Adenophlegmon: symptoms and treatment
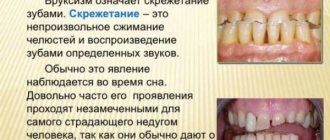
Cellulitis is an acute purulent diffuse process in the subcutaneous fat layer. Adenophlegmon is localized near the lymph nodes, the abscess inflammation of which is the direct cause of the pathology.
Please note: dental surgeons most often have to deal with adenophlegmons, since in most cases the parotid, submandibular and chin areas are affected.
Treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting.
Possible causes of the acute process
And denophlegmon develops against the background of a weakening of the body's defenses . Normally, the lymphatic system is a barrier to the spread of infection. In the lymph nodes, the process of capturing and destroying cells identified as foreign takes place. With inflammation of the nodes, lymph outflow is significantly reduced, and vascular permeability. A focus of purulent inflammation (abscess) is formed, from where pathogenic microflora penetrates into nearby tissues. As a result, the acute process acquires a diffuse character.
The most common causes of adenophlegmon:
- dental diseases (with chronic foci of infection);
- traumatic injuries of soft tissues;
- tonsillitis;
- infectious diseases;
- some dermatitis;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- infection during medical procedures (in violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis);
- cystic neoplasms of the jaws;
- malignant tumors.
Microorganisms that provoke the development of adenophlegmon include staphylococci (including aureus), diplococci and streptococci.
Symptoms of adenophlegmon
With the development of a pathological process in the area of the lymph nodes, a swelling that is painful with light pressure is formed, which grows quite quickly . The patient experiences increasing symptoms of body intoxication - weakness, headache and general malaise. Body temperature rises (in some cases – up to 39-40°C).
Important: if inflammation begins in a child, he becomes inhibited, has little contact and lethargy, complains of pain and refuses to eat.
Upon examination, pronounced hyperemia (redness of the skin) is revealed in the center of the swelling. The formation has a dense elastic consistency. During palpation, fluctuation is detected, which indicates the presence of fluid in the formed pathological cavities. Multiple pinpoint hemorrhages may be visible on the skin or surface of the mucous membranes (in the area of the vestibule of the oral cavity). At a late stage, the abscess may break out and form a fistulous tract.
The progression of the pathology threatens with complications such as mediastinitis (inflammation of the mediastinum), sepsis (blood poisoning) and infectious meningitis. If emergency measures are not taken for adenophlegmon, life-threatening conditions for the patient develop - cardiac, respiratory and (or) renal failure.
Submandibular adenophlegmon
Most often, adenophlegmon is detected in the submandibular region. Patients complain of deterioration in general condition, increased temperature and swelling . During the collection of anamnesis, it usually turns out that there has previously been a painful lump near the lymph node. On examination, swelling, hyperemia, tissue infiltration and severe pain are detected. If purulent inflammation is localized in the lower submandibular triangle, swallowing and speech are difficult. Due to the pain reaction, patients find it difficult to even open their mouth.
A blood test reveals leukocytosis, neutrophilia and a significant (up to 500 mm/h) increase in ESR.
Please note: the cause of adenophlegmon of the submandibular zone can be an impacted (unerupted) or semi-impacted third molar (wisdom tooth). It remains deep in the periosteum and is partially hidden under the mucous membrane. The presence or absence of such a focus of chronic infection can be easily determined using x-ray examination.
Adenophlegmon of the neck
In the anterior and lateral region there are anatomical spaces in which a significant amount of pus can accumulate.
The pathology develops against the background of an infectious disease and a significant decrease in immunity. The infection can spread from the submandibular lymph nodes to the deep cervical lymph nodes . Adenophlegmon of this localization often results from insufficient hygiene of the oral cavity and scalp; The impetus for the start of the process is the accumulation of a critical amount of coccal microflora.
Adenophlegmon of the axillary region
Primary phlegmon of this localization in most cases becomes a consequence of infected wounds of the upper extremities . Pathogenic microflora penetrates the axillary lymph nodes hematogenously. Lymph nodes increase in size (lymphadenitis develops), uniting into “packets” of dense consistency. Then the swelling loses its clear outline and a fluctuation appears, clearly indicating the development of phlegmon.
