthy lifestyle, it is absolutely safe, but in a smoker it can cause laryngeal spasm, which can lead to respiratory arrest. Consequences after anesthesia can be pneumonia, bronchitis, heart failure. Against the background of everything, smokers experience the development of purulent and inflammatory processes.
To reduce the risk of complications, smokers should carefully prepare for elective surgery. The main thing is to quit smoking 1-1.5 months before the expected date of surgery.
If the operation is emergency, such a patient may require an increased dose of anesthetics, which in turn will affect the duration of the recovery period.
Plastic surgeons strongly recommend that their patients refrain from smoking in the preoperative period and for some time after surgery - at least until the moment when the results of the operation are finally consolidated (for example, breasts after mammoplasty continue to form throughout the year).
This is a known fact, but British surgeons, concerned that many patients are not willing to strictly follow medical recommendations, published a scientific article in which they explained what medical considerations determine the instructions to stop smoking after plastic surgery.
Smoking affects the blood vessels of the entire body: they narrow, as a result of which the blood supply to certain areas may be reduced or difficult. In a healthy state, this phenomenon may not even be noticed, but after anesthesia and surgery, the immune system is in a weakened state, and the body reacts especially acutely and sensitively to any functional disorders.
Quitting smoking, British doctors are confident, will not only protect patients from the risk of postoperative complications, but will also help them maintain health for many years.
Non-standard smoking methods and their impact
Is it possible to smoke in the postoperative period? What type of smoking (regular or electronic cigarette, hookah) is safe? Surgical patients face these questions and naturally want answers to them.
Many people believe that smoking hookah is a safe alternative to regular cigarettes. But there are some nuances here that are hidden from smokers. Yes, hookah tobacco contains a minimal amount of nicotine - 0.5%, and there is no tar, unlike a standard cigarette, but the carbon monoxide released when smoking causes enormous harm to the body.
Carbon monoxide from hookah smoking is not the only harmful substance; there are others that accumulate in the body. For example, increased concentrations of arsenic, lead, chromium, carboxyhemoglobin, nicotine. Unlike regular cigarettes, a person can smoke a hookah for quite a long time (up to several hours). Therefore, the amount of harmful substances entering the human body when smoking hookah tobacco is much greater.
Scientists have proven that if you smoke a hookah for an hour, the harm to the body will be the same as from smoking a hundred standard cigarettes.
Another common alternative to standard smoking is electronic cigarettes. People generally think that when they start smoking electronic cigarettes, they cause minimal harm to the body. Therefore, there is a false opinion that standard cigarettes can be replaced with this type after anesthesia or anesthesia.
Electronic cigarettes use a special smoking liquid that contains nicotine. Everyone already knows that it negatively affects internal organs and the nervous and cardiovascular systems, and also causes addiction and dependence.
Electronic cigarettes cause nicotine addiction
It is known and proven that regular cigarettes adversely affect the course of anesthesia and the recovery of the body after surgery. Contribute to the development of pneumonia, bronchitis and complications from the cardiovascular system. When you can start smoking in the postoperative period, you need to ask your doctor.
Smoking after surgery:
- Before our eyes. During the recovery period, you should stop smoking cigarettes. When smoking, the pressure in the eyes changes dramatically, and tobacco smoke can enter the eyes, which adversely affects the healing process. Experienced smokers need to minimize the number of cigarettes they smoke.
- For appendicitis removal. Smoking is prohibited in the first three days after surgery.
- In the oral cavity. Smoking is not recommended during the first two postoperative days.
- On the heart. It is necessary to stop smoking not only during the recovery period, but also to quit this harmful habit altogether.
- And other surgical interventions.
The postoperative period for recovery of the body is different for everyone, depending on the complexity and how long the surgical intervention lasted. Therefore, the period of quitting smoking varies, and in some cases it is necessary to completely forget about cigarettes forever.
