Each of us has had to take antibiotics. And many, during or at the end of treatment with these drugs, began to feel a bitter taste in their mouths. By the way, almost every instruction for this type of medicine warns about the possibility of such a side effect. Why does such a problem arise? What to do when bitterness appears in your mouth and what can you drink to avoid it? We will try to answer all these questions later in the article.
About antibiotics
Antibiotics in medicine are comparable to “heavy artillery”, since, despite their obvious effectiveness, they can have a lot of contraindications and side effects.
Doctors, not without reason, consider antibacterial agents to be one of the most effective medicines, because they can suppress the growth of pathogenic microorganisms and thus ensure the patient’s recovery. But uncontrolled use of these drugs or an incorrect dosage prescribed by a doctor can lead to serious health problems, which, by the way, will manifest themselves not only as bitterness in the mouth. After antibiotics, the growth of both pathogenic and beneficial microflora in the human body is suppressed, ultimately leading to dysbiosis; There is a disruption of the biliary tract and a strong decrease in immunity.
Possible causes of bitterness in the mouth
The reasons that cause bitterness in the mouth can be different. And most often they are associated with dysfunction of the liver or gallbladder. Thus, bitterness in the morning after eating can be caused by acid reflux, gastritis, cholelithiasis or dysfunction of the biliary tract. Often the named symptom appears with various lesions of the duodenum (inflammation, ulceration, the appearance of tumors).
It should be noted that all of the listed diseases, as a rule, the patient already has (to one degree or another) even before treatment with antibacterial drugs, and taking these drugs only provokes their exacerbation and causes various manifestations of the pathological condition, including bitterness in the mouth after antibiotics.
Medicine Klacid for gastritis of the stomach
Klacid is an antibiotic developed by a German pharmaceutical company. The medication contains clarithromycin, which has a bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect and disrupts intracellular protein synthesis.
Antibiotic Klacid is available in tablets, granules and powder for suspension. Soluble forms are used in childhood and are characterized by rapid action. The selection of cheaper analogues for children and adults should be carried out by a doctor, according to the results of an analysis of bacterial resistance.
The medicine is used in complex therapy for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori, which causes gastritis and stomach ulcers. Used in conjunction with De-Nol and proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole, Pantoprazole, Esomeprozole).
The medicine is used in complex therapy for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori, which causes gastritis and stomach ulcers.
Medicine and analogues based on Clarithromycin are used as prescribed by a doctor. Drink twice a day, every 12 hours. If you miss a dose, do not double the dosage.
The course of treatment depends on the disease and averages 5–7 days. The exact dosage is selected based on the patient’s personal data (child or adult, weight, old age), and the presence of a history of other diseases (liver and kidney failure). Prescription restrictions include pregnancy and breastfeeding, severe cardiac dysfunction, and liver failure.
The medicine Klacid, according to the instructions, can be taken regardless of meals. After use, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, intestinal disorders (constipation, diarrhea, flatulence), and allergic reactions may occur. To prevent unwanted effects, it is recommended to drink the antibiotic after meals with a sufficient amount of plain water.
Taking a drug to eradicate Helicobacter pylori:
- combination treatment with three drugs: clarithromycin 500 mg 2 times a day lansoprazole 30 mg 2 times a day amoxicillin 1000 mg 2 times a day for 10 days; clarithromycin 500 mg 2 times a day omeprazole 20 mg per day amoxicillin 1000 mg 2 times a day for 7-10 days;
- combination treatment with two drugs: clarithromycin 500 mg 3 times a day omeprazole 40 mg per day for 14 days with the appointment of omeprazole at a dose of 20-40 mg per day over the next 14 days; clarithromycin 500 mg 3 times a day lansoprazole 60 mg per day for 14 days. For complete healing of the ulcer, additional reduction in the acidity of gastric juice may be required.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with a seal that has appeared in the sky
The safety of clarithromycin during pregnancy and lactation has not been studied. Clarithromycin is known to be excreted in breast milk. Therefore, Klacid should be used during pregnancy and lactation only in cases where there is no safer alternative, and the risk associated with the disease itself outweighs the possible harm to the mother and fetus.
Why taking antibiotics leads to bitterness
as already mentioned, the drugs described are potent drugs, and their metabolism (conversion) occurs mainly in the liver. Therefore, it is not surprising that this organ is the first to be targeted by their main active substances. And if the liver has already been affected by some kind of illness, then the patient will definitely develop a bitter taste in the mouth from antibiotics.
