A cyst on a child’s gum is a very common pathology that is regularly reported by many parents. This formation occurs as a result of an inflammatory process caused by an infection in the oral cavity.
In fact, it is a microabscess, not a cyst. However, this designation has been fixed in medical sources.
The main reason is that the area of inflammation is limited to the fibrous capsule, giving the pathological structure a truly cystic structure.
What it looks like and why it is dangerous
A cyst on the gum is visualized as:
- hyperemic swelling resembling a pea;
- sometimes whitish or yellowish spots can be seen on the swelling when the neoplasm is abundantly filled with purulent contents;
- neoplasm with uneven edges, varies greatly in size and color, from very small to 15 mm in diameter, from pale pink to bright red;
- if a small white tubercle (up to 3 mm) is detected, then this is most likely a Bohn's node - a type of cyst, formed from the residual epithelium of the salivary gland, very similar to Epstein's pearls (which are located on the palate), almost always resolves in the first months of life.
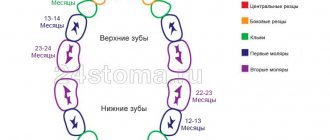
The most typical locations for such pathologies are the gums of molar teeth. The infection is just a side, triggering factor of the disease, and the key is psychosomatics, disturbances in it.
Children with cysts on the gums often experience psychoneurological problems and gastrointestinal diseases, which make the child emotionally unstable and restless.
Treatment
Elimination of cystic formations on the gums is carried out using conservative treatment or surgical intervention, and depends on the reasons for the formation of the cyst and the age of the child.
When a cyst forms in the area of a baby tooth, which provokes the development of an inflammatory process, it is necessary to extract it.
For pathologies in children with molars, drug treatment is prescribed in combination with surgery.
Treatment of purulent cysts
Treatment of purulent cysts in a child consists of eliminating the inflammatory process with the possibility of preserving the affected tooth. If there is purulent content inside the cyst, it must be opened surgically or completely removed.
Surgical treatment includes 3 techniques:
- cystomy – removal of the anterior wall of a cystic formation without the risk of damage to tooth germs;
- cystectomy - manipulation with cutting of gum tissue and complete removal of the cyst;
- laser dialysis - used to treat cysts localized at the tooth root, and consists of disinfecting pathogenic microorganisms by introducing a laser into the canal.
In the conservative treatment of a dental cyst in a child, no incision is made on the gum, but only the dental canals are cleaned, after opening which the pus will flow out. Next, an antiseptic is injected into the cleaned cavity, and the canals are sealed again.
After the manipulations have been performed, the child is prescribed antibacterial therapy with drugs.
What to do with eruption cysts in babies
In addition to pathological cysts, there are neoplasms caused by physiological processes. A cyst on the gums of a baby may appear during teething. During this process, soft tissues are injured by teething teeth, which leads to redness and severe swelling of the mucous membrane, pain and the formation of a soft hematoma. The color of the neoplasm can vary from transparent to dark blue.
What to do in such cases? Observe the child's behavior and condition. Often, radical treatment methods are not used.
Surgical intervention is required if the resulting cyst becomes infected and there is a severe inflammatory process.
Symptomatic therapy is used to relieve pain in a child and includes drugs:
- painkillers – Nurofen, Paracetamol;
- antihistamines - Fenistil, Suprastin, Zyrtec;
- anti-inflammatory - Cholisal, Dentinox, Pansoral, Kamistad.
Panadol Baby
How to treat gum cysts in newborns
Gum cysts in newborns develop from the dental plate - the basis for the formation of teeth. They look like small white lesions that do not change in size. Such formations, located on the gums of a baby, are mistakenly confused with congenital teeth.
Such neoplasms do not require treatment, as they rupture on their own due to friction during feeding.
Kinds
Based on which gum the cyst is located on, there are:
- molar cysts;
- wisdom tooth cyst;
- canine neoplasm;
- pathology of the front tooth (incisor).
Despite the common cause of exposure to an infectious pathogen, this disorder is divided into scenarios of occurrence.
