Treatment of caries in a teenager
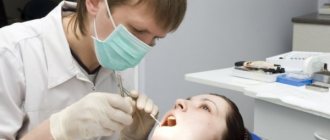
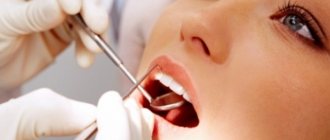
Problem: a 14-year-old girl came to the endodontist of the Dial-Dent clinic with complaints of tooth pain (top left) while eating. During the examination, caries of the chewing tooth on the left upper jaw was discovered, as well as unsatisfactory oral hygiene, which accelerates the development of dental caries.
Solution: taking into account the age of the patient and the degree of tooth destruction, caries was treated under a microscope and direct tooth restoration (light filling) with the composite material Filtek™ P60 was carried out, recommendations were given on dental hygiene for the prevention of caries
When examining the patient, the endodontist revealed unsatisfactory oral hygiene and caries of the chewing tooth (shown by the arrow in the photo).
A lot of plaque has accumulated on the teeth, especially in the gum area and between the teeth. Plaque eats away the enamel of teeth, making it looser and more pliable. Bacteria, which are always contained in saliva, have the ability to penetrate deep into the tooth, where the tooth tissue is softer. If caries is not detected and treated in time, the process can reach the tooth pulp, which will lead to the development of pulpitis with acute pain in the teeth.
The girl was explained the need to treat caries, and also that at the moment the tooth was not very badly damaged and a filling could be used. If the process is started, then when caries spreads, a dental inlay or crown may be required to restore the tooth after treatment. Treatment of advanced caries takes longer and requires greater financial expenditure.
Caries treatment was carried out on the day of visiting the dentist. Before treatment, the teeth were cleaned of plaque. When treating caries, the endodontist used a dental microscope. A dentist armed with a microscope sees the affected area several times better and can thoroughly clean the cavity with maximum preservation of healthy tooth tissue. The small cavity created as a result of caries treatment was closed using a direct restoration - restoration performed directly in the mouth. Such restorations are called fillings. Light-curing composite material Filtek™ P60 was selected for the dental filling. This is a high-strength material that provides excellent adhesion to the walls of the cavity, which guarantees the reliability and durability of the light seal.
Treatment time is 1 hour 15 minutes.
The cost of a light seal is 5,500 rubles.
The dentist told the girl how to brush her teeth in order to remove plaque as much as possible, and recommended toothpastes that would not only help clean her teeth, but also strengthen the enamel and prevent the development of caries. Professional teeth cleaning using the Air Flow method, which can be done by Family Dental hygienists Elena Smirnova or Tatyana Kondratyeva, is an excellent measure for caries prevention. Professional teeth cleanings should be done every six months, as should a visit to the dentist for a check-up. Taking a responsible attitude towards the health of your teeth is very important! Prevention of dental caries saves not only time and money, but also the overall health of the body, because it is known that the presence of carious teeth can provoke the development of other diseases, since teeth affected by caries are a source of infection in the body.
See other examples of dental caries treatment here.
Make an appointment for a consultation by phone +7-499-110-18-04 or through the form on the website. You can ask questions about dental treatment to the chief doctor of the clinic, Sergei Vladimirovich Tsukor, on Facebook.
Teenage features
The period of growing up is marked by the completion of the replacement of baby teeth with molars, permanent ones. Forms a bite that will last a lifetime. And bad habits, such as excessive consumption of sweets, fast food, and smoking, cause health problems:
- unpleasant odor;
- swelling of the gums;
- darkening of the enamel.
A teenager is dependent on the opinions of others, so the aesthetic factor is of great importance. Flaws in appearance can affect success in school, communication with peers, and personal development.
Typical problems of teenagers
Doctors at Family Dentistry often work with children and adolescents and know how to deal with the diseases that most often affect them.
Anomalies of the jaw structure
30% of adolescents have jaw anomalies; they can affect both individual teeth (too large or small teeth, rotations, displacements) and the dentition (chapped teeth, malocclusion). Having noticed a defect, the specialist will refer you to an orthodontist, who will select the optimal treatment and bring the bite back to normal.
