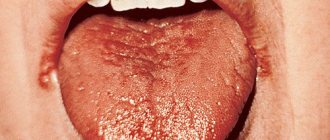
Fungal infection of the mucous membrane of the mouth and tongue is called Candidiasis or thrush. The infectious disease occurs not only in newborn babies, but also in adults, under the influence of some factors that we will consider. As a rule, fungus on the tongue is quite common; its mild form can be found in smokers, people with digestive problems and diabetics.
Conditions and symptoms of occurrence
Mycotic lesions of the oral cavity are usually caused by Candida fungus, which is a saprophytic yeast fungus.
An increase in the number of its spores occurs under the following conditions:
- endocrine diseases;
- long-term antibiotic therapy leading to dysbiosis and disruption of the intestinal flora;
- violations of personal hygiene rules;
- weakened immunity as a result of chronic diseases, incorrect treatment, infancy, hormonal disorders.
Fungus on the tongue occurs as an independent phenomenon with heavy smoking:
- the smoker's tongue becomes covered with a light brown film;
- a coating of grains covering the mucous membrane of the tongue.
Plaque is difficult to remove when scraped; bleeding wounds often appear at the site of scraping.
In an adult, tongue fungus can occur without symptoms of burning and itching for a long time, turning the disease into a chronic form.
Symptoms of tongue fungus:
- itching of the surface of the tongue;
- sensitivity to spicy, salty and sour foods;
- slight pastiness;
- the appearance of bright red spots, white plaque, film;
- formation of cracks in the tongue.
Yeast fungus on the tongue of a child, as a rule, occurs in parallel with oral thrush.
In children, Candidiasis occurs with the formation of a cheesy coating on:
- buccal mucosa;
- mucous membrane of the palate;
- mucous membrane of the tongue.
At first, the plaque is easy to remove, but after a few days a whitish film forms on the surface of the tongue, covering the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Symptoms of fungus in children:
- formation of white grains;
- the appearance of cheesy masses on the tongue;
- cracks in the corners of the mouth;
- distortion of taste sensations;
- formation of a dense film;
- bleeding of the mucous membrane.
Factors
The causes of fungus may be hidden in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract that have not been fully cured, or dysbacteriosis.
Factors provoking infection:
- introduction of a pathogen during a dental examination or manipulation;
- careless attitude to oral hygiene;
- frequent smoking;
- neglect of personal hygiene;
- eating unwashed vegetables or fruits;
- HIV infection;
- endocrinological diseases;
The main reason causing the development of fungal flora in the body is a violation of the immune system that controls the development and growth of saprophytes.
The second option for the development of fungal infections is the introduction of a pathogen due to mechanical damage to the skin or mucous membrane.
In the case of a fungal disease of the oral cavity, damage can occur when:
Diagnostics
In order to cure mycosis, a diagnosis is carried out, including taking tests.
Diagnosis of tongue mycosis:
- scraping from the tongue, oral mucosa;
- blood sugar test;
- blood chemistry;
- scraping a fragment of film from the tongue for microbiological examination.
Diseases of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue can also be the cause of intestinal dysbiosis or untreated mycosis of another part of the body.
If personal hygiene rules are neglected, self-infection through the oral cavity is possible. If there is mechanical damage in the mouth, tongue or cheeks, fungal spores colonize the oral cavity, leading to mycosis.
Treatment
Therapy for fungus if it is on the tongue includes:
- rinsing;
- antiseptic sanitation of the oral cavity;
- the use of local lozenges with a fungicidal effect.
The food system is also changing and stricter control over body and oral hygiene is being established.
Treatment of such an ailment as tongue fungus in the first, non-aggravated forms of mycosis can be carried out through the use of local remedies:
- antiseptic treatment;
- gargling with herbs.
ethnoscience
Treatment with folk remedies is quite possible, among which are rinses:
- decoction of oak bark;
- calendula tincture;
- baking soda solution;
- solution of borax or boric acid.
An alternative treatment can be used with lemon, the slices of which are dissolved on the tongue after sanitation of the oral cavity.
Why does thrush occur in the mouth?
