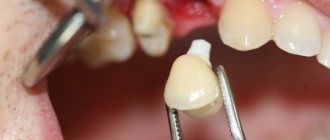
Dental prosthetics is a unique chance to fill a missing row of teeth, neutralize the manifestations of other complications and prevent pain syndromes in the oral cavity. Who among us is not familiar with toothache? There are hardly many people who would disagree with such a statement. They can rightfully be called lucky. But, in our lives, the majority still know firsthand about problems with teeth and try to do everything possible to avoid such a development of the situation. Especially when it comes to lost or weakening teeth that need a full replacement. Science and technology have advanced so successfully in this direction that finding a high-quality and reliable analogue for your tooth will not be difficult. The same can be said about the manipulation itself to replace one or several teeth. Today, performing dental prosthetics is not a problem, since quite a few dental clinics are able to cope with this task at a professional level. In such a matter, the main thing is to find an institution that will properly supply new teeth and meet your expectations.
Why do you need dental prosthetics?
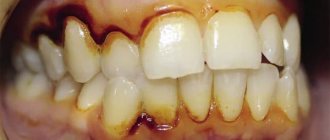
After tooth loss, adjacent units lose natural support. Under the influence of chewing load, they begin to deviate towards the resulting gap. Over time, the consequences of tooth loss worsen. If the defect is not corrected in a timely manner, treatment will be lengthy and require significant financial investments. The position of neighboring teeth will have to be corrected, and only after that will it be possible to carry out prosthetics.
After tooth extraction, neighboring teeth deviate from their natural position
In addition, the bone tissue at the site of the lost tooth does not experience chewing load, and a process of degradation occurs in it. If in the future a person decides to install an implant, a complex operation will be required to restore the volume of bone tissue. Therefore, it is worth inserting the tooth in place of the removed one in a timely manner in order to avoid more expensive and lengthy treatment.
Stages and technologies of implantation
A patient with this diagnosis comes to a specialist in the manufacture of dentures only at the final stage of therapy, when the main symptoms of the disease have either already passed, or the degenerative processes are localized within individual teeth.
At the first stage of contacting an orthopedist, it is determined which teeth can still be restored and saved, and which are already doomed to be removed due to severe destruction of the periodontal space.
Then the loose masticatory organs are fixed.
On this topic
- Prostheses
Rules for caring for removable dentures made of plastic
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- October 5, 2020
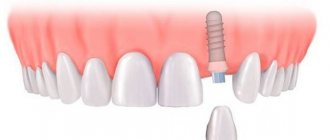
At the next stage, implants are inserted in place of the lost units.
At the end of the course of treatment, the doctor performs cosmetic treatment to restore the correct bite and uniform load on the teeth.
Dental prosthetics for any condition of the patient requires a preparatory stage, which can last for several weeks depending on the pathologies discovered by the dentist. This is especially true when a person orders a comprehensive restoration of the jaw through implantation.
This stage includes the following operations:
- treatment of periodontal disease through physiotherapeutic procedures, taking medications with a high content of antioxidants and vitamin complexes, gum massage;
- detection and elimination of caries, especially complicated forms affecting nerves and tooth roots, as well as restoration of those teeth that are located near the site of the future implant;
- removal of chewing organs that cannot be treated;
- deep cleaning of the jaw, including ultrasonic treatment, removal of tartar, plaque, and complete cleaning of gum pockets;
- gums that cannot be restored with their subsequent extension as necessary.
Advanced periodontal disease may require not only the restoration of gums by building up artificial tissue, but also the implantation of additional sections of bone, because some types of the disease lead to deep-seated deformations, including bone atrophy. The same degenerative processes occur when a tooth is lost, when the bone area underneath it no longer bears the chewing load.
The next stage involves the installation of temporary supporting structures that reduce and redistribute the chewing load. An orthopedist can also install removable dentures before completing the periodontal disease treatment course.
All of these measures are applied if necessary and are usually excluded when gum disease is quickly detected and its symptoms are localized.
On this topic
- Prostheses
Learn more about how to treat sore gums under dentures
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 5, 2020
Prosthetics occurs only if the patient does not have:
- bleeding gums;
- plaque and tartar;
- inflammatory processes;
- caries;
- malocclusion ;
- periodontal pockets;
- other untreated defects .
Once the above conditions are achieved, the dentist selects the correct dentures. This is done taking into account the individual qualities of the patient’s body, the structure of his jaw and bite, and also, of course, depending on the degree of periodontal disease and the stage of atrophy of the gum tissue.
