Why does pathology occur?
There are many factors that provoke the appearance of stomatitis. They are:
- Presence of bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse, taking drugs.
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Infection provokes the development of herpetic stomatitis. Factors provocateurs include streptococci, staphylococci and candida fungus.
- Stressful situations. Constant anxiety, nervous feelings or unexpected shock sometimes contribute to the appearance of rashes.
- Allergy to pharmaceutical drugs. Heavy metal salts, antibiotics, medications with bromine or iodine and vitamin complexes can cause the disease in question.
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract that occur in a chronic form. Often stomatitis occurs with ulcers, colitis, duodenitis, gastritis or dysbacteriosis. In addition, it may indicate the presence of parasites in the body.
- Injuries to the oral cavity that occur simultaneously or systematically. This often happens to people who wear dentures.
- Excessive eating of nuts or seeds.
Most often, stomatitis is treated with symptomatic therapy - eliminating inflammation of the mucous membrane. But it also happens that you have to take antibacterial drugs, antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs.
How long does it take for stomatitis to go away? There is no exact answer to the question; the standard treatment time is 7 days.
Duration of the disease
It is impossible to say exactly how long stomatitis lasts. The duration of the disease depends on many factors:
- type of disease;
- timely contact with a specialist;
- correctness of the diagnosis;
- well-chosen means for treatment;
- compliance with doctor's recommendations;
- state of immunity.
It is important for patients to remember that the state of their health and the speed of recovery depend on the speed of contacting a specialist. The more advanced the disease, the longer and more difficult it takes to treat. There is a risk of the pathology becoming chronic.
This usually happens in the background:
- taking certain medications;
- vitamin deficiency;
- weak immunity, immunodeficiency;
- disruptions in the hormonal system;
- chronic stress;
- history of chronic diseases.
Herpetic stomatitis
The cause of this form of the disease is the herpes simplex virus (type 1). It is easy to become infected with this disease - it is transmitted through airborne droplets, as well as through contact with an infected person.
Complications of stomatitis occur with decreased immunity or exposure to certain unfavorable factors. This could be stress, infection, oral trauma, antibacterial therapy, overheating or hypothermia, allergies, vitamin deficiency.
Herpes stomatitis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- redness and inflammation of the oral mucosa;
- the appearance of blisters due to stomatitis on the gums, the inside of the cheeks and lips, and the tongue;
- painful sensations that increase when eating solid food;
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes;
- increased salivation (not always);
- increased temperature (sometimes up to 40°C).
On the 2-3rd day of the disease, the formed blisters open. Erosion forms at this site and is covered with fibrinous plaque.
To treat the viral form of the disease, antiviral drugs, immunomodulators, and vitamin complexes are needed. If the temperature rises significantly, antipyretic medications are used.
Catarrhal stomatitis
This type of disease is characterized by an intense inflammatory process in the absence of defects on the surface of the oral mucosa. This form of stomatitis is the most common.
The danger of catarrhal pathology lies in the mild manifestation of symptoms. Patients do not notice warning signs or pay attention to them late, when the disease is already advanced. The clinical picture of catarrhal stomatitis manifests itself:
- inflammation of the gums, teeth, inner surface of the cheeks;
- whitish coating on the affected area of the mucosa;
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness of the mucous membrane;
- bad breath;
- weakness and loss of appetite (more often in children).
Aphthous form of stomatitis
This type of pathology is provoked by the negative impact of harmful bacteria on the body.
It is characterized by the appearance of cloudy ulcers with a red rim. The duration of the course depends on the stage of stomatitis.
Acute aphthous stomatitis most often affects children suffering from diathesis and gastrointestinal pathologies. In this case, babies experience fever and increased salivation.
How long does it take for stomatitis to go away? If you take the medicine on time, the person recovers within 7-10 days.
The chronic course of the pathology is manifested by the periodic appearance of single papules in the oral cavity, which either disappear after 5-10 days or turn into ulcers.
Aphthous lesion
Aphthosis in adults is also quite common. The causes of this disease are various. Finally, to the question “what causes stomatitis in adults?” Science has not yet answered.
