25.11.2019
Oral hygiene for children begins even before the first teeth erupt. Some parents are greatly mistaken, believing that baby teeth do not need attention and quality care, because after some time they will fall out in any case. However, today it has already been proven that the health of permanent teeth and soft tissues of the oral cavity as a whole directly depends on the condition of the temporary units. We will talk about proper care and prevention further in our article.
The importance of maintaining oral hygiene at an early age
About 92% of people around the world do not know how to brush their teeth properly1. It turns out that parents, without a clear idea of how to correctly carry out this procedure, teach their children to deliberately brush their teeth incorrectly. But the structure of the dental system of an adult is significantly different from that of a child. Accordingly, oral hygiene in children has some peculiarities.
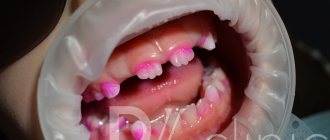
World experts in the field of pediatric dentistry advise closely monitoring the growth of the first molars. They are also called “sixes” and are more vulnerable than the rest of the teeth in the row. The first molars usually appear faster than others, and often the distal cusps are freed from the “hood” with some delay. And that, in turn, provides ideal conditions for plaque to appear.
Children's primary teeth are more susceptible to caries. And this is due, first of all, to the fact that the child’s fragile immune system is not yet able to fully resist bacterial attacks. And also with the peculiarities of the oral mucosa and the structure of the teeth, with the thinness of the enamel-dentin layer, with the short length and fairly large width of the canals and their direct location.
On a note! The best solution to teaching your child the basics of maintaining oral hygiene is to consult with a professional dental hygienist. The doctor can show your child how to use a toothbrush correctly, tell you how often to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with plain water.
Your child should get into the habit of thoroughly brushing their teeth twice every day – after waking up and before going to bed. He must clearly understand that after each meal he needs to rinse his mouth with plain water to remove food particles. It’s even better if the baby ends the meal with a piece of apple or carrot, they will naturally remove plaque from the enamel and polish it, plus the baby will receive the necessary vitamin support, and not glucose from sweets, which harmful bacteria that cause caries love to “absorb.”
And parents need to closely monitor the growth of teeth and the development of their child’s dental system, and do not forget about the importance of preventive examinations in the dentist’s and orthodontist’s office (in order to promptly identify malocclusions and correct them). You need to take your child to the first specialist 3-4 times a year.
hygiene for preschoolers
Oral hygiene in children (Memo for parents)
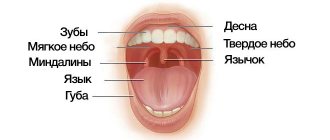
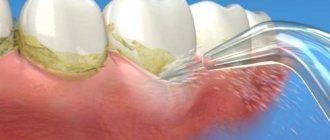
Oral hygiene is one of the simplest and most widespread measures to prevent dental diseases. The quality of oral care significantly affects the intensity of diseases of the teeth and surrounding tissues. Lack of regular dental care in children during the period of teething and the formation of the chewing apparatus leads to the accumulation of microbial plaque, which interferes with the process of enamel maturation. In places where plaque accumulates, caries and gum inflammation occur.
Proper oral hygiene, which prevents the accumulation of microbial plaque, provides significant preventive results. Moreover, it is of particular importance in childhood. Parents must be well versed in proper hygiene in order to monitor their children on a daily basis.
HOW TO CHOOSE THE CORRECT TOOTHBRUSH
A toothbrush is the main item of oral hygiene. Without it, it is impossible to clean your teeth from plaque and food debris. Children need to use a small toothbrush so that they can manipulate it freely in the mouth, consistently cleaning the teeth from all sides. The length of its head should not exceed 20-25 mm, and the width 8-10 mm. The bristles of a children's toothbrush should not be very hard, since the enamel of children's teeth is less durable than that of adults, and the mucous membrane of the gums is delicate and easily vulnerable. The rows of bristles should be spaced sparsely, at a distance of 2-2.5 mm, no more than 3 in a row.
A toothbrush is a personal item. Under no circumstances should two or more people, even close relatives, use the same brush.
