About the profession
A general dentist must know and be able to do quite a lot; in fact, he can do almost everything in this specialty, because he is a bit of a dentist-therapist, an orthopedist, a hygienist, and a surgeon. He will inform the population how to care for the oral cavity and provide first aid, and will cure the damaged tooth, remove it, if necessary, and prescribe the necessary examinations. It can help almost any patient suffering from toothache and various types of inflammation of the oral mucosa.
Types of surgical dentistry
To eliminate deep damage, the doctor needs to create a path to it. This is called online access. It can be open or closed. The first is made through incisions on the side of the cheek or chin. The closed one is passed through an endoscope - a device for filming and manipulation.
The surgical office offers not only tooth extraction, but also tooth-preserving operations, as well as services for the treatment of gums and jaws that cannot be cured with conventional dental procedures or medications. Then the doctor excises pathological formations and dead areas, cleans and drains purulent cavities and performs plastic surgery after tooth resection.
Inflammatory diseases in surgical dentistry
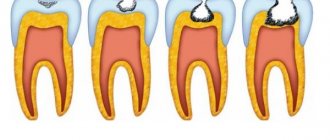
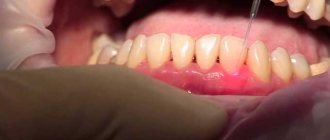
One of the areas of surgical dentistry is the elimination of purulent processes in the oral cavity and maxillofacial area. They develop with acute or chronic pathology of teeth and periodontal tissues. The resulting pus is removed only through an incision in the gums.
Inflammatory pathologies include:
- Periodontitis
– inflammation of the ligaments that hold the teeth; - Periostitis
is a lesion of the periosteum of the process of the upper jaw, which is characterized by the discharge of pus. Outwardly this manifests itself as gumboil; - Osteomyelitis
– purulent destruction of all bone elements; - Sinusitis
- accumulation of inflammatory fluid in the cavity of the maxillary sinus; - An abscess
is a limited abscess.
A specific complication is pericoronitis of “figure eights,” when their sharp growing edges cut into soft tissue and cause damage. Because of this, local bacteria can cause inflammation around the crown. In mild cases, the dentist cuts the gum, separating the “hood” under which the purulent mass accumulates. If the molar grows correctly, then it will easily erupt. Otherwise, if it is in an abnormal position, it must be removed along with the bone plate.
Non-inflammatory diseases in surgical dentistry
Inflammation does not include all congenital and acquired anomalies, tumors and injuries of the dental system. In adults, dental damage, jaw fractures and injuries are usually diagnosed. In mild cases, the dentist restores the teeth and blocks the sensitive branches with novocaine to relieve severe pain. In case of complications, the bones are excised, the muscles are sutured and the nerve is released if it is compressed or tightened by a scar.
The following problems are solved in children:
- Short frenulum of the tongue or upper lip
. Because of this anomaly, children will develop complications: infants have difficulty sucking the breast, slow growth of the jaw bones up to 3 years of age, and impaired diction up to 7 years of age. - Malocclusion
. From 5 to 15 years old, mouthguards and braces are usually used to correct the bite and irregularities of the dentition. But if the bone is bent, it has to be excised. The operation is performed by a specialist who has completed an internship in the field of orthodontics.
In adults and children, tumor-like formations in the jaw area are surgically eliminated; the most common of them are cysts, osteomas, tumors from blood vessels, fatty tissue and cartilage. After removing these formations, the surgeon performs plastic correction of displaced and damaged structures: increases the missing bone volume and closes the defects using natural or artificial materials.
Implantation
Implantation is usually used to restore one tooth. It takes place in several stages. First, the doctor prepares hard and soft structures, builds up or sharpens the bone plate, drills a bed for the pin, and then screws it in. After the implant is fixed in the gum, an abutment is placed on it, and then an artificial crown or prosthesis.
Educational process
The educational process is implemented in two departments: propaedeutics of dental diseases and general and clinical dentistry. The educational program is designed for persons with higher medical education. The training is aimed at training highly qualified specialists in the field of treatment of basic dental diseases, for independent work in public health institutions or in private practice. The training is practice-oriented in nature and is aimed at developing systemic knowledge and professional competencies that allow for therapeutic activities.
Sources
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
- Surgeon Nikolai Pirogov (train)
- Surgical instrument
See what “Surgical dentistry” is in other dictionaries:
- Dentistry
— The request “Dentist” is redirected here. A separate article is needed on this topic... Wikipedia
Dentistry
- a field of science that deals with the study and treatment of diseases of the oral cavity, jaws, teeth and surrounding tissues. The subsections of dentistry are: public health (specialty dentistry), endodontics, therapeutic dentistry ... Medical terms
DENTISTRY
— (dentistry) is a field of science that deals with the study and treatment of diseases of the oral cavity, jaws, teeth and surrounding tissues. The subsections of dentistry are: public health (specialty dentistry), endodontics, therapeutic... ... Dictionary of medicine
Dentistry
— I Dentistry (Greek Stoma, stomatos mouth + logos teaching) is a field of clinical medicine that studies the etiology and pathogenesis of diseases and injuries of the teeth, oral organs and maxillofacial area, developing methods for their diagnosis, treatment and ... Medical encyclopedia
dentistry
- And; and. [from Greek stoma (stmatos) mouth and logos doctrine] A branch of medicine that studies diseases of the teeth, oral cavity, jaws and border areas of the face and neck. Surgical village Orthopedic s. S. childhood. ◁ Dental, oh, oh. S.... ... Encyclopedic Dictionary
dentistry
- And; and. (from Greek stóma (stómatos) mouth and lógos teaching) see also. dental Branch of medicine that studies diseases of the teeth, oral cavity, jaws and border areas of the face and neck. Surgical dentistry. Orthopedic dentistry.... ... Dictionary of many expressions
surgical dentistry
- section S., devoted to the study and diagnosis of diseases and injuries of the oral cavity and maxillofacial region, the development of surgical, including surgical, methods of their treatment ... Large Medical Dictionary
Dentist
Dentist
— Examination in a dentist’s office Dentistry is a branch of medicine that deals with the study of teeth, their structure and functioning, their diseases, methods of their prevention and treatment, as well as diseases of the oral cavity, jaws and border areas... ... Wikipedia
Bezrukov, Vladimir Maksimovich
— Vladimir Maksimovich Bezrukov Date of birth... Wikipedia
Books
- Surgical dentistry, . The textbook provides brief information about the history of the development of surgical dentistry and the organization of dental surgical care in clinics and hospitals. Provides information about...