Often there is an allergic reaction to toxins of certain types of bacteria; sometimes aphthae appear during exacerbation of intestinal diseases.
Thus, the answer to the question “how long does it take to treat stomatitis in adults?” also depends on how severe the underlying disease is.
The first signs of stomatitis in adults are tingling and burning, and then within 24 hours erosion appears, covered with a white coating. Usually the number of afts is not significant.
Patients do not notice symptoms such as deterioration of well-being or fever. The uncomplicated form of aphthous stomatitis heals literally in 7-10 days.
To relieve local symptoms, it is rational to use pain-relieving gels and herbal rinses.
It is advisable to eliminate all foci of chronic infection in the oral cavity: treat all teeth, remove dental plaque, eliminate tonsillitis.
If after sanitation of the oral cavity, aphthae appear again within a year, it is advisable to consult a gastroenterologist, therapist and allergist.
Therefore, the answer to the question “which doctor treats stomatitis in adults” depends on the immediate cause of the disease.
Possible consequences and complications of stomatitis
At first glance, stomatitis is not such a complex disease. However, without treatment, it can cause consequences that will cause severe damage to the body and even become a threat to life.
- Attachment of a secondary infection;
- Tooth loss;
- Hoarseness and hoarseness, which can develop into laryngitis;
- Infection of all parts of the body;
- Scarring of the oral cavity (due to numerous cracks) can lead to limited mobility;
- Herpetic stomatitis with complications affects visual functions;
- With gangrenous stomatitis, there is a possibility of death;
- Cases have been recorded when the consequence of stomatitis is Behcet's disease - inflammation in the blood vessels, lungs, brain, colon;
- Advanced viral stomatitis entails the appearance of rheumatism and diseases of the cardiovascular system.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Medicines used in dentistry.
No disease should be left unattended. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, immediate treatment should be started under the supervision of a dentist.
Herpetic form of stomatitis
When herpes first enters the body, a person often develops stomatitis. This is indicated by the following symptoms: an increase in temperature up to 40 degrees, severe muscle pain, redness and swelling of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, the appearance of transparent blisters with liquid, an enlarged lymph node and pain when touching it.
A complicated form of pathology requires immediate hospitalization of the patient. How long does stomatitis last in adults?
If treatment has not been carried out, then the symptoms go away after a couple of weeks, the bacteria remain on the mucous membranes, and the disease becomes chronic.
Chronic herpetic stomatitis can be mild or severe. At a mild stage, the disease makes itself felt several times a year and is characterized by a small number of ulcers.
But a severe form of stomatitis appears once every two months and provokes severe damage to the oral cavity and increased salivation.
To help the patient cope with the problem, experts prescribe the antiviral drug Acyclovir, an anesthetic and an antipyretic.
Inflammation in the mouth: types of stomatitis, symptoms
On average, symptoms go away in one to two weeks , but not without timely help and a course of treatment tailored to the type of disease. The exact timing cannot be given due to many factors, for example, the state of the immune system and its sensitivity to the pathogen. If you leave everything to chance, the disease will develop into a chronic stage and more time will be required for treatment.
Attention! It is important not to avoid prescribed procedures and to be treated until complete recovery.
- Catarrhal . Occurs due to insufficient oral hygiene and vitamin deficiency. 5–7 days to eliminate inflammation .
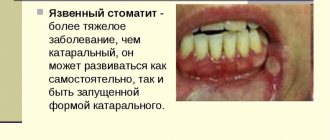
- Ulcerative . It is difficult to treat and has dangerous consequences, so treatment cannot be done without the intervention of a doctor. Recovery will occur in five days .
- Aphthous . The reason lies in the functioning of the digestive system and the body's vulnerability to allergies. If you follow the treatment course, it goes away in 7–10 days .
- Herpetic . It is less common among adults; children aged one to three years . It will pass in seven days .
- Fungal . It directly depends on the state of the immune system and often indicates the presence of a concomitant disease. Takes on average 7 – 30 days .
