About the disease
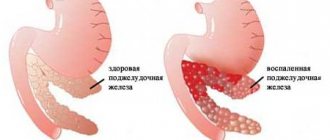
Diabetes mellitus can be referred to as a whole group of endocrine diseases characterized by inadequate absorption of glucose, which occurs due to a small amount of the hormone insulin produced in the blood.
The main indicator of this disease is an increase in blood sugar levels.
Patients suffering from diabetes get tired easily, are very sensitive to pain, and the immune system is easily weakened. For this reason, there are problems during operations, including implantation.
Diabetes and dental implants
Diabetes is a disease that manifests itself in a malfunction of the endocrine system. It is expressed in the fact that the pancreas cannot produce the required amount of insulin, the hormone responsible for the breakdown of glucose. This leads to the fact that the sugar consumed by a person is not completely broken down, but accumulates in the body, causing negative health consequences.
The two types of diabetes are significantly different from each other
Diabetes mellitus is divided into two types. They differ in the complexity of their course and the reasons for their development.
- Type I diabetes (insulin dependent). Typically, this type of disease appears at a young age. The cause may be a viral infection or bad heredity. The patient's pancreas is unable to produce the required amount of insulin. This is dangerous for the body, and in the absence of quality treatment, a person can die
- Type II diabetes (non-insulin dependent). It is an acquired disease, the cause of which is an unhealthy lifestyle. Usually appears in adulthood. The peculiarity of type 2 diabetes is that the cells become insensitive to insulin and the glucose level in the blood increases. This form of the disease is not as serious as the insulin-dependent form and is treated with a properly selected diet and medications that lower blood sugar. If the disease is started, it can become insulin-dependent.
Diabetes mellitus affects the condition of all organs, including the oral cavity, so the decision to undergo dental implantation in the presence of this disease must be carefully weighed. The negative impact of the disease on dental implants is manifested in the following:
- High levels of sugar in the body provoke the development of various dental problems
- The chemical composition of salivary fluid changes, and it becomes a favorable environment for the development of infectious processes
- The overall immunity of the body decreases, and this makes it difficult to carry out various surgical operations and significantly lengthens the rehabilitation period
- Since the metabolism in the body is disrupted, bone and gum tissue take a long time to heal after surgery, and it is difficult for a dental implant to take root
Modern approach
Thanks to the high level of development of dentistry in our time, it is possible to solve various dental problems even in complex cases.
A decade ago, implantation for patients with diabetes was prohibited, but today this procedure has become quite possible.
New effective methods of controlling and maintaining the desired level of glucose in the blood reduces the risk of inflammatory processes after implantation to a minimum.
However, a diabetic can be allowed to undergo surgery only if he carefully monitors his health, regularly visits an endocrinologist and does not allow the disease to worsen.
As for dentistry, there are also new unique methods in this area that can reduce the trauma of the operation and facilitate the recovery process after implantation.
Basal implantation
Another modern method that can be used for dental prosthetics in diabetes is basal implantation. With this type of orthopedic treatment, the implant is installed in the basal layer and cortical plate without affecting the alveolar region. The technique allows you to install a prosthesis in case of bone tissue atrophy.
Basal implantation is considered less traumatic and complications are less likely to occur after it. When installing prostheses, deep incisions are not made, but punctures are used.
As with other methods, basal implantation requires consultation with an endocrinologist, and a prerequisite for a successful operation will be compensated diabetes mellitus.
The effect of the disease on the oral cavity
Factors affecting the oral health of a diabetic include:
- inflammation of the gums (they can often hurt and even bleed due to a jump in sugar levels), due to disruption of the bacterial microflora and the rapid proliferation of harmful microorganisms;
- dry mouth, thirst, which is caused by low saliva production;
- the presence of a large number of caries lesions on the teeth due to the fact that saliva contains a lot of sugar;
- poor sensitivity to tastes;
- the presence of oral infections (candidal stomatitis and other types);
- the presence of wounds and ulcers that heal very slowly.