The fact is that tissue damage in the liver disrupts its detoxification capabilities, and the antibiotic is precisely perceived by it as a source of toxic substances, which as a result provokes an exacerbation of all existing problems.
In addition to bitterness, the patient may develop jaundice, fever, urine becomes dark, and feces, on the contrary, become discolored. Violation of the accumulation of glycogen (a kind of glucose conserved in the body that feeds muscles) causes weakness and apathy.
Therefore, if you already have any problems, be sure to check with your doctor to see how much the antibiotic can affect liver function. Drugs such as Levofloxacin or Moxifloxacin are considered especially dangerous in this regard.
Klacid description of the drug
The drug Klacid is a semi-synthetic antibiotic belonging to the group of macrolide antibiotics. The main active ingredient of the drug is clarithromycin, which has an antibacterial and bacteriostatic effect, which occurs through interaction with the ribosomal units of microbial cells and inhibition of protein synthesis.
Pharmaceutical companies produce this medicine in the form of tablets, in which the active ingredient is clarithromycin (dosage - 250 and 500 mg). In addition, solutions for intravenous administration are produced under this name.
The drug Klacid is a semi-synthetic antibiotic belonging to the group of macrolide antibiotics
For adults, the maximum daily dose of the drug is no more than 2 g. The children's dose per day is 2 times less. For people suffering from diseases associated with impaired liver and kidney function, the permissible dose is reduced by 2 times. A single dose for patients over 12 years of age ranges from 0.25 to 1 mg.
Clarithromycin quickly penetrates into the intercellular space and tissues of the body, where 3-4 hours after its use it reaches its maximum concentration. In the digestive system, it is quickly adsorbed even in the presence of large amounts of food. The drug is eliminated through the kidneys. It is excreted in the urine unchanged or after transformation into a metabolite. The drug has a wide range of effects on microorganisms.
The drug “Klacid SR” is produced separately, presented as coated tablets with prolonged action. They are characterized by their oval shape and yellow color. Such tablets are sold in packs of 5 to 56 pieces.
Klacid" is produced in three different versions:
- powder for suspension: it is placed in a 60 or 100 ml bottle with a line mark and is presented as almost white granules with a fruity smell. When mixed with water, it forms a white, opaque liquid that smells like fruit. This form is produced in two different dosages, allowing the medication to be used for children of different ages. A plastic spoon or syringe with divisions is attached to the bottle to accurately measure the required amount of sweet medicine;
- tablets: they have a yellow shell and an oval shape convex on both sides. Such tablets are also produced in two dosages and are packaged in blisters of 7, 10 or 14 pieces. One pack contains from 7 to 42 tablets;
- lyophilisate for injections: it is presented as a white powder with a slight specific odor. This product is placed in hermetically sealed glass bottles, which are sold in 1 piece or in a pack of 121 pieces.
The medicine Klacid is an antibiotic for adults with an active substance content of 250 and 500 mg, for children. It is an original, patented form.
Klacid for children
Klacid for children can be used from the age of three. In most cases, children are prescribed Klacid suspension. Reviews for children indicate that this drug is quite effective. At the same time, the price of the suspension is quite high. The dosage for children is as follows: 7.5 mg per 1 kg of child’s weight twice a day. The highest daily dose is 500 mg.
Children over 12 years of age are prescribed 250 mg (tablets) twice a day. There is evidence that children tolerate Klacid more easily than other antibiotics. Therefore, the drug is often prescribed for bronchitis, pneumonia, etc. However, we should not forget that side effects still occur.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Clasp prosthesis for the upper and lower jaws
Bitterness in the mouth after antibiotics: what to do?
Regardless of how antibiotics can affect the liver, taking them in some situations turns out to be vital, which is why doctors decide to prescribe these drugs. Although because of this, the symptoms listed above, including bitterness in the mouth from antibiotics, can, alas, become your companions for some time. What to do?
As a rule, during the course of treatment with these medications, the patient is advised to follow a gentle diet, as well as take hepatoprotectors - medications that help the liver in the process of combating intoxication caused by antibacterial drugs and increasing its cellular potential.
How to take antibiotics correctly
In order to reduce the risk of side effects and not feel bitterness in the mouth after antibiotics, you must follow the mandatory rules for taking these medications.
- To maintain a constant level of the drug in the body, you should take the drugs strictly at the prescribed time.
- Take the tablets only with non-carbonated drinking water or weak tea.
- After finishing the course of antibiotics, after consulting with your doctor, you can take probiotics that restore dead microflora in the gastrointestinal tract or drink yoghurt.
- Follow an appropriate diet (do not eat spicy, fatty or fried foods).
- Avoid alcohol.