Please note: a simple abrasion when shaving the armpit can lead to adenophlegmon.
Adenophlegmon of the inguinal zone
The impetus for the development of pathology can be prolonged hypothermia, against the background of which the body’s defenses are weakened and the bladder or urethra becomes inflamed.
Important : quite often, even long-term antibiotic therapy for cystitis or urethritis does not lead to a complete cure, but transforms the acute process into a chronic, sluggish state with periodic relapses.
Infection from the pelvic organs spreads hematogenously (through the bloodstream). Adenophlegmon of the inguinal lymph nodes tends to progress rapidly .
Diagnosis of pathology
In most cases, identifying adenophlegmon does not present any particular difficulties. The doctor makes a diagnosis based on the patient’s complaints, as well as medical history, examination and laboratory tests. The dynamics of the process must be taken into account.
If necessary, an additional ultrasound scan of the affected area is prescribed. In some cases, radiography is required to exclude cystic formations and osteomyelitis.
To establish the type of pathogenic microflora and the degree of its sensitivity to certain antibiotics, biomaterial (punctate from the outbreak) is inoculated onto nutrient media.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with “classical” phlegmon, inflammatory infiltrates, actinomycosis, osteomyelitis, periadenitis and tuberculosis.
Please note: With an acute purulent process, there is a significant deterioration in the general condition, and, for example, with tuberculosis it is quite satisfactory.
Treatment of adenophlegmon
When the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is hospitalized in a specialized department of the hospital, where complex treatment is carried out.
At the first stage, surgical intervention is performed under general or local anesthesia (for children - only under anesthesia). If the source of infection is a diseased tooth, it is removed. The purulent focus is opened by cutting the skin and subcutaneous fat layer with spreading the edges of the wound using the jaws of a surgical clamp. Emptying the lesion occurs easily; pus comes out under pressure. There is no need for additional exploration of the cavity if osteophlegmon has been excluded. The next stage is antiseptic treatment (rinsing with a solution from a syringe) and placement of drainage (the wound is not sutured). Then a sterile dressing is applied, which is changed at least once a day.
The patient must be prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and restorative drugs (immunostimulants, immunomodulators and vitamins). If necessary, resort to detoxification therapy. During dressing, the incision site is washed daily with an antiseptic solution; change drainage if necessary.
Important: prevention of adenophlegmon involves timely sanitation of chronic foci of infection, treatment of infectious diseases until complete recovery and strengthening of the immune system.
With timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, the prognosis for adenophlegmon is quite favorable . Complex therapy allows you to achieve complete recovery in a fairly short time. A real threat to life is posed by an advanced process, accompanied by the development of a septic condition.
Plisov Vladimir, medical observer
10, total, today
What is adenophlegmon
Phlegmon is usually understood as an acute inflammatory process with accompanying suppuration, which occurs in the subcutaneous fatty tissue. As such, phlegmon does not have clear boundaries; it is often blurred.
Adenophlegmon of the submandibular region (hereinafter referred to as APO) is localized in the lymph nodes and is characterized by abscess inflammation. The most common sites for the formation of adenophlegmon are the supra- and submandibular region, the ear-jaw area, and the chin.
Causes of the problem
The etiology of this disease is very simple. After any infectious-inflammatory pathology (often lymphadenitis leads to APO), an immune failure occurs in the body, and the lymphatic system loses its full protective properties.
Lymph nodes become inflamed, swollen, and stop resisting pathogenic microflora, which massively attacks the body with reduced immune function. Bacteria settle in the lymph nodes, seep through their walls, enter the adipose tissue and cause an acute inflammatory process in it.
The following factors can also be “provocateurs” of APO in children and adult patients:
- soft tissue injuries of the neck;
- past infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- dental problems;
- inflammation of the lymphoid apparatus of the pharyngeal ring;
- jaw cysts;
- infection during medical procedures;
- malignant neoplasms;
- various pathologies of the excretory (genitourinary) system.
Features of children's APO
Children aged 3 to 7 years are at risk. The trigger for the development of pathology can be untreated acute osteomyelitis of the jaw. At an older age (10–14 years), adolescents are faced with adenophlegmon resulting from soft tissue injuries, followed by infection of the wound canals.
