NSAID injections for back and lower back pain
Injections of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed more often than other drugs. This is because they quickly affect the source of inflammation, relieving unbearable pain and stiffness. In addition, injections reduce temperature and eliminate swelling.
Indications for use include pain of a shooting, pulling, constant or wave-like nature. NSAIDs are prescribed for radiculopathy, intercostal neuralgia, osteochondrosis, trauma, and intervertebral hernia. Let's consider what injections are advisable to give for back and lower back pain.
No. 1. Diclofenac
A kind of “gold standard” among drugs with anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity. Relieves pain of any etiology (from inflammation, neuralgic, etc.). Just 1 injection eliminates discomfort caused by excessive contraction of muscle tissue and overexertion. For inflammatory-degenerative diseases affecting the spine, injections are given daily in a 5-day course.
No. 2. Ketonal
Injections of ketoprofen (the active substance) give rapid positive dynamics for back and lower back pain, and are also included in the rating of the best medications in the NSAID group. "Ketonal" has a powerful analgesic effect and the ability to suppress the inflammatory process. 3 minutes after administration, any discomfort caused by neuralgia, injuries, radiculopathy, etc. goes away. The dosage is calculated with an emphasis on the intensity of the pain syndrome. Injections are given 1-3 times a day for a course of 5 days.
No. 3. Meloxicam
NSAIDs based on movalis are included in the list of new generation drugs, which means they have a minimum of side effects and contraindications. It is well tolerated and has a prolonged effect. Relieves fever, inflammation, unbearable pain in the back. It is especially often prescribed after surgery, for spondylitis, arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, osteochondrosis, etc. The duration of the course should not exceed 3 days, provided the drug is administered once a day.
Classification of antibiotic drugs
To be effective, an antibiotic must have three important properties:
- Destroy and suppress further growth of bacteria.
- Remain low toxic to humans.
- Be resistant to living biological environment.
Today, 2 thousand different antibiotics are known, only 50 of them meet the necessary requirements and are included in medications. There are highly specific substances, and there are broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Penicillin antibiotics
Natural penicillins have a narrow spectrum of action. They are destroyed by the acidic environment of gastric juice and have a short duration of action of the active substance. They are rarely used for sore throats.
Synthetic antibiotics are protected from the enzymatic activity of a living organism and have a wider spectrum of action.
The most effective:
- Ampicillin.
- Ticarcillin.
- Amoxicillin.
The combined drug Ampiox is prescribed if tests reveal the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
If a patient has an allergic reaction to penicillins, then the doctor prescribes cephalosporins. There are only 5 generations of them. 1st generation drugs treat the throat from diseases caused by streptococci and staphylococci. This is Cephalexin, Cephalotin. The action of 2nd generation drugs is directed against rod-shaped and coccoid bacteria, which most often affect the upper respiratory tract of humans (Cefuroxime, Cefaclor).
Antibiotics of the 3rd and 4th generation work against enterobacteria and Pseudomonas aeruginosa and can be used outside the hospital. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Ceftriaxone and Cefotaxime. The 5th generation drug Ceftobiprol destroys Staphylococcus aureus, pyogenic microorganisms that cause pain, inflammation, suppuration in the tissues of the oral cavity and pharynx.
Flemoxin Solutab, a new generation cephalosporin that is resistant to the biological environment and has a wide range of beneficial properties, is often prescribed for children. Therapy up to the age of 12 years is permissible and is carried out in smaller dosages, based on the child’s body weight.
If you do not follow your doctor's recommendations regarding the dose and time of taking an antibiotic, the pathogenic bacteria will evolve, developing resistance to the drug.
Contraindications for taking penicillin antibiotics are typical for the group - childhood, renal and liver failure, pregnancy and lactation, individual intolerance. Caution should be exercised, as many of them are toxic, cause dysbacteriosis, and have side effects.
Macrolide antibiotics
Macrolide class drugs have a complex chemical composition; they are able to suppress the proliferation of a wide range of microbes. Drugs of this group penetrate into human cells, which is why they are used to treat intracellular infections. Macrolides are available in the form of tablets or capsules, which is convenient for their use according to the regimen recommended by the doctor. For children, syrups or suspensions and powders are often provided for self-preparing medicine.
The most popular drugs from the macrolide group:
- Erythromycin. It is used in the treatment of bacterial infections of the ENT organs (laryngitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, external and otitis media). The period of action is 4-6 hours, taken orally 1-1.5 hours before meals, or 2-3 hours after. The permissible daily dose for adults should not exceed 4 g. The drug is used to treat children from birth - 20-50 mg per 1 kg of weight, depending on the age of the child. The duration of therapy is 5-14 days, and can be adjusted by the doctor personally for each patient.
- Azithromycin. Erythromycin derivative. Indications for use are bacterial lesions of the ENT organs. The drug is resistant to acids, has a minimal number of side effects, and can be used to treat children from birth. The medicine has a long duration of action, which is an advantage in the treatment of severe pathologies when relapses occur. The release form is varied - tablets, capsules, suspension, powder for preparing a solution for oral administration.