Reasons for the threat of smoking before surgery
Many smokers very often do not listen to doctors who forbid them to smoke before surgery. All this is due to the fact that they simply do not have a complete picture of how this can affect health.
Scientists have long been engaged in such research as smoking and the effects of nicotine on the body before anesthesia (since the early 50s).
As statistics have shown, during an operation (usually surgical), patients had a number of serious complications.
Often it came to blood transfusions in large quantities. Surgeries to remove a brain tumor very often had such a sad result as death. The operations on the spine were also disastrous. The patient could take a long time to rehabilitate or stop walking altogether.
As neurosurgeons note, it is strictly forbidden to allow at least one cigarette to be smoked before surgery. This is especially important in complex procedures involving risk to life. Every patient must remember that his own life depends not only on the doctor, but also on himself. Of course, it is difficult to convince a smoker, for whom drinking cigarettes is a process of relieving stress, anxiety and calming the nervous system, of this, especially before surgery under general anesthesia.
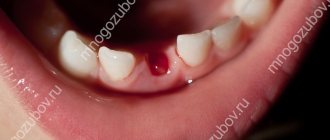
Smoking after wisdom tooth removal
For the first two to three hours after tooth extraction, smoking is strictly prohibited, as cigarette smoke will only injure the wound.
Chemicals that are components of cigarette smoke can cause inflammation of the wound, significantly slow down the healing process, and also cause bleeding.
If several hours have passed since the extraction, and during this time blood continues to flow from the wound, then you should wait until the blood stops completely at the site of the extracted tooth and from that moment, after two hours, you can smoke one cigarette.
If the tooth extraction was long and complex - with cutting the gums and suturing, then you should forget about your addiction, on average from two days to 8 - 10 days from the date of the operation.
Such a long period is associated with the healing of sutures; within 10 days they should completely heal and resolve. The use of cigarettes during this period of time will significantly “slow down” this process.
Why do dentists recommend stopping smoking cigarettes in the first few hours after tooth extraction surgery?
After a tooth has been removed, a blood clot called a “blood callus” forms in the area of the empty socket.
This blood should not be removed, especially by rinsing the mouth.
During smoking, especially if a person intensively spits saliva, this blood clot begins to slowly move to the side, exposing the wound. Carcinogenic substances that are part of cigarette smoke irritate the oral mucosa and negatively affect the wound healing process.
After removing a complex tooth, or wisdom tooth, the doctor, as a rule, prescribes a medicine that needs to be moistened with a tampon and changed several times a day. Smoking will also create discomfort and reduce the medicinal effect of the prescribed drug.
The minimum time that needs to be spent without a cigarette, even for the most heavy smokers, is two hours from the moment of tooth extraction.
Smoking cigarettes is a serious harm to dental health, especially during the recovery period after extraction.
Smoking cigarettes almost immediately after tooth extraction can provoke the formation of a so-called “dry socket.”
If the resulting blood clot is completely dislodged from the wound, then a free “entry” for infections is formed, and bleeding may also begin.
If any infection occurs, an inflammatory process with symptoms characteristic of this condition may begin in the wound:
- body temperature rises;
- general condition worsens;
- the gums will become purple-red in color;
- the process will be accompanied by pain.
In this case, you will have to seek help from the dentist again so that the doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs. If measures are not taken to treat inflammation in time, alveolitis may develop.
If we are talking about removing a wisdom tooth, then you must strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions. Removing a tooth of this type is complicated by the fact that it is quite large in size, has long and overgrown roots, so the wound will be quite deep and the healing process will take a longer time.
The doctor gives his recommendations regarding wound care in each individual case. It is necessary to inform him about the presence of an addiction, and ask him after what minimum period of time he can smoke a cigarette. But in order for a deep wound to heal quickly and without any complications, it is better to completely forget about smoking for a week.