The list of main causative agents of the inflammatory process includes:
Treatment of tooth abscess
- staphylococci (white, golden);
- streptococci;
- diplococci, etc.
Important! If the baby suddenly begins to be capricious, begins to refuse to eat, complains of pain under the jaw, there is severe hyperthermia (sometimes the body temperature jumps sharply to 40 degrees) - this is a reason to immediately seek medical help from a pediatrician.
An appropriate diagnosis is made by a specialist based on a visual examination, anamnesis and clinical studies. Treatment of adenophlegmon is carried out exclusively in a hospital setting under the supervision of a doctor. Adenophlegmon of the neck is a dense, hyperemic, inflamed formation (tumor), painful on palpation.
A patient who comes to the doctor for a consultation voices classic complaints of general malaise, weakness, and swelling under the lower jaw.
Subsequently, doctors usually discover that there were symptoms of lymphadenitis (a dense ball of varying sizes is present in the area of the lymph nodes).
The doctor notes the presence of infiltration, swelling, hyperemia and other signs of APO that are accessible to visual inspection and palpation.
Important! If the lower submandibular triangle is affected by a purulent-inflammatory process, patients experience dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), problems with speech, and discomfort when opening and closing the mouth.
Adenophlegmon, localized in the submandibular region, is the most common type of this disease
Laboratory studies demonstrate an increase in ESR (indicating the presence of acute inflammation in the body), an increase in the number of neutrophils and leukocytes. It happens that APO develops within a few weeks after the patient undergoes dental treatment.
The doctor has no complaints about the condition of the teeth and gums, but under the lower jaw, a small ball appears at first, and then increases in size, a dense ball, which is also painful on palpation.
Often such patients are referred to an otolaryngologist, but he also does not find any respiratory abnormalities.
The cause of the pathological process and pain syndrome in this case is the same adenophlegmon under the lower jaw.
After the diagnosis has been confirmed, the patient is sent to the hospital. Treatment of APO includes several successive stages:
- Surgical intervention. It is performed under local (adults) or general (children) anesthesia. In a situation where a tooth has become the source of infection, it is subject to extraction or depulpation (the dental canal is cleaned and a filling is placed). If necessary, an incision is made on the skin and the pus is released from the capsule - often such manipulations are not required, the contents come out on their own under internal pressure. As such, additional cleaning of the affected area is not carried out; the postoperative area is covered with a protective bandage (it is changed daily).
- Drug therapy involves taking anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and restorative drugs.
- The wound is treated with local antiseptic solutions.
Treatment of APO is exclusively surgical - removal of pus from the capsule followed by the use of local antiseptics and systemic anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs.
At home, in addition to traditional treatment, you can use several proven effective recipes.
First of all, the action of the following compositions is aimed at strengthening the body's defenses and improving the general well-being of the patient.
Take 100 g of dry St. John's wort and 50 g of propolis, pour in 300 ml of vodka (medicinal alcohol). The mixture is poured into a glass container and sealed tightly. The medicine is infused for 7 days in a cool, dark place, filtered. When ready, the tincture is used for rinsing the mouth (the procedure is carried out at least 6 times a month, proportions - 20 g / 100 ml of warm water) and therapeutic compresses. Taking an anamnesis, analyzing complaints, visually examining the patient and assessing the results of clinical studies are components of the diagnosis of adenophlegmon
A few tablespoons of crushed dry eucalyptus leaves are poured into a thermos and steamed with boiling water and left for several hours.
It is recommended to take a third of a glass of this infusion at least 4 times a day before meals. Burdock leaves are washed under running water, finely chopped, mixed with sour cream (2:1).
The finished mass is applied to the affected area and left for half an hour. Manipulations are carried out daily.
Prevention
A measure to prevent the appearance and further development of adenophlegmon is timely diagnosis and treatment of any infectious and inflammatory diseases (especially ENT organs and the oral cavity).
It is recommended to pay due attention to strengthening the immune system - practice regular physical activity, take vitamin and mineral complexes several times a year, avoid stress and overwork.