- Sumamed. Prescribed for children and adults for the treatment of sore throat, pharyngitis, and their complications. Sold in powder form, which is used to prepare a suspension. In finished form, the medicine is stored for a limited time. The dosage is calculated based on weight - up to 3 years, 10 mg per kg is used. If the child’s weight is from 18 to 30 kg, then it is necessary to take 125 mg 2 times a day. Children over 30 kg use 125 mg 3 times a day. The maximum dose should not exceed 375 mg.
- Macropen. The drug is intended for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract, whooping cough. The medicine is used before meals. Doses depend on age and weight. Adults are usually prescribed 1 tablet 3 times a day, children - from 20 to 40 mg per 1 kg of body weight, depending on the symptoms and severity of the disease. Treatment of pregnant women is permissible if prescribed by a doctor. During treatment, breastfeeding is stopped for a while.
Doctors recognize macrolides as the safest antibacterial agents. They are prescribed if the patient has an allergic reaction to a penicillin antibiotic.
Antibiotics of the lincosamide group
This class of drugs is based on the natural antibiotic Lincomycin. The medicine of the same name has a bacteriostatic effect, that is, it stops the proliferation of bacteria. It is prescribed for sore throat, pharyngitis, pneumonia, sepsis, as well as in case of relapse. The drug Lincomycin is active against most gram-positive bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. It slowly develops resistance, is quickly and evenly distributed in the tissues of the body, penetrates bone tissue, passes through the placental barrier, and enters breast milk. The release form is different - ointment for external use, capsules orally, ampoules for intramuscular and intravenous administration.
The doctor gives instructions for use. There are many side effects. The product should be used with caution by people with liver and kidney damage.
The derivative form is the antibiotic clindamycin. A well-known drug that is widely used in pediatrics. Available in various forms, it is used in the treatment of infectious diseases. Directed against gram-positive aerobic bacteria, resistant (resistant) strains, viruses, fungi (including yeast). The method of application and dosage depend on the form used - there are options for external and internal use.
The drug is not prescribed to newborns, the elderly, during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Use with caution in case of gastrointestinal disturbances, liver and kidney failure, ulcerative colitis, bronchial asthma, sensitivity to lincomycin and clindamycin
Injections of B vitamins for back and lower back pain
Vitamin injections are given along with analgesic drugs for back and lower back pain. According to experts, the list of the best vitamins includes thiamine, pyridoxine, cyanocobalamine (vitamins B1, B6, B12, respectively).
Taken together, the substances provide a strong analgesic and neuroprotective effect, having a beneficial effect on irritated nerve endings.
The complexes concentrate lidocaine, which enhances the positive effects of individual vitamins by 5-8 times. Among the effective drugs are the following:
The basis of all complexes are B vitamins and lidocaine. Only the concentration of active compounds differs.
The drugs are used strictly according to indications, including sciatica, radiculopathy, lumbago pain, intercostal neuralgia, osteochondrosis, and intervertebral hernia.
As for the prohibitions, the list includes heart failure, hypersensitivity to components, lactation period and bearing a child.
Injections for back and lower back pain are given into the muscle once daily (preferably in the morning). Having chosen any medication from the list of the best, use it for a course of 5 to 10 days. Next, switch to taking B vitamins in tablets.
Systemic antibiotics for sore throat and other throat diseases
According to the method of influencing pathogenic flora, antibiotics are classified into:
- Bactericidal. They affect the membranes of pathogenic microorganisms, disrupt their integrity, paralyze, and completely destroy them.
- Bacteriostatic. They inhibit the proliferation of microbes, reduce their activity, and contribute to mass death. Additionally strengthen local immunity.
To eliminate sore throats, depending on the stage and nature of the pathological process, the following groups of systemic antibiotics are prescribed:
- beta-lactams (cephalosporin and penicillin drugs);
- fluoroquinolones (Levofloxacin, Sparfloxacin);
- macrolides (Clarithromycin, Azithromycin).
Penicillins
Antibiotics for a sore throat are prescribed taking into account the sensitivity of synthetic components to pathogenic flora. Penicillin drugs have low toxicity, a pronounced bactericidal effect, and a wide range of dosages. On average, the course of treatment varies from 7 to 10 days. Such antibiotics have several forms of release and are well tolerated by the body. Popular drugs:
- Augmentin. These are tablets, a solution for suspension with amoxicillin, clavulanic acid in the chemical composition. They help with infections of the genitourinary system, soft tissues, ENT organs, and skin. The antibiotic acts mildly, but is not recommended if the body is hypersensitive.
- Amoxiclav. A universal antibiotic in the form of tablets, powder and suspension. Use orally. Prescribed for infectious lesions of the lower respiratory tract. Amoxicillin trihydrate and clavulanic acid destroy bacterial infection and symptoms of the disease. The medicine is not prescribed for infectious mononucleosis, lymphocytic leukemia, or intolerance to components.