Removing any tooth is a stressful situation for the body and pain. Many people see their addiction as a way to reduce pain. Sometimes, indeed, it is possible to relieve pain, but at the same time, harm is done to the body. For speedy healing, it is better to give up cigarettes altogether for a day.
Any doctor will tell you that it is better to abstain from cigarettes for the first day, but if this is not possible, then you should not smoke for the first two to three hours after tooth extraction.
Why use an additional irritant yourself, which will only slow down the healing time of the wound.
The process of smoking itself in the first hours after surgery will cause a lot of discomfort.
The jaw has not yet recovered from the anesthesia, the lips are numb, so holding a cigarette and taking a puff will be quite problematic.
Once a tooth has been extracted, it will leave an open wound that may bleed slightly for several hours after extraction. Even if there is no active bleeding, with any movement of the tongue, bleeding can reactivate. Chemical substances that are part of tobacco smoke, getting into an open wound, can not only cause bleeding, inflammation, but can even cause cancer.
If after tooth extraction there is pain in the wound area, you should not light a cigarette just to relieve the pain.
You can use painkillers, or apply an ice cube or any other cold compress to the cheek in the area of the extracted tooth.
The maximum time is 10 minutes, every hour, for 3 hours.
Smoking after tooth extraction can provoke the development of a disease such as alveolitis. This is an acute inflammatory process of the walls of the socket in the place where the tooth was removed. The causes of this complication are direct injury to the wall of the socket, infection in the wound, bleeding, and violation of the sterility of the wound.
As the inflammatory process develops, intoxication occurs with chemicals contained in cigarette smoke. The patient may feel general malaise, headache, fever and muscle aches. At the first stage of inflammation, swelling of the gums is observed, then it spreads to the soft tissues of the facial area.
After a few hours, you can observe swollen and blue gums, and if treatment measures are not taken in time, this can cause tissue necrosis. Alveolitis is a serious inflammatory process that causes osteomyelitis - the formation of a purulent focus and fistula in bone tissue.
To smoke or not to smoke after tooth extraction - everyone chooses for himself personally. But is it worth putting your health at serious risk for the sake of a little stress relief?
The best option is to abstain from cigarettes for 24 hours to 10 days, depending on the complexity of the operation. Quitting cigarettes during the recovery period will allow the wound to heal faster without any additional complications or inflammatory processes.
Before the invention of ether, pain relief techniques were primitive and even dangerous. Patients could be “intoxicated,” their carotid artery could be pinched, or even hit on the head.
On October 16, 1846, the American surgeon Warren performed the first public operation “under ether.” The patient was put to sleep by a doctor who had previously tried the method on his patients. And then they began to invent more and more new drugs. This is how the science of anesthesiology was born.
Doctors say that there are no people who do not tolerate anesthesia well. There is only bad anesthesia and lack of proper control. The patient must be monitored every second.
The term "anesthesia" comes from the Greek word aisthesis, which means "sensation", "feeling". The prefix "an" is a negation. Those. “anaesthesia” is a complete loss of sensation. During the operation, anesthesia ensures a complete absence of pain, i.e. protects the patient's body from surgical aggression.
General anesthesia provides us with protection not only from psychological and painful shock. Even when we are unconscious, the body can react to pain with a strong release of “stress hormones.” Anesthesia reduces this reaction and relaxes the muscles, providing them with peace, and providing the surgeon with optimal conditions for the operation.
After the patient has fallen asleep reliably (deep anesthesia has been achieved), the anesthesiologist gives the command to administer muscle relaxants. Muscle relaxants are medications that paralyze the patient’s skeletal muscles, making independent movements, including breathing, impossible. This is done to make it more convenient for surgeons to work, and easier for an anesthesiologist to ventilate the patient’s lungs with an anesthesia-respiratory apparatus.
After intubation (and in the event of an emergency operation, even before induction of anesthesia), a special gastric tube is inserted into the patient’s stomach, through which everything that is there and that is released in the stomach during the operation will be brought out. This is important because otherwise acidic stomach contents can enter the respiratory tract, causing aspiration pneumonia, which is very difficult and time-consuming to treat and is a potentially fatal complication.