- Allergic . The treatment time is related to the speed of identifying the allergen, which is important to exclude in time. Recovery on average takes 1.5 – 2 weeks .
How many days does it take to treat catarrhal type?
Inflammation can be stopped at the first symptoms of the disease; on average, it takes 5–7 days of treatment. The difficulty is that it is difficult to recognize the signs of onset; patients notice something is wrong when the disease is already advanced.
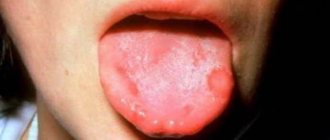
Photo 1. Catarrhal appearance: the most striking symptom is hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane. And a severe form of ulcerative stomatitis: the ulcers grow and merge, and can reach deep into muscle tissue, tendons and even bone.
How long does ulcerative stomatitis last in adults?
Ulcers can quickly grow and merge with each other, affecting the mucous membrane. The patient has difficulty eating and talking. Fever and bad breath are often added to the general condition
The doctor prescribes mouth sanitation . This procedure removes dead cells and mucous tissue and cleanses the teeth. The patient is prescribed a course of therapy using vitamins, antiseptics and oral disinfection. With prompt treatment, recovery occurs already on the fifth day .
Peculiarities! This type of disease is difficult for adults, and especially for children .
How long to treat aphthous type
The duration of therapy is directly related to the nature of the disease. Inflammation of the mucous membrane is accompanied by burning and pain , and in some cases, fever .
On average, inflammation lasts from two to five days ; complete healing of aphthae occurs on days 7–10 .
Aphthous stomatitis often goes away on its own , but if the body is often susceptible to this disease and suffers pain, then use an anesthetic and exclude spicy, salty and spicy foods from the diet.
Herpetic stomatitis in adults: will it go away in a week or not?
The causative agent of this species is herpes simplex virus . Bubbles appear on the oral mucosa, which burst and quickly turn into ulcers .
If, with the correct selection of medications, recovery can be achieved in 4–7 days , then the main problem lies in the healing of the ulcers. Herpetic stomatitis retains symptoms for two weeks , so a course of vitamins and medications ; for fever, regular antipyretics will do.
How long does fungal growth last?
The disease is characterized by redness of the oral cavity, where the mucous membrane is covered with white cheesy deposits , which are easy to clean off in the early stages, but as it grows, this procedure becomes painful. The speed of recovery is directly related to the state of the immune system, so the duration of treatment is difficult to determine; in general, it lasts from one week to a month .
Photo 2. Fungal appearance: the main symptom is a white coating on the tongue, palate, and inner surface of the cheeks. And allergic stomatitis: clinical manifestations are varied, but include ulcers and swelling.
How long will it take for allergies to go away?
This type of pathology is recognized by the presence of edema, ulcers, erosion and pain . The essence of therapy is to completely eliminate contact with the allergen and disinfect the mucous membrane with solutions. For mild forms of the disease, treatment takes 1.5 – 2 weeks .
Attention! The duration and complexity of the disease depends on the factor that caused it. Therefore, for cure it is important to find and eliminate the allergen , which turns into a problem.
Ignoring doctor's orders
It happens that the length of time it takes to treat stomatitis is influenced by a neglectful attitude towards the doctor’s recommendations.
Perhaps the disease was discovered by a therapist or pediatrician and sent the patient to the dentist for complete sanitation of the oral cavity - a set of therapeutic and preventive measures to improve the health of the oral cavity and prevent dental diseases. If you ignore this step of treatment, then it will take longer than usual to get rid of inflammation of the oral mucosa.
The same thing will happen if you do not follow the regimen of taking prescribed medications for stomatitis. Or aggravate the situation with poor nutrition, neglect of personal hygiene, smoking, and alcohol abuse.
Poor quality work by doctors
Sometimes stomatitis does not go away for a long time due to the fault of doctors. The doctor may have made an incorrect diagnosis or prescribed an ineffective treatment plan. Or did not take into account that the patient may have an allergy to a substance included in the prescribed medications.