Macrolides
Such antibiotics are prescribed for the activity of staphylococci and streptococci. Macrolides have no toxic effects, are safe for the digestive tract and nervous system, and are well tolerated by the body. On average, the course of treatment lasts 5–7 days; according to indications, it can be extended to 10 days. Effective medicines:
- Azithromycin. Tablets, powder for suspension are used orally. Azithromycin dihydrate is prescribed for all forms of tonsillitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, pneumonia, otitis media, laryngitis, chronic bronchitis. Contraindications include high sensitivity of the body to the components of the antibiotic.
- Sumamed. Tablets, capsules, powder for suspension. The active ingredient is azithromycin dihydrate. The drug is effective for damage to the ENT organs and upper respiratory tract. Acts systemically in the body. Macrolide is contraindicated in case of liver/renal failure, hypersensitivity reactions.
Article on the topic: Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
Cephalosporins
These are strong antibiotics that are effective for complicated forms of tonsillitis. They can be prescribed when penicillins and macrolides have little effect or the desired effect is absent. It is not recommended to start complex treatment with cephalosporins, since an addictive effect develops in the body. Popular products with a pronounced bactericidal effect:
- Ceftriaxone. Antibiotics help with sore throat and cough and act systemically. The active component of the same name inhibits the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Ceftriaxone is not available in tablets. The only dosage form is a solution for infusion therapy. Contraindicated in renal/liver failure, ulcerative colitis, enteritis, pregnancy, lactation.
- Cefixime. The medicine is produced in the form of tablets, powder, and belongs to the 3rd generation cephalosporin group. Recommended for pharyngitis, sinusitis, otitis media, all forms of tonsillitis, bronchitis. Cefixime is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity of the body to the components of the medication.
Injections of steroid hormones for back and lower back pain
Hormonal drugs are prescribed in the most difficult cases, when other groups of drugs are not able to relieve back and lower back pain. Steroid injections come with a long list of side effects. Intravenous administration will relieve pain that cannot be endured on your own. Injections are administered into the inflamed area to quickly obtain results, but the effect is short-lived.
No. 1. Prednisolone
It is placed into a muscle or administered intravenously using a dropper. In the first case, one injection is given daily, in the second, 10 ampoules are combined with saline and the drip method is used. The duration of the therapeutic course is up to 7 days.
No. 2. Hydrocortisone
Intravenous injections are prescribed for pain of any etiology, in particular rheumatic. The drug shows high effectiveness in the treatment of intervertebral hernia. The dosage of the administered medication must be determined by the doctor, who will compare the patient’s health status with contraindications. Therapy lasts a maximum of 7 days.
No. 3. Diprospan
The drug is a steroid hormone aimed at relieving pain shock. The medicine negatively affects the functioning of the adrenal glands. For this reason, injections are given exclusively in the hospital. 2 mg is injected into the muscle at a time. During therapy, it is important to monitor the patient’s well-being at all times.
Muscle relaxant injections for back and lower back pain
Injections are prescribed for severe pain that is felt in the back and lower back. Below is a list of the best medications that promote maximum muscle relaxation. The active substances block pain receptors, which reduces muscle tone. Relief comes.
Popular muscle relaxants are presented in the form of:
Injections are prescribed during the acute period in the first 7 days. They are placed intramuscularly 1-2 times a day. It all depends on the dosage; contraindications must be taken into account. During the course, adverse reactions may occur.
What drugs are prescribed?
The doctor must select the appropriate antibiotic based on the patient’s condition, the presence of allergic reactions and the characteristics of the drugs themselves, which have the following requirements:
Antibiotics used in dentistry are divided into systemic and local. Drugs of the first group have a general effect, affecting not only the inflamed area of the oral cavity, but also the body as a whole.
Popular options for systemic antibiotics
Augmentin (Amoxiclav). It belongs to the semisynthetic antibiotics of the penicillin group. The main active ingredients of the antimicrobial drug are clavulanic acid and amoxicillin, which quickly block microbial enzymes.
Augmentin is available as a powder for suspension (usually prescribed to children) or film-coated tablets. Take 250 mg twice a day (1 tablet) or three times a day 20-40 ml when choosing a suspension (for children over 6 years old, the dosage is reduced to 10 ml).
Azithromycin (Sumamed). It is an antibiotic of the macrolide group, characterized by a complex multi-level formula of the active substance in the form of azithromycin hydrate. The main form is gelatin capsules with white crystalline powder, which are taken without separating to ensure effective absorption of the components of the product directly in the small intestine. In dentistry, Azithromycin is used in a dosage of 250 mg , prescribed twice a day .
Injections with chondroprotective drugs for pain in the lower back and back
Chondroprotectors restore cartilage tissue, preventing the spinal discs from deteriorating further. As a result, pain and inflammation are reduced.
