My tongue hurts, as if it was burned - how to find out the cause and how to treat it
The feeling of burning pain, not associated with drinking hot drinks or suffering a certain injury, is a signal notifying about disorders and problems of the body.
Why does the tip of the tongue hurt, as if it were burned? Let's figure it out.
Glossalgia is a term for pain in the tongue. According to doctors, glossalgia is rarely primary.
Typically, tongue pain is the first sign of injury or underlying problems that later develop into other health problems.
Local causes of pain
The painful sensation is often provoked by local irritants and diseases of the oral cavity. These include:
- allergic reaction;
- fungal infection;
- violation of hygiene rules;
- microtrauma;
- inflammatory process in the oral cavity.
Mechanical damage or microtrauma occurs unnoticed.
For example, a person may have an incorrect bite in his sleep. Other causes of microdamage include seeds, small fish bones, sucking candies (lollipops), poorly ground fillings and new dentures.
Fortunately, such mechanical injuries rarely cause swelling or redness. In this case, the sensitivity of the damaged epithelium worsens.
A mild allergic reaction can occur to toothpaste, medications or food. In such cases, a burning sensation on the tongue is not accompanied by external changes.
For example, a similar sensation can be caused by eating sour apples, pineapple or unripe grapes.
Their development occurs in infected wounds of the gums or mucous membrane of the tongue.
It can also be caused by a recent stressful condition or general weakness of the body.
Are you worried about a burning sensation in your mouth and esophagus? Read what you can do in this case.
Glossalgia is described in detail in this material. Causes and treatment.
Features of vestibuloplasty are described here. As well as reviews and videos.
How it manifests itself
Mechanical damage is most often caused by seeds, fish bones, dentures, and poorly processed fillings. Such microtraumas do not always cause redness and swelling; sometimes ordinary pain occurs.
When allergic reactions occur, a burning sensation of the tongue is felt, but no external changes occur. The same feeling comes from eating unripe or sour fruits.
If, a few days after painful sensations, ulcers form on the mucous membrane or when a coating appears on the tongue (or vice versa, it becomes glossy), this signals an inflammatory disease. Inflammation begins from infection of small wounds on the gums, when the body is already weakened, especially due to stress.
Due to a long illness and a decrease in immunity due to antibiotics, a fungus of the genus Candida appears in the oral cavity. This fungus is constantly present in the oral cavity, but with any changes it is activated and becomes the cause of candidiasis. When you get a fungus, your mouth feels burning, dry, a white coating appears on the tongue and cheeks, and itching on the lips.
Disease as a cause of pain in the tongue
However, burning of the tongue is not always associated with one of the local irritants. The following pathologies can also contribute to increased sensitivity:
- diabetes;
- neurosis;
- hypovitaminosis;
- osteochondrosis;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- gastrointestinal disease;
- neuralgia of the cervical nerve;
- liver disease.
In this case, sensitivity will be expressed not only by burning, but also by aching pain, temporary numbness of a certain area of the tongue, tingling, dryness, tingling and sharp pulsation.
Do not delay the visit, as this is not a microtrauma, which should have healed over this period of time. After visiting a specialist, you will be prescribed initial examination methods:
- General blood analysis.
- If there is a suspicion of osteochondrosis, then fluorography or x-ray.
- Throat swab.
- Checking your sugar level.
Classification of pain
According to localization, there are the following types of pain:
Pain on the tip of the tongue occurs for the following reasons:
- Mechanical damage.
- Glossalgia is a feeling of thermal burn. When treatment is started, the disease can affect other organs. Patients with this disease say that a burning sensation is felt not only on the tongue, but also on the cheeks, gums and lips;
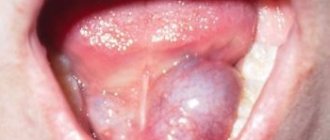
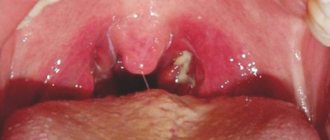
- Glossitis is an infectious disease where the lesion is observed only on the tip of the tongue. An inflammatory process is observed at the site of damage;
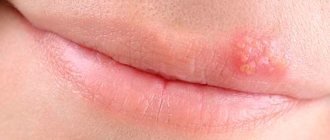
- Stomatitis is the appearance of small ulcers on the surface of the tongue. Any touch is accompanied by acute pain.