Temporomandibular joint diseases
A teenager's skeleton is constantly growing, and muscles and ligaments do not always keep up with the bones. Sometimes the lower jaw begins to stretch the ligaments, causing their tone to be lost, severe tension appears and chronic inflammation of the joint develops. This can lead to the early appearance of deforming arthrosis. Doctors at Family Dentistry offer comprehensive measures - first a conservative option (medicines, diet, physical therapy), and if this does not lead to the desired effect, surgical intervention will be required.
Delay in tooth replacement
Often the molars begin to grow before the milk teeth have made room. In such cases, dentists recommend removing the temporary tooth so that the bite can form correctly.
Caries
There are several causes of teenage caries:
- insufficient treatment in early childhood;
- unbalanced diet;
- poor oral hygiene.
In “Family Dentistry”, an individual approach is applied to each patient - they not only heal the affected areas, but also carry out special preventive measures and give advice to parents and teenagers themselves on caring for their teeth and oral cavity.
Plaque on teeth
The composition of saliva changes during adolescence. Eating habits also change - a young person begins to drink tea and coffee more often. Sometimes bad habits appear - smoking, alcohol. All this leads to the deposition of plaque, which causes caries. Dental plaque can only be removed in a clinic, using special dental products.
Juvenile gingivitis
When hormones “rage”, an inflammatory process of gum tissue can develop, accompanied by an increase in tissue volume. Most often, adolescents experience gingivitis of the front teeth. If the disease is not treated, periodontitis will develop.
Prevention of caries in children and adolescents
It is a well-known fact: it is better to prevent any disease than to try to get rid of it later. This is especially true for the prevention of caries in children. And it should begin even before the baby is born.
Endogenous prevention of caries
Endogenous caries prevention is a set of measures whose goal is to strengthen dental tissue by affecting the body from the inside. At the same time, it can be conditionally divided into two periods in a woman’s life – before the birth of a child and after the birth of the baby.
Prenatal preventive measures
Research (Palmer, 2000) found that there are four factors that increase the risk of future dental caries in children: stress during pregnancy, a lack of dairy products in the expectant mother's diet, the presence of serious diseases and the use of antibacterial drugs. It is precisely to eliminate these factors that an extensive set of measures is aimed, which is carried out until the birth of the child. It consists of several stages.
- Complete examination before planned pregnancy
. A woman must be fully examined and eliminate all identified foci of infection, both chronic and acute. In addition, if pathologies of the cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous or digestive systems are detected, it is necessary to carry out appropriate treatment, and if it is impossible to completely get rid of the disease, remove the acute period and stabilize the condition. - Adequate rest, no stress
. During pregnancy, it is important to try to avoid stressful situations and experience more positive emotions. Walking in the fresh air, daytime rest and good sleep are the main recommendations of doctors. - Balanced nutrition during pregnancy
. In order to provide the mother and baby with the necessary nutrients, the need for which almost doubles, food must be rich in vitamins and minerals, and also have a balanced composition of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. This means that you should not overuse some products and neglect others. Moreover, proteins and fats must be of both plant and animal origin. - Taking vitamin-mineral complexes
. No vitamin diet can fully provide the expectant mother’s body with the necessary vitamins and minerals. Therefore, the doctor must prescribe special vitamin preparations designed for pregnant women, taking into account their daily need for nutrients. - Regular visits to the gynecologist and timely testing
. This will allow you to take timely measures if even the slightest deviations appear in the normal course of pregnancy.
Preventive measures to prevent the development of caries for a child
Prevention of caries in children should begin from the first days of life. It includes several areas.