No. 1. Aflutop
Thanks to regular injections, the regeneration of cartilage tissue increases, pain subsides, and inflammation subsides. The medication is well tolerated by the body, but sometimes nausea and dizziness occur. The injection is given once a day intraarticularly or intramuscularly. There are contraindications.
No. 2. Adgelon
Injections are given intramuscularly once a day to relieve back and lower back pain. "Adgelon" is on the list of the best chondroprotectors. It restores cartilage and fights intervertebral hernia. The dosage and duration of therapy are determined by the doctor. The medication is contraindicated for children and pregnant women. During the course, adverse reactions rarely occur.
Treatment of bacterial infections
The choice of antibiotic depends on what type of bacteria is causing the sore throat. Before prescribing, specific diagnostics must be carried out to determine the causative agent.
Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus
This is the most common causative agent of tonsillitis and pharyngitis in children (about 30%).
Main symptoms:
- discomfort or pain in the throat that gets worse when swallowing;
- ear pain;
- deterioration of general condition;
- fever;
- sore throat and cough - with pharyngitis;
- the presence of purulent plugs or plaque on the tonsils - with tonsillitis;
- enlargement and tenderness of the cervical lymph nodes;
- joint pain;
- skin rashes - with scarlet fever
Local or systemic antibiotics are used for treatment.
Antibacterial therapy for streptococcal tonsillitis is of extreme importance. If untimely and inadequate treatment is used, it can lead to complications such as rheumatism followed by the formation of heart disease or glomerulonephritis, which can lead to kidney failure.
Local antibiotics used:
- Inhalipt, spray - adults, 2 injections 3-4 times a day; children 1-2 times a day;
- Grammidin, lozenges - adults, 1 tablet 3-4 times a day; children 1-2 times a day;
- Gramicidin C, lozenges - adults, 2 tablets 3-4 times a day; children: 1 tablet.
A previously actively used antibiotic for topical use in the form of a spray, fusafunzhin (Bioparox), was withdrawn from sale due to the high risk of allergic reactions.
The list of the best systemic drugs is presented in the table.
| Antibiotic group | Drug name | Dosage for adults | Dosage for children |
| Penicillins | Phenoxymethylpenicillin | 1500 mg per day | Less than 25 kg - 400 mg in 2 divided doses, More than 25 kg - 800 mg in 2 divided doses |
| Amoxicillin (Flemoxin Solutab) | 1500 mg in 3 divided doses | Less than 25 kg - 400 mg in 2 divided doses, more than 25 kg - 800 mg in 2 divided doses | |
| Cephalosporins | Cephalexin | 1000 mg in 2 doses | 40 mg/kg in 2 divided doses |
| Cefuroxime (Zinnat) | 500 mg in 2 doses immediately after meals | 20 mg/kg in 2 divided doses | |
| Ceftibuten (Cedex) | 400 mg 1 time per day | 9 mg/kg 1 time per day | |
| Cefixime (Suprax) | 400 mg 1 time per day | 8 mg/kg 1 time per day | |
| Cefditoren | 400 mg in 2 doses | Contraindicated under 12 years of age, then adult dosage | |
| If you are allergic to penicillins and cephalosporins | |||
| Macrolides | Erythromycin | 1500 mg in 3 divided doses | 45 mg/kg in 3 divided doses |
| Azithromycin (Sumamed) | 500 mg 1 time per day | 12 mg/kg 1 time per day | |
| Clarithromycin (Fromilid) | 500 mg in 2 doses | 20 mg/kg in 2 divided doses | |
| Josamycin (Vilprafen) | 1000 mg in 2 doses | 40 mg/kg in 2 divided doses | |
| Spiramycin (Rovamycin) | 6 million IU in 2 doses | 300 thousand IU/kg in 2 doses | |
| Midecamycin (Macropen) | 1200 mg in 3 divided doses | 50 mg/kg in 2 divided doses | |
| For allergies to penicillins, cephalosporins and macrolides | |||
| Lincosamides | Clindamycin | 150 mg 4 times a day | 10 mg/kg 3 times a day |
| Lincomycin (Neloren) | 500 mg 3 times a day | 10 mg/kg 3 times a day | |
| For recurrent tonsillitis | |||
| Penicillins | Amoxicillin/clavulanate | 625 mg 3 times a day | 15 mg/kg 3 times a day |
| Cephalosporins | Cefuroxime (Zinnat) | 250 mg 2 times a day immediately after meals | 10 mg/kg 2 times a day |
| Lincosamides | Clindamycin | 150 mg 4 times a day | 10 mg/kg 3 times a day |
| Lincomycin (Neloren) | 500 mg 3 times a day | 10 mg/kg 3 times a day | |
All antibiotics are taken for 10 days. The exception is azithromycin, the course of which is 5 days.
Streptococci C, G and Staphylococcus aureus
Tonsillitis and pharyngitis caused by these bacteria are more common in adults. They have the same clinical manifestations and treatment as group A beta hemolytic streptococcus.
Arcanobacterium haemolyticum
Clinical manifestations are similar to beta-hemolytic streptococcus. However, the treatment is somewhat different.
