Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, whether inflammation of the roots of teeth, gums or mucous tissues, are most often treated by taking antiseptic drugs. Strengthened oral hygiene also helps to cope with some diseases.
Taking antibiotics is relevant even in more serious forms of the disease or after complex and large-scale surgery.
Antibiotics
Causes of gum inflammation and toothache
The most common reasons why gums may become inflamed and pain radiating into the tooth enamel may include the following factors:
- Low immunity, poor health.
- Common chronic diseases.
- Unbalanced diet.
- Alcohol abuse and smoking.
- Circulatory problems.
- Difficulty in teething.
- Congenital malocclusion.
- Deficiency of nutrients and vitamins.
- Lack of calcium.
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
- Ecological problems.
- Constant stress.
- Being in a state of depression.
Inflammation of the gums is a cause for concern.
You can understand that the inflammatory process has begun by the following symptoms:
- Pain in the gums or mucous tissues of the mouth.
- Sensitivity to hot, cold and sweets.
- Plaque deposits.
- Sores and sores.
- Bad breath.
- Swelling.
- Feeling of heat in the mouth or high body temperature.
- Physical weakness.
Methods of application
You definitely need to know how to properly use any antibiotic for dental inflammation. It is better to first consult with a doctor, because a specialist will be able to prescribe the optimal regimen for using drugs of this type.
In the field of dentistry, antibiotics have long been used in the treatment of dental flux. Their use makes it possible to stop the development of the purulent process, and they also prevent its spread throughout the body.
It is advisable to use medications at the initial stage, they will help prevent the development of pustules, and this means that they will provide treatment for gumboil at the earliest stage of its development. But in the later stages, the use of antibacterial agents is possible only after opening the purulent formation.
To understand how to use antibiotics, it is worth considering important recommendations:
- antibiotics, which are produced in the form of capsules, tablets, powders, must be taken orally. Medicines available in the form of tablets and capsules must be taken with a sufficient amount of water when taken. The powder should be dissolved in water. The solution can be used as a rinse or for oral administration;
- in the form of ointments. The drugs are recommended for external use; they are applied to the area with inflammation. They should be used at least 2-3 times a day;
- injections. Medicines in this form are considered the most effective for flux. Injections are recommended to be administered intravenously or intramuscularly.
In what cases are antibiotics prescribed?
With gingivitis, the inflammatory process affects only the gum tissue, without in any way disrupting the connection between the gums and teeth. Antibiotics are prescribed only when other treatments have not had the desired effect. Most often this is a problem for people with weak immune systems - children and pregnant women.
With periodontitis, inflammation disrupts the periodontal junction. Only antibiotics can suppress this pathological process.
Periodontitis. Photo.
With periodontitis, the disease affects the bundle-shaped ligaments of connective fibers, which are responsible for fixing the tooth in the socket. Antibiotics are used in cases of emergency when antiseptics are powerless.
Periostitis sometimes appears as a result of advanced periodontitis. This is an inflammatory disease of the periosteum, which can be eliminated with antibiotics.
Antibiotics are used only when antiseptic and bactericidal drugs do not have the required effect.
Rules for taking antibiotics
For tooth pain caused by inflammation, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. The duration of treatment can be from 5 to 14 days . The doctor will tell you what antibiotics to take for tooth inflammation and in what mode. Before the appointment, you need to warn the dentist:
- about cases of severe allergic reactions to any medications;
- about chronic diseases;
- about medications taken on a regular basis (to determine compatibility).
Since the effect of any, even the most effective antibiotic for tooth pulpitis and other inflammatory diseases will begin only after 24–48 hours, it is better to warn the doctor about the presence of pain. If your jaw hurts, disrupting the normal rhythm of life, taking painkillers is indicated. They can be drunk for 5 days until the infectious process is suppressed.
Read also: Is Chlorhexidine an antibiotic or not?
Important! After the clear symptoms (pain, swollen gums and soft tissues) disappear, some patients stop taking the prescribed medications. This should not be done - the course must be completed to the end, otherwise the sore spot will continue to inflame with renewed vigor.
Another category of self-medicators begins to take the drug in an increased dose from the first days of treatment. This is also unacceptable. Bactericidal agents have strong side effects and have a toxic effect on the body, so you can take exactly as many tablets as the doctor prescribed.
Why and how to use probiotics
Given the tendency of the active substances of antibiotics to disrupt the microflora, many dental clinics simultaneously prescribe probiotics that restore it.
The names of these drugs are known to everyone: The first dose of the probiotic can be taken even before the start of treatment, and after completing the main bactericidal course, you need to drink the medicine for another two weeks.
Compatibility of antibiotics with alcohol
Alcohol of any kind is absolutely incompatible with antibiotics, so it should be excluded for the entire period of their use. Hepatologists advise waiting to drink alcoholic beverages and medications for at least 2 weeks after finishing antibacterial treatment.
What antibiotics are used in dentistry for toothache and inflammation?