- Breast-feeding
. Now all doctors, without exception, recommend that mothers breastfeed their children. Dry artificial formula is the most extreme case when a woman has no or very little milk, since it contains all the substances the baby needs in the optimal volume. And research (Erickson, 1999) has proven that breast milk does not affect the acid-base balance in the mouth and even remineralizes tooth enamel. While most dry milk formulas, on the contrary, make the environment in the oral cavity acidic, due to which opportunistic microorganisms - streptococci - begin to actively multiply there. But they are the ones who are blamed for the destruction of tooth enamel. In addition, breast milk contains immunoglobulins IgA and IgG, which inhibit the proliferation of streptococci, and lactoferrin, which is a natural antibiotic. It has a detrimental effect on pathogenic microflora. - Complete nutrition
. The child is growing. Breastfeeding, first complementary foods - everything is long gone. The timely start of consuming food other than breast milk and artificial formulas not only plays a major role in the prevention of caries, but also contributes to the normal development of the dental system. However, the child’s diet must meet his age needs, be balanced, rich in vitamins and minerals, especially calcium, vitamins D and C. These substances strengthen tooth enamel and also increase the child’s immunity. Ascorbic acid is found in many berries, fruits and vegetables, and vitamin D is found in fish, liver and chicken eggs. In addition, children should eat fresh vegetables, fruits more often for other reasons. This will promote self-cleaning of the teeth, massage the gums and evenly distribute the load on the periodontium. You should exclude from your diet foods that stay in your mouth for a long time or tend to stick to your teeth, such as candies or some dried fruits. - Taking vitamin-mineral complexes
. A child’s body needs significantly more nutrients than is contained in foods. Especially in winter and spring, when many vegetables and fruits are used up, and those brought from abroad are of dubious benefit. In this case, the doctor may prescribe vitamin and mineral complexes to maintain dental health. Manufacturers produce drugs for children and adolescents. This division by age allows you to select the optimal composition in accordance with the individual needs of a growing organism. - Prevention of colds
. Dry mouth is also a cause of tooth decay. Most often, this situation occurs with nasal congestion. Therefore, daily cleaning of the nasal passages is necessary, and in case of illness, the use of drugs that facilitate nasal breathing. Naturally, only a doctor can prescribe them.
How do plates and braces help get rid of malocclusion?
The plate is created from plastic. Accordingly, it cannot significantly affect a teenager’s bite. It cannot be used if the teenager has serious problems with teeth (crookedness).
Plates are recommended to be used only if the teenager does not have any special problems with his teeth. And if he has minor ailments associated with malocclusion. That is, they are at the first, safest stage.
Also, plates can be prescribed for those teenagers who have had braces on for a certain amount of time. The teeth were cured. And now they want to consolidate the result. Make sure your teeth remain straight. And they did not return to the original position that was before treatment.
Plate installation rules
The plate can be installed in the following cases:
- A teenager's teeth are straight. However, there is a chance that over time they will begin to shift.
- The teeth gradually shift. However, this process began only recently. And it didn't cause any noticeable damage.
- A teenager has problems with the palate. And its width.
The plates are recommended for use if only minor anomalies are detected in a teenager. Which are associated with the jaw and teeth. Braces are recommended for use in the presence of larger bite problems. They are constantly in the teenager's mouth. Due to this, they put pressure on the teeth. And they bend them to the dimensions that the doctor needs to treat the curvature.
Prevention of caries of primary teeth in young children
You should take care of your baby’s dental health from a very early age, namely from the 5th week of your pregnancy. A method of antenatal prevention has been developed especially for expectant mothers and the following are recommended:
- a complete diet for a pregnant woman, including foods high in calcium and phosphorus - milk, cottage cheese, fish and seafood;
- taking vitamin preparations as prescribed by a doctor;
- sanitation of the oral cavity in the second trimester of pregnancy, timely elimination of foci of carious infection.
Prevention of caries in preschool children
From the age of 3, young patients are given caries prevention on an outpatient basis.
To avoid an allergic reaction, the child’s gums are treated with Vaseline oil.
If chalky spots are already visible on the surface of the enamel (stage I of caries), which indicates a lack of calcium and fluoride ions, the dentist will recommend remineralization - for example, applications with Diplen-Denta F film. The composition of the medicine that the doctor sticks to the surface of the teeth:
- chlorhexidine, which has bactericidal properties;
- sodium fluoride, which strengthens tooth enamel.
The course of treatment consists of 8-10 applications applied at one-day intervals. To consolidate the results of therapy, the procedure is repeated after 1-1.5 months.
Methods for preventing childhood caries
Dentists pay special attention to methods of endogenous and exogenous prevention, the use of which is already relevant in preschool age.
Endogenous prevention of caries - what is it?