- Painful sensations at the base of the tongue cause problems with speech, interfere with eating, thereby disturbing the emotional state. The causes of pain when swallowing are very different: from an allergic reaction to an inflammatory process.
- Glossalgia - in this case, pain occurs both at the tip and at the base;
- Allergic reaction;
- Vitamin deficiency - tingling in the area of the root of the tongue;
- Abscess, phlegmon is a purulent disease that causes bad breath and excessive salivation. Consequences: the tongue swells, speech becomes slurred, and breathing problems occur. Both diseases are dangerous to health, so at the first symptoms you need to consult a specialist.
- Pain on the sides is most often provoked by stomatitis, various rashes, mechanical injury and glossalgia. However, there are several other factors that can cause a burning sensation:
- The sharp edges of a poorly regulated process;
- Smoking;
- Neuralgia.
Types and degrees of tongue burns
- thermal (thermal);
- chemical;
- electrical;
- radial.
- 1st degree. Only the top layer of the mucous membrane is damaged - it turns red, and after a while the tongue swells. At the same time, a burning sensation is felt. A first-degree burn does not require seeking medical help or any special measures; it heals on its own.
- 2nd degree. The deeper tissues of the tongue are injured, and bubbles with a colorless liquid inside appear on the surface. It's going well. Rinse with antiseptics. If you have a 2nd degree burn, you should consult a doctor.
- 3rd degree. Changes affect deep structures, ulcerative and erosive phenomena, and necrosis develop. Accompanied by severe pain. If you have a 3rd degree burn to your tongue, you must immediately consult a doctor. However, even if all urgent treatment measures are taken, the normal structure of the victim’s tongue may not be fully restored.
- 4th degree. Irreversible changes occur in all tissues of the tongue, and charring is possible. A 4th degree tongue burn often leads to death. If the victim’s life can be saved, then it is almost impossible to preserve the tongue and its functions.
Chemical burn
You can burn your tongue not only with hot tea. A chemical burn of the tongue occurs when, as a rule, accidental ingestion of certain chemical compounds (for example, acid or alkali) into the mouth. Most often, people are burned with sodium hydroxide, sulfuric, hydrochloric or ethanoic acid. Burns are less common
, mercuric chloride and Lysol.
First aid for a chemical burn is to rinse the tongue with water for at least an hour. The exception is burns caused by aluminum compounds, calcium oxide, and alkalis - in such cases, you should never rinse your tongue with water, as this may aggravate the situation.
After washing with water, the chemical reagent should be neutralized:
- The acid is neutralized with soda diluted in water: 1 tsp. for 0.5 liters of water.
- Alkali is neutralized with acids. To do this, it is recommended to use a solution of acetic or citric acid in low concentration.
- To neutralize quicklime, you need to rinse your tongue with a 20% sucrose solution.
After neutralizing the chemical compound, the pain in the tongue should decrease. If the pain is difficult to bear, you can take an over-the-counter pain reliever.
Chemical burns are usually the most severe in terms of consequences of all types of burns. Therefore, even if after the measures described above the pain in the tongue has subsided, still consult a doctor as soon as possible.
If the burn occurs due to contact with the surface of the tongue of a poisonous plant, consult a doctor immediately.
Electrical burn
Electrical burns to the tongue are a fairly rare occurrence. It can be obtained due to a malfunction of medical equipment, for example, in an office
We suggest you read: Proper nutrition when wearing braces - what can and cannot be eaten?
or when
. To prevent a child from getting such a burn, young children’s access to electrical appliances should be limited, and the dangers of electricity should be clearly explained to older children.
With an electrical burn of the tongue, convulsions, breathing problems, and fainting are possible, while the pain in the tongue characteristic of a burn may not be felt.
An electrical burn to the tongue cannot be treated at home; in such cases, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Radiation burn
Radiation burn of the tongue is usually a consequence
. Its symptoms are similar to a sunburn. Treatment of a radiation burn depends on its severity, the type of cancer, and is prescribed exclusively by the attending physician.
My tongue hurts, as if it was burned: what to treat before visiting a doctor
If pain on the tip of the tongue occurs due to minor injuries, then this place is lubricated with Lugol's solution soaked in glycerin.