Stomatitis can drag on due to poor quality work of a dentist or orthopedist. For example, after a tooth is removed, a piece remains in the gum socket. If its sharp edge constantly injures the oral mucosa, then the disease will not go away. The same can happen after a burn from dental or medicinal solutions, prolonged exposure to a poorly installed filling, or poorly fitted dentures.
How long does it take to treat stomatitis?
When the first signs of the disease appear, you must visit the dentist to identify the cause of stomatitis and prescribe a course of treatment.
In order to get rid of the disease, medications are prescribed depending on its form.
- For herpetic stomatitis, topical painkillers, wound healing and anti-inflammatory drugs, antiviral and antihistamines, multivitamins and immunomodulators are prescribed. It is recommended to adhere to a diet - nothing salty, spicy, sour or sweet. Avoid cold and hot food and drinks. If all recommendations and prescriptions are followed, the treatment period for the disease will be from 5 to 10 days.
- Fungal stomatitis is treated with antifungal drugs, gels and ointments. It is recommended to carry out disinfectant rinses of the mouth and not to eat foods with a high carbon content during treatment. In the absence of complications, the disease can be eliminated in 10-15 days.
- Treatment of bacterial stomatitis involves the use of healing, anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. It is recommended to consume food and drinks only warm, and to exclude spices, pepper, acid and salt from the diet during treatment. It can range from 7 to 14 days.
- Aphthous stomatitis involves treatment using systematic rinsing of the mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs, adherence to a strict diet - no tobacco, alcohol, solid food, sugar, salt and spices. In addition, antihistamines and vitamins are prescribed. Procedures are carried out to cleanse the body of toxic substances. With timely treatment, aphthae heal in 7-10 days.
We suggest you read: Is it possible to rinse your mouth with soda for stomatitis, treatment with soda solution in children and adults, rinsing with water for a child, how to treat
Why does stomatitis not go away?
There can be many reasons that negatively affect the effectiveness of treatment. The most common ones are listed and discussed in detail below.
Errors in diagnosis and treatment
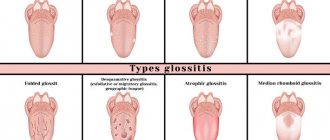
It is very important to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of stomatitis, and not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication. Stomatitis has seven forms, each of which differs in clinical course, pathogenesis and therapy. Infectious forms develop when pathogenic microbes and bacteria, fungi (mainly yeast and mold, less often dermatophytes) and viruses come into contact with the mucous membranes. Depending on what type of microorganism became the causative agent of the infection, there are three types of infectious stomatitis, the symptoms and features of which are given in the table.
| Type of disease depending on pathogenesis | Image | Signs and clinical course | What treatment is prescribed? | How many days does it take to recover (averages for adults)? |
| Bacterial | A dense coating of a yellowish tint on the surface of the mucous membranes, bad breath, a slight increase in temperature, hyperemia of the mucous membranes, erosive defects of soft tissues | Antibiotics, topical agents with the addition of antiseptics and anesthetics | 5-7 days | |
| Viral (herpetic) | Multiple blisters, the cavity of which is filled with exudate, covered with a cloudy film on top (in severe cases, their number can reach 20-30 pieces). Increased body temperature, swelling of the mucous membranes, redness, severe pain | Immunomodulatory drugs in the form of oral medications or rectal suppositories, antiviral ointments | 3-5 days | |
| Fungal (mainly candidiasis) | Milky or curdled plaque, hyperemic areas, ulcers, putrid odor from the mouth. Body temperature may remain within the subfebrile range | Antimycotic oral drugs of systemic action, antifungal solutions, ointments and creams | Up to 7 days |
As can be seen from the table, the treatment of each type of stomatitis has its own characteristics, therefore incorrectly selected therapy is one of the main reasons for the protracted course of the pathology. To avoid this, you must contact a specialist in a timely manner and follow all instructions. In no case should you treat the disease on the advice of friends, since the drugs that helped them may be ineffective for other forms of stomatitis.
Important! To treat bacterial stomatitis, the patient may be prescribed antibiotics. If stomatitis does not go away while taking antibacterial and antimicrobial drugs, the reason may be the lack of sensitivity of microorganisms to the active substance. In this case, bacterial culture and antibiotic selection are required in accordance with the results obtained.