Next, the anesthesiologist begins to maintain anesthesia.
- anesthesia (putting you to sleep). Medicines used for this purpose (hypnotics) depress the patient’s consciousness, so during the operation he sleeps, hears and sees nothing. Most hypnotics do not have an analgesic effect, so analgesics must be added to anesthesia.
- analgesia (pain relief). Surgical aggression is very painful. Moreover, operations are often performed on so-called reflexogenic zones, where even the slightest irritation can cause a strong reaction in the body, even shock. Analgesics (painkillers) suppress the transmission of pain impulses in nerve fibers, and the person ceases to feel pain. Narcotic analgesics are often, although not always, used during surgery. The anesthesiologist ensures that the permissible dosage is not exceeded. It is impossible to become a drug addict as a result of using drugs during surgery!
- myorelaxation (muscle relaxation). Relaxed muscles greatly simplify the work of surgeons. And in the case of laparoscopic interventions (a modern method of minimally invasive surgery, when the operation is performed through several punctures in the anterior abdominal wall), muscle relaxation is an absolute necessity; a tense abdomen will completely prevent surgeons from working in the abdominal cavity.
How to eat properly after surgery and anesthesia
Depending on what kind of surgery was performed, specialists make some restrictions on food intake.
If the surgical intervention involved the digestive organs, then how long after the operation you can eat is determined by the doctor in each specific case, depending on the operation and recovery from anesthesia. As a rule, in such cases, you should not drink water or eat food by mouth for the first 4 days. A special diet must be prescribed, taking into account the nature of the operation performed and the consequences after it. In most cases it looks like this:
- For the first 4 days after surgery, eat only liquid foods (very thin porridges, low-fat soups, drink compotes);
- Semi-liquid meals are introduced gradually after this time has passed. What can you eat after anesthesia in this case: liquid soups with a small addition of potatoes and cereals, which are pre-chopped or mashed, liquid kazhi (except pearl barley and corn);
- After this time, you can gradually introduce regular pureed food.
Even in cases where the operation was not too long and complex, after anesthesia it is necessary to adhere to a diet for about 7-10 days. As for water, you can drink it within an hour after the operation and restoration of the person’s consciousness. If there are other instructions from the anesthesiologist, then you should adhere to them.
It is correct to take water in the following order. At first, the patient is asked to take only a few sips, gradually increasing the amount taken after a certain time.
How long after general anesthesia can you eat if the operation was not complicated? Eating is allowed 5 hours after complete recovery from anesthesia; this is checked by a doctor. In this case, you should adhere to the following diet:
- More chicken or turkey broths.
- If you wish, you can eat jelly, preferably not very sweet and without adding fruit.
- Eat pureed soups.
- Boiled rice porridge is one of the best ways to eat during this time, but do not overdo it.
When asked whether it is possible to eat in the usual amount after anesthesia, doctors give a categorical refusal. You need to eat in small portions and at least 7 times a day, that is, every 2 hours. This diet can last from 5 to 15 days, depending on the complexity of the operation, the speed of recovery of the body and the absence of other side effects.
Why you shouldn't drink before surgery
The main reason why you should not drink alcohol before going to the surgeon’s table is its properties. Alcoholic drinks greatly thin the blood, so during surgery there will be a risk of heavy bleeding, which is almost impossible to cope with. It is equally important that alcohol directly interacts with all types of anesthesia, that is, drinking before surgery causes the risk of waking up during the process or an overdose of the substances used for anesthesia.
The minimum period from drinking alcohol to surgery is a day. On average, you can drink it within 3-4 days; in special cases you should stop drinking it even earlier.
If, before the upcoming intervention, most patients obediently follow doctors’ orders, then the question “is it possible to drink alcohol after surgery?” it costs much more.
