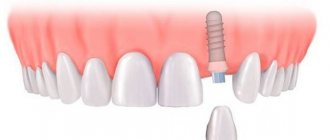
Today, dentists have a lot of options for prosthetics - restoring a damaged or missing tooth. One of the most effective solutions is metal ceramics - it is reliable and aesthetic. With its help, you can restore one or more teeth, and the structure is supported by implants or the patient’s own teeth.
Metal-ceramics are orthopedic structures - crowns and bridges, which are made by spraying or casting ceramics onto a metal base or frame. This method of prosthetics is in great demand, since the material used to restore the shape and function of the tooth does not cause allergic reactions. Metal-ceramic prosthetics are more often performed for the masticatory region, since in this case the strength of the structure is a priority, but this does not at all deprive artificial teeth of their aesthetics. Such designs closely replicate the structure and color of natural teeth.
Structure and types
Metal-ceramic dental prosthetics got its name due to the structure of the structures: inside it has a cast metal frame with a thickness of 0.3-0.5 mm. The material of manufacture is cobalt or nickel-chromium alloys. In some cases, alloys of precious metals - platinum or gold, palladium and others in different proportions - can be used. Crowns are divided into corresponding types according to this parameter.
The use of gold has an undeniable advantage - due to the natural yellowness of the precious metal, it is possible to achieve a natural shade of the structure, which is especially in demand when it is necessary to replace the front teeth.
The metal frame is covered with ceramics. The base is veneered using manual layer-by-layer application of ceramic mass. The structure is fired in a kiln after each layer is applied - this allows for the best connection between metal and ceramics.
As for the structure of the structure, the following types of metal-ceramics in dental prosthetics are distinguished:
- Actually single crowns. They are widely used to restore teeth in the lateral zone when they are more than ⅔ destroyed.
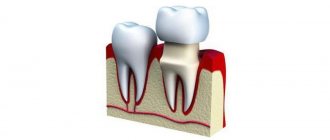
- Bridges. They are designed to restore several missing teeth in a row. The most reliable design is considered to be two crowns for supporting teeth and 2 artificial teeth between them.
Properties of dental porcelain
Porcelain is a brittle material with little ductility. The compressive strength is approximately 170 MPa. bending strength is 50-75 MPa and tensile strength is about 25 MPa. The values of other physical properties include an elastic modulus of 69-70 GPa (enamel - 46 GPa), a linear coefficient of thermal expansion (12-14) x 10 * 6 / ° C, similar to the coefficient of tooth structure, and a surface hardness of 460 KHN (versus 344 KHN at enamel).
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with washing the tonsils from purulent plugs
Also read: Wax modeling of teeth: what is it, modeling methods
Advantages and disadvantages of metal ceramics
Compliance with manufacturing standards and installation technology almost completely eliminates possible harm from installing the structure. The use of modern materials eliminates the release of toxic substances, but it is important to remember that an individual reaction may occur.
The ceramics itself, used in the manufacture of artificial teeth, does not cause allergies - a possible reaction is provoked by the metals in the frame of the structure. For example, chromium-nickel alloys can provoke an allergic reaction to nickel, and the use of base metals under the influence of saliva can be susceptible to oxidation reactions. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- burning in the mouth;
- metallic taste;
- swelling of the gums in the area of contact of soft tissues with the crown.
If such symptoms occur, it is important to consult a dentist - you will probably need to replace the structure with an all-ceramic crown or use another prosthetic method.
Other disadvantages include the possibility of exposing the metal frame in the event of receding gums. It is worth noting that structures made of zirconium dioxide are not subject to this phenomenon. In addition, the technology of metal-ceramic dental prosthetics involves grinding the tooth under a crown and removing the pulp in many cases, which is also a disadvantage.
The advantages of metal ceramics include high strength and long service life. Today, metal-ceramics are used for both single crowns and bridges - it is in demand when it is necessary to replace teeth with a significant chewing load. The frame made of aluminum dioxide or zirconium is strong enough, so the dentures can withstand heavy loads.
A long service life - 10-12 years for alloys of base metals and about 15 in the case of using a gold-platinum alloy - is a key advantage of the designs. This is only relevant for those prostheses that are made using individual casts. It is also important to follow the doctor’s recommendations for care - in this case, the prosthesis will last as long as it should. This is necessary because one of the common reasons for premature crown removal is the development of secondary caries at the junction of natural and artificial tissues, so it is very important to visit a doctor in a timely manner.
To summarize, we can say that the advantages of metal ceramics are as follows:
- comfort of wearing structures;
- functionality - function is restored due to the flawless modeling of masticatory hillocks;
- strength;
- long service life;
- acceptable aesthetics;
- biological compatibility - in the absence of allergic reactions to metals;
- the possibility of prosthetics for both anterior and chewing teeth;
- shade fastness - ceramics are not susceptible to the action of dyes;
- comparative cheapness;
- the possibility of restoring the structure without removing it in the event of minor chips.