Chronic decreased immunity
Stomatitis is a disease whose nature is not fully understood. Most experts believe that the disease is associated with the functioning of the immune system, and the pathological signs of the disease are a response of lymphatic cells to contact with irritants entering the oral cavity. For successful treatment of pathology, it is necessary that the cells of the immune system exhibit sufficient activity towards elements that they cannot recognize and perceive as foreign.
Chronic decreased immunity
If the patient’s immunity is weakened, his body cannot fully fight pathogenic factors, therefore, in cases where stomatitis does not go away within a week, it is necessary to identify these factors and try to eliminate them. Immunity may be weakened by one or more of the following factors:
- abuse of alcoholic beverages and uncontrolled intake of toxic substances (including potent drugs);
- frequent respiratory infections;
- unbalanced diet with a small content of fruits and vegetables, cereals, fish, milk and meat;
- rare and short walks;
- reduced level of physical activity that does not correspond to age and physiological needs;
- unfavorable social, climatic and environmental living conditions.
Symptoms of decreased immunity
Important! Chronic stress and severe emotional upheaval can negatively affect the immune system and slow down recovery, so during the treatment period it is necessary to follow a gentle regimen and avoid any anxiety and worry.
Nicotine addiction
Prolonged stomatitis (longer than one week) is often observed in chronic smokers, and there is a scientific explanation for this. Tobacco smoke contains 58 substances harmful to health that negatively affect the health of the oral cavity, namely:
- change the chemical composition and viscosity of salivary secretion;
- have an irritating effect on injured mucous membranes and prevent their healing;
- almost 4 times reduce the concentration of lysozyme, a substance produced by the salivary glands and which has a powerful antibacterial effect.
Nicotine addiction is one of the causes of prolonged stomatitis
It is lysozyme that influences the formation of local immunity and the ability of mucous membranes to resist the effects of pathogenic factors. If a person with stomatitis continues to smoke during treatment, it is necessary to understand that therapy may be delayed due to the natural decrease in protective functions and the constant traumatic effect that tobacco smoke and nicotine tars have on the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Advice! To minimize the negative effects of smoking, it is necessary to thoroughly rinse your mouth with boiled water after each cigarette. To improve the condition of the gums, you can use decoctions of medicinal plants with wound-healing and anti-inflammatory effects: thyme, string, St. John's wort, oregano or chamomile.
Failure to comply with gentle treatment
Stomatitis is a disease with quite painful symptoms. In almost all cases, the pathology is accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the mucous layer and the formation of ulcerative and erosive defects. To speed up healing, medication correction alone is not enough - the patient must follow a gentle regimen that excludes any irritating effect on the oral cavity for at least 3-5 days from the start of treatment.
Types of stomatitis
The main recommendations of dentists for quickly getting rid of stomatitis and preventing complications are as follows:
- It is recommended to brush your teeth with a brush with soft synthetic bristles - such material does not injure the gums and avoids increased pain;
- until the acute stage is stopped, all food should be served in a puree or mushy state;
- the temperature of prepared dishes should not exceed 35-36 degrees, since hot dishes will irritate the injured mucous membrane and prevent its healing;
- All actions during hygienic or therapeutic care must be performed very carefully, avoiding too active exposure to the affected areas.
If the patient follows all the doctor’s recommendations, uses prescribed medications, and maintains an enhanced hygiene regime, the disease should resolve within 3-7 days from the start of treatment. If this does not happen, you should consult your doctor.
Video - Aphthous stomatitis
Poor hygiene
Maintaining hygiene during the treatment of stomatitis is one of the most important conditions for successfully getting rid of the problem. From the first day of illness, the patient should purchase a new toothbrush to avoid re-infection of tissues, which is usually more severe than the primary infection. It is necessary to change hygiene items even after the end of therapy, so as not to provoke a relapse of the disease.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment, during this period it is recommended to use medicated toothpastes with anti-inflammatory effects (the total duration of use should not exceed 3 weeks). The brush should be washed with hot water and antibacterial or laundry soap every day, drying it thoroughly after each use, since a humid environment creates ideal conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, especially if stomatitis is fungal in nature.