Read also: How to take dental x-rays Also, do not forget about regular rinsing of the mouth - Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, sage and chamomile decoction.
By the way, they are recommended not only for painful sensations on the tongue, but also for various diseases of the oral cavity.
Painkillers such as Paracetamol, Ketonal, Ketorol or local anesthetics such as Anestezin will help to dull the pain a little.
If the cause of pain is nerves and stress, then to alleviate the condition, drink sedatives: valerian, Glycerin, motherwort or herbal tea, including valerian tincture.
It is worth knowing that the cause of a burning tongue is often inflammation of the lymph nodes and tonsils. The appropriate treatment will be determined by your therapist.
Unpleasant sensations in the tongue will go away as the inflammatory processes associated with sore throat decrease.
If pronounced sensitivity of the tongue is accompanied by a curd coating, then this is a sign of candidal stomatitis and only a doctor can prescribe treatment.
You can learn how to treat stomatitis in the video below:
If you are tormented by painful sensations and you cannot understand the nature of their occurrence, then to find out the cause, consult a dentist or therapist, and before that do not take any independent action.
How to diagnose?
If the cause is systemic disorders, the patient may be prescribed nootropics to restore the functioning of the nervous system, vitamins B, C, PP, sedatives and mild tranquilizers, a course of folic acid, analgesics and antidepressants. Local agents are also mandatory to be prescribed to normalize the condition of the oral tissues.
To eliminate the feeling of being burned, it is necessary to determine the cause.
Before treating the problem presented, it is necessary to understand the causes. It is recommended to seek specialized diagnostics if the symptom does not go away within five days. To determine the specific cause of the development of pathology, dentists prescribe a whole course of examinations.
X-ray and fluorographic examination may be necessary. This is recommended when a burning sensation is associated with osteochondrosis. Another mandatory stage of diagnosis is a smear taken from the throat.
If the burning sensation and pain do not go away after several days, you should urgently go to the hospital so that they can determine the source of the discomfort and prescribe appropriate treatment. To find out the reasons, you first need to do:
- Donate blood for tests.
- Measure blood sugar.
- Make a swab of the throat.
- Take an x-ray or fluorography (if necessary).
When inflammation of the salivary glands, lymph nodes, or cancer occurs, the source is determined immediately, since they are accompanied by certain external signs. If other symptoms occur, then most likely this indicates gastritis, ulcers and other similar diseases of the digestive and liver systems. Such diseases are characterized by the formation of plaque and unpleasant odor from the mouth, heartburn, and belching.
Why does my tongue hurt?
Glossalgia is a disease of the mucous membrane of the tongue or the entire organ, accompanied by pain, burning, numbness or swelling of the tongue. Most often, complaints that the tongue hurts, as if burned, are made by people over 40 years of age who do not adhere to the principles of proper nutrition and suffer from excess weight and metabolic disorders.
The most common causes of tongue pain:
- traumatic injury - biting the tongue while eating, minor injuries that occur due to unsuccessfully placed dentures or dental chips can cause inflammation and infection of the mucous membrane of the tongue;
- inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity - glossitis - inflammation of the tongue or stomatitis can develop due to a viral infection, decreased local and general immunity, poor oral hygiene and long-term use of antibiotics, hormones and other drugs that inhibit the body's protective functions;
- diseases of the digestive system - severe dysbacteriosis and other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in which the digestion and absorption of food is disrupted, often accompanied by changes in the tongue - it becomes covered with a thick white or yellow coating, swells and hurts;
- allergic reactions – mild allergic reactions to some food or medicine. In such cases, the tongue hurts after eating food, especially after sour foods, fruits such as kiwi, pineapple, as well as after seeds, smoking or alcohol;
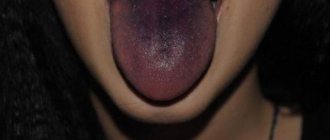
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements - a lack of iron, vitamin B12 and some other microelements is accompanied, among other symptoms, by changes in the mucous membrane of the tongue. The tongue may become smooth “glossy”, change color, become coated, increase in size and begin to hurt very much, as if burned;
- neuralgic diseases - diseases of the tongue that arise due to damage to the nerves innervating the tongue and the oral mucosa are quite difficult to diagnose and treat. The most common disorder is glossalgia, which can occur as a result of psychological trauma, severe fear or endocrine disease. With neurological damage, the patient suffers from pain and numbness of the tongue, tingling, burning in it and fatigue when speaking;
- Oncology is the most severe and unpleasant cause of constant pain in the tongue - these are benign and malignant tumors of the oral cavity.