Introduction
When carrying out complex dental rehabilitation, very high demands are placed on the quality of manufactured restorations.
They must be stable, functionally efficient, precise and made from high quality materials. Another important quality criterion, which is of decisive importance for many patients, is aesthetics. This term is widely used in our professional environment, but most often very pragmatically, to emphasize certain advantages of the manufactured restoration. At the same time, no one can clearly explain what aesthetics actually is. This concept does not have a clear definition and its content is highly dependent on fashion, age, social environment and many other factors that have nothing to do with dentistry.
In short, for us aesthetics means:
- beauty and functionality of each tooth,
- harmonious combination of individual elements with each other,
- harmonious combination of restoration with lips, face and individual features,
- beautiful and natural appearance overall.
The answer to the question of what materials and technologies can be used to satisfy these requirements depends greatly on the size of the restoration. It is recommended to make single crowns of teeth in an aesthetically significant area from ceramics, since all-ceramic restorations have optimal optical properties close to the properties of natural teeth. For chewing teeth, metal, metal-ceramic and all-ceramic crowns based on zirconium dioxide can be made.
During complex sanitation, there are no natural teeth with which restorations can be compared, so the best option, of course, is metal-ceramics. The stability and precision of restorations is ensured by a metal frame, and the aesthetic characteristics are formed by facing ceramic materials, the properties of which have been brought to near perfection over the past decades.
Metal-ceramic restorations are widely used in daily practice. Many dental technicians have perfected the technology for their production to the point of automation. Fitting, mechanical correction and cementation of such restorations usually does not cause any problems. That is why in this case we decided to make stable, reliable and beautiful metal-ceramic restorations for our patient.
Color of metal-ceramic structures
Separately, I would like to note the advantage of metal-ceramics, due to which many patients prefer it - ceramics, which is used for the manufacture of structures, allows you to imitate the shade and structure of your own tooth enamel. Therefore, the prosthetic tooth is similar to the patient’s natural teeth. The shade is selected according to the Vita scale - the selected color will remain that way throughout its entire service life, since ceramics are not subject to darkening and do not tend to absorb dyes from drinks and food.
The only thing that can change the shade of an artificial tooth is pigmented plaque, which is easily removed with professional oral cleaning.
Indications for metal-ceramic prosthetics
A doctor may recommend this method of tooth restoration for the following indications:
- severe tooth decay as a result of caries or injury - the impossibility of restoring it with fillings;
- anomalies of dental development that disrupt the function and aesthetics of the dentition;
- the absence of 2 or more teeth in a row and the presence of supporting teeth on the sides of the dentition defect (cermet bridges can be used here);
- inability or unwillingness to use other prosthetic methods.
Contraindications
This prosthetic method cannot be used for:
- periodontal disease;
- bruxism (in this case, it is important to first correct the condition or cure the disease, otherwise the structure may damage the teeth that come into contact with the crown when the jaws close);
- malocclusion;
- allergic reactions to metals and alloys;
- shortened crown parts of teeth;
- periodontitis is a temporary contraindication that requires preliminary treatment of the disease.
Stages of metal-ceramic prosthetics
The process of dental prosthetics with metal-ceramics can be divided into two large stages: preparation and prosthetics itself. An initial consultation with an orthopedic dentist allows you to determine the scope of work to be done, assess the condition of the oral cavity, and discuss options for restoring the shape and function of the tooth. According to the drawn up treatment plan, the patient is sent for diagnostics.
Preparing teeth for metal-ceramic prosthetics consists of the following:
- Performing X-ray diagnostics. It allows you to determine the absence of inflammatory changes in the periodontal tissues and evaluate the quality of filling if endodontic treatment was previously carried out (the pulp was removed and the root canals were sealed). If the canals are sealed poorly - not completely or, conversely, with the filling material extending beyond the apex of the root, the doctor will unseal them and carry out repeated treatment.
- Professional teeth cleaning and caries treatment, replacing old fillings, if necessary.
- Depulpation - removal of a nerve. If the damaged tooth has not been depulped previously, the doctor performs this procedure in the following cases:
- the presence of inflammation at the apex of the tooth, pulpitis;
- the need for prosthetic replacement of a single-rooted tooth - the pulp must be removed.
If prosthetics of a multi-rooted chewing tooth is required, the pulp can be left intact - but the final decision on this is made by the dentist, taking into account the individual characteristics of the condition of the oral cavity and the structure of the dental system.
In order to determine how dental prosthetics are done with metal-ceramics, it is necessary to take into account the degree of tooth destruction. Thus, a stump inlay for a metal-ceramic crown is made in cases where the tooth’s own crown is destroyed by more than half - at the root, or if only thin walls remain.