Medicines that are recommended to be taken for Arcanobacterium haemolyticum infection are presented in the table.
| A drug | Dosage for adults | Dosage for children |
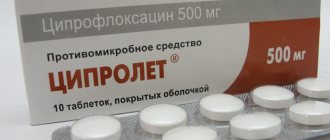
| Ciprofloxacin (Ciprolet) | 250 mg 2 times a day | The drug is contraindicated under 18 years of age |
| Doxycycline (Unidox Solutab) | 100 mg 1 time per day | from 8 years - 2 mg/kg 1 time per day |
| Minocycline (Minolexin) | 100 mg 2 times a day | from 8 years - 2 mg/kg 2 times a day |
| Clindamycin | 150 mg 4 times a day | 10 mg/kg 3 times a day |
| Azithromycin (Sumamed) | 500 mg 1 time per day | 12 mg/kg 1 time per day |
Diphtheria
Diphtheria is an acute infectious disease that is life-threatening. Children are most susceptible to infection. A specific toxin released by bacteria poses a mortal danger.
Clinical symptoms of diphtheria are similar to ordinary sore throat, however, it has some features:
- bluish color of the pharynx upon examination;
- dirty gray plaque on the tonsils, which is difficult to remove with a spatula;
- when plaque separates - bleeding of the tonsils;
- swelling of the neck.
Body temperature during illness may be normal.
If treatment is untimely, infectious-toxic shock and inflammation of the heart muscle occurs, which can lead to death.
At the slightest suspicion of diphtheria, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Specific antitoxic antidiphtheria serum (APS) is immediately administered. When administered, there is a risk of allergic reactions, so treatment must be carried out in a hospital and under the supervision of a doctor.
The patient needs to take the antibiotics erythromycin and azithromycin according to the standard regimen.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is an infection transmitted through sexual contact. The genital organs are most commonly affected, but the eyes and throat may be involved.
Main symptoms:
- fever;
- itching and burning in the genital area;
- purulent discharge from the urethra;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- dryness, sore throat and sore throat - pharyngitis;
- lacrimation, photophobia, swelling of the eyelids, purulent discharge from the eyes - conjunctivitis.
Gonococcal pharyngitis is less treatable than gonococcal infections of other locations.
The drugs prescribed for the treatment of gonococcal infection are presented in the table.
| A drug | Dosage for adults | Dosage for children |
| Ceftriaxone | 500 mg once intramuscularly or intravenously | 125-250 mg once |
| Cefixime (Suprax) | 400 mg once | 8 mg/kg once |
| Spectinomycin (Trobitsin) | 2 g once intramuscularly | 40 mg/kg once |
| Azithromycin (Sumamed) | 1 g once | 24 mg/kg once |
| Doxycycline (Unidox Solutab) | 100 mg 2 times a day for 7 days | From 8 years: 2 mg/kg 2 times a day |
What antibiotics for back pain?
Doctors investigated chronic lumbar pain and made a discovery that was assessed by neurologists as “worthy of a Nobel Prize”!
The first study proved that there is a close connection between chronic (lasting more than 6 months) low back pain and infectious lesions of the intervertebral discs! The most common cause of lumbar pain is herniated intervertebral discs. Disc herniations can form in any part of the spine, but most often they are observed in the lumbar and cervical regions, and in the lumbar region - 15 times more often than in the cervical region.
61 people took part in the study. All patients had chronic low back pain and had magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) signs of bone marrow edema (Modic type 1 intervertebral disc changes named after Michael MoDiC, who first described 3 different types of intervertebral disc changes on MRI).
Under conditions of strict sterility, scientists collected material for bacteriological research from the intervertebral discs of patients and, as a result, anaerobic microbes were found in most of them. And in 86% of all findings, Propionibacterium acne was found - the same microbe that is most often the cause (causative agent) of acne.
Thus, scientists have demonstrated that in 40% of cases the cause of constant lower back pain is the propionibacter microbe that has penetrated into damaged and displaced intervertebral discs and caused inflammation in them, which is normally found in human hair follicles and gums. The penetration of bacteria leads to chronic infection in the intervertebral disc, resulting in pain and swelling.
There is a strong association between low back pain and the presence of Modic type 1 changes (bacterial inflammation) on MRI. Research shows that the pain of such patients differs from the lumbar pain of patients who do not have signs of inflammation in the intervertebral discs. For example, 75-80% of patients with inflammation in the discs have constant pain that does not disappear day or night. There may be a change in the intensity of these pains, but they never completely go away. Studies have also shown that patients with inflammatory changes have more severe pain than patients with “normal” low back pain.
Moreover, therapeutic exercises, which usually bring relief to patients with lumbar pain caused by other reasons (not infection), do not help patients with signs of inflammation at all. Quite the contrary, these pains intensify when doing physical exercise.