In order to avoid the listed companions of diabetes, you need to carry out oral hygiene as thoroughly as possible, regularly go to the dental clinic and give up bad habits (primarily smoking).
Risks of implantation
With diabetes, there is a disruption in metabolic and hormonal processes, wounds heal worse and bone tissue regeneration becomes more difficult, which is a serious threat of complications after surgery. For this reason, the implanted implant can be rejected quite quickly. In addition, it does not survive well in type 1 diabetes. In the second type of disease, there is an absolute deficiency of the hormonal component due to destabilization of the algorithm for the formation of new bone tissue. At the same time, the patient’s immunity is reduced, and any manipulation quickly tires him. For these reasons, dental implantation is prohibited in case of insulin-dependent diabetes and its decompensation stage.
The disease in question can become a complete contraindication to implantation if the following aggravating circumstances are present:
- the presence of pathologies of the heart, blood vessels and hematopoietic system;
- oncology;
- presence of mental illness;
- arthritis, rheumatism;
- tuberculosis;
- immunodeficiency, leading to a clear decrease in the body's strength.
What are the risk factors for implantation in diabetic patients?
Diabetes mellitus is caused by disruption of the endocrine system. Against this background, the body produces less insulin than is needed to break down the sugars coming from food. This negatively affects metabolic processes, leads to disruption of blood microcirculation, which impairs tissue regeneration.
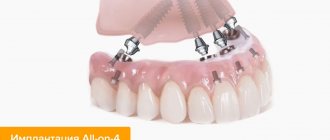
Despite this, diabetes is not a death sentence for implantation. Today, implantation protocols have been developed and successfully applied to treat this category of patients. It is possible to restore individual teeth or the entire jaw using the “All on 4” technique.
When can implantation be performed?
When getting dental implants for diabetics, it is important to follow the following rules:
- In the second type of compensated diabetes, the procedure can be performed only if there are no disorders of bone metabolism.
- Implantation and subsequent treatment should occur under the constant supervision of an endocrinologist.
- Blood glucose levels should not exceed 7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) both before implantation and throughout engraftment.
- The patient does not smoke, does not drink alcohol, and follows basic oral care rules.
- The patient does not have any other serious diseases that, together with diabetes, can become a contraindication to the procedure.
- All recommendations of specialists before and after the implantation procedure must be strictly followed. The patient must monitor his well-being. Any even the slightest illness, such as a cold, can significantly aggravate the situation, disrupting the immune system and causing implant rejection.
- The patient’s existing chronic diseases must not be allowed to enter the acute stage.
- You should take all medications prescribed by doctors in the form of antibiotics, drugs to stabilize sugar levels, immunomodulators and others.
- The patient's diet should be dietary to prevent surges in blood sugar. Sometimes temporary insulin therapy may be required.
In any case, doctors should approach dental implantation in a diabetic with extreme caution. This procedure can only be performed by highly qualified specialists who are proficient in the technique of conducting this treatment in the type of patients in question. Otherwise, negative consequences cannot be avoided.
Conditions that must be met by a diabetic for implantation include:
- antibiotics should not be taken for longer than 10 days after implantation;
- You will have to visit the dentist quite often after the operation until the implant is completely implanted;
- The implant will take longer to take root than in ordinary patients (about five months on the lower jaw and about eight on the upper jaw), so you will need to be patient.
You cannot rush to open the implant; you need to wait until it is completely osseointegrated to avoid complications. In addition, diabetics cannot undergo implantation with immediate loading.
How is implantation performed for diabetes?
A patient with diabetes must undergo a number of preliminary studies, which are carried out by an endocrinologist and a dentist. Even if specialists eventually give the green light to implantation, the risk of complications still remains quite high. The final success depends on the professionalism of the doctor, the correctly chosen treatment protocol, materials and equipment.