The cyst may be:
- follicular (dental) - formed when a pathogen enters an unerupted tooth germ;
- radicular - occurs as a complication of periodontitis during chronic course of the latter (periodontitis - inflammation of the connective tissue that holds the tooth in the alveolus);
- retromolar (paradental) - if the third molars (wisdom teeth) are cut for a long time and with difficulty, pathogenic bacteria often penetrate into the damaged tissue, and a focus of inflammation develops;
- primary or keratocyst - is a true cyst, since it arises from what remains of the dental tissue during tooth formation;
- eruption cyst - often observed when baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones (i.e. in children aged 6-11 years), often resolves spontaneously;
- residual - a common form that occurs as an infectious complication after tooth extraction;
- the most common is carious, which occurs as a result of a chronic focus of infection in the area of carious tooth decay.
Several varieties can be diagnosed simultaneously.
What type of spots can pose a danger to a newborn?
Not always spots on a baby’s gums can be caused by relatively harmless reasons. That is why it is important not to leave the problem unattended, even if there are no signs of concern.
If you notice a deviation from the usual appearance of children's gums, you should consult a doctor:
- Periodontitis appears as white or clear blisters. Due to the fact that the baby puts everything in his mouth, they can burst, and an infection will enter the fragile body, then a purulent pimple will appear, and the infection threatens to spread further.
- Thrush manifests itself in the form of a white coating on the gums and tongue, the wounds underneath cause significant discomfort, because of this the baby may completely refuse to eat. To avoid this, it is necessary to undergo antifungal therapy, give the baby water, and also walk in the fresh air.
- Due to infection in the body, cysts can form on the gums. It is quite difficult to diagnose; an accurate diagnosis can only be made on the basis of x-rays.
- Wen is a relatively harmless disease, but it causes discomfort to the child, so, as a rule, the doctor decides to remove it.
- A gum tumor with a white head looks like a lump or cyst, but there may be cancer lurking inside. Any tumor should be immediately examined by a specialist.
Read also: Medicine for gumboil
Stages of development of formations on the gums
It is no coincidence that the full stages of formation of the described pathological structure are noted in childhood (from infancy to 12 years).
In adults, a gum cyst may not manifest itself in any way for many years.
The peculiarities of the development of cysts in the gums in children are explained by the characteristics of their immune system. Children's immunity has not yet come into contact with most of the main infectious agents. It is not fully formed. And at the same time, it is distinguished by a high level of sensitization, that is, it reacts violently even to a small amount of the pathogen.
Adult immunity successfully suppresses inflammation in the oral cavity without causing symptoms.
In children, a fibrous capsule begins to form around the lesion - this is a natural reaction of the body when the area of inflammation is sufficiently pronounced.
- Initial stage. — In infants, the initial stage of the disease is already clearly visible. — Inflammation of the periodontium, pulp or apex of the tooth root is manifested by pain: the child constantly cries, screams, sleeps poorly, eats poorly. — In a newborn, the gums can become inflamed spontaneously, without a visible prior source of infection.
- Progressive stage. — As the disease progresses, you can already notice swelling on the gums. — It is typical that sometimes at this stage the pain syndrome decreases. It is not known exactly what this is connected with: migration of the inflammation focus to the cyst area, gradual death of the tooth nerve as a result of chronic inflammation.
- When the process is running. — If no measures are taken, the inflammation becomes purulent. — Suppuration of a cyst is an extremely undesirable phenomenon, since it puts a serious immune and toxicological burden on a fragile organism.
Prevention of ulcer formation
To prevent pustules in infants and older children, preventive measures should be followed.
Carry out daily oral care; in very young children it is not necessary to use toothpaste. The main thing is to remove food debris and prevent the appearance of pathogenic bacteria and their active activity.
It is important to teach your child hygiene from an early age. Timely treatment of chronic diseases of the whole body, inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. Strengthen the immune system, since a weak immune system is a high risk of the appearance of pathogenic microorganisms and suppuration. If dental problems or diseases appear, you cannot stop caring for your oral cavity. Excessive consumption of sweets and starchy foods contributes to the spread of pathogens and their active functioning. After moderate consumption of these products, it is important to rinse your mouth.
Treatment of an abscess on a child’s gum must be qualified and timely. This will reduce the risk of complications and pathological conditions.
It is important to follow preventive measures to prevent recurrence of a purulent abscess
Bibliography
- Kenneth M. Hargreaves, Louis H. Berman - Cohen's Pathways of the Pulp - 2020.
- Leontyev V.K., Pakhomov G.N. — Prevention of dental diseases, M., 2006.