In the second study, researchers tested a combination antibiotic to treat low back pain. The double-blind study involved 162 patients with chronic low back pain, displaced intervertebral discs, and inflammatory changes on MRI classified as Modic 1. The patients were divided into 2 groups, one of which received antibiotic treatment for 100 days, the second group During the same period of time, she took a placebo (a substance with no apparent medicinal properties).
All patients were examined in detail before the experiment, 100 days and 1 year after the start of the experiment. Antibiotic treatment was effective in 80% of cases! The authors write that after a course of antibiotic treatment, patients experienced a significant reduction in low back pain, and the rate of disability was significantly reduced. In the group taking placebo, no changes for the better were noted.
This study showed that almost half of patients with displaced intervertebral discs simultaneously had a bacterial infection, mainly Propionibacterium acne. Scientists are confident that this bacterium causes about 40% of chronic lower back pain.
This discovery by scientists is very reminiscent of the time when the connection between the occurrence of peptic ulcer disease and a microorganism called Helicobacter pylori was proven. After that, everything “fell into place” - peptic ulcer disease began to be considered by doctors as an infectious disease, they began to treat it with antibiotics like any other bacterial infection, and the need for surgical treatment of patients disappeared. And in 2005, two scientists who discovered the medical significance of Helicobacter pylori were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine.
The British daily newspaper The Daily Telegraph quotes Dr Peter Hamlyn, a renowned neurosurgeon expert from University London Hospital, as saying: “This is the tipping point, the point where we will have to rewrite the textbooks. This is Nobel Prize material.”
From microbiology it is known that the bacterium propionibacter is sensitive to antibiotics of the tetracycline, fluoroquinolone series and macrolides. But, unfortunately, treatment with antibiotics (and also as long as in the treatment of chronic pain in the spine) leads to intestinal dysbiosis if not accompanied by the intake of probiotics (necessarily in an acid-resistant capsule!), with all the ensuing consequences. First of all, the consequence of disruption of the intestinal microflora under the influence of antibiotics is a decrease in the body’s immune defense.
Effects of mixing alcohol and antibiotics
Tetracyclines
The tetracycline class includes doxycycline
and
minocycline
. This class helps in treating a wide range of bacterial infections. People should not drink alcohol while taking doxycycline because it may reduce the effect of the antibiotic. Alcohol speeds up the elimination of doxycycline from the body and therefore makes it less effective. Liver toxicity is a rare side effect of taking minocycline. Since alcohol also has negative effects on the liver, mixing alcohol with minocycline should be avoided.
Oxazolidinones
Linezolid
belongs to the class of oxazolidinone antibiotics. Doctors use oxazolidinones to treat infections of the gastrointestinal tract, skin, lungs, and urinary tract. In addition to its antibacterial effect, linezolid reduces the action of enzymes called monoamine oxidase-A and monoamine oxidase-B. Monoamine oxidases break down tyramine, a compound found in draft beer and red wine. When people mix beer and red wine with linezolid, the amount of tyramine in the blood may increase. People may experience the following side effects after drinking alcohol while taking oxazolidinones:
- sweating;
- fast heartbeat;
- fever;
- change in mental state;
- rapid breathing;
- vomit;
- seizures;
- high blood pressure;
- coma;
- muscle stiffness;
- muscle spasms.
People should avoid red wine and draft beer while taking linezolid. They should also avoid other foods that contain tyramine, such as hard cheeses and smoked foods.
Sulfonamides
Doctors prescribe sulfonamide antibiotics to treat infections of the urinary tract, respiratory tract, and gastrointestinal tract. Sulfonamides include the combination drug sulfamethoxazole
and
trimethoprim
, which is also called Septra. Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim affect the metabolism of folic acid in bacteria. In rare cases, trimethoprim may also affect the metabolism of folic acid in human cells. People with folate deficiency may be at risk of further decreases in folate levels when taking sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. Regular alcohol consumption also leads to decreased folic acid levels. Doctors should use caution when prescribing sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim to people who frequently drink alcohol.
Fluoroquinolones
Fluoroquinolone medications have possible mental health side effects that may include:
- attention disorder;
- disorientation;
- nervousness;
- memory loss.
Mixing alcohol with fluoroquinolones may increase the side effects listed above. In rare cases, seizures may occur during treatment with fluoroquinolones. Doctors recommend that people with seizures avoid mixing alcohol and fluoroquinolones.
Nitroimidazoles
A prominent representative of the nitroimidazole group is Metronidazole
, which doctors prescribe to treat gastrointestinal infections, sexually transmitted infections, and other infections associated with anaerobic bacteria. Metronidazole interferes with the function of a key enzyme that helps the body break down alcohol. When metronidazole inhibits the enzyme aldehyde dehydrogenase, levels of acetaldehyde accumulate in the blood. This causes the toxic effects of alcohol. Mixing alcohol with metronidazole may cause:
- abdominal cramps;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- headache;
- facial redness.
People should avoid drinking alcohol during treatment and for 3 days after the last dose. Despite this interaction, not everyone experiences these reactions. Possible individual risk. However, people should avoid drinking alcohol while taking metronidazole.