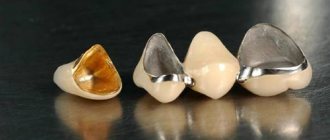
What implants can be used?
In order to make implantation possible for a diabetic, special implants must be used. The healing and general condition of the patient after the procedure will depend on them.
The structures used must be made of high-quality alloys. Nickel and chromium or cobalt and chromium products are best. When using other metals, the patient may experience a severe allergic reaction, and the quantity and quality of saliva produced will be affected.
It is also very important that implants for diabetics correctly distribute the load during chewing.
As for crowns, ceramic ones are most often recommended for diabetics. They provide high aesthetics and durability.
Regarding the manufacturer, you should choose the most reputable, long-existing and highly popular brands. Diabetes mellitus is not a case when you can save on products used for implantation.
On a note! For those who have no teeth left, or the remaining ones are in extremely poor condition, it is recommended to consider methods that involve complex restoration and allow you to secure the prosthesis immediately after fixing the implants. We are talking about implantation “all on 4”, on three or six implants, as well as the basal protocol. They involve minimally invasive installation of implants, which reduces tissue trauma. In addition, implantation is carried out in a very short time, which reduces the level of stress for the patient.
Factors that may affect the success of the procedure
How successful implantation will be in a diabetic depends on the following factors:
- How correctly the patient was prepared for the procedure. A complete sanitation of the oral cavity and professional teeth cleaning must be carried out. This will reduce the risk of infection. Taking antibacterial drugs before implantation also reduces the risk of complications.
- Length of illness. The less the patient suffers from the disease, the more the risks after implantation are reduced.
- The presence of concomitant ailments - caries, periodontitis, xerostomia, infectious and cardiovascular diseases also affect the success of the operation.
- Type and stage of the disease. If diabetes compensation is high, implantation can be performed. Diabetics who keep the situation under control with the help of a special diet and do not use hypoglycemic drugs can also become patients of the implantologist. And for diabetics who do not cope well with increased sugar levels and who are forced to inject themselves with insulin, they are at risk of complications after surgery. Implantation is not recommended for them.
- Implant location. When implanting implants in this group of patients, doctors must take into account that the upper jaw has a greater chance of engraftment than the lower jaw.
- Implant length. As noted earlier, medium-length implants are more suitable for diabetics than those whose length exceeds 13 millimeters or does not reach 10 millimeters.
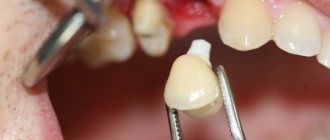
Implant installation
The procedure for implanting an artificial tooth root in a diabetic is no different from that performed on ordinary patients, except that all manipulations must be carried out as carefully as possible.
The implant must be installed as carefully as possible, without severe tissue injury. This procedure can only be entrusted to a trusted and experienced specialist.
Implant installation includes the following steps:
- Introduction of anesthesia.
- Opening the bone tissue, preparing a bed for the implant in it by drilling.
- Installation of the structure.
Due to high patient fatigue, all stages of the procedure must be carried out quickly.
Prices
The cost of dental implantation for diabetes mellitus is practically no different from standard implant installation. But it is necessary to take into account additional costs for examination, sanitation of the oral cavity, and in some cases, drug therapy.
| Service | Price |
| Consultation | for free |
| Making a treatment plan | for free |
| Nobel implants (the price includes an orthopantomogram and installation of a gum former) | 55 000 ₽ 33 900 ₽ |
| Straumann implants | 60 000 ₽ 34 900 ₽ |
| Osstem implants | 25000 ₽ 17990 ₽ |
| AnyOne implants | 12 000 ₽ |
| Service | Price |
| Consultation | for free |
| Making a treatment plan | for free |
| Nobel implants (the price includes an orthopantomogram and installation of a gum former) | 55 000 ₽ 33 900 ₽ |
| Straumann implants | 60 000 ₽ 34 900 ₽ |
| Osstem implants | 25000 ₽ 17990 ₽ |
| AnyOne implants | 12 000 ₽ |
See the full price list for NovaDent implantation
To discuss whether dental implantation for diabetes is possible in your case and how best to prepare for it, make an appointment with one of the dentists at the nearest NovaDent clinic in Moscow.