Endogenous measures are “directed inside” the body, their task is to compensate for the lack of microelements and enhance the mineralizing properties of saliva, which nourishes the hard tissues of the teeth and protects them from pathogenic microflora. As a preventive measure using this method, the pediatric dentist will recommend:
- take vitamin supplements for children (Multi tabs Baby calcium, VitaMishka calcium plus);
- limit food intake containing carbohydrates and polysaccharides - cariogenic bacteria “love” sweets and starchy foods;
- include hard fruits in your child’s daily diet: they remove food debris from the interdental spaces and increase salivation.
In some cases, medications containing phosphorus and fluorine and vitamin D are prescribed.
Exogenous prevention of caries in children
Exogenous prevention measures involve protecting baby teeth from external unfavorable factors - soft microbial plaque and the enamel-damaging effects of certain foods. This:
- daily oral hygiene using children's toothpastes, flosses and rinses (Den Tek, Cura Prox, Silca, Oral-B);
- choosing the right toothbrush - 1) medium hardness; 2) X-shaped arrangement of cleaning beams of different lengths; 3) timely replacement - once every 3 months;
- coating of teeth with fluoride-containing products.
Fluoridation of teeth and the use of toothpastes with optimal fluoride content strengthens tooth enamel by creating fluorapatite, a solid compound that fluoride ions form with hard tooth tissues.
Basic Rules
In order for teenagers to always have healthy teeth, they need:
- To drink a lot of water.
- Follow a healthy diet with a predominance of vegetables and fruits (carbonated drinks and sweets should be consumed as rarely as possible).
- If possible, limit the number of snacks between meals (especially for foods high in sugar).
- Use dental floss at least once a day.
- Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste (ideally, you should work with your dentist to choose the most appropriate toothpaste).
- Brush your teeth regularly and get periodic check-ups with your dentist.
- Select toothpaste and dental floss according to age (that is, they should no longer be children’s).
- Do not use your teeth to open any packages or crush ice. In addition, it is strictly not recommended to try to remove food debris from the interdental spaces using a knife or fork.
ROCS offers a line of products for teenagers
Prevention of caries in school-age children and adolescents
Ages over 8 years and puberty in children are characterized by extensive hormonal changes in the body: the mineralizing properties of saliva weaken, and the dentin in the already emerging permanent teeth softens. Therefore, dentists strongly recommend that school-age children undergo a primary caries prevention procedure, which allows them to preserve the integrity of their first chewing teeth.
Primary prevention of caries in adolescents
Primary prevention is aimed at protecting and strengthening the enamel of healthy teeth not damaged by caries. For this purpose, school-age children and adolescents undergo fissure sealing.
Dental sealants
The 6th and 7th teeth, which are the first permanent teeth to erupt and form the bite, are “sealed” with a composite or glass ionomer sealant. Sealants (dental sealants) are composites that contain fluoride and have a more fluid texture than a conventional filling. Once on the surface of the tooth, they spread and fill the fissure.
To control the safety of the coating, special colored sealants are used in pediatric dentistry.
The procedure is carried out by a dentist-therapist, takes no more than 10-30 minutes and includes the following steps:
- Cleaning teeth with a special abrasive paste.
- Apply a few drops of phosphoric acid and rinse with water.
- “Sealing” the fissure with sealant and “exposure” with a halogen lamp.
- Removal of composite residues by preparation (drilling).
Fissure sealing step by step:
Fissure sealing allows you to protect chewing teeth from caries for a period of 2 to 8 years. If carious lesions are observed not only on the enamel, but also on the dentin of the tooth, preparation, installation of fillings and secondary prevention of caries are carried out.
Secondary prevention of caries
Secondary prevention involves identifying the disease at an early stage, eliminating the source of infection and protecting the teeth located next to the patient from caries.
Since the age of 8-11 years is a period of active development of the skeletal system of the body, in addition to infiltration and preparation of carious cavities, the doctor may prescribe medications. For example, tableted fluorine or sodium fluoride, calcium lactate, Phytin or Vitaftor.
Fissure sealing, silver plating and fluoridation are absolutely painless procedures, so this is where your child’s visit to the dentist should begin. And if you provide brushing your teeth and rinsing your mouth after meals in the form of a fun game or competition (“Who’s first?”, “Who has whiter teeth?”), then caries simply won’t have a chance.