Medicines for back pain
Back pain is a natural reaction of the body to severe overexertion, injury or prolonged stay in one position. Various medications and pain-relieving ointments help get rid of it. They are presented on pharmacy shelves in a wide variety, so it is always difficult to choose the right option. But it is worth remembering that it is not always possible to self-medicate using over-the-counter medications; there are situations when immediate contact with a specialist is required.
How to relieve back pain?
Pain in the back is a fairly common symptom. The reason may lie in a variety of disorders of the body. Discomfort manifests itself in an acute form, which limits a person’s movement and does not allow him to move normally or perform even simple tasks. The problem is eliminated with the help of modern drugs. Painkillers or anti-inflammatory drugs come to the rescue. They are selected taking into account the following factors:
- Patient's weight and age.
- Existing diagnosis.
- The severity of disease progression.
- The cause of the pain syndrome.
- Stage of development of the pathology.
- Presence of contraindications or allergic reactions.
- What medications are the patient already taking?
Rules for choosing a drug
Painkillers for back pain are always selected individually. For some patients, this form may simply not be suitable and, according to the doctor’s decision, it is more advisable to use injections, droppers, or external ointments. You also need to be careful with the dosage, since exceeding the recommendation is fraught with serious consequences.
When choosing the right medicine, you need to consider the following points:
- You should not just purchase a potent remedy that helped a friend get rid of post-operative pain. You should always start with a milder and safer drug. And only if there is no effectiveness, the medication should be changed.
- In case of pinched nerve endings or exacerbation of serious pathologies, ordinary pills for back pain cannot eliminate the acute pain syndrome; novocaine blockades or injections are required.
- If heat and swelling are felt at the site of pain, there is an inflammatory process. Any good NSAID will help you cope with it. Analgesics and similar painkillers do not cope with the task.
- An effective drug relieves discomfort fairly quickly after administration. The next tablet should be taken before the previous one has expired.
- Chronic pain in the back and lower back requires an integrated approach. Constantly treating the patient with medications only worsens the situation and contributes to the progression of the pathology.
- Ointments, gels and patches combine well with any other medications, and the resulting analgesic effect allows you to reduce the dosage and thereby minimize the likelihood of side effects.
People with peptic ulcers, renal failure, and liver pathologies should not purchase non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs without a prescription. A safe analogue is selected for them individually. The presence of a malignant tumor requires the use of narcotic painkillers; treatment with their use is carried out in a hospital.
Antibiotic throat spray
Medicines in this form of release quickly relieve acute pain and prevent painful swallowing. The active components are not absorbed into the bloodstream and act without side effects. The aerosol abundantly irrigates the arches of the pharynx. The solution acts on the area of inflammation. Relief occurs 5–15 minutes after the procedure and lasts for several hours. Such medications are prescribed to adults and children as part of drug therapy.
Article on the topic: Oxiracetam for improving the memory process
Bioparox
An antibacterial spray for irrigation of the pharynx acts directly on the site of pathology. Description:
- Ingredients: fusafungine.
- Mechanism of action: relieves inflammation, kills microbes, accelerates the restoration of injured tissues.
- Directions for use: dosed aerosol for inhalation.
- Dosage: 3–11 years - 1 spray in the nose or 2 in the mouth 4 times a day. From 11 years old and adults – 4 injections through the mouth or 2 through the nose, 4 times a day.
- Contraindications: age under 3 years, pregnancy, hypersensitivity reactions.
Octenisept
The local antiseptic is produced in the form of a liquid in bottles with a special spray bottle. Octenisept has an extensive list of indications, including sore throats of bacterial origin. Description:
- Ingredients: octenidine, phenoxyethanol.
- Mechanism of action: destroys yeast fungi, dermatophytes, reduces the activity of gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms, herpes virus.
- Directions for use: gargle with a sore throat between meals.
- Dosage: use a concentrated solution or pre-dilute it in a ratio of 1:5. Single dose – 20 ml.
- Contraindications: individual intolerance to the active substances of the antibiotic.
Stopangin
The combination drug is sold in pharmacies without a prescription. With its help, sore throat and other symptoms of colds, flu, and ARVI disappear. The solution acts locally and does not disrupt the functioning of internal organs with side effects. Description:
- Ingredients: hexetidine, complex of essential oils (anise, eucalyptus, sassafras, peppermint, orange tree).
- Mechanism of action: relieves pain, envelops the oral cavity, kills germs, stops the inflammatory process.
- Method of use: the aerosol is sprayed in the oral cavity, and the pathology areas are rinsed with the solution between meals.
- Dosage: 1 spray 2 times/day. Gargle 10–15 ml of solution for half a minute, 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 5–7 days.
- Contraindications: atrophic pharyngitis, children under 8 years of age, individual intolerance to the components.