Before use, a new brush must be washed thoroughly and then left thickly soaped in a glass overnight. After soaping, the brush should be rinsed well. In between brushing your teeth, the brush should be in an individual glass or cup, head up. The brush can be stored in closed cases only temporarily, when traveling.
WHEN, HOW AND WHAT TO BRUSH YOUR TEETH?
A child should be taught to brush their teeth and rinse their mouth from the age of three. First of all, the child should be taught to brush his teeth with one brush moistened with water, without toothpaste, and especially accustom him to thoroughly rinsing his mouth. In this case, the child must be shown how to hold the toothbrush, how to move it in relation to the teeth and then how to rinse the mouth. It is very important, from early childhood, to instill in your child a sense of the need for daily brushing of teeth, and to accustom him to rinsing the mouth after every meal.
The most effective scheme of hygiene measures should be brushing your teeth in the morning and evening after meals with mandatory rinsing of the mouth after breakfast, lunch, and dinner. One-time cleaning is less effective. Irregular care does not achieve anything, since plaque has time to become saturated with salts and is not removed by brushing; the harmful effects of food residues and microbes remain.
When brushing teeth, the movement of the brush is usually carried out along the axis of the tooth, capturing part of the gum and simultaneously massaging the soft tissues. In order to clean your teeth well, you need about 300 paired (up and down) movements with a toothbrush. All dental surfaces are cleaned sequentially: labial, lingual, chewing. The toothbrush should penetrate into the interdental spaces, between the cusps of the teeth, that is, into the places of greatest accumulation of plaque and retention of food debris. The entire procedure should take at least 3-5 minutes. If these conditions are met, the degree of cleaning of teeth from plaque will be quite good.
THE BETTER WAY TO BRUSH YOUR TEETH
For children with a healthy gum mucosa, pastes with pleasant taste properties can be recommended for oral care: “Well, wait a minute!”, “Yagodka”, “Little Red Riding Hood”, “Children’s”, “Artek”, “Carlson”, etc.
The use of tooth powder for dental care is not recommended on the grounds that young children, who have not yet learned to regulate their breathing, may accidentally inhale the powder, which will cause coughing and discomfort. The child will develop a dislike for brushing his teeth and subsequently it will be difficult to accustom him to this procedure. The use of toothpaste eliminates such phenomena. In addition, tooth powders wear away more of the hard tissues of teeth, which are less durable in children than in adults.
If teeth are affected by caries in children, as well as to prevent it, you should use Cheburashka toothpaste, which contains special anti-caries additives. For this purpose, you can also use therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes “Arbat”, “Zhemchug”, “Remodent”, “Ftorodent”. If children have inflammation of the oral mucosa (gingivitis, stomatitis, etc.), then, in agreement with the attending dentist, you can use chlorophyll-containing toothpastes “Extra”, “Novinka-72”, as well as pastes, in which include extracts of medicinal plants - “Sputnik”, “Chamomile”, “Azulena”, “Enchantress”, “Leningradskaya” or containing biologically active drugs: “Yagodka”, “Prima”, “Bee”.
In conclusion, it must be emphasized once again that underestimating or ignoring the importance of oral hygiene in the overall complex of preventive measures often negate the therapeutic and health-improving actions carried out by health authorities. Adults and children should know about the importance of performing and strictly observing hygiene skills. Only under this condition will oral hygiene become one of the most widespread and effective methods of prevention.
General hygiene rules
- Brushing your teeth with toothpaste and a brush should be done at least 2 times a day: after breakfast and in the evening in preparation for bed. Brush with soft bristles, paste - without abrasives, with minimal fluoride content,
- Dental floss: a mandatory hygiene attribute that plays an important role in cleaning interdental spaces after eating,
- gels and rinses: hygiene products that help provide even more thorough care for the baby’s oral cavity, but their use must be agreed with the treating dentist,
- limiting the consumption of sweet mixtures: the best prevention of such a form of the disease as bottle caries.
It is also useful to start accustoming your baby to a device such as an irrigator. But it should be used under the strict supervision of an adult. And don’t forget to offer your baby more clean drinking water rather than sweet juices.