- V. A. Zelensky, F. S. Mukhoramov. - Pediatric surgical dentistry and maxillofacial surgery, M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008.
- Vinogradova T.F., Maksimova O.P., Melnichenko E.M. — Diseases of periodontal and oral mucosa in children, M., 1983.
- Ralph E. McDonald, David R. Avery, Jeffrey A. Dean - Dentistry For The Child And Adolescent - Mosby - 2004.
- L. V. Kharkov, L. N. Yakovenko - Directory of a dental surgeon: diagnosis, clinic, principles of surgical and drug treatment (in children and adults), M.: Book Plus, 2008.
Causes of cysts in childhood
This pathology arises as a result of a list of specific diseases or temporary physiological processes:
- caries, which destroys the enamel and reaches the dentin, provokes pulpitis and, accordingly, gum disease;
- The occurrence of cysts is further promoted by rarer internal caries, which begins to act from the root of the tooth;
- chronic periodontitis - inflammation of the connective tissue root membrane of the teeth and adjacent tissues;
- the focus of inflammation is not necessarily associated with the teeth - such a cyst occurs against the background of sinusitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, especially if these pathologies have become chronicled;
- various diseases of the tongue, which are often observed in patients with a gastrointestinal tract, anemia, autoimmune processes, allergic reactions;
- severe trauma and poor-quality sanitation after tooth extraction increases the risk of cystic formation (this also includes poor-quality filling, and ordinary tooth trauma from an impact or fall);
- Children may experience pain when teething, which forces them to touch their mouths with their hands, and this is one of the sources of infection;
- The described pathological structures can appear when changing baby teeth, since after the loss of a baby tooth a bleeding wound inevitably remains.
The root cause is always the same - viral and bacterial infection. But, as a rule, it has a bacterial etiology. This means it is more dangerous, because the bacterium provokes a purulent process.
Causes
The development of cysts can be caused by reasons related to physiological processes in the body (for example, teething) and external factors. This:
- Insufficient or improper treatment of dental diseases: caries, periodontitis, pulpitis. If the root canal is poorly treated and there are unclosed areas under the filling, the infection continues to actively develop. The body's defenses prevent foreign bacteria from entering the body by creating such cystic “reservoirs.”
- Injuries. Strong blows, falls, which lead to cracking of teeth, injury to the gums - can provoke the formation of a lump.
- The eruption of molars or baby teeth is sometimes associated with the appearance of a painless, bluish cyst. This shade is given to it by the blood inside the cone. It appears, as a rule, 2-3 weeks before the appearance of a new incisor or molar and imperceptibly “resolves” when this happens. Such a cystic formation does not cause any discomfort.
Obvious symptoms
A cyst in the gum often shows its symptoms already in the second stage. Despite the sensitization of children's immunity, the disease can proceed covertly for some time.
It is worth paying attention to the following manifestations:
- hyperemia and swelling are regularly recorded on the gum or gums;
- the child complains of pain when biting (the pain can be typical dental, or reminiscent of the pain syndrome due to periodontal disease);
- periodic spontaneous occurrence of pain in the jaw area without the ability to accurately localize it;
- over time, inflammation of the gums intensifies, a characteristic tubercle is formed, often having a bluish tint;
- it is not difficult to notice whitish or yellowish spots on the tubercle - the purulent contents are visible;
- with further development, a fistula is formed, through which the outflow of pus occurs; the fistula is not always noticeable visually, but its presence is indicated by protruding pus when pressing on the gum.
Systemic manifestations include:
- general weakness;
- evening low-grade fever;
- decreased appetite;
- headache;
- enlargement of the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes, pain on palpation.
But this is typical for a mature cyst, which in the future, in the absence of proper treatment, risks developing into a gumboil or fistula.
Purulent lump
The main reasons for the development of pustules on the gums:
- The most important factor that leads to the formation of a purulent lump or gumboil is periodontitis, which develops as a result of untreated caries. In this case, the size of the carious defect does not matter, and even the smallest lesion can cause a strong inflammatory reaction.
- Also, the cause of the formation of an abscess over a tooth can be an injury received from a fall or blow.
- Sometimes flux is a consequence of tissue damage from sharp objects (for example, if a child has the habit of chewing a pencil or toothpick).