Since the child’s body is highly susceptible to various pathologies, the main reason for the appearance of fungus in the mouth is insufficient hygiene of the mother’s breasts during breastfeeding. If the child is on artificial formula, then the result of the appearance of fungus is the lack of proper sterilization of nipples and bottles. Important factors influencing susceptibility to infectious and fungal diseases: poor immunity due to prematurity of the child, dysbiosis (violation of the integrity of the intestinal microflora) due to the use of antibacterial agents, vitamin deficiencies or the passage of the fetus through the infected birth canal of the mother.
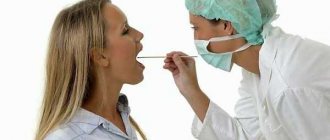
To collect the scraping, just do a couple of simple manipulations. Using a special spatula or a regular cotton swab, the laboratory technician makes several light movements along the surface of the tongue so that the contents of the saliva are accurately caught on the sampling material. After collection, the resulting material is sent to a special metal container to be sent for laboratory research. Mothers do not need to worry about their baby; the smear will not cause any discomfort to the newborn. The earlier the sampling is carried out, the faster the cause of the disease will be identified, and the faster the child will recover.
What other tests may require scraping from the surface of the tongue?
A smear from the surface of the mouth can be carried out not only to identify pathogens, but also to determine bile acids. To carry out the analysis, you need to use the diagnostic method of color thin layer chromatography. In order for the diagnostic result to be reliable, the study must be carried out on an empty stomach in the morning before breakfast without prior drinking or taking medications. After collection (the procedure is simple and the same as described above), the collected material is placed in a special test tube and filled with ethyl alcohol. Next, the sampling material is tightly sealed and left for several hours specifically so that all the substances dissolve well among themselves.
This is followed by an evaporation procedure using a water bath exactly until the volume of the liquid decreases by half. Then a chromatographic plate is required, it needs to be heated in a dryer for an hour, then a drop of the test substance is applied to the plate, which is sent to the dryer, and then it is cooled and developed. Then you can examine the result; if there are individual spots, then bile acids are present in large quantities.
In the process of diagnosing various diseases, an analysis such as tongue scraping may be prescribed. We will figure out why it is performed, what information it provides about the state of the body and how it is carried out.
How to remove plaque on the tongue and prevent its appearance?
Getting rid of deposits on the tongue should begin with identifying the exact cause of their appearance. Thus, a white-yellow coating on the tongue can be easily eliminated by regular hygiene measures:
- Thorough cleaning of the mouth with a toothbrush
with a special surface for cleaning the tongue. An ultrasonic device can also be used. After brushing your teeth, make a few brushing strokes from the base of your tongue to the tip to remove food debris and bacteria, then use an antibacterial mouthwash. Bonus: fresh, clean breath.
- Gargling with infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants
. Chamomile, oak, mint, eucalyptus, and sage have proven themselves to be excellent in this matter. Crushed parts of these plants can be purchased at the pharmacy. “Green healers” will not only cleanse your tongue, but also help fight gum and throat diseases.
- Using antibacterial sprays
between meals. A few sprays - and the number of bacteria in the oral cavity decreases significantly, and your breath becomes fresher. The method is not a panacea, but it is great if you need to freshen your breath and there is no way to brush your teeth.
If a coated tongue is a consequence of a disease, then you need to fight the root cause. For example, for candidiasis, antifungal drugs will be prescribed, for gastritis and ulcers - antacids and enveloping agents, and poisoning will require special antidote therapy. Plaque after staining with food coloring or after a course of treatment with antibiotics or other drugs will gradually go away on its own. Tobacco plaque is more difficult to remove, but will also disappear if you stop smoking.
Remember that all organs and systems are interconnected, and you cannot deal with only one problem, neglecting recommendations for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Strive to maintain a balance in everything, promptly responding to your body’s signals about problems, then it will respond to you with good health and a beautiful appearance.
When can such an analysis be prescribed?
First of all, scraping is prescribed to diagnose the oral cavity and the state of the digestive system. If pathogenic microorganisms have settled in the gastrointestinal tract, they will certainly be found on the tongue. Indications for this analysis are:
- gingivitis;
- glossitis;
- stomatitis;
- somatic pathologies;
- immunity deficiency;
- HIV.