What can you do at home?
How to remove an unpleasant symptom at home? To do this, you can use the following techniques:
- put ice on the itchy area,
- rinse with soda solution, water with added honey (if there is no allergy), potato juice,
- chew sugar-free gum
- rinse with herbal decoctions - chamomile, coltsfoot, oak, sage,
- hold a piece of propolis in your mouth.
Rinsing with a decoction of oak bark will help in treatment.
Recovery will come faster if you exclude damaging factors: alcohol and cigarettes, sour foods and drinks, soda, spicy foods.
At home, people can use various folk recipes. For example, decoctions with antiseptic properties, such as chamomile or sage, will help prevent the spread of inflammation to healthy areas of the mucous membranes in the mouth.
If there is minor damage at the tip of the tongue, it can be lubricated with Lugol's solution. Chlorhexidine can also be used to rinse the mouth.
Treatment of tongue pain
Treatment of a tongue that hurts, as if burned, must begin with a visit to a therapist and otolaryngologist; only a qualified doctor, having conducted all the necessary studies, from a general blood test to a puncture of the tongue, will be able to accurately determine the cause of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. If the cause of pain in the tongue is injury due to an incorrect prosthesis or a chipped piece of enamel, then before visiting the dentist you should rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions as often as possible and try not to injure it when eating and talking.
Read also: Toothache at night
Before visiting a doctor or if pain in the tongue occurs only occasionally and does not affect the patient’s well-being, you can:
- if numbness and pain in the tongue are caused by stress and nervous tension, the patient is prescribed valerian preparations, peony or motherwort tincture;
- for any pathologies of the oral cavity, it will not be superfluous to regularly rinse your mouth with a solution of chamomile, sage, furatsilin or other antiseptics;
- for severe pain in the tongue, you can take painkillers and tranquilizers - paracetamol, ketonal or phenazepam;
- Local anesthetics help cope with unpleasant sensations - anesthesin, a solution of citral in peach oil, a solution of trimecaine and others;
- In case of anemia, vitamin deficiency and other deficiency conditions, pain in the tongue can only be dealt with by taking vitamins and mineral complexes.
Most often, tongue pain is not an independent disease, but a symptom that appears in various pathologies of the body, so treating tongue diseases separately is useless; you need to determine the cause of the pathology and get rid of it.
Providing first aid
First actions
Your initial response to a tongue burn determines the speed of your recovery, and this first step is simple. As with any minor burn, cold water can quickly regulate tongue irritation.
Drink a glass of water to lower the temperature of your tongue and keep your mouth moist (saliva flow is key to ensuring that bacteria don't cause further harm to the area). Stay away from hot foods and drinks, which will only irritate the burn until it heals.
Cool down
After the “event” itself, drink something soft and cold so that the numbness begins to be felt naturally throughout the day. Choose foods that are easy to eat, such as fruit porridge, yogurt, or applesauce, all of which will help soothe the burning sensation. Also, be sure to drink a glass of water to wash away any food debris that may damage your tongue.
Rinsing
Once your mouth has cooled, you will need to rinse with the warm salt water mixture. Add 1/8 teaspoon salt to a glass of warm water, gargle gently in your mouth, and then spit it out. Salt is a natural antiseptic that can reduce swelling and pain, ultimately relieving burn symptoms.
A little sugar
Sugar is a little-known painkiller available in any home. A tiny drop on your tongue can dull the pain when you burn your tongue. Sprinkle some sugar on your tongue, let it dissolve and feel how it helps - but be careful with your portions as it's not so good for your teeth.
Honey is another delicious burn remedy used in countries like India for its antibacterial properties to speed up the healing process of ulcers. The most important advantage of these remedies is that they are available in almost every home and can very quickly help dull the pain.