For inflammation
- Lincomycin is most often prescribed against inflammation of the tooth root, gumboil, periodontitis, pulpitis and periostitis. It is also widely used after dental implantation, if tissue inflammation has developed. The substance accumulates in bone tissue, thereby preventing the spread of pathogenic bacteria throughout the oral cavity. It has 3 release forms - capsules, solution and ointment. In cases of severe periodontitis, antibiotics are injected into the muscle.
- Clindamycin is a drug with broad antibiotic action. Available in the form of capsules and injections. The duration of the course is most often 10 days, 2 tablets or 2 injections per day.
- Tsiprolet is a drug from the group of fluoroquinolones, available in the form of tablets with a dosage of 500 mg. It has a wide spectrum of action, eliminates periostitis, periodontitis, abscesses and other problems of suppuration. While taking the drug, it is not recommended to consume dairy products and dietary supplements high in magnesium, calcium and iron .
Lincomycin
For the treatment of flux
- Ampiox - combines two antibiotics - oxacillin and ampicillin. It has a complex effect, killing pathogenic microorganisms. Eliminates gumboil and periostitis in a short time.
- Lincomycin – an antibiotic agent belonging to the group of lincosamides. Available in the form of capsules, solution and injections. It is used to treat ulcerative gingivitis, abscesses, fistulas, as well as inflammatory processes that destroy jaw bone tissue. And also used in the postoperative period.
The drug negatively affects the digestive system and can cause intestinal dysbiosis.
- Tsifran even affects bacteria resistant to tetracycline compounds. Not recommended for use by teenagers.
After tooth extraction
- Amoxicillin is quite often used to treat dental diseases. Safe for children and pregnant women if the antibiotic is taken under the supervision of a doctor. Relieves inflammation and prevents secondary infection.
- Azithromycin - has a complex formula of the active substance in the form of azithromycin hydrate. The most popular form of release is 250 ml gelatin capsules with powder. The capsule dissolves in the intestines for effective absorption of the antibiotic. Take 2 capsules per day.
- Ibuklin - relieves pain due to the action of prostaglandins on the nerve endings in contact with foci of inflammation. Reduces swelling, relieves fever. Absorption occurs immediately after the substance enters the stomach, as a result of which the effect is felt after two hours.
Azithromycin
When treating dental infections
- Amoxiclav – has antibacterial activity and is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. Available in tablet form.
- Tsifran - has a bactericidal effect, inhibits the synthesis of bacterial DNA. Widely used for inflammatory diseases of the gums and oral cavity.
- Tsiprolet – effectively destroys both reproducing microorganisms and bacteria in the resting phase.
After installation of a dental implant
Doctors disagree about the issue of taking antibiotics after having a dental implant installed. Most often, postoperative therapy is limited to taking antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. Particularly in cases where the operation was completed without complications.
According to medical research, infectious complications rarely accompany the installation of dental implants.
However, antibiotics are mandatory when the operation was very long and difficult, for example, when removing an impacted wisdom tooth, bone augmentation, flap surgery on the gums, etc.
Amoxiclav
In this case, antibiotic drugs of the penicillin group are prescribed. The duration of treatment varies depending on the specific situation from 5 to 8 days. If the implantation was long and complex, and the tissues heal very poorly, then the course can be extended to 14 days.
Penicillin and its analogues are most often used:
- Amoxiclav - contains clavulanic acid and amoxicillin. It is quite effective and costs slightly more than amoxicillin.
- Amoxicillin is used much more often in dental practice due to its non-toxicity and low cost. It has virtually no side effects or they are mild.
Nowadays, cephalosporin drugs are increasingly used for the prevention of purulent infections. These are broad-spectrum antibiotics that differ from their analogues in that they exhibit high activity against penicillin-resistant bacteria and mixed aerobic-anaerobic infections.
The basic requirements for antibiotic drugs used for prophylactic purposes in the postoperative period are as follows:
- Wide spectrum of action of the drug.
- High degree of efficiency.
- Quick destruction of harmful bacteria.
- A small list of contraindications.
- Well tolerated by the body.
The daily dose and length of the antibiotic course should be determined by the attending physician, based on the patient’s body weight and the specific situation. The most common contraindications to taking antibiotics are pregnancy and lactation, as well as kidney disease.
Briefly about the action of antibiotics
Antibiotic therapy is only effective if the prescription and use were made correctly. When the drug is transferred through the bloodstream, bacteria and their development are destroyed.
Antibiotic treatment is only effective if it is chosen correctly
This is interesting: antibiotics are drugs that help suppress the reproduction of living cells. It does not take into account whether these cells are healthy or diseased.
Antibiotics are:
- bactericidal (they kill bacteria);
- bacteriostatic (the immune system has time to prepare to reject the bacteria by stopping the development of pathogenic cells).
Action of antibiotics
The drugs protect patients from the possibility of complications when treating the disease that caused the toothache. This pain in most cases indicates some kind of damage: soft tissues, gums, or the development of diseases.