For the analysis to be successful, you need to follow simple rules:
- It is better to take it before breakfast.
- You can take it a couple of hours after your meal.
- Before collecting material, you should not brush your teeth, rinse your mouth, or carry out antifungal treatment.
First of all, scraping is prescribed to diagnose the oral cavity and the state of the digestive system.
Important! A dense white or yellow coating on the tongue is a direct indication for scraping. Additional indications are bad breath, discomfort and burning sensation, cracks in the corners of the mouth and on the surface of the lips.
Diagnosis of plaque on the tongue
If you are concerned about the appearance of your tongue, you should see your dentist. The doctor will examine the oral cavity, evaluate the general appearance of the organ, examine its mobility, color and structure, determine the presence of deposits and their intensity. He also makes a decision on referral to specialists of a different profile (hepatologist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, etc.).
What studies can be ordered?
- General and biochemical blood test
- FGDS for suspected gastrointestinal pathology
- Sowing from the tongue to the flora
- Analysis for Helicobacter Pylori for stomach ulcers
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs for suspected liver and biliary tract diseases
- Coprogram (stool analysis) for intestinal problems.
A full examination will help identify disturbances in the functioning of the body and understand why the white-yellow coating on the tongue does not want to go away or changes its color to darker shades. You should not neglect tests and other diagnostic methods, because the root of the problem may lie deep, and it is better to identify it in a timely manner.
Candidiasis
Most often, scraping is prescribed if there is a suspicion of infection with Candida fungus. It is he who provokes the development of thrush. The resulting material is examined under a microscope. In this case, very thin threads are revealed, which are formed by Candida pseudomycelium.
Thrush is a common oral lesion. It can provoke gingivitis, cheilitis, stomatitis, glossitis. Very often newborns suffer from such damage.
There are many reasons for infection in newborns:
- improper hygiene of the mother who is breastfeeding;
- insufficient sterilization of pacifiers and nipples;
- prematurity;
- infection during the passage of the birth canal;
- weak immune system;
- antibiotic treatment;
- avitaminosis;
- dysbiosis.
What is candidiasis on the tongue
There are several disorders in the functioning of internal organs and systems that go hand in hand with candidiasis of the tongue. Some doctors consider this disease a harbinger of diabetes mellitus, since an environment that develops against the background of active consumption of foods rich in simple carbohydrates is ideal for the activity and proliferation of the Candida fungus. The disease may also be accompanied by:
- Candidal cheilitis is the contamination of the mucous membrane of the lips and the skin around them with fungal spores, after which the pathogenic microorganism enters the mouth.
- Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums, in which the number of pathogenic microbes increases and the composition of the microflora is disrupted, which makes the Candida fungus active.
- Mycotic seizures - appear against the background of a broken bite, create minor injuries through which fungus can penetrate into the tissue.
- Dysbacteriosis - a violation of the intestinal microflora, if left untreated, can provoke problems with the microflora of the oral cavity.
Technology for scraping for candidiasis
2 hours before the procedure you should not drink, eat, brush your teeth, rinse your mouth or take medications. To get the most informative results, it is best to take this test right in the morning, immediately after sleep. The collected material will be sent for laboratory testing. It will be carefully examined under a microscope.
Thrush very often affects newborns and infants. Here the parents are faced with the question: “How to take the material correctly?” While this does not present any difficulties for an adult, taking a scraping from a small child can sometimes be difficult.
You need to take a special spatula for the surface of the tongue or a simple cotton swab and carefully rub it across the tongue several times. The taken material must be placed in a sterile flask and sent to the laboratory. The child will not feel any discomfort.
For high-precision analysis, the material is taken in the morning.
If the scraping shows signs of Candida fungus, the doctor will diagnose “oral candidiasis.” In this case, under a microscope, cells or filaments from pseudomycelium grouped into buds will be visible.