Forecast
If you seek help from a doctor in a timely manner and complete the full course of treatment, the prognosis for APO is favorable. The use of antibacterial drugs in the initial stages of pathology can prevent the acute form of an abscess and reduce the risk of further complications.
So, adenophlegmon is an infectious-inflammatory process in fatty tissue, localized in close proximity to the lymph nodes. The favorite places for the tumor to be affected are the area under the lower jaw, near the ears, in the groin, and on the neck.
Treatment of the pathology is exclusively surgical, followed by drug correction of the general condition. With timely medical care, the prognosis for this disease is favorable; otherwise, adenophlegmon can provoke sepsis.
Source: https://pcvoice.ru/bolezni/chto-takoe-adenoflegmona
Adenophlegmon
Brief information:
Doctors:
Possible symptoms and signs of the disease:
Photos of possible symptoms:
Description of Adenophlegmon:
Pathogenesis of Adenophlegmon:
The occurrence of adenophlegmon is a manifestation of the failure of the barrier-fixing function of the lymph node, in which filtration of lymph occurs, retention of microorganisms by reticuloendothelial cells and their phagocytosis with the transfer of information about their antigenic structure to the immunocompetent organs. When the outflow pathways from an inflamed lymph node are blocked, microorganisms and their metabolic products of an antigenic nature can penetrate through the lining of the lymph node into the surrounding tissue, causing inflammation in it. Clinical picture. From the anamnesis it is often possible to find out that the onset of the disease was preceded by trauma, inflammatory processes of the scalp, mucous membrane of the oral cavity, nose, and tonsils. Then, in the suprahyoid region, in the neck area, a moving, painful “ball” with clear contours appeared.
As the “ball” grew larger, it lost its clear contours, and signs of the body’s general reaction such as headache, general malaise, and increased body temperature became more pronounced. Complaints and objective examination data, reflecting the local picture of the inflammatory process, depend on the localization of adenophlegmon. With a similar localization and prevalence of the infectious-inflammatory process, the disturbance of the general condition and the severity of the general reactions of the body in patients with adenophlegmon are usually less than in patients with phlegmon.
The possible complications are the same as in patients with phlegmon: progressive spread of the infectious-inflammatory process to adjacent anatomical areas, spaces and vital organs (brain, its membranes, mediastinum), generalization of infection - development of sepsis, increasing cardiopulmonary, renal , liver failure as a result of infectious-toxic damage to these vital organs and systems.
Symptoms of Adenophlegmon:
Sick children are characterized by adynamism, lethargy, lack of contact, severe weakness and sweating. In approximately a third of children with facial phlegmon, concomitant diseases are diagnosed: ARVI, bronchitis, pneumonia, acute otitis media, exudative diathesis, etc. The source of infection can be teeth, ENT organs, traumatic injuries, including post-injection injuries, due to violation of aseptic rules .
The clinical picture of the disease in these patients is characterized by rapidly increasing symptoms of intoxication and the severity of local changes: the presence of diffuse swelling in one or several anatomical areas with pronounced hyperemia in the center. The swelling is painful, has a dense consistency with signs of fluctuation. Multiple pinpoint hemorrhages are observed on the skin and mucous membrane of the vestibule of the oral cavity, tending to merge in the skin area.
Causes of adenophlegmon of the submandibular region
The occurrence of adenophlegmon is closely related to damage to the lymph nodes. Normally, the lymphatic system prevents the spread of infection by destroying foreign cells in the lymph nodes. As a result of infection, lymph flow slows down, vascular permeability increases, and microbes accumulate in the lymph nodes, which spread into surrounding tissues and cause inflammation. The causative agent of the purulent process is a bacterial infection: staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli.
Causes of purulent inflammation:
- dental diseases (caries, pulpitis, purulent cyst of the root apex),
- tonsillitis,
- jaw tissue cyst,
- oncological diseases,
- infectious diseases,
- soft area injuries.
In children, the cause of purulent inflammation of the submandibular zone is often an impacted tooth. Due to improper location, it remains in the gum and causes inflammation of nearby tissues.
Adenophlegmon
Adenophlegmon is a purulent-inflammatory process that affects the submandibular lymph node. The capsule of the node “melts”, and the necrotic tissue that has formed in it as a result of inflammation spreads to surrounding areas. Adenophlegmon is often a consequence of untreated lymphadenitis.