Ingalipt
The drug is given in the form of a spray or aerosol. It helps well with difficulty breathing, painful swallowing, inflammation of the oral mucosa and nasopharynx. Ingalipt is prescribed as part of complex treatment for follicular and other forms of tonsillitis. Description:
- Ingredients: streptocide (sulfonamide), thymol, glycerol, eucalyptus oil.
- Mechanism of action: suppresses the vital activity of microbes, draws exudate from tissues, relieves pain, eliminates purulent deposits and plugs on the tonsils.
- Directions for use: irrigate the mucous cavities of the nasopharynx and mouth.
- Dosage: 2-3 sprays per 1 inhalation (do not swallow for 5 minutes). The course of treatment is 5–7 days.
- Contraindications: hypersensitivity reactions.
Types of medications for back pain
Patients are prescribed tablets for lower back pain of various types, depending on the type and nature of the pain. Taking into account the location of the affected area and possible side effects, anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, synthetic drugs, muscle relaxants and corticosteroids come to the rescue. Each group has its own characteristics and is aimed at relieving pain of a certain nature.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs are one of the groups of drugs that are widely used for low back pain. They are aimed at reducing the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms, relieve fever, and stop the inflammatory process. When the medication enters the body, it reduces the effects of biologically active substances, thereby eliminating discomfort, pain, and swelling. The most famous representatives of the group are:
- "Naproxen." It is based on an active substance of the same name, which effectively affects the body, eliminating fever and pain. It is offered to users in the form of tablets with different dosages. It is used if the cause is a pathology in the spine. Use with caution in the presence of chronic diseases, since the medicine increases the time of hematopoiesis and can also enhance the effect of taking indirect anticoagulants. These drugs include Warfarin, Acenocoumarol and Neodicoumarin.
- "Ketoprofen". It is prescribed as an alternative to Ibuprofen, since it is similar in structure and effect. It is offered in pharmacies not only in the form of tablets, but also suppositories, capsules, solution for injection or intramuscular injections. The big advantage is the affordable price of the drug, as well as the effective elimination of unpleasant symptoms.
- "Ketoprolac". Used to treat spinal injuries and chronic pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. Included by doctors in the course of rehabilitation after surgery. Available at the pharmacy in the form of tablets or solution for injection (intravenously and intramuscularly). The medication perfectly eliminates pain, inflammation, and relieves fever. The dosage is selected individually, depending on body weight.
- "Diclofenac". One of the popular representatives of NSAIDs, which allows you to remove the ball, effectively relieve pain and relieve inflammation. The drug is available in the form of capsules, tablets, suppositories or injections. The tablet form is widely used in the treatment of back pain because of its convenience and simplicity. The drug is prescribed for pain caused by injuries, exacerbations of chronic diseases, hypothermia, sprains, and pathological processes. Not used while taking medications based on St. John's wort, sleeping pills or medications that lower blood pressure.
What type of antibiotics is suitable for the throat?
So, when it became clear that a bacterial infection would have to be treated, you need to choose a drug and decide whether it will be a local antibiotic or for oral administration.
The first will begin to act directly on the diseased mucosa, and the second will reach the source of infection along with the bloodstream when it is absorbed into the intestinal mucosa.
You need to choose based on how severely the disease has developed:
- If the sore throat is not too severe (there is not a large amount of plaque and purulent plugs), you can limit yourself to topical medications for the throat. This will speed up the treatment process and reduce the harmful effects of this type of medication on the intestinal mucosa.
- If the sore throat is severe (with a lot of purulent plugs and plaque), then antibiotics should be taken both locally and orally. In this case, consulting a doctor is strictly necessary.
Topical medications come in mainly two types: lozenges and aerosol or throat spray. You can choose the form of medication that seems most convenient to you.
You can also use both types of medications, alternating them, but in this case you must strictly adhere to the dosage and number of doses. To do this, you need to either carefully study the instructions for use or consult a doctor for advice.
If you do not want to take two drugs from the same group, then you can combine throat tablets with an antibiotic and an aerosol with antibacterial substances, for example, sulfonamides (Ingalipt). In addition to using certain medications, you can gargle and gargle with special solutions with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Treatment will proceed faster if you follow a few simple rules:
- Use a spray (for example, Bioparox) or throat tablets containing an antibiotic (for example, Grammidin), and also regularly gargle, for example, with a solution of soda, salt and iodine;
- After the next procedure, it is extremely undesirable to eat or drink for half an hour, because at this time the effect of the components of the drug takes place;
- It is advisable to treat the throat and oral cavity with an antibiotic every 3 hours; rinsing with other means is allowed more often, but with an interval of at least 1.5 hours;
- Even if noticeable symptoms have passed and the sore throat does not bother you, you should complete the course of treatment to the end in order to completely get rid of harmful bacteria and prevent the disease from reoccurring.
Important: for sore throat, medications can be used locally or for oral administration, depending on the severity of the condition. You can choose different forms of topical drugs or use additional antibacterial agents. For a speedy recovery, it is important to follow the treatment regimen and complete the course completely.