And if a larger volume of tissue is preserved, a pin can be used - it is screwed into the root canal, and an artificial crown is installed on it.
The actual stages of dental prosthetics with metal-ceramics are as follows:
- Tooth preparation - grinding. The question of whether teeth are anesthetized during metal-ceramic prosthetics, as a rule, is not raised - of course, the specialist performs preliminary anesthesia to eliminate the patient’s discomfort during the procedure.
The doctor grinds the teeth and then takes impressions - this is necessary for the further production of artificial structures according to individual parameters. Turning is carried out in one of two ways:
- with a ledge - the orthopedic dentist forms a circular ledge along the lower edge, which protects the gums from contact with the metal frame and reduces the likelihood of possible complications - swelling, irritation from contact of tissues with metal. This method also allows the use of metal ceramics with shoulder mass - it is applied in the area of the ledge to increase the aesthetics of the structure, and makes it possible to hide a strip of metal that can be visible through the ceramics at the base of the structure. Turning with a shoulder also makes it possible to extend the life of the structure;
- without a ledge - this method is outdated, so it is rarely used today. It has significant disadvantages - it does not provide enough space for a crown and can disrupt the contours of the gums. A space is formed between the structure and the gum tissue, in which dental plaque accumulates, and the edge of the denture looks quite unaesthetic. The design may cause irritation to soft tissues.
When contacting the clinic, find out how dental prosthetics are done with metal-ceramics - using the first or second method. This will avoid possible troubles with further wearing of the structure.
- Making an impression. Using impression material, the doctor takes impressions of the ground teeth. In order to accurately reproduce the parameters of the teeth, the gums are shifted using rings or retraction threads.
- Installation of a temporary crown. Due to the fact that the production of a permanent structure takes a certain time - about 1-2 weeks, the doctor installs a temporary crown made of plastic. This is necessary to protect the tooth core from food and saliva, as well as to ensure aesthetics. While the patient wears a temporary crown, a metal frame is made in the dental laboratory, onto which ceramic mass is subsequently applied layer by layer.
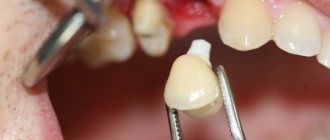
- After the permanent crown is made, it is installed using temporary cement after preliminary fitting of the structure. If it does not cause discomfort, the doctor will fix the crown using other, permanent materials.
What are metal-ceramic crowns?
Various metal alloys are used to make the frame.
Metal-ceramics is a material that consists of two components - a metal base and a ceramic coating. Different types of metals can be used as a base:
- The alloy of nickel and cobalt is used most often due to its affordable cost. Another advantage is its flexibility in processing. However, in some cases it can cause a metallic taste, especially in patients with allergic reactions.
- The alloy of cobalt and chromium is more stable due to its increased hardness. These are hypoallergenic alloys with high biocompatibility, and their price is slightly higher than that of nickel-cobalt based prostheses.
- An alloy of gold with palladium or platinum . This option eliminates allergic reactions and has optimal biological compatibility, as well as aesthetics, since the yellow color of the metal makes it possible to achieve a good resemblance to the natural shades of enamel. In addition, in this case the porcelain layer can be reduced, which means less turning will be required. However, such prostheses are expensive, so not all patients choose them.
- The titanium frame requires special ceramics to be used as the top layer. For this reason, such designs are quite expensive. At the same time, they have many advantages: titanium is ideally compatible with body tissues, it is lightweight, and it does not corrode.
After the frame is made from the selected material, ceramic mass is applied to it. This is done in layers, with each layer being fired. It is with the help of this technology that it is possible to achieve a strong and reliable bond between ceramics and metal.
How is a crown made?
Many patients wonder how long it takes to have metal-ceramic dental prosthetics. It is important to understand here that the procedures for preparing the teeth and the installation itself are carried out quite quickly, but the manufacture of the structure takes longer. As a rule, 1-2 weeks are enough to make a metal-ceramic crown. Based on the casts created, specialists make a plaster model - it is cast according to the impression after a preliminary assessment of its quality.
Then a dental laboratory specialist models a framework for metal-ceramics using wax. The finished frame is fixed on a plaster model and sent to an orthopedic doctor so that he can try it on in the patient’s mouth.
Then ceramic mass is applied to the frame. Before this is done, it is fired in a kiln and sandblasted - this allows for better adhesion of the metal and the ceramic mass.
The opaque is applied first - this is an opaque composition, then the structure is covered with a dentin layer (more transparent), and then with an enamel layer. This technology makes it possible to recreate the natural appearance of a tooth, taking into account the individual characteristics of the color of the enamel of your own teeth.
After the patient has tried on the design, glazing and final firing are carried out - then the crown is installed.