Symptoms
Adenophlegmon is accompanied by a transient and severe deterioration in general health. In addition to soreness in the neck and throat, the patient’s sleep and appetite worsen, the temperature rises, and lethargy.
During the examination, the doctor reveals severe swelling and hyperemia of the designated area. There are also infiltration processes and adhesion to surrounding tissues. A general blood test will help confirm the diagnosis: adenophlegmon causes an increase in leukocytes, neutrophils and a significantly increased ESR.
A feature of the diagnosis of adenophlegmon is its similarity to other diseases - phlegmon, actinomycosis and tuberculosis. Often the final diagnosis can be made after opening the inflamed node. So, with tuberculosis, the discharge from it will have a curdled form, with actinomycosis - granular.
Treatment of adenophlegmon
It is necessary to get rid of a complex and dangerous disease in a hospital setting. Complex treatment of adenophlegmon consists of the following stages:
- Surgical opening and removal of pus, installation of drainage. Anesthesia can be local or general (if the process has spread to surrounding tissues).
- Drug treatment - taking antibiotics, drugs with desensitizing properties.
- External treatment of the wound, regular washing with antiseptics.
If adenophlegmon is not surgically removed, the pathological process moves lower and affects the mediastinum. Prevention of the disease is a general strengthening of the immune system and timely consultation with a doctor in the event of odontogenic and otogenic infections.
Description of the disease
Cellulitis of the maxillofacial area
Phlegmon is a purulent inflammation that occurs in soft tissues.
The pathological process does not have clear boundaries, which is why it quickly spreads to blood vessels, nerve endings and organs.
Phlegmon of the maxillofacial area mainly affects bone tissue and tendons, salivary glands, and muscle tissue.
Cellulitis is a dangerous pathological condition. Due to the purulent-inflammatory process, a large amount of toxic substances enter the bloodstream, which causes general intoxication of the body.
The disease is acute, characterized by the rapid development of symptoms, against the background of which the functions of the masticatory apparatus, swallowing, and breathing are impaired in patients.
Phlegmon in ICD 10
In the international classification of diseases, phlegmon of the maxillofacial area is included in the group of diseases of the skin and skin tissue (L00 - L99). The pathology is included in the block of infectious skin diseases and is designated in the ICD by code value L 03.2.
Adenophlegmon: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Phlegmon is an inflammatory process that is purulent in nature and has an acute course. Phlegmon is localized, as a rule, under the skin in fatty tissue; this process does not have clear boundaries.
Adenophlegmon, which is a type of phlegmon, is located only in the area of the lymph nodes.
Adenophlegmon is manifested by severe inflammation of this area of an abscess nature. The most typical localization of such an inflammatory process is considered to be the supramandibular lymph nodes, submandibular lymph nodes, as well as the lymph nodes of the chin and ear region.
Causes of adenophlegmon
The main etiological factor leading to the occurrence of adenophlegmon is considered to be a sharp weakening of the body’s defenses, due, for example, to a serious illness or severe vitamin deficiency. In this case, the barrier functions of the lymphatic system are disrupted. This leads to the fact that individual pathogenic microorganisms, which should be destroyed specifically in the lymph nodes, survive and lead to the development of an acute inflammatory process. The outflow of lymphatic fluid from the node completely stops against the background of the development of the inflammatory process, and microbes, releasing their toxins, can freely pass through the walls of the node and enter nearby tissues, in which an abscessed focus of inflammation begins to form.
There are several main reasons that can lead to the occurrence of adenophlegmon:
- traumatic injury to soft tissue;
- history of severe infectious disease;
- inflammatory diseases of the skin and subcutaneous fat;
- inflammatory and infectious lesions of teeth and gums;
- inflammatory process in the area of the lymphoid pharyngeal ring;
- diseases related to the genitourinary system;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules when performing injections.
Thus, there may be several causes for this disease, but they all lead to the same result, namely, the formation of a focus of purulent inflammation in the structure of the lymph node due to an infectious agent introduced from outside.