Sowing the contents of the gingival pocket for anaerobic flora
A microbiological study aimed at isolating the pathogen and, if identified, determining its sensitivity to antibiotics in order to select the optimal therapy for periodontitis. When pathogenic and/or opportunistic microorganisms are identified, their sensitivity to antimicrobial drugs (antibiotics and bacteriophages) will be determined. When microorganisms that make up the normal microflora are detected, sensitivity to antibiotics and bacteriophages is not determined, because has no diagnostic value.
Synonyms Russian
Sowing for facultative anaerobic bacterial flora; microflora in diseases of periodontal tissues; culture for anaerobes; culture for anaerobic bacteria; anaerobic bacteria, culture, gingival pocket discharge.
Research method
Microbiological method.
What biomaterial can be used for research?
A smear from a gingival pocket.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not perform oral hygiene on the day of taking biomaterial for examination.
General information about the study
A gingival, or periodontal, pocket is a depression between the gum and tooth. If this depression pathologically increases, then we are talking about the appearance of a periodontal pocket. During the development of periodontitis, inflammation of the gums occurs due to exposure to bacterial agents. Changes associated with the occurrence of a pathological periodontal pocket are associated with changes in the microbial composition of dental plaque. Normally, gum tissue contains a small amount of bacteria: rods and cocci. During inflammation, the number of mobile rods and spirochetes increases. The presence of a periodontal pocket can be suspected when there are complaints of localized pain, thickening of the gums, gingival bleeding and suppuration, tooth mobility, and a blue-purple color of the gingival margin. The main diagnostic method is to probe the gingival margin along each tooth surface. The contents of the gingival pocket consist mainly of a mixture of microorganisms, leukocytes and their metabolic products, food debris, and epithelial cell debris. Changes in the periodontal attachment due to periodontitis can be of a constant progressive nature, during which periods of remission and exacerbation are distinguished. If during remission the inflammatory reaction is reduced or absent altogether, then during an exacerbation there is an increase in clinical manifestations with the presence of gingival exudate, in which a large number of mobile bacteria and spirochetes can be identified. Various methods are used in treatment: antibacterial therapy, curettage, surgical treatment, etc., including combinations of various methods.
Anaerobic microflora are microorganisms that do not require oxygen for their life and reproduction; for many of them, on the contrary, it is destructive. Anaerobes inhabit the human body normally (in the digestive tract, respiratory organs, genitourinary system). With a decrease in immunity or injuries, damage, activation of infection with the development of the inflammatory process is possible. The human body can then essentially become a source of infection for itself (endogenous infection). Less commonly, anaerobes enter the body from the outside (deep puncture wounds, infected abortion, wounds to the abdominal and thoracic cavity, insertion of needles and prostheses). Developing in the thickness of the skin, soft tissues and muscles, anaerobic organisms can cause cellulite, abscesses, and myositis. Symptoms that allow one to suspect an anaerobic infection of soft tissues: dense swelling, gas formation (a feeling that air bubbles under the skin are bursting when pressed), putrefactive inflammation, fetid odor.
The main treatment for anaerobic inflammation is surgical. In this case, it is necessary to eliminate the source of inflammation or open the wound, providing access to oxygen, which is harmful to anaerobes.
For differential diagnosis of anaerobic and aerobic infections, the biomaterial is cultured for flora, since the principles of treatment in one case or another will be different. Anaerobic microorganisms are sensitive to a rather narrow range of antibacterial drugs, so it is advisable to carry out drug therapy after determining sensitivity to antibiotics. Based on the grown culture, the type of microorganisms that participate in the formation of the inflammatory reaction is determined. Knowing the type of pathogen, you can select an antibacterial drug that can successfully influence these microorganisms and contribute to more effective sanitation of periodontal pockets.
After identifying a bacterial culture, it is advisable to determine their sensitivity to various antibiotics. Due to the fact that the development of antibiotic resistance in microorganisms is increasingly observed, the selection of antibiotics according to their spectrum of action on bacteria can lead to ineffective or completely unsuccessful treatment. The advantage of the method for determining sensitivity to antibiotics is the accurate determination of the antibacterial drug that has the highest effectiveness in a particular case.
List of tested antibiotics:
- Vancomycin / 5 mcg
- Clindomycin / 2 mcg
- Erythