Dental technician's office
The dental table is the main place of work. It is usually equipped with a lamp, a jet nozzle that is used to blow on the work surface, a suction funnel, sometimes a built-in socket for the grinding motor, and, of course, a chair.
Specialization
Often a dental technician makes a certain type of denture and improves in its manufacture. Therefore, there is a division in the profession in the following areas:
- Metal-ceramist (fixed prosthetics). Works with artificial material, which is an alloy of metals and ceramics. Such designs are characterized by wear resistance, resistance to corrosion and heat. A metal-ceramic prosthesis is a metal frame coated with ceramic mass.
- CAD/CAM system operator. A specialist in this field must have a good understanding of the modeling and milling processes.
- Prosthetics on implants . The essence of the method is that an implant is implanted into the jawbone tissue, which replaces the lost tooth root and serves as a support for an artificial tooth.
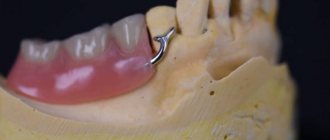
- Removable prosthetics . It can be complete, when the dentition of one or both jaws is completely absent, or partial, worn in place of one or more lost teeth.
- Orthodontic devices. Designs for aligning the dentition.
By process, the work is also divided into: casting metals and polymers, plaster casting into an articulator, modeling prosthetic frames, casting models. Thus, from two to fifteen people work together to produce one prosthesis in a dental laboratory.
General provisions
1.1. The position “Dental technician” belongs to the “Specialists” category.
1.2. Qualification requirements: incomplete higher education (junior specialist) in the field of training “Medicine”, specialty “Orthopedic Dentistry”. No work experience requirements.
1.3. Knows and applies in practice: - current legislation on health protection and regulatory documents regulating the activities of health care institutions; — organization of dental care for adults and children; — rights, duties and responsibilities of a dental technician; — performance indicators of medical institutions; — international classification of diseases; — etiology and pathogenesis of diseases of the oral cavity and maxillofacial area; — priority technologies used in modern orthopedic dental practice, modern technologies for the manufacture of dentures (solid casting and prosthetics from porcelain and ceramics, production of dentures from precious metals); — operating principles of modern orthodontic appliances; — modern technologies for the manufacture of prostheses that replace defects in the soft tissues of the face; — basics of asepsis and antiseptics; — personal protective equipment against acute respiratory viral and especially dangerous infections; — safety rules when working in dental laboratories; — rules for processing medical documentation; - modern literature on the specialty.
1.4. A dental technician is appointed to a position and dismissed from a position by order of the organization (enterprise/institution).
1.5. The dental technician reports directly to _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ .
1.6. The dental technician supervises the work _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ .
1.7. During absence, a dental technician is replaced by a person appointed in accordance with the established procedure, who acquires the appropriate rights and is responsible for the proper performance of the duties assigned to him.
Features of the profession
This profession is considered technical and is somewhat similar to the work of a jeweler. Almost always, the product is modeled by hand, individually for each patient, and must perform the functions assigned to it: exactly suit the patient’s needs, have an aesthetic appearance, high-quality durable materials are used in the work.
Design modeling begins with working on a dental wax model. Only after checking all the parameters is the model converted to metal, ceramics or composite.
A dental technician uses knowledge from various sciences in his work: physics, chemistry, anatomy. He needs the skills of a mechanic, a milling machine operator, a galvanizing chemist, and a welder. And modern technologies require knowledge of 3-D computer graphics.
Due to the nature of the profession, the tools used in the work are also very diverse: anvils, machines for stamping crowns, jigsaws, hammers.
Profession risk
Often the manufacture of such structures involves inhalation of harmful chemicals. For these reasons, the technician wears protective gloves, a mask and goggles.
Regularly, every two to three years, a dental technician undergoes advanced training courses to become familiar with new technologies and materials. Today this is a very popular profession, since a beautiful smile is the desire of every sane person.
Obtaining a specialty
The specialty of a dental technician is called “orthopedic dentistry”, and it is obtained in secondary medical institutions, and the training itself lasts exactly as long as indicated in the program and at this moment the course is 2 years and 10 months. Admission is usually carried out on a competitive basis based on the results of the Unified State Exam and special attention should be paid to the Russian language, physics and chemistry. You can enroll in secondary education at any medical college that has the required faculty.
While a student is studying to become a dental technician, he will need to study many disciplines and gain all the necessary skills, and among them the most relevant are:
- Creation of removable and non-removable dentures;
- Manufacturing of orthodontic and maxillofacial structures;
- Foundry;
- Modeling.
In addition, the profession of a dental technician is one of the medical specialties where they teach not only the main type of activity, but also what is useful in other areas, namely:
- Genetics;
- Topographic anatomy;
- Pharmacology;
- Physiology;
- Surgery;
- Knowledge of Latin;
- Therapy.
The student will learn not only by sitting in lectures, but also by consolidating the acquired knowledge in a practical form, being in the laboratory and creating prosthetics of varying complexity. Of course, all this will happen under the close supervision of teachers and specialists in their field. Using this method of learning, the student will better understand the essence of the process, and will also get used to working with various materials.
After graduation, a young specialist has three areas where he can prove himself and start earning money, namely:
- medical and preventive care;
- management activities;
- production and technological business.
Job responsibilities of a dental technician
I. General provisions
1. A dental technician belongs to the category of specialists.
2. A person with secondary medical education is appointed to the position of dental technician
qualification category(s).
3. Appointment to the position of a dental technician and dismissal from it are made by order of the director of the organization.
4. The dental technician must know:
4.1. Fundamentals of medical dental care.
4.2. Organization of production of a dental laboratory.
4.3. Fundamentals of the structure and functions of the dentofacial system, biomechanics of the masticatory apparatus.
4.4. Information about the main dental diseases.
4.5. Theoretical and clinical foundations of orthodontic treatment.
4.6. Rules for reading diagrams, formulas and sketches of the oral cavity.
4.7. Characteristics of basic and auxiliary materials used in denture technology.
4.8. Assortment, labeling, basic properties of the materials used and semi-finished products.
4.9. Purpose and rules of use of devices, instruments and devices used in the dental laboratory.
4.10. The main clinical stages and manufacturing technologies of dental (removable, fixed, clasp, maxillofacial prostheses and orthodontic) devices.
4.11. Basic principles of melting and casting metal alloys.
4.12. Purpose and requirements for each element and unit in prostheses, including intermediate stages of their manufacture.
4.13. Fundamentals of the design of modern dental equipment for firing porcelain, muffle furnaces, foundry equipment, ultrasonic and light-curing devices, etc.
4.14. Technology of using porcelain and metal-ceramics in denture technology.
4.15. Reasons leading to defects and ways to identify, eliminate, and prevent them.
4.17. Legislation on labor and labor protection of the Russian Federation.
4.18. Internal labor regulations.
4.19. Rules and regulations of occupational health, safety, industrial sanitation and fire protection.
II. Job responsibilities
Dental Technician:
1. Prepares dental equipment and dental laboratory equipment for work, monitors serviceability and correct operation.
2. Independently manufactures various types of artificial crowns, including metal-ceramics; simple designs of post teeth; designs of bridges; removable plate dentures; clasp dentures; orthodontic and maxillofacial structures corresponding to programs.
3. Evaluates casts (impressions) and obtains appropriate working models from various materials.
4. Manufactures individual trays, wax bases with occlusal ridges and installs artificial teeth.
5. Creates elements, units and parts of dentofacial prostheses and orthodontic devices from wax.
6. Replaces the wax composition with a plastic or metal alloy.
7. Performs stamping of prostheses from stainless steel and other materials.
8. Conducts soldering, alloying, firing, bleaching, finishing, polishing of parts, prostheses and devices, etc.
9. Conducts aseptic processing of casts and prostheses.
10. Complies with labor protection, safety, occupational health, fire safety requirements when operating premises, equipment and apparatus used in dental practice.
11. Prepares medical documentation established by the Ministry of Health of Russia.
12. Receives, stores, and records the use of medicines, dental materials, and instruments. Prepares requests for dental materials.
13. Complies with moral and legal standards of professional communication, fulfills the requirements of labor discipline.
14. Conducts sanitary and educational work.
15. Regularly improves skills.
16. Provides first aid in case of emergency conditions.
III. Rights
The dental technician has the right:
1. Receive information necessary for the high-quality performance of functional duties.
2. Make proposals to management to improve the quality of dental care for the population and improve the organization of work.
3. Give orders to the junior medical staff of the dental laboratory, control the volume and quality of the work they perform, and exercise control over the work of the equipment repair technician.
4. Take part in meetings, conferences, sections where issues related to professional competence are discussed.
5. Improve qualifications and get certified for assignment of qualification categories.
IV. Responsibility
The dental technician is responsible for:
1. For improper performance or failure to fulfill one’s job duties provided for in this job description - within the limits determined by the current labor legislation of the Russian Federation.
2. For offenses committed in the course of carrying out their activities - within the limits determined by the current administrative, criminal and civil legislation of the Russian Federation.
3. For causing material damage - within the limits determined by the current labor and civil legislation of the Russian Federation.
Where to get a specialty
You can obtain a specialty as a dental technician at a medical college. It is possible to enroll after 9th grade, then the duration of study will be 4 years. Or after 11th grade, in this case, the period of study at college will be reduced to 2 years 9 months.
To be admitted you must pass a competition. Particular attention should be paid to subjects such as physics, Russian language and chemistry . A person with a higher medical education can become a dental technician. To do this, it will be possible to take a retraining course for specialists.
During training, the student consolidates all theoretical knowledge with practical exercises. This practice is very important for the future technician, as it will allow you to develop and consolidate most of the necessary skills. A young specialist will be able to start working immediately after receiving a diploma.