Baby and permanent teeth in a child. Peculiarities
The enamel of milk and young (immature) permanent teeth in children is thin and highly permeable to inorganic and organic substances. Enamel permeability increases sharply in the earliest stages of caries. The dentin layer is quite thin (especially in the area of the horns of the pulp cavity) and is penetrated by dentinal tubules of increased diameter.
Milk and immature permanent teeth in children have a large pulp chamber (cavity), and the horns of the pulp chamber are significantly recessed into the dentin. There are 2 periods in the development of the pulp of a baby tooth: the period of formation and reverse development (when the resorption of the roots of a baby tooth begins).
The roots of baby teeth are fully formed by the age of 3, and then begin to gradually dissolve (resorption). The roots of pulpless primary teeth are reabsorbed more slowly than healthy ones, and this can affect the eruption of permanent teeth. The roots of baby teeth have relatively wide apical openings, so the inflammatory process in the pulp (pulpitis) can quickly develop into the periodontium (periodontitis).
The roots of young (immature) teeth are short, the root canal is wide. The final formation of the roots of permanent teeth occurs at the age of 10-15 years.
The hard tissues of primary teeth are less mineralized than the hard tissues of permanent teeth.
The structural features of primary and permanent teeth in children must be taken into account when treating caries in children.
Is it possible to stop childhood caries?
Every year, caries appears earlier in children. You should not hesitate to treat baby teeth (especially the first front ones), naively believing that they will eventually be replaced by permanent ones and the problem will go away on its own. It is necessary to consult with a pediatric dentist on how to stop caries, since timely treatment of teeth in childhood determines their condition in adulthood.
It will not be possible to stop caries of baby teeth in an advanced state (when the infectious process spreads from purulent roots to soft tissues). The only correct option would be to remove the baby carious tooth prematurely. This procedure at an early age can traumatize the child’s delicate psyche and cause fear associated with the dentist and the dental office, which will last a lifetime.
Caries of permanent (immature) teeth in children has features
Caries of immature (young) permanent teeth in children has, in comparison with dental caries in adults, a number of features. Features are associated mainly with the stage of formation of permanent teeth, insufficient mineralization of hard tissues, and reduced protective function of the pulp (during the formation of the roots of a permanent tooth). Therefore, in children with young (immature) permanent teeth, acute caries of permanent teeth predominates. The intensity of caries is higher, the earlier the erupted permanent tooth is affected by caries. In children, if left untreated, permanent tooth loss can occur within 6 months.
In the period of formed permanent teeth (with a stabilized structure of dentin and enamel, functional maturity of the pulp - the ability to produce replacement dentin), children predominantly experience a chronic type of caries of permanent teeth.
The large size of the pulp chamber in young (immature) teeth is the reason that the dental pulp is under increased threat of inflammation (since, on average, a young permanent tooth of a child has less hard tissue and the carious process easily reaches the pulp chamber).
Causes of childhood caries
As always, there are a lot of causes for diseases of this kind, but they are all quite typical.
- Insufficiently thorough oral hygiene. With the appearance of the first milk teeth, you need to give them due attention - clean them with soft gauze moistened with water. As soon as the baby can brush his teeth and rinse his mouth on his own (at 2-3 years), you can purchase a special children's toothbrush with soft bristles and toothpaste (always with a natural composition without fluoride). Parents should supervise the process so that the child does not swallow the toothpaste, and finally rinse the mouth very thoroughly to remove any remaining toothpaste.
- Long-term use of bottles with pacifiers when feeding . As soon as the child is able to chew food on his own, the bottle should be abandoned immediately, as the so-called “bottle caries” of the front teeth may develop.
- Infection from parents. This is possible in cases where parents who have caries:
- chew food and give it to the child;
- share a spoon or fork, taking turns eating, and then feed the child with the same utensil;
- moisten the pacifier with their own saliva when the pacifier has fallen to the floor.
- Heredity and congenital tendency to caries. This is possible due to a genetic predisposition to the disease, as well as due to the bad habits of the mother during pregnancy. The condition and health of teeth during pregnancy is reflected in the condition of the teeth in the developing fetus. Therefore, it is important to begin caries prevention while planning pregnancy.
- Unbalanced diet, lack of important vitamins and microelements. Excessive consumption of sweets and foods high in carbohydrates contributes to the spread and proliferation of bacteria that damage tooth enamel.