Take a pill
When all of the above suggestions fail to provide you with the relief you need, there are always standard over-the-counter pain medications. Take the recommended dose of acetaminophen or ibuprofen to treat inflammation.
Keep in mind that hot foods can also harm the surfaces of your teeth, so to ensure your tongue heals completely, use a toothbrush with very soft bristles.
If you are unsure about the cause of your burning tongue symptoms or if they simply do not go away, consult your dentist to rule out burning tongue syndrome, which is a chronic problem.
Small sips and bites should be taken when eating and drinking hot things. And if your burning tongue doesn't improve, call your dentist to find out what you should do next.
We also recommend watching the video:
Analysis of the reasons
Women most often make such complaints. Usually everyone is in the same age category (from 40 years old) and everyone has common metabolic disorders. However, the provoking cause is much more complex than problems with metabolism, but there is only one diagnosis - glossalgia.
Glossalgia manifests itself as inflammation of the mucous membrane or the entire tongue, causing a lot of unpleasant sensations: burning, pain, swelling of the entire tongue or a separate area of it, a feeling of numbness.
If you do not seek treatment, the burnt tongue will stop bothering you. But this is temporary relief - the pain will definitely return. You can completely get rid of glossalgia only by eliminating the root cause. So why does my tongue hurt?
External factors
The reason can be external and internal. The first one is much easier to deal with and the treatment will not be long or very difficult. External provoking factors include:
- injuries and microtraumas of the tongue;
- allergic reactions;
- failure to comply with hygiene standards;
- inflammation occurring in the oral cavity;
- bacterial or viral infections.
Biting the tip of your tongue in your sleep is normal. We really don’t always notice that we have somehow injured our speech apparatus - we cut ourselves with a piece of candy or a bone, bit a little, or overate some seeds. Owners of dentures also often accidentally injure their tongue; you can even get scratched by a poorly ground filling. However, the injury will not hurt much. And it won’t cause swelling.
Swelling often occurs with allergies, but then it practically does not hurt. If the tongue is very swollen, which causes difficulty breathing, then you should urgently call an ambulance! Allergies can trigger anaphylactic shock and even death!
If all the rules of oral care are not followed, inflammation may well begin. Bacteria feel like they are at a feast, and the body’s own defenses are simply no longer enough. If we add to this the weakening of the body, then stomatitis or an even more severe bacterial or viral infection may well begin.
Prolonged use of antibiotics or strong drugs can provoke disturbances in the oral microflora. That is why, along with antibiotics, it is recommended to take drugs to maintain the body’s microflora. What to do in this case? Restore the body with special antibacterial medications.
Internal problems
If you haven’t burned or injured your tongue and are sure that the problem is not bacteria, then the problem lies inside. Not all diseases immediately manifest themselves externally, so it is better to consult a doctor and undergo a full examination. Otherwise, it is simply impossible to detect pathology.
Read also: How to relieve toothache at home
The tongue may hurt, as if burned, due to:
- Tartar. Yes, such a little thing can seriously damage the tongue, because tartar is formed due to accumulations of harmful bacteria that provoke tooth decay and inflammation on the tongue.
- Xerostomia. This deviation provokes a disruption in the normal production of saliva. The oral cavity and tongue are always insufficiently moisturized, which causes inflammation. Occurs most often in diabetics and with frequent dehydration.
- Diabetes mellitus. Diabetics have difficulty with regeneration. In addition, they often feel dry mouth.
- Vitamin deficiency. A lack of essential vitamins and other substances can trigger the development of glossalgia. More often it occurs when there is a lack of iron and B vitamins in the body.
- Bruxism. Due to uncontrollable movements of the jaw, microtraumas of the tongue are possible. Bruxism occurs during sleep during nervous tension.
- Candidiasis. This is a fungal disease that occurs due to a weakened immune system and lack of vitamins. The entire oral cavity is at risk from candidiasis.
- Leukoplakia. This pathology affects the epithelium of mucosal tissues and provokes long-term and very severe pain in the tongue.
- Herpes. This viral infection most often affects the inner parts of the cheeks, gums and palate. But it may well cause inflammation on the tongue. Most likely, the damage will affect only the very tip and root, but the entire organ may become inflamed.