The best models for this diagnosis may be the following implants:
- Clasp with interlocking overlay elements. This type is fixed so that the load is evenly distributed over the entire jaw, giving rest to damaged gums. Another advantage of the models is related to their fastening. Clasp dentures do not block the edges of the gums, making it possible to continue treatment of periodontitis.
- Splinting the inner plane of the teeth. A special material connects several chewing organs, easing the load and forming a splint in which the teeth will hold on to each other and will not fall out of the gums.
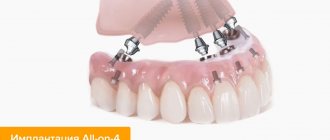
- Basal prosthetics method, in which the main load-bearing structure of the implant is implanted into the deep layers of bone tissue that are not affected by the lesion. This allows you to restore chewing functions at any stage of the lesion.
- Replacement of the front lower and upper teeth with veneers or lumineers.
On this topic
- Prostheses
5 materials used in dentistry for dentures
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- October 5, 2020
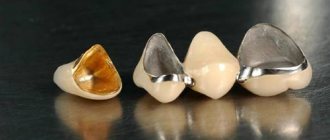
The established diagnosis makes it impossible to use the following types of crowns:
- solid metal or porcelain;
- cantilever, in which a special intermediate element, a console, is installed on the root, on which the main crown is then placed;
- metal acrylic;
- dental bridges.
All of the listed varieties will either fall out due to weakening of the gums, or will cause even greater harm to the affected tissues, causing mechanical injuries and irritation.
Prosthetics - an effective method of restoring dentition
Often, with significant tooth decay, patients insist on therapeutic treatment. In some cases, it is possible, but the restored tooth will not last long. After a few years, and sometimes even after a shorter period of time, you will still have to contact an orthopedist. That is, you won’t be able to save money. First you will have to pay for therapeutic treatment, and after a while, prosthetics. If a tooth has been removed, you should find out how to insert a new one in consultation with your doctor.
Also, do not refuse the services of an orthopedist if there is significant tooth decay. Its task is to restore the dentition not only for aesthetic purposes, but also to preserve the health of the remaining natural teeth. An orthopedic dentist will prescribe the necessary examination and select the optimal prosthetic technique.
It must be taken into account that preliminary treatment by other specialists may be required (for example, in the presence of periodontitis). When the preparation is completed, impressions are made, from which orthopedic structures are made. Dentures can be removable or fixed. For most people, the second option is preferable, since in this case the prostheses do not cause psychological discomfort. Fixed dentures (crowns, bridges) are visually indistinguishable from natural teeth. How long after tooth extraction a prosthesis can be inserted depends on the type of prosthetics chosen. The doctor will provide detailed information during the consultation.
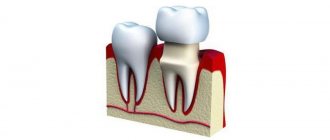
Fixed prosthetics
The use of this method allows you to restore the dentition and is the most preferred among patients and dentists. Fixed dental prosthetics is important in case of severe caries damage, excessive abrasion of dental tissues, in the absence of one or two teeth in a row, as well as for changing the color of the enamel and giving the tooth the desired shape. Such structures are characterized by permanent fixation, that is, they cannot be removed without damage. For the manufacture of fixed dentures, metal-ceramics, ceramics and metal alloys are most often used.
In modern dentistry, the following options for fixed prosthetics are used:
- Dental crowns;
- Bridges;
- Microprostheses
Which method of fixed prosthetics will be used in a particular case is determined by the doctor after examining the patient, taking into account individual indications, preferences and financial capabilities.
Dental crowns
Crowns are considered the most common method of fixed prosthetics. The following materials are most often used for their manufacture:
- Metal ceramics. It is distinguished by its low price, durability and attractive appearance. At the same time, metal-ceramic crowns can be made on the basis of alloys of precious and non-precious metals.
- Metal-plastic. These crowns consist of a cast metal part coated with plastic. These products can last no more than two years and are most often used as temporary dental prosthetics for the period of implant healing.
- Metal. This type of prosthesis is considered the simplest and most durable. Crowns can be made from pure alloys of precious and base metals. The service life of such products is up to 15 years, while the installation cost remains affordable.
Metal-free products, which are considered the most aesthetic and expensive, should be included in a separate category of crowns. Unlike metal-ceramics, artificial teeth made of zirconium dioxide, aluminum oxide and pressed ceramics do not cause allergic reactions or darkening of the gums, and therefore are very popular among people with good incomes.
Bridges
A bridge is a dental structure that allows you to restore the integrity of the dentition. So-called bridges can be made of metal-ceramics, ceramics and metal-plastic. The product consists of the following parts:
- Support. The supporting elements are usually the adjacent teeth on which crowns are installed. In some cases, implants can become supports. Abutment teeth must be healthy and stable, therefore, before prosthetics, they must be treated and carefully prepared.