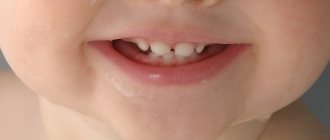
In the photo: an abscess on the upper gum of a child
Manifestations
The symptoms of this pathology are quite specific. At the initial stages of development of the purulent process, the child complains of pain and a feeling of fullness in the tooth area. At this time, a red swelling appears on the gum in the projection of the tooth root, which gradually increases in size, and pus accumulates in its center. This lump is soft to the touch and hurts when you press on it. As inflammation progresses, the formation becomes whitish and a white abscess forms.
At the same time, the general condition of the baby may suffer. Children become restless, refuse to eat, and their temperature rises.
If full treatment is not carried out at this stage, then as pus accumulates, the pressure inside the abscess increases and spontaneous opening of the white lump occurs. In this case, a fistula is formed, which connects the surface of the gums with the pathological focus. After the lump bursts, the child experiences relief of symptoms: pain decreases.
Treatment
If a purulent lump is detected in the child’s mouth, it is necessary to contact the dentist as early as possible.
If the cause of the formation of an abscess or fistula is a baby tooth, then treatment will be reduced to its urgent removal. It is impossible to leave such a tooth, since the preservation of even a slight focus of inflammation can lead to the death of the permanent tooth germ.
If flux has formed over a molar, then all therapeutic measures will be aimed at preserving it. In this case, the dentist will open the lump, clean the cavity from purulent masses and treat it with an antiseptic. Removing a permanent tooth is a last resort and is carried out only when there is significant destruction.
Complications
Despite the fact that purulent bumps are rarely large, their complications can be extremely serious and dangerous.
- The death of the rudiments of permanent teeth leads to edentia. Such a condition in childhood can cause improper development of the maxillofacial apparatus and bite pathology, which will require serious orthodontic treatment in the future.
- Chronic purulent lesions and fistulas in the oral cavity are a source of infection, which can spread and cause inflammation in other organs: tonsils or adenoids.
- The constant inflammatory process changes the activity of the immune system, which becomes more sensitive to the effects of various allergens. In this case, the child may develop hypersensitivity reactions even to those substances to which allergies were not previously observed.
- If the abscess does not open outward, then the pus can spread deep into the tissues with the formation of phlegmon - a severe complication that is life-threatening.
Memo to parents
If you find a purulent lump in your child, then you need to remember several important nuances:
- It is strictly forbidden to try to open an abscess on your own. This can lead to pus entering the bloodstream and the development of sepsis - blood poisoning.
- You cannot carry out any warming procedures: apply compresses or rinse your mouth with hot liquid. This will only worsen the inflammation.
- Cold can be applied externally to the cheek in the area of the lump; this will somewhat alleviate the symptoms and slow down the development of the abscess.
- At the first symptoms of gumboil, you should contact your pediatric dentist for professional treatment.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis in this case consists of an initial clinical examination, when the dentist monitors the patient’s oral cavity.
And the main point is a detailed radiography of the lower or upper (depending on the location of the formation) jaw. X-rays can accurately determine the type of cyst.
In some cases, a biopsy may be taken, sampling the biomaterial of the cyst to study its cellular morphology.
Methods of therapy
Dentistry and, in some cases, facial surgery are used to eliminate cysts on the gums.
As in all other cases of treatment, there are:
- conservative;
- surgical.
Conservative treatment is implied if the formation is up to 10 mm in size and no serious complications have arisen.
Even if the cyst resolves spontaneously or bursts, treatment is still required. After all, if you leave everything as it is, there is a high probability of a relapse.
Conservative treatment
Currently, conservative therapy is carried out using two methods:
- Since new growth is almost always associated with advanced caries, the dentist's first task is to clean the root canal. — The cyst cavity connects to the inflamed root. — The tooth is drilled, the canal is cleaned, and washed with antistatic solutions. - Then bactericidal and lysing agents are added, which neutralize the pathological contents of the cyst. — At the final stage, substances that promote osteogenesis are loaded into the cleaned cavity. — These drugs provide care and recovery. — Then the tooth is filled. — After six months, it is necessary to take a control X-ray, which is necessary to check the quality of the filling and prevent the development of a new cyst. — The effectiveness of the described conservative therapy is about 70%.