- Irregularities in the work of the housing and communal services. These disorders are accompanied by the formation of a thick coating on the tongue. Most often, the plaque is yellow or white, and the tongue swells all over and is very painful.
- Deviations in liver function. These disorders provoke not only inflammation of the tongue. You may also notice changes in skin color, the appearance of strange taste preferences and disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Hormonal disorders. This refers to the restructuring of the body in women at the beginning of menopause. But other disruptions of the endocrine system can cause complications such as glossalgia.
- Neuralgic disorders. Any pinched nerves can have unexpected consequences. Normal muscle tone decreases, and the whole chain of consequences can affect the functioning of the speech apparatus.
- Neurosis. The body always reacts to stress with sudden changes in health. Some people develop a rash, some begin to have stomach problems, and others have a swollen tongue and pain.
There are many real reasons, but all are diagnosable. If there is pain on the tongue, as if it were burned, then it is initially necessary to exclude bacterial and infectious causes. To do this you will have to visit the hospital.
First, you will be directed to donate blood to check your general indicators and sugar levels. To check the microflora in the vagina, a swab of your throat will be taken. It will show which bacteria provoked the inflammation and whether bacteria are to blame. They may also send you for an x-ray to rule out osteochondrosis as the cause of discomfort in the tongue.
What to do?
Now you can figure out if your tongue hurts, as if it was burned, then how to treat it. Of course, it is necessary to eliminate the internal cause itself, and here it is worth listening to a doctor. If the disease is not cured, glossalgia will certainly appear again.
However, before going to the hospital, you can also help yourself to at least slightly relieve the pain and reduce swelling. Rinsing works very well. Both pharmaceutical preparations and homemade decoctions are suitable. From the pharmacy, choose furatsilin or chlorhexidine, and the best decoctions are chamomile or sage. These compositions will be useful for the entire oral cavity.
Painkillers also come to the rescue. You can use tablets or topical anesthetics. Tablets include ketorol, paracetamol and ketonal. If you know a drug that relieves pain better for you, then take it. The main thing is that it has an anti-inflammatory effect. Of the local anesthetics, Anestezin is the most famous. If your tongue is injured, you can lubricate the area with Lugol's solution, but first dip the cotton wool in glycerin.
How to prevent the appearance of spots and scars at the site of a burn
Expensive and not always successful treatment can be avoided if you act correctly:
- immediately after a burn, treat the affected area with cool water. The stream should be weak. Ice should not be applied to a wound or blister. If possible, lie in a bath with lukewarm water for 10 minutes (to avoid catching a cold);
- Apply a special spray, cream or ointment to the red, painful area. The compositions have a light consistency and do not contain fatty components. Effective drugs - Panthenol, Olazol, Agrosulfan, Sulfargin. Actively heal wounds, relieve pain and redness Solcoseryl, Bepanten, Furacilin ointment (especially for children), Levomikol ointment, Lioxazin gel;
- An excellent option is to apply anti-burn wipes to the burn site. Active gel will reduce inflammation, cool, reduce pain (contains lidocaine);
- wash the blister or red spot with chamomile tea several times a day. The healing liquid perfectly relieves inflammation, heals wounds, and prevents microbes from multiplying;
- if the skin lesion has affected deep tissues, do not treat the wound with anything, call an ambulance. Before doctors arrive, protect the affected area from infection. The patient is hospitalized and given the necessary treatment.
Now you know several effective ways to remove burn marks on various parts of the body. Start fighting unwanted skin manifestations as early as possible. Fresh scars and blemishes disappear much faster. For mild skin lesions, even folk recipes will help. Be healthy!
From the following video you can learn a few more tips for getting rid of pain and marks after a burn:
A burn is a very unpleasant injury. It not only hurts and burns for a long time, but also leaves behind dark spots, the so-called “secondary hyperpigmentation of the skin.” Stains from mild burns may be barely noticeable and will disappear on their own over time, but with more serious damage it is not so simple. Their condition can remain unchanged for up to a couple of years, or even more, if measures are not taken to remove them.
To ensure that burn stains go away, you need to take care of them regularly and carefully. It’s better not to experiment, use proven means. The best treatment would be complex therapy consisting of several remedies:
- Dry the stain and protect it from infection.
- Relieve inflammation.
- Lubricate with ointments.