Drinking after surgery is prohibited in the following cases:
- To avoid blood poisoning, antibiotics are prescribed that are not compatible with alcohol.
- Any alcoholic drink causes the manifestation of “dormant” and chronic diseases. In an organism weakened by surgery, this leads to complications, including the need for repeated surgery.
- The direct effect of alcohol on blood clotting, that is, if the ban on drinking is violated, heavy bleeding may occur.
- Alcohol has an effect on the central and peripheral nervous system, and in combination with residual substances after anesthesia, drinking in any quantity leads to various disorders (including blindness), hallucinations and breathing problems.
Important! All anesthetics used for general anesthesia cause liver damage by affecting hepatocytes. Alcohol enhances this process.
Why is anesthesia dangerous for people who smoke?
Nicotine and carbon monoxide are the main culprits of anesthesia complications in smokers. Inhaling nicotine when smoking releases large amounts of adrenaline in the body, which causes increased heart rate and increased blood pressure. But in order to beat frequently and maintain unusually high blood pressure, the heart needs to work harder and, therefore, receive more oxygen.
However, a person who smokes, on the contrary, receives even less oxygen. This happens because carbon monoxide inhaled during smoking blocks hemoglobin, which is the main carrier of oxygen in the body. Thus, the smoker’s heart experiences a large oxygen deficiency, especially pronounced during anesthesia. That is why smokers during anesthesia are at significant risk of developing cardiovascular complications.
Smoking significantly alters the functioning of the body's enzyme systems, which are responsible for breaking down external toxins and drugs. Therefore, administering anesthesia to smokers is associated with some unpredictability in the action of the drugs used for anesthesia.
Considering that the lungs of smokers are a target for constant exposure to harmful substances contained in cigarettes, anesthesia in smokers is associated with a high risk of developing respiratory complications. Patients who smoke have a 5 times greater risk of developing complications such as atelectasis, bronchitis and pneumonia.
In addition, during anesthesia, the airways of smoking patients become very susceptible to any external influences. Thus, tracheal intubation often causes a sharp closure (spasm) of the lumen of the larynx (laryngospasm) and bronchi (bronchospasm); these disorders can pose a threat to the patient’s life.
Also, smokers after anesthesia have a higher incidence of suppuration of postoperative wounds.
What to do if you are planning to undergo anesthesia and you smoke?
It is necessary to completely normalize the level of nicotine and carbon monoxide in the smoker’s blood so that during anesthesia the risk of cardiovascular complications is significantly reduced. To do this, it is necessary that at least 24 hours pass between the start of anesthesia and the last cigarette smoked. To reduce the risk of respiratory complications, the patient must completely quit smoking, and at least 2 months must pass from the last cigarette smoked to the time of anesthesia.
Interestingly, the best results, in terms of the risk of developing post-anesthesia complications, are observed in patients who either quit smoking more than 2 months ago, or their last cigarette was smoked 24 hours before anesthesia. Paradoxically, patients who quit smoking several days to a month before anesthesia have an even greater risk of respiratory complications than patients who did not quit smoking. These patients cough up sputum very poorly, and moreover, it is produced in larger quantities than usual. All this predisposes to the development of bronchitis and then pneumonia after anesthesia.
Providing anesthesia to smokers has a number of specific features. Thus, during anesthesia, patients who smoke require the administration of large doses of anesthetics and narcotic analgesics. After anesthesia, smoking patients often need to breathe oxygen, as impaired lung function begins to make itself felt. Also, after anesthesia, smokers have an increased need for painkillers; these drugs are administered more often and in larger doses. To prevent respiratory disorders, smoking patients after anesthesia should do breathing exercises; in addition, a course of chest massage and other physiotherapeutic procedures is recommended.
Given the high risk of developing complications from the lungs and heart, patients who smoke should avoid anesthesia and, if possible, choose regional (spinal, epidural) or local anesthesia.