- Intermediate part. These are artificial teeth that restore dental defects.
The material for the manufacture of structures is selected by the dentist. Whether this will be metal-ceramic prosthetics or the installation of a ceramic product is decided by the doctor, based on the preferences and individual characteristics of the patient.
Microprostheses
To save a damaged tooth, many doctors use microprostheses. Methods for such restoration of the dentition may be different, and the optimal option is selected by a specialist individually. Microscopic dental prosthetics is carried out using:
- Tabs. Relevant if there is damage to the outside of the tooth. The materials from which the inlays are made have special requirements, namely low thermal conductivity, high strength, biocompatibility with the body, minimal shrinkage. Designs can be made of precious metals, base metals and ceramics. Less commonly, dental metal-ceramics and composite materials are used to make inlays.
- Veneers. They are porcelain or composite plates with a thickness of 0.2 mm that replace the outer layer of teeth. They are widely used to correct defects in the dentition and enamel color, and also perform a protective function. At the moment, veneers are very popular due to their excellent aesthetic properties, but such dental prosthetics have a number of contraindications. The products are not suitable for people with malocclusion or severely damaged teeth.
Doctor's recommendations for prosthetics
- Orthopedic structures require more daily care than natural teeth.
- When performing daily procedures, it is important to strictly follow all doctor’s recommendations.
- The strength of artificial structures is lower than that of natural units of the dentition, so it is advisable to avoid eating too hard foods.
- While wearing temporary dentures, you must avoid viscous sweets and chewing gum. The doctor will provide the entire list of recommendations.
- To maintain the guarantee provided by our clinic, it is necessary to visit a doctor in a timely manner for preventive examinations.
Theory of application of methods
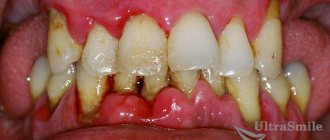
Periodontitis is a lesion of the periodontal soft tissues and bone, with a violation of the histological form and functionality. Pathological changes in the structural composition of tissues lead to a reduction in the area of the attachment apparatus. As a result of these disorders, root displacement occurs, which manifests itself as looseness.
The chewing function is an irritating factor affecting the gums. Blood flow in tissues is disrupted, resulting in vascular sclerosis. Mobility of teeth causes swelling of the gums. Violation of the structure of tissues greatly reduces their endurance, thinning of the walls of blood vessels occurs, which is manifested by bleeding at the slightest mechanical load.
Selective splinting during grinding
Orthopedic treatment of periodontitis using the Jenkelson method is indicated for:
- deformations;
- edentulism;
- accelerated wear of dental crowns;
- periodontal inflammation with tooth dislocation.
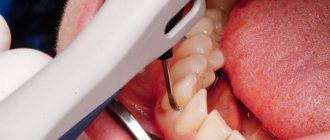
Selective grinding is used after curettage and non-permanent splinting, as well as before surgery to replace part of the soft dead tissue.
Taking into account the depth of the periodontal pockets, treatment is carried out in 4–5 stages. At the initial stage, carbon paper is installed on the upper jaw, at this moment the lower jaw moves back and forth. This method allows you to determine hypercontact between dental crowns. The bump is sharpened by sanding, then repair therapy is carried out by applying fluoridated varnish.
Clasp prosthetics for periodontitis
The next procedure is carried out after 3-5 days. At this stage, the lower jaw is polished. The teeth are not ground down, but are ground to 45 degrees, increasing the circumference of the equatorial region. Hard tissues are ground off the cutting edge of the tooth only if it is significantly lower than the others. The third procedure involves checking the occlusion of the maxillary region according to class 2. Done in 10 days.
The fourth procedure involves checking class 3 occlusion, and on the last visit all three classes are checked, crowns are polished and repair therapy is carried out.
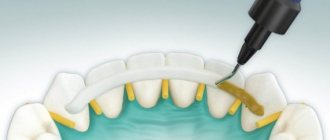
Splinting
Splinting involves complete immobilization of the moving crowns or the entire jaw. The splint makes a block of several dental crowns, limiting movement in three directions. The splint is made of durable, rigid material that will fix the teeth without causing mechanical irritation to the periodontium and the dental crowns themselves.
Periodontitis significantly complicates the splinting procedure.
Even in elementary cases, inflammation of the gums complicates the choice of teeth to restore the functionality of the masticatory apparatus. If the integrity of the complete dentition has been preserved, it is necessary to splint the movable crowns by combining them into one block.
Splinting teeth with composite