Symptoms of adenophlegmon
It is very important to detect adenophlegmon at its earliest stages and promptly contact a specialist who can make a final diagnosis and prescribe the correct therapy.
So, the early signs of adenophlegmon include:
- rapidly progressing signs of intoxication syndrome (weakness, lethargy, decreased or complete lack of appetite);
- the formation of a tumor at the site of the supposed localization of the lymph node (at first the swelling will be barely noticeable, but after a short time it will become clearly visible);
- when feeling (palpating) the swelling, quite severe pain will be felt;
- redness will begin to increase, starting from the center of the tumor towards its edges;
- to the touch, the swelling will have a dense consistency and also have signs of fluctuation (the presence of a certain amount of liquid inside the swelling, usually pus);
- on the skin and mucous membranes, small hemorrhages can be detected;
- children with adenophlegmon quickly become very lethargic, their sweating increases sharply;
- There is an increase in body temperature, up to febrile values.
At a later date, the abscess often breaks out through a hole in the skin.
As inflammation progresses, the possibility of developing various complications increases, as the pathological process grows and can invade neighboring areas and affect vital organs. Among the most serious complications of adenophlegmon are sepsis, encephalitis, meningitis, as well as cardiopulmonary, renal and liver failure.
VIDEO
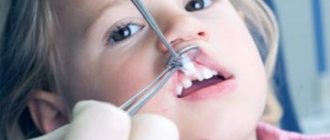
Adenophlegmon in children
In most cases, adenophlegmon affects children between the ages of three and seven years. A feature of adenophlegmon in children is that osteomyelitis of the jaw dominates among the complications of this process. In children aged twelve to fourteen years, adenophlegmon develops as a result of trauma to this area or the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms through existing wounds on the skin.
The main causative agents of adenophlegmon in children are staphylococci, streptococci and diplococci. However, we should not forget that other microorganisms that are pathogenic for the human body can cause the development of inflammation in the lymph node.
Clinical manifestations of this pathological process in children include:
- a sharp increase in body temperature, sometimes even up to 40 degrees;
- severe intoxication syndrome (weakness, loss of appetite, sleep disturbances);
- soreness in the area of the lymph node.
At the first indicated signs, parents need to show the child to a doctor who will make a diagnosis and prescribe therapy. Most often, in this case, minor surgical intervention and a course of medicinal procedures in a hospital setting will be required.
Diagnosis of adenophlegmon
Stages of diagnosis by a medical specialist:
- interviewing the patient regarding the presence of any complaints, in other words, collecting an anamnesis;
- clinical examination;
- ultrasound examination of the affected area, which makes it possible to make a diagnosis and determine the exact localization of the abscess process;
- radiography of the affected area (most often performed to exclude other diagnoses with similar clinical symptoms (tumors of the jaw and lymph nodes, jaw cyst, etc.);
- assessment of laboratory test data (general blood count, biochemical blood test, etc.), which play only a supporting role, indicating the presence of a focus of the inflammatory process in the body.
It is necessary to distinguish adenophlegmon from diseases such as actinomycosis, tuberculosis or simple phlegmon. The main difference is considered to be an acute inflammatory process, localized specifically in the area of the lymph node, accompanied by a deterioration in the general condition and severe pain in the area of the affected lymph node.
Treatment of adenophlegmon
Adenophlegmon requires mandatory treatment in a hospital, and the course of treatment must take place in several successive stages.
Adults usually undergo the surgical procedure under local anesthesia, but children must be placed under general anesthesia before surgery. First you need to find the source of the infection; if it is a tooth, then it is either filled or simply removed. Then an incision is made into the skin and subcutaneous tissue, after which, as a rule, the pus itself comes out of the capsule under pressure. Usually, there is no need for additional cleansing of the area. After the operation is completed, a sterile dressing is applied to the incision site, which is changed every day.
Drug therapy
Conservative therapy is carried out comprehensively, it usually includes drugs such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and restorative components.
Daily treatment of the incision site with specialized solutions that have an antiseptic effect.
Attention! Disease of the lymphatic system with adenoiditis in children - adenophlegmon
CategoriesComplications
One of the most dangerous forms of lymphatic diseases is adenophlegmon. This pathology, as a rule, occurs during acute modifications of adenoid pathogenesis, as a consequence or complication of untreated lymphadenitis.