Firing dental ceramics
All-ceramic restorations can be fabricated on refractory casts produced by duplicating working casts, or by using platinum foil (0.025 mm thick) which is pressed around the cast to obtain an accurate shape.
Both the fireproof model and the platinum foil hold the mixed porcelain powder in the porcelain kiln and maintain their shape during the firing process. The technician mixes porcelain powder of the appropriate shade with distilled water and applies it to the fireproof model or platinum foil with a thin brush. First, the “dentin layer” is applied. In order to condense wet porcelain particles and obtain a dense mass, it is necessary to carry out moderate vibration with a hand tool. Blotting with an absorbent cloth helps remove excess moisture. The porcelain dentin mass is applied with a reserve, increasing the shape, to compensate for the significant shrinkage that occurs during porcelain firing.
Also read: Fixed dentures: indications for installation, photos
Repeated firings are usually used to obtain a layering effect and correct shrinkage. An enamel layer is added in a similar manner (usually a more transparent shade). Once cooled, the restoration can be “fitted” mechanically to ensure the correct shape, contour, size and fit.
Next, you can carry out the final firing, which ends the melting of the porcelain. At this stage, shrinkage is minimal, because most of it occurs during the primary firing (bisque firing stage). By controlling the final firing temperature, time and atmospheric firing (no vacuum), a “self-glazing” layer can be produced over the outer surface of the restoration. Alternatively, a low melting glaze can be applied to the surface and fired separately.
Firing should be carried out with a controlled rise in temperature in the kiln (i.e. 100°C), because Porcelain is a poor conductor of heat. Raising the temperature too quickly can burn out the outer layer before the inner layer has sufficiently melted. Both the condensation of particles and the firing regime significantly influence the properties of the porcelain and, therefore, the final quality of the porcelain restoration (Vergano el al, 1967).
Features of caring for metal ceramics
Everyday hygiene measures do not differ from normal procedures - it is important to brush your teeth twice a day, and also rinse your mouth, if possible, after eating.
Cleaning the teeth should be carried out as follows: using sweeping movements, you need to go over all the teeth in the direction from the gums to the cutting edge. You should not ignore the use of dental floss, or better yet, an irrigator.
You can clean metal ceramics in the same way as regular teeth - a toothbrush should be purchased in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations (the degree of stiffness of the bristles is determined by individual characteristics), the toothpaste can also be selected based on your needs.
Remember that it is better to protect metal-ceramic structures from mechanical damage. It is not recommended to bite into hard foods - this can result in cracks and chips, and subsequent breakage of the prosthesis.
Removable dental prosthetics
Such dentures are partially or completely removable. Partially removable ones can be worn for a long time without taking them off, they are comfortable and adaptation to them is quick. Completely removable dentures are often used in cases where there are no teeth left at all. They must be removed at night.
- Acrylic dentures (Acry-Free). The basis of such a prosthesis is made of acrylic, which is similar in structure to real gums. This is a plastic material that does not injure the mucous membrane. However, you should be aware that acrylic can cause allergies. In addition, acrylic has a porous microstructure, and this promotes the growth of bacteria. That is why it is recommended to rinse such a denture after every meal and brush it daily, just like your teeth.
- Clasp prosthetics. Clasp dentures consist of a base (metal hyoid or palatal arch), a plastic base and crowns. Most often, such dentures are used in the absence of chewing teeth.
Completely removable dentures can be:
- on suction cups. In fact, there are no suction cups in the usual sense. The removable denture is held in place due to the elasticity of the material, as if enveloping the gums;
- fixed using special creams. However, it is important to remember that a well-made removable denture adheres perfectly to the gums, and additional fixation with cream (or so-called glue) may be required in the future only due to atrophy of the ridge and bone, as well as due to loss of stabilization.
Warranty for metal ceramics
A good dental clinic provides a guarantee for metal-ceramic dentures - its period, as a rule, is less than the service life of the structure. If the prosthesis breaks before the warranty period expires, the clinic provides restoration or replacement services free of charge.
Restoration is carried out in case of mechanical damage to the crown - for example, chips. In this case, the prosthodontist assesses the extent of the problem and determines whether the framework of the structure is exposed. Restoration of a small chip that does not expose metal is carried out using composite materials. However, restoration when the frame is exposed may be impossible; the optimal solution here would be to remove the structure and re-prosthetics. In order to prevent unpleasant situations (chipping, crown loss), it is important to promptly replace metal-ceramics after their service life has expired.
It is important to make a choice regarding the type of metal-ceramic structure, taking into account how long you plan to wear the structure. Of course, the best can be considered to be made from a gold-platinum alloy; its service life reaches 15 years, and zirconium dioxide crowns can last even longer with proper care. However, the cost of such solutions will vary.