- Today, a more modern method is increasingly being used - depophoresis, the effectiveness of which is much higher, 95%. — Its difference is that copper-calcium hydroxide is placed into the drilled channel, and then an electric current is applied to the tooth. — Copper and calcium ions, under the influence of an electromagnetic field, penetrate into all tooth canals and into all parts of the cyst cavity, producing a powerful disinfecting effect. — And even after the filling is placed, the hydroxide still acts as a bactericidal agent for some time.
The choice of method is determined strictly individually.
Surgery
Surgical removal of a cyst on the gum is important for:
- large size of the formation, more than 12 mm;
- ineffectiveness of conservative therapy;
- repeated relapses.
Surgical treatment has three options:
- Cystectomy. - It is carried out in most cases. — The operation consists of removing the cyst and the affected part of the root. “At the same time, there remains a good chance to save the tooth itself.
- Cystomy. — A puncture is made in the gum tissue. — It is even easier to puncture a cyst if it is clearly visualized. — The puncture allows you to efficiently pump out the purulent contents. — Such intervention is relevant when the cyst is large and there is a large purulent focus.
- Hemisection. — It is used only for advanced, large lesions, when inflammation has begun to spread to neighboring tissues. — Essentially, a fairly large area of gum with the remains of a decayed tooth is removed here. — Subsequently, dentures are required.
The first two intervention options are performed under local anesthesia and almost never require hospitalization. The third option is depending on the severity of the disease.
ethnoscience
It is possible to cure a cyst on the gum while remaining at home, quickly and reliably, only in the very early stages of the development of the disease.
But this is not always possible due to the asymptomatic onset of the pathology.
Rinse solutions
A well-known and affordable option of traditional medicine is to treat the oral cavity with rinses.
All products for preparing rinses can be easily purchased at your nearest pharmacy.
Examples of recipes (it is recommended to use boiled water):
- sea water - 200 ml of warm water, a teaspoon of baking soda, a pinch of table salt and a couple of drops of an alcohol solution of iodine;
- Dissolve Nitrofural (Furacilin) tablet in 200 ml of warm water;
- add 1-2 teaspoons of calendula in alcohol to 200 ml of water;
- similarly, you can add a few drops of Fukortsin (Castellani liquid);
- Thoroughly dissolve several crystals of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) in 200 ml of water (it is important to make sure that the crystals are completely dissolved so as not to burn the oral mucosa).
All rinsing is carried out according to 3 rules:
- rinse at least 3 times a day;
- after rinsing, do not eat or drink anything for at least 20 minutes;
- Carefully move each portion of the solution in your mouth for at least 10 seconds.
If a child is allergic to some remedy, it can be replaced with a herbal decoction: chamomile, St. John's wort, multi-herbal mixture.
Lotions and compresses
For very young children (under 3 years old), rinsing procedures can be a problem. In this case, the analogue is lotions and compresses.
If lotions are applied directly to the affected area of the gums, then compresses can be applied to the surface of the jaw (to improve the general condition).
It is recommended to use herbal decoctions as a solution for lotions and compresses.
Compresses made from fresh cabbage, boiled or freshly grated potatoes help:
- apply a fresh cabbage leaf to the jaw and wrap it with a bandage;
- Place boiled or grated potatoes in a bandage and secure it to the jaw.
Alcohol tinctures
To treat cystic formation, alcohol tinctures are sometimes used. Alcohol tincture of calendula has already been mentioned.
Vodka compresses are very popular in folk medicine. But since we are talking about children, alcohol tinctures are not recommended.
Natural oils
Natural oils are used for applications to the affected gums.
Oils have an anti-inflammatory, absorbable effect and improve the microflora of the oral cavity.
Apply: sesame, clove, lemon, almond, eucalyptus oils.
Application:
- soak a cotton pad or swab and apply it to the gum for 15 minutes;
- then the mouth must be rinsed with warm water.
Prevention and dental advice
Preventive measures will not harm a single person. Moreover, those who take care of the condition of the oral cavity protect themselves from the development of various diseases. If a lump on the gum is detected early, this will help eliminate the pathology very quickly. Since the diagnosis is made by a specialist, you should not scare the baby, but in every possible way make it clear that dental treatment is not so scary.