How to care for your toothbrush
After each meal and drink, you should rinse your mouth with herbal balms, mineral or table water, and also use dental floss. In between morning and evening brushing of teeth, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with disinfectant solutions or herbal decoctions. Of the pharmaceutical drugs, “ Furacilin ”, “ Chlorhexidine ”, “ Miramistin ” and “ Hexoral ” cope well with inflammation. For phyto-recipes, you can use decoctions and infusions of string, thyme, lovage and chamomile.
How to prevent the development of stomatitis
In order to avoid the risk of the disease in question, you need to follow several basic recommendations. We should consider them in more detail:
- Care for the oral cavity from the first days of a baby’s life.
- Wash your child's toys regularly.
- Clean your rooms more often.
- Visit the dental clinic regularly.
- Try not to damage the oral cavity.
- Do not communicate with patients who have been diagnosed with stomatitis.
- Wash your hands after visiting public places.
- Do not trigger pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Eat right and on time.
- Brush your teeth at least 2 times a day.
- Use special toothpastes and rinses.
- Timely treat caries and other pathological processes in the oral cavity.
- Remove tartar in specialized clinics.
In cases where stomatitis occurs too often, doctors may refer the patient to be tested for the presence of parasites in the body.
If any are detected, the person will be prescribed appropriate treatment and a special diet, which is based on avoiding sweets, spicy, fatty and smoked foods.
People should remember that stomatitis is a serious disease that needs to be treated with pharmaceutical drugs, so self-medication is prohibited.
To prevent pathology from becoming chronic, you need to monitor your body and respond adequately to changes in it.
Only highly qualified specialists are able to relieve a sick person from pain and dangerous complications.
Prevention
It is very important to know how you can protect and keep your child safe, especially during periods of decreased immunity and the development of viral and bacterial infections. The main preventive measures include:
The main preventive measures include:
Maintain good hygiene, but not brushing your teeth enough or too much can be harmful. Sour and spicy foods should be consumed with caution. It is necessary to visit the dentist regularly. If wounds appear in the oral cavity, it is necessary to monitor them and rinse regularly. It is very important to treat any disease in a timely manner, since stomatitis can manifest itself as a complication of other pathological changes in the body. If someone around you has a worsening herpes, you need to avoid close contact with the child (hugs, kisses) and wash your hands more often.
Prevention can not only simplify the process of treating the disease, but also get rid of it.
Treatment of allergic stomatitis
Treatment of allergic stomatitis in adults begins with limiting contact with the allergen. Antihistamines are used to treat allergic stomatitis: tavegil, fenkarol.
Tavegil is prescribed to adults and children over 12 years of age - 1 tablet in the morning and evening.
Side effects of Tavegil: headache, dry mouth, nausea.
In case of individual sensitivity and pregnancy, the drug is not prescribed.
The drug Fenkarol for the diagnosis of “allergic stomatitis in adults” is used at a dose of 25-50 mg 3-4 times a day.
Side effects: gastrointestinal disorders.
The drug is not prescribed to pregnant women. Prescribe with caution to nursing mothers.
Eggs, coffee, and chocolate should be excluded from the diet of a patient with allergic stomatitis. Do not overuse seasonings and spices.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis in adults in recent years has been carried out using gels that are applied directly to the mucous membrane. You can apply the drug Viferon-gel 3-4 times a day for 5-7 days.
The drug Amiksin is used to stimulate the immune system. Treatment of stomatitis in adults with Amiksin is carried out every day for the first two days (one tablet), then every other day. The course of treatment is 20 tablets. Amiksin helps the body fight the herpes virus. Contraindications: pregnancy, lactation, childhood, individual intolerance. Side effects include skin itching, rash and urticaria.
Folk remedies for getting rid of stomatitis
Peroxide rinse. Fill the glass halfway with water and add a small spoon of peroxide. Rinse your mouth 4 times a day. Propolis tincture with alcohol will help. Dilute it in the same proportions. It is permissible to alternate with rinsing with peroxide.