- Insufficient amounts of calcium and fluoride in the diet can cause tooth enamel to soften. Calcium is the main strengthening and protecting “building” material of tooth enamel, preventing the development of caries.
- Regular consumption of foods that “stick” to the teeth, such as potato chips, chocolate, crackers, peanuts, bananas, contributes to the spread and aggravation of the problem of caries in baby teeth.
- Insufficient amount of food that requires careful and intensive chewing, during which salivation increases and the teeth are cleaned naturally - with saliva.
To understand how to stop and prevent caries in a child, it is necessary to pay due attention to oral hygiene from the earliest period of his life and eliminate the causes that contribute to the development of this problem.
What teeth appear first in children?
The rudiments of baby teeth and even some molars begin to form at the stage of intrauterine development, so modern diagnostic technologies make it possible to track this process and prevent some deviations. After birth, the first teeth usually begin to erupt when the baby reaches six months of age. This means he will soon be ready to eat more solid foods. In the vast majority of cases, the incisors appear first: as a rule, the lower central incisor becomes the “pioneer”.
Symptoms
The main symptom of caries is increased sensitivity of the diseased tooth to hot and cold drinks, sour and sweet foods, discomfort due to food residues between the dental lumens.
When viruses and bacteria get on the enamel, caries pathogens begin to corrode it. As a result, a depression forms in the tooth, and the enamel begins to crumble and fall apart. Bacteria get inside - into the pulp, pain and sensitivity increase.
In advanced cases, the infection spreads further and can affect other systems of the fragile small body.
Possible purulent complications such as:
To avoid complications in baby teeth, it is important to promptly seek help from a dentist and begin treatment at the first signs of caries.
Causes of pulpitis of permanent teeth in children and adolescents under 16 years of age in mixed dentition
The tooth is nourished through a neurovascular bundle called the pulp. Its inflammation is called pulpitis.
- Typically, pulpitis develops as a complication of untreated caries, when the carious process “goes” deep into the tooth tissue, destroys the pulp chamber and bacteria infect the pulp. Such a diagnosis requires serious intracanal (endodontic) treatment.
- In adolescence, children have a habit of not telling their parents that something is bothering them, so very often they do not receive timely treatment. As a result, patients often come to the appointment already with severe pain, complications and deterioration of their general condition (fever, headache, weakness)
- Read more about other non-carious causes of pulpitis, its main forms, symptoms and possible treatment methods in Treatment of pulpitis (dental canals/endodontic treatment).
Treatment of caries in children
Let us repeat once again that when caries appears in children, it is important to promptly contact a pediatric dentist, who will tell you how to stop dental caries and prevent it from spreading to healthy areas.
Treatment of caries in a medical facility
You can treat baby teeth from caries in the dentist’s office using the following procedures:
- Remineralization (restoration) of damaged enamel and dentin;
- Fluoridation of deep layers of damaged dentin and enamel;
- Drilling a carious cavity using a drill;
- Drilling with further filling of dental cavities cleared of caries.
How is the treatment of caries of permanent teeth in children and adolescents under 16 years old at the GALA DENT clinic?
Treatment of caries of permanent teeth in children should be carried out with maximum consideration of the psychological factor and must be done by a CHILDREN'S dentist with full local anesthesia and, if necessary, sedation. Read more about anesthesia for children.
We select the anesthetic drug and its dose individually for each young patient and use the latest generation of anesthetics that are safe for children.
Dental treatment under general anesthesia is not advisable, because it affects the child’s entire body and is justifiably used only in the most extreme cases, although to parents the “put to sleep and cure” option sometimes seems to be the best way out.
Uncomplicated caries of permanent teeth in children is treated in the same way as in adults. First, anesthesia is performed, then the tooth is thoroughly cleaned of damaged tissue and filled. For permanent teeth in children, we use high-quality photopolymer (light-hardening) filling materials, the same as for adults, with precise color matching to the natural color of the enamel.
Also, do not forget about the restoration of the chewing surface of the tooth - for adolescents this is a very important stage of treatment, because the correct formation of the entire dental system, which is in a period of active growth, depends on the quality of interdental contacts.
The total duration of treatment for one visit to the dentist in adolescence should be no more than 40-50 minutes.