Caring for babies' mouths and teeth
Care for the mouth of a baby and infant should be done with extreme caution. There are no teeth yet, but the body is already configured to erupt them, the process of preparing bone and soft tissue is underway. Therefore, at the first stage you should:
- several times a day, gently wipe the child’s gums and tongue with a cloth moistened with boiled water;
- do not use active and irritating agents - soda, “adult” balms, rinses;
- on the recommendation of a doctor, use saline solution to cleanse the baby’s mouth;
- By the time of teething, be prepared for swelling and soreness of the gums, take the measures prescribed by doctors to relieve pain and prevent inflammation.
Particular attention is paid to examining the mouth, identifying spots, ulcers and manifestations of [aphthous stomatitis]. After a year of life, when milk immunity begins to weaken, during examination it is important to promptly identify the signs of herpes infection in the child’s mouth. Hygiene of a baby’s first teeth is aimed at removing bacterial plaque, which contains a huge number of microorganisms.
READ Symptoms and treatment of periodontitis in baby teeth
How to care for the oral cavity in the first years of a child's life
During the first six months of life, the most suitable conditions for the rapid proliferation of harmful bacteria are formed in the baby’s mouth, which can lead to the development of infection, caries and stomatitis, as well as other diseases of the teeth and oral cavity that require serious treatment. At the same time, a serious danger of infecting a child arises in cases where adults, being carriers of the infection, neglect basic safety rules, for example, kissing the baby, licking a fallen pacifier, or trying food from a feeding spoon.
To eliminate the risks of developing caries and other diseases, it is important to ensure the proper level of hygiene from a very young age. Even before the first teeth appear, parents need to use special wipes and fingertips to carefully remove bacteria and plaque from the gum tissue. Typically, such hygiene products contain xylitol, which is capable of blocking the proliferation of microbes, which are the main cause of carious lesions.
How to brush baby teeth
After the first baby teeth appear, it is time to teach your baby to brush them daily with a brush and toothpaste. Experts advise starting with 15-20 seconds of carefully cleansing the enamel and gums from plaque and bacteria accumulation. Gradually, the duration of the procedure can be increased. At this stage, parents need to try to interest the child in this, albeit routine, but extremely necessary procedure. For example, experts offer the following options:
- game form: in order to awaken a child’s interest in brushing his teeth, you can, for example, tell how the “magic brush” makes his teeth beautiful and healthy one by one, carefully driving away harmful microbes,
- example from adults: children tend to copy the behavior of their parents, and this can be used to teach your baby to brush their teeth daily using a brush. To do this, it is enough to perform the hygiene procedure together, while helping the child do it correctly. Over time, daily brushing will become a habit, and if the toothpaste also has a pleasant taste, then the baby will definitely enjoy this procedure.
A brush and paste are essential accessories for maintaining oral hygiene. When it comes to caring for children's teeth, it is important to carefully choose hygiene items and products. It is better to give preference to a low-abrasive paste, as well as a brush with soft bristles. Experts say that it is better to start with a model with short bristles (about 2 cm), as well as a narrow small head and two rows of tufts.
For one-time cleaning, a volume of paste equal to the size of the baby’s little fingernail will be sufficient. It is better that the paste has a pleasant taste and does not contain fragrances - then it will be easier to accustom the child to daily hygiene. During training, carefully ensure that the baby does not swallow the paste, otherwise too much of the product swallowed can lead to the development of allergies and irritation of the mucous membranes.
Memo for parents “Oral hygiene for your child”
Currently, there are many models of toothbrushes. Each toothbrush consists of a handle and a working part - a head with bushes of bristles planted in it. The available types of toothbrushes differ in the shape and size of the heads, the location and density, the length and quality of the bristles (natural bristles or synthetic fiber), the size and shape of the handles.