Get aloe juice. To do this, pass the leaf through a meat grinder and squeeze through gauze. Rinse several times after meals. You can chew a piece of a plant leaf for a while. This will also have a healing and antiseptic effect.
Potatoes are used. It is cut thinly and placed in the oral cavity, kept for about 15 minutes. Squeeze the juice out of carrots or cabbage and add a little water to it. Rinse the mouth.
Herbal infusions are prepared to relieve the discomfort. To protect oral health: chamomile, calendula, eryngium, sage, St. John's wort, blackberry, raspberry, sea buckthorn.
Use each of the ingredients or all together. You need to steam a couple of tablespoons of dry herb with boiling water (3 tbsp.). Leave for 3-5 hours. Before each use, warm the infusion and rinse your mouth.
Treatment of fungal stomatitis
Treatment of fungal stomatitis in adults includes therapy with antifungal drugs in the form of tablets, such as Nystatin. Adults are given 500,000 units 3-4 times a day or 250,000 units 6-8 times a day. Daily dose – 1,500,000 – 3,000,000 units. Side effects of the drug include nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. There are no contraindications other than individual sensitivity.
The drug imudon to strengthen the immune system is prescribed in the form of lozenges, 5-8 tablets per day. The course of treatment with the drug is 2-3 weeks.
Aloe and Kalanchoe liniment is used to treat fungal stomatitis in adults as follows: apply to the mucous membrane for 20 minutes 3-4 times a day.
Treatment of various types of stomatitis in adults
In mild forms, treatment of stomatitis in adults is usually local. If the inflammation of the oral mucosa is of non-viral, non-fungal and non-allergic etiology, first of all you need to try to eliminate the inflammation and heal the aphthae. Traditional medicine, known for its healing properties, can help you with this.
An effective local antiseptic for stomatitis is chlorhexidine bigluconate. In dentistry, a 0.05% solution is used 2-3 times a day. They are used to rinse the mouth or irrigate ulcers when the mucous membrane is inflamed. Side effects of the drug: dry skin, itching, rash, dermatitis. Can be used by pregnant women. There are no contraindications other than individual sensitivity to chlorhexidine.
We suggest you read: How long does it take to treat stomatitis in children?
Signs of stomatitis in adults
Symptoms of the pathology in question in an adult patient vary depending on the type of disease.
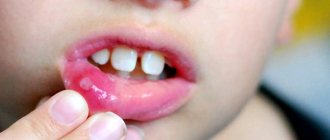
With aphthous stomatitis, the mucous membrane is covered with plaque and round or oval blisters with a border around the entire circumference.
Ulcerative stomatitis is characterized by the formation of painful gray ulcers and an increase in body temperature.
The catarrhal form of stomatitis does not form ulcers or wounds. When it appears, the throat turns red, the mucous membranes swell and become inflamed. An unpleasant odor from the mouth may appear.
How many days stomatitis is treated depends on many factors.
Terms of treatment for pathology depending on its form
It should be immediately clarified that stomatitis can be an independent disease, for example, after injury to the mucous membrane or penetration of bacteria.
But it can also be a consequence of some other pathology: flu, colds, sore throat. How long does stomatitis last?
The inflammation will not go away until the infection leaves the body. In addition, an inflammatory process in the mouth indicates iron deficiency anemia.
The treatment regimen is selected taking into account what type of stomatitis is diagnosed in a particular patient. How many days does it take for the pain to go away?
In the case when the pathology began to be treated in a timely manner, the person recovers in 1-2 weeks. This period depends on the patient’s health and immune system.
Treatment time for various forms
Each type of stomatitis develops for its own reasons and is caused by a specific pathogen. How much stomatitis is treated for each specific form depends on the resistance of the infectious agent to external influences.
- Aphthous stomatitis - occurs only chronically, can periodically recur, and is not completely cured. This type of disease requires long-term therapy. But with adequate treatment, symptoms disappear within 1-2 weeks. The height of the disease is preceded by an incubation period lasting from 8 to 10 days.