General rules for taking antibiotics
To ensure that taking antibiotics does not cause harm to the body, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Follow the dosage prescribed by the doctor - do not shorten or extend the course of treatment.
- Take your pills at the same time every day.
- Follow the instructions - take the medicine before or after meals, depending on the instructions.
- Take the medicine only with clean water, not drinks.
- Submit a bacterial culture. Thanks to this research, you can choose the most suitable medicine.
- Do not take antibiotics without a doctor's prescription.
- Restore the intestines after taking antibiotics - fermented milk products and drugs such as Linex and Hilak Forte are suitable for this purpose.
- Enrich your diet with healthy foods, raw fruits and vegetables and reduce your intake of fatty and fried foods. This is necessary in order to strengthen the body after taking antibiotics.
Rules for the use of antibiotics
Caution when taking dental antibiotics is an immutable rule. When prescribing a medicine, the doctor takes into account several factors: spectrum of action, ease of administration, degree of toxicity, presence of side effects and their number, contraindications. If you are prescribed such a remedy, follow these recommendations:
- study the list of side effects and monitor your condition;
- strictly follow the dosage prescribed by your doctor;
- Take it according to the instructions for the drug;
- take the tablets only with drinking water;
- find out which medications the prescribed drug can be used with;
- Avoid alcohol while taking an antibacterial agent;
- do not interrupt the course of treatment;
- Please note that their effect of the drug begins after 24-48 hours.
It is all the more important to follow the rules of administration because antibacterial drugs have a strong effect on the body. An overdose leads to serious complications; the wrong course of administration does not give the desired effect and negatively affects other organs. If the dentist has told you how to take the medicine and pointed out special nuances, you must strictly follow his recommendations. It is obvious that self-medication of the mouth with such drugs carries an increased danger for the patient.
For the treatment of flux
Flux not only hurts, it also causes physical discomfort. The easiest way to deal with flux is with antibiotics. However, you should not resort to them yourself; let your dentist prescribe the appropriate remedy for you. Typically, the doctor prescribes medications such as:
It should be borne in mind that they all have special properties, so you cannot take them on your own. Lincomycin works effectively, but it has many contraindications, but Ampiox has practically none. Tsifran st is prohibited for use by children under 16 years of age. The maximum course of treatment is 7 days, the dosage is determined individually.
Read also: Analgin for toothache, method of use
To relieve inflammation from gums
For gingivitis and periodontitis, similar products are also used. As a rule, the dentist prescribes Metronizadol in combination with stronger antibiotics. For example, Lincomycin, which is taken in tablet form or given by injection. The drug should not be given to children under 6 years of age.
Clindamycin is also used, a drug with fewer side effects. For swollen gums, it is advisable to take the medicine in tablet form. Injection into the gums is dangerous due to the high concentration of the drug, it begins to quickly kill microorganisms, they accumulate, and toxins are released, causing negative processes in the area of attachment of the tooth to the bone.
After tooth extraction
After removing a patient's tooth, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics. Drugs are prescribed that have analgesic and strong anti-inflammatory properties:
- Amoxicillin,
- Azithromycin,
- Levomycetin,
- Ibuklin,
- Metronidazole.
After tooth extraction, it is important for the doctor to prevent the spread of possible infection to the periosteum and other tissues, and to relieve the patient’s pain. The course of administration is limited so that an overdose does not occur and complications do not arise after removal from the antibacterial agents themselves.
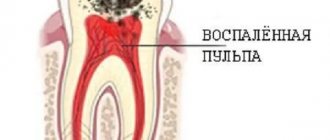
Inflammation of tooth roots
When there is inflammation in the root of the tooth, depulpation is added to antibiotic treatment. Infection during caries or penetrating under the crown requires immediate relief to avoid its spread to the entire bone tissue. Taking antibiotics to prevent the growth of the process also becomes a mandatory measure. For drug treatment of pulpitis, the dentist selects osteotropic and penicillin medications, having studied the nature of the infection.
As a rule, drugs such as Ciprolet, Biomycin, Amoxiclav, Ciprofloxacin, Doxycycline, Augmentin are prescribed. Their task is to eliminate the inflammatory process and reduce pain.
For the treatment of other dental infections
For maxillofacial injuries and pericoronitis, antibiotics are taken under the supervision of a specialist.
To alleviate the condition and prevent further infection of the body, penicillin medications are used. Painkillers are also prescribed. The dentist, focusing on the patient’s condition, can prescribe Lincomycin, Doxycycline, Ampicillin, Tsifran st, Tsiprolet. An advanced form of caries, chronic sinusitis, pulp burn, infection through the bloodstream in the presence of another disease - all these are indications for a course of medication.
- For diabetic patients, it is better to take special medications with minimal side effects (Nomitsin, Tarivid, Sifox).
- For odontogenic infections, dentists prescribe Gentamicin.