Surgical dentistry
is a branch of dentistry that specializes in performing surgical interventions in the oral cavity, both on soft and hard tissues.
Currently, the goal of surgical dentistry
is to maximize tooth preservation.
The functions of a dental surgeon
are not limited to tooth extraction.
Modern advances in dentistry make it possible to effectively treat diseases while preserving teeth. Surgical methods are used to treat various types of inflammation, tumor processes, mechanical damage, as well as congenital and acquired deformities and defects.
Dental surgery
is closely related to other dental specialties, such as orthopedics, orthodontics, and therapy.
Often, complex treatment of dental diseases
includes several therapeutic measures carried out sequentially using methods of therapeutic, surgical, orthodontic and orthopedic dentistry.
Practice
After practicing their skills in simulation courses, residents are assigned to departments of dental clinics in Moscow, where, under the guidance of department professors, they have the opportunity not only to expand their knowledge, but also to see its application in practice. In addition, one of the clinical bases of the Department of General and Clinical Dentistry is the Russian Scientific Center of X-Ray Radiology (FSBI RSCRR), where the department implements one of its main clinical and scientific areas “Providing dental care to patients with somatic pathology.” Within the framework of this area, the department considers issues of early diagnosis of oncological diseases in the mouth, dental support for oncological and oncohematological patients, dental rehabilitation of patients with complex somatic pathology. This area is very rare and very popular, since today most patients have concomitant pathology.
When should you contact a dental surgeon?
To the dentist-surgeon
should be contacted if:
— the presence of mechanical injuries to the maxillofacial system; - if there are indications for tooth extraction; - the presence of an area of infection that cannot be cured with therapeutic methods; — congenital or acquired defects of the maxillofacial area; — presence of supernumerary or impacted teeth; - inflammatory processes in the oral cavity; — indications for orthopedic, periodontal and orthodontic treatment.
Surgical dentistry services
Surgical dentistry includes
provision of the following services:
— dental implantation; — tooth-preserving procedures of varying complexity; — complete or partial removal of teeth; - treatment of various types of inflammatory processes (abscesses, periodontitis, phlegmon, osteomyelitis and others); - treatment of oral tumors; — preparation of the oral cavity for the installation of dentures; — removal of small tumors on the face; — performing plastic and reconstructive surgeries on the jaws; — treatment of diseases of the trigeminal nerve; — performing operations on periodontal tissues.
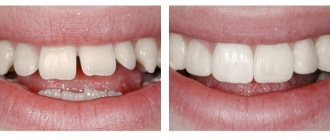
Dental restoration
Dental restoration is one of the main areas of dental surgery
. In dentistry, great attention is paid to tooth-preserving operations. Such operations include:
— amputation of tooth roots is carried out if one of the roots of a three-rooted tooth cannot be treated, but the tooth is preserved; — corono-radicular operations; — removal of tumors in the soft tissues and bones of the oral cavity.
The most common operation is removal of a dental cyst. Usually a cyst forms at the apex of the root, and the cyst is usually removed along with the root of the tooth, while the tooth itself is preserved;
— restoration of pulpless teeth.
This procedure is carried out to strengthen the remaining tooth walls, which, after depulpation, lose moisture and become fragile. Pins are used as support for the monolith, which occupies the entire chewing surface.
There are two types of dental care: therapeutic and surgical. In the therapy room, they treat and prevent only those diseases that can be eliminated by superficial manipulations.
In the surgical room, defects are corrected and damaged organs are restored in a planned and emergency manner. As a rule, dental surgeons receive additional specialization in the field of maxillofacial surgery and accept patients with serious problems of the dental system, soft and hard tissues of the face.
On the portal Stom-Firms.ru you will find out when you need to contact the department of surgical dentistry and how much dental surgery costs in different centers.
Job description
Provides orthopedic treatment of defects and deformations of the maxillofacial area. Conducts orthopedic treatment of pathology of the temporomandibular joint.
Evaluates the quality of dentures manufactured by a dental technician. Carries out rehabilitation measures after the application of dentures and conducts clinical observation.
Provides education to patients regarding proper oral hygiene. Prepares accounting and reporting documentation approved for use in the Russian Federation. Determines the amount of necessary first and emergency aid and provides it. Identifies indications for urgent or planned hospitalization. Identifies possible complications of drug therapy.