Expert of the article you are reading: Dashizhapov Mayur Borisovich Oral and maxillofacial surgeon, dental surgeon, implantologist, orthopedist, leading specialist of the NovaDent network
23 years old
Clinical experience Free consultation with this specialist
What to do after surgery?
Once a diabetic has received an implant, they should monitor their blood sugar levels as closely as possible. You will need to take antibiotics for approximately 10 days after implantation, as well as carefully monitor your oral hygiene and regularly visit your doctor (every two to three days after installation). A complete cessation of alcohol and smoking also plays an important role. The food should be dietary, which will ensure an even glucose level and also protect the implant from overload (solid foods should not be consumed).
The recovery process after surgery for diabetics is quite long. The most acute period can be considered the first 12-14 days after implantation. At this time, the patient feels pain, the soft tissues at the implantation site are swollen and swollen, and the body temperature may rise.
To alleviate the condition, the patient is recommended to use painkillers at this time. If the listed symptoms continue for more than a week, this may be a signal of the development of inflammation, which requires urgent medical attention.
Preparing for implantation for a diabetic
If a person has diabetes and wants to have implants installed, he will have to undergo more extensive diagnostics than a healthy patient. In addition to X-ray and CT, you will need to take a general blood test + sugar level, a general urine test and saliva test for bacterial flora. Next, you need to visit an endocrinologist and therapist with the results of the examinations. Both doctors are required to issue a conclusion that there are no obstacles to implantation. A CT scan should also confirm that there are no hidden problems with bone regeneration and help assess the size, quality and density of the bone.
At the Partner-Med dental center you will undergo thorough preparation for the upcoming procedure. Our experienced specialists pay special attention to the following activities:
- Professional hygienic cleaning of the oral cavity. Soft plaque and hard tartar are removed.
- Treatment of caries in order to remove foci of infection.
- Prevention and treatment of gum diseases (gingivitis, periodontitis).
Also, at the request of the patient, a teeth whitening procedure can be performed. Next comes the implantation stage, which our dentists carry out as carefully as possible. It consists of the following steps:
- Local anesthesia.
- Carefully drilling the bone and preparing a bed for the future root.
- Installation of a metal pin.
During the postoperative period, specialists at the Partner-Med clinic recommend closely monitoring blood sugar levels, taking antibiotics for 10 days, and also carefully maintaining oral hygiene. Every 2-3 days after implantation, you must visit the dentist and completely stop smoking and alcohol. During the rehabilitation period, it is recommended to consult a doctor for examination at least once a month. Strict adherence to the given recommendations guarantees successful implantation.
Our doctors
Brodsky Sergey Evgenievich
Deputy Chief Physician, Candidate of Medical Sciences, specialties: dentistry and medical microbiology.
Work experience: since 1999.
Salatsky Dmitry Nikolaevich
Chief physician, orthopedic dentist, gnathologist, maxillofacial prosthetist.
Work experience: since 1988.
Shirinyan Sarkis Kimovich
Dentist, implant surgeon, orthopedist, therapist
Work experience: since 2000.
Skranzhevskaya Svetlana Vladimirovna
Hygienist, dental assistant
Work experience: since 1994
Seredin Evgeniy Vasilievich
Implant surgeon
Work experience: since 2004
Malanova Olga Andreevna
Dentist, orthodontist, therapist
Work experience: since 2020
Makarov Danila Vladislavovich
Dentist-therapist, endodontist
Work experience: since 2013
Molodtsov Dmitry Evgenievich
Osteopathic dentist
Work experience: since 1998
Artemyeva Oksana Alexandrovna
Orthopedic dentist, therapist
Work experience: since 2001