In cases of aphthous stomatitis, the virus lives in the human body throughout life, and can periodically manifest itself
Read also: Order of teeth in the mouth
It turns out that an attack of aphthous stomatitis lasts up to 4 weeks. This form of the disease can be treated throughout life. When immunity decreases, symptoms of relapse appear again, but with less force. There is no specific period for how long stomatitis of this type goes away. The intervals between exacerbations can be lengthened or shortened depending on the patient’s health and immunity.
- Candidal stomatitis - in mild forms, the disease disappears within a week; in severe cases, treatment takes several months. How long stomatitis caused by fungi lasts depends on the timely start of treatment, the adequacy of the prescribed therapy and the patient’s compliance with the doctor’s instructions.
- Herpetic stomatitis - symptoms of exacerbations disappear from 10 to 14 days, but this type of disease never appears once. It always becomes chronic, so its treatment lasts a lifetime. No one can answer how long stomatitis caused by herpes is treated. Stages of exacerbation are replaced by long-term remissions. Sometimes herpetic stomatitis ceases to manifest itself. To do this, you need to maintain a high level of immunity and prevent protracted infectious diseases.
- Leukoplakia does not refer to stomatitis, but to its consequences. This is a dystrophic change in the mucosa against the background of a chronic course with frequent relapses. Leukoplakia cannot be treated and is manifested by foci of keratinization. In the presence of such a condition, stomatitis occurs again and again, it is impossible to cure it.
How long does it take to treat stomatitis?
All life. Chronic forms require constant drug support, adherence to diet and lifestyle.
Chronic form of stomatitis
How long does stomatitis last in adults? According to statistics, if stomatitis does not disappear within 30 days, doctors diagnose its chronic form.
This is facilitated by ignoring visits to specialists and lack of adequate treatment.
There are several factors that provoke an exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease: weakening of the body’s immune defense, the presence of a virus, chronic diseases, injury to the mucous membranes, poor oral hygiene, damage to the gums with a toothbrush, the bad habit of putting everything in the mouth.
Most often, the aphthous type of disease becomes chronic. A person should try to get rid not of the accompanying symptoms, but of the very reason that causes it.
To do this, you need to consult a doctor and undergo examination in a hospital setting. Patients should be examined by an endocrinologist, laryngologist and gastroenterologist.
To restore immunity to the proper level, a person is recommended to take a complex of vitamins and regularly harden the body.
Causes
The main factors that provoke inflammation in the mouth include:
- decreased immunity;
- hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- presence of a traumatic factor;
- neuropsychiatric disorders;
- hypovitaminosis;
- unfavorable conditions (poor oral hygiene, poor hygiene of the whole body).
How can parents understand whether their baby has a disease? Recognizing the disease is easy.
Anna Losyakova
Dentist-orthodontist
If your child refuses to eat and has a fever, look in his mouth.
All types of stomatitis have common symptoms:
- The first symptom is slight redness of the mucous membrane. Localization can be in any part of the mouth.
- The reddened areas swell over time, and ulcers (blistering rashes) appear on them, which are very painful, preventing you from eating normally.
- As the inflammatory process intensifies, the ulcers may merge.
- The child refuses to eat, becomes weaker, and develops a fever.
It is impossible to miss the disease. The main thing is to react to the symptoms in time and consult a doctor.
In the video, famous pediatrician Evgeny Komarovsky talks about how to recognize and treat stomatitis in children:
How many days does it take for stomatitis to go away?
Stomatitis in adults is not diagnosed so often, but sometimes it can be a sign of various abnormalities in the body, including disorders of the digestive system, cancer, and HIV. How long it takes for stomatitis to go away depends on the cause of its occurrence.
If the mucous membrane is inflamed, regularly affected by ulcers, and the recovery process seems endless, then it makes sense to undergo a full examination by specialists and find the true cause, rather than fight recurrent inflammation of the mucous membrane with traditional methods. A long-lasting process is a reason to seriously think about the reasons for its occurrence.
We will tell you how long it takes to treat stomatitis, depending on the causes and form of the disease.