The disease develops rapidly, with a purulent abscess factor. It affects not only the odontogenic areas that are more often encountered in practice (maxillofacial, cervical, postauricular).
Inguinal, axillary, popliteal non-odontogenic locations are susceptible to adenophlegmon.
Parents of children with weak immunity and prone to adenoidoplasia (hypertrophied tonsils) should familiarize themselves in detail with the description of adenophlegmoid pathogenesis. Timely information received will help them recognize a serious disease in a child and take the necessary measures - seek emergency medical help.
In what cases does adenophlegmon occur?
First, let us briefly explain what adenophlegmon is in general. Adenophlegmon is based on a separate pathoinvasion, phlegmon. The resulting abscess gets its name from the Greek phrase “Phlegmone” (heat, source of inflammation).
According to clinical characteristics, this is purulent infiltration of the fatty internal epidermis. It should not be confused with a “truly clean” abscess, which has clear boundaries of hyperemia (furuncle, carbuncle).
Phlegmon hyperplasia does not have a root canal (column) inherent in boils and carbuncles; it transforms into a cavity (sac).
Microbiologists use laboratory tests (histology, biopsy) to identify various root causes of adenophlegmon formation:
- white or golden staphylococcus;
- streptococcus;
- bacteroids – “Pasturella multocida”, “Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae”;
- anaerobic mycoses, clostridia (spores of pathogenic fungi);
- order of diplococci (peptostreptococci, meningococci, pneumococci);
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli;
- Proteus vulgaris;
- herpes virus.
Articles on the topic An insidious consequence of adenoids in children - Sialadenitis
Adenophlegmon, in itself, is a non-contagious disease and is not transmitted by contact. The main route of intoxication of any part of the child’s body is hemolytic (through the bloodstream) or lymphatic.
In some cases, adenophlegmon infection is provoked by osteomyelitis, follicular tonsillitis, and abscessing stomatitis.
It can enter the child’s body through skin cuts, wound abrasions on the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, as a postoperative complication after adenectomy or tooth extraction.
Primary signs of adenophlegmon in children, what should alert you?
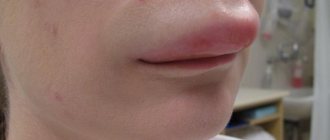
Photo of a child with adenophlegmon 5 hours after the onset of illness.
A distinctive feature of adenophlegmon is that the disease is rapid, accompanied by rapid swelling of the subcutaneous dermis of the epithelium (fluctuation). “Fluctuatio” - translation from Latin - in a closed cavity limited by elastic walls, purulent exudate, secretory fluid, and decay products of viral toxins are located and accumulate.
If parents notice that the child has become:
- unreasonably capricious, restless;
- complains of headache;
- his high temperature rises sharply;
- one side of the face (or two at once) gradually warps, while the eye “swims”;
- or a growing red tumor has appeared on a bodily area (under the armpit, knee, groin);
- children feel a growing pain in these places, these are the primary signals, symptoms of incipient adenophlegmon.
Such a pathogenic picture in children requires urgent action from adults. Regardless of whether the disease began in the morning, afternoon, evening, or night, immediately seek professional medical help, call an ambulance.
Do not expect that you can apply a compress, give your child a painkiller (analgesic) and wait until the morning, then go to see a surgeon. Adenophlegmon does not tolerate delays.
This is a form of purulent pathology that disintegration and infection of tissues occurs within a few half hours.
Then it transforms into severe sepsis processes, spreading throughout the body through the bloodstream and lymph flow.
If there is a delay in providing assistance, the child develops tachycardia or bradycardia, rapid, uneven heartbeat (arrhythmia). Painful spasms in the temporal, occipital region of the head. This indicates that purulent intoxication of the child’s circulatory system, lymph system, and gray matter of the brain is progressing.
Adenphlegmon is “treated” by surgical opening. Then a long-term intensive program of conservative treatment is carried out.
Postoperative treatment of adenophlegmon
The treatment method for adenophlegmon prevails not only on a specific focal zone of infection, but also takes into account the aspect of the antibacterial effect on the entire child’s body.