For many years, only natural bristles were used for toothbrushes; recently, preference has been given to synthetic fiber (nylon, setron, perlon, derlon, polyurethane, etc.). Toothbrushes made from artificial fiber have a number of advantages over brushes made from natural bristles. As a result of clinical observations, there was no difference in the cleansing properties of artificial and natural bristles. The quality of teeth cleaning is not affected by the shape of the toothbrush handle. However, the effectiveness of using toothbrushes, and therefore the correct individual selection of a brush, depends on the so-called hardness of the brush field. There are four levels of toothbrush hardness: hard, medium hard, soft and very soft. The exception is children's toothbrushes, which are made from soft and very soft bristles. If used incorrectly, hard brushes can injure the gums and hard tooth tissues (abrasion of enamel and dentin). Pre-treating brushes with warm water makes them softer. Medium-hard brushes are most effective, since their bristles, being more flexible, clean the gingival sulcus and penetrate better into the interdental spaces. Very soft brushes are recommended for use during the period of treatment of periodontal diseases, when the condition of the gums does not allow vigorous brushing of the teeth. Using a very soft toothbrush in combination with careless brushing can sometimes lead to the formation of pigmented stains (brown, black, etc.) on the teeth. Therefore, if the teeth and periodontal condition are normal, it is recommended to use medium-hard and soft brushes.
The frequency and arrangement of the bristles (bush planting) are important in the design of the brush. The optimal distance between bristle bushes is considered to be 2-2.5 mm. The simplest and most effective is their parallel arrangement. However, they often produce brushes with a dense bush, which reduces the cleansing effect on the lateral surfaces of the teeth. Pairwise inclined (V-shaped) bush planting is widely advertised abroad (Germany, Norway). However, studies have shown that it does not have any great advantages over parallel.
In addition to the frequency of arrangement of tufts of bristles, there is the concept of “trimming the brush field and bushes.” Most modern brushes have a serrated surface, with the edge bristles in the bushes sitting lower than the central ones. This design allows the central long bristles to enter the narrow interdental spaces, but if the bristles are hard, then only the central bristles have the cleaning ability, since they do not allow the side bristles to touch the surface of the tooth during brushing. Brushes made of soft bristles with a smooth cutting surface remove plaque well without damaging the mucous membrane of the gums. Brushes with complex contours of the brush field surface are also available for sale. Special clinical observations have shown that such brushes can be traumatic, since during cleaning the entire load falls on a small number of bristles protruding from the tuft.
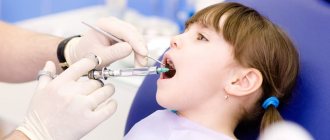
Professional oral hygiene for children
Hygienic procedures in the dentist’s office are united by a single goal - strengthening the tissues of the oral cavity and ensuring high-quality prevention of the development of dental diseases. Such measures include careful removal of plaque and deposits, sealing fissures, that is, natural depressions on chewing teeth, as well as treating the enamel with protective fluoride-containing compounds.
At a preventive appointment, the dentist will also tell you how to treat the baby’s oral cavity if it is too early for him to brush his teeth on his own, how to ensure proper care of baby teeth and how to choose suitable hygiene products, as well as give valuable advice and recommendations on the prevention of dental diseases. Parents need to listen carefully to all the instructions of the specialist and do not forget to put them into practice - a responsible approach will ensure the health of the child’s oral cavity in the future, when permanent teeth appear.
Category Children Published by Mister stomatolog
What destroys teeth in children
From the listed features of the structure of the mouth, we can conclude about factors that can harm this complex and sensitive system:
- penetration of bacteria and viruses - as medical statistics show, the saturation of microorganisms in the mouth is the highest in comparison with any other organ and department of the gastrointestinal tract;
- physical, chemical and thermal effects on teeth and mucous membranes from food, errors in care, ingress of foreign substances;
- constant temperature changes from inhaling cold air, drinking hot and cold drinks;
- fluctuations in the acid-base balance, which, when moving towards the acidic side, negatively affect the condition of tooth enamel, consisting of calcium compounds.
READ Review of the best ointments and gels for stomatitis in the mouth
Caring for a child’s oral cavity should include all measures to reduce the destructive effect of these factors. In addition, it is very important to take into account the age component, since teeth actively change as they grow older, and the preventive measures taken must be adequate to their condition.