- You should not take antibiotics during meals (only an hour before or an hour after).
- Never prescribe antibiotics yourself!
Recipes for decoctions against bitterness
A decoction of berries should be prepared as follows: add a tablespoon of berries (optional) to 200 ml of boiling water. Infuse for ten minutes and take several sips throughout the day. Hawthorn, viburnum, lingonberry and rose hips are suitable for relieving discomfort.
A tincture can be made from calendula and burnet root. Pour the root of the latter (2 tbsp) with a liter of water and cook for about one hour. Sip the cooled broth throughout the day.
To get a calendula tincture, you need to take a small handful of dried flowers (about 10 g) and pour a glass of boiling water. Then infuse, strain and drink a few sips before meals.
How to understand what caused bitterness
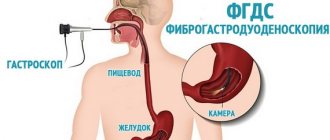
If you still have a strong bitter taste in your mouth after taking antibiotics, you should immediately inform your doctor about it. He will refer you to a gastroenterologist to clarify the causes of the unpleasant symptom. A specialist will help with this by performing a gastroscopy (removal of inflamed stomach tissue using a probe). Thanks to this diagnostic procedure, the doctor will be able to detect existing inflammation or tissue modification.
Often, less informative methods are used to make a diagnosis - ultrasound or x-ray of the stomach - which, nevertheless, can also help identify existing pathological processes. In such cases, blood sampling for clinical and biochemical analysis will also provide important information.
Only as a result of the listed studies can one reliably establish how serious the causes of bitterness are, and whether only stopping the medication taken will be sufficient to get rid of it.
How to get rid of bitterness in your mouth
Treatment of bitterness in the mouth, unfortunately, may not be possible without eliminating the disease that caused this symptom, but most often a small therapeutic effect is sufficient. It is carried out under the supervision of a doctor, and he also adjusts the stages of this treatment to make it more effective.
To do this, the patient is first helped to cleanse the intestines of pathogenic flora. For these purposes, medicinal herbs that have an antibacterial effect are prescribed (these include anise, blackberry, calamus, etc.). In addition to them, it is also suggested to take adsorbent agents (activated carbon, the drug “Almagel”, etc.). Then comes the turn of procedures that normalize the functioning of the intestines, for which, as a rule, vegetable bitters are used (calamus, yellow gentian, etc.).
And the last stage, which helps to completely solve the question of “how to get rid of bitterness in the mouth,” usually becomes the “population” of the intestines with beneficial microflora. For this purpose, lactobacilli and bifidobacteria are used in medicine, creating optimal conditions for normal intestinal function. They are found in preparations called probiotics.
Prevention measures
To prevent the appearance of bitter taste sensations when using antibiotics, a number of rules should be followed:
- taking the medication at the same time, 1 hour before or after meals (antibacterial tablets cannot be combined with food);
- strict adherence to prescribed dosages;
- treatment only under the supervision of a physician;
- drinking the drug with a sufficient amount of water (at least half a glass);
- regular and nutritious nutrition during antibiotic therapy to avoid excessive stress on the digestive organs and liver;
- abstinence from alcohol throughout treatment.
Experts recommend combining antibiotic therapy with the use of probiotics. Moreover, after treatment, these maintenance medications must be used for prophylaxis for at least 1 month. Compliance with these rules will allow you to undergo a course of antibiotic therapy without any discomfort and with the greatest effect from treatment.
Clarithromycin is a medicinal drug belonging to the group of macrolides . This is the name for the latest generation of semi-synthetic antibiotics.
Their effectiveness in the fight against microbes and pathogenic flora is explained by the fact that the drugs penetrate directly into the tissue cell so that, once inside, they stop the development and multiplication of the infection.
Once again about how to avoid bitterness in the mouth
From all of the above we can draw clear conclusions:
- Most often, in order to get rid of the risk of bitterness in the mouth during antibiotic treatment, it is enough to strictly adhere to the doctor’s prescriptions and recommendations and follow a special diet.
- And if bitterness and other side effects still begin to bother you, then the doctor in such cases reconsiders the prescription, refusing the drugs that cause the said reaction, or replacing them with suitable analogues.
- Those who have felt the negative effects of the drug can come to the aid of taking hepatoprotectors that support liver function and probiotics that restore microflora.
In cases where the bitterness in the mouth after antibiotics does not go away even after finishing the course of taking the drugs, you should urgently undergo an examination to identify the diseases that caused the described symptom. And you can’t delay this, as the problems that arise can turn out to be very serious!