If the location of inflammation is of a serous, purulent etiology, chemotherapeutic drugs are selected that have an intensive register of effects of at least 7-10 days.
Thanks to this time period, antibiotics necrotize the purulent epidermis in the affected area and produce additional antibacterial, antimicrobial sanitation throughout all organic systems of the child’s body. For example:
- In the odontogenic form of stomatonsillar adenophlegmon, in the abscess formation stage, a course of intravenous drip infusion is prescribed - “Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid - Vial”;
- In cases of non-odontogenic variant of the disease (inguinal, axillary adenophlegmon), the best effect is recorded by drugs - “Lincomycin”, “Metranidazole” in combination with “Oxacillin”;
In terms of disinfectant dressings, sterile dressings are used, sponges that are impregnated with a medicinal composition - “PermaFoam”, “Activex”, bactericidal patches “Veropharm”, wound healing wipes “Multiferm”.
Some thoughtful advice in conclusion
You can protect your child from adenophlegmon. If you follow and constantly remember useful and harmless tips, such as recommendations:
- If a child suffers from adenoid pathogenesis, carefully monitor the cleanliness and sanitary requirements when carrying out the prescribed home treatment (inhalation, rinsing, instillation of drugs into the nasopharynx). In frequent cases, adenophlegmonous invasion in a child is caused by accidental injuries during manipulation.
- Prohibit your child from scratching pimples on the face, neck, and under the arms. With especially dirty hands, trim your child’s nails promptly and regularly. It is under them that pathogenic layers of microflora accumulate.
Articles on the topic: Blood from the nose due to adenoids
Source: https://adenoidy.com/oslozhneniya/vnimanie-zabolevanie-limfaticheskoj-sistemy-pri-adenoiditah-u-detej-adenoflegmona.html
Adenophlegmon in children
Most often, adenophlegmon occurs in children between the ages of three and seven years. In second place is a complication that develops secondarily as a consequence of untreated or untreated adenophlegmon - acute osteomyelitis of the jaw. Older children (12-14 years old) more often suffer from the primary form of phlegmon, the etiology of which is usually associated with soft tissue injuries or infection through wound channels.
The causative agents of the disease, especially in children, are most often pathogenic pathogenic bacteria: streptococcus, white and aureus staphylococcus, diplococcus and others.
If a child begins to be capricious, sleeps poorly and refuses to eat, and begins to complain of pain, parents should immediately seek advice from a pediatrician, who, in turn, will refer him to a specialized specialist. As the disease develops, there is an increase in body temperature. The numbers can rise to critical levels - 40°C.
The diagnosis of adenophlegmon is made by a doctor based on a visual examination, clinical studies and taking into account the medical history. The baby undergoes a course of treatment with surgical intervention in a hospital, under the supervision of doctors.
[9], [10], [11], [12]
Symptoms of adenophlegmon
Having considered the symptoms of adenophlegmon, do not forget that only a specialist can make a final diagnosis, but he will also draw up a treatment protocol. You just need to recognize the onset of the disease in time and see a doctor.
With further progression of the disease, complications may arise due to the fact that the inflammatory process gradually begins to invade more and more new anatomical areas, affecting vital organs. In this case, pathological conditions such as sepsis, inflammation of the cerebral cortex, as well as the development of life-threatening renal, hepatic, cardiac, pulmonary... failure may occur.
Treatment of adenophlegmon
If the doctor makes a diagnosis, then treatment of adenophlegmon takes place only in a hospital and includes several stages:
- Surgical intervention. Children undergo it under general anesthesia, while adults undergo it under local anesthesia. If the source of infection is a tooth, then it is either removed or depulped, cleaning the dental canal and closing it and the tooth itself with a filling. Only after this do they move on to the next stage. An incision is made in the skin and fat layer (if such a need arises). In most cases, pus under internal pressure comes out of the capsule on its own. No additional cleaning of the pus-filled area is required. Next, a bandage is applied, which is changed daily.
- Drug therapy. The patient subsequently receives comprehensive treatment: antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial support, and restoratives.
- In parallel with the medications, the postoperative wound is treated with special antiseptic solutions.