The child must be aware of the following recommendations:
- brush your teeth regularly and correctly;
- after each meal, it is necessary to rinse your mouth, showing your child by example how to do it correctly (infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants and antiseptics are used as a solution);
- You should choose a soft toothbrush, preferably with natural bristles; As an item of personal protection, it must be stored in a closed case and treated with boiling water or an antiseptic after each cleaning;
- if the child is still small and his teeth are just beginning to emerge, you need to use gels that have antibacterial properties and eliminate pain;
- You need to treat the baby carefully, remove all objects that could injure the jaw or gums, and make sure that the toys are clean;
- Constantly examine the baby’s mouth for the presence of suspicious formations and inflammations; if pathogenic processes are detected, one should not postpone a visit to the dentist.
You should not self-medicate. Naturally, many years of using traditional medicine is a good help, but you still can’t do it without the help of a specialist. Only a dentist will select the necessary treatment method and prevent complications from occurring.
We looked at what to do with a cyst on a child’s gum.
Possible complications
Since patients are still pre-pubescent, an untreated or undertreated cyst in the gum of a tooth can have the following consequences:
- the focus of purulent inflammation can spread to neighboring tissues. The infection can penetrate, first of all, into the palatine tonsils, triggering the onset of a purulent sore throat;
- the constant presence of infection keeps the sensitized immune system in an even more tense state. This can provoke the development of allergic reactions, and even worse, the development of autoimmune reactions;
- a chronic focus of bacterial infection attacks the heart, pericarditis or myocarditis may occur;
- a large cyst disrupts the position of the tooth; permanent teeth may erupt incorrectly, and this will lead to disturbances in diction.
Sometimes less serious, temporary complications occur:
- gum pain after cyst removal;
- secondary infection occurs.
These phenomena can be relieved by taking analgesics, local disinfection, and sometimes a short course of antibiotics.
Impact stages
Anyone interested can look at a photo of what a cyst on the gum looks like - it’s a kind of lump with liquid contents. When the pressure of pus increases, the mucous membrane can burst and the pouch opens. An unpleasant consequence of this is the release of pathological fluid into the oral cavity, because the inflammatory focus has not been eliminated. To prevent this, you need to consult a doctor in time.
Dental gum cysts are treated in various ways; the effects can be therapeutic, surgical, or complex. In the first case, the crown is first removed, then the canals are unsealed, as well as their subsequent filling. Finally, a new crown is placed. Only a doctor can understand what to do in a specific situation. To do this, he determines the exact cause of the formation of the cyst and assesses the patient’s condition. And only then is it decided on the tactics of influence.
The operation to remove the cyst along with the upper part of the root is called cystectomy. When it is necessary to completely cut out the root, as well as remove part of the tooth, hemisection is performed. The resulting defect is corrected by installing a crown. In the most difficult situations, when the tooth is loose or severely damaged, the bone formation is completely removed. How long the gums heal after cyst removal is determined by the complexity of the operation.
It is especially important that the doctor removes all pathologically formed particles so that the disease does not develop again
Valuable recommendations: having discovered signs of an inflammatory process in the oral cavity, in no case should you self-medicate, much less hope that the “pouch” will resolve on its own. Even if the cyst opens, this does not mean that the inflammation has passed. Its progression will lead to the bone tissue beginning to deteriorate and the tooth will have to be removed.
Along with other dental problems, the formation of a cyst requires prompt medical consultation, both for adults and children. The effectiveness of therapy is directly related to how quickly you get an appointment with a doctor, and how quickly the necessary studies are carried out. If such a diagnosis is suspected, radiography is of key importance - from the images the dentist will be able to determine:
- location of the pathological neoplasm;
- dimensions of the cavity with liquid contents;
- structure and density of the cyst;
- the presence of caries near the affected area, etc.
Even in the absence of pronounced symptoms, the problem can be very serious; accordingly, the condition should not be allowed to worsen
It is equally important to fully follow your doctor's instructions, especially for those undergoing post-operative recovery. Provided proper surgical intervention, the risk of complications is very small, but in order to prevent inflammation, you need to adhere to certain rules of hygiene and adhere to a special diet
If we talk about general recommendations, you should refrain from eating sour, sweet and spicy foods, so as not to damage healing tissues, and also include foods rich in vitamins and minerals in your diet.
Prevention at a young age
The main prevention of such a disease is oral hygiene.
- regular teeth cleaning;
- You should rinse your mouth with regular running water throughout the day, especially after eating sweet and sour foods;
- Hypoallergenic toothpaste is recommended, and a toothbrush with a hardness no higher than medium.
We must remember that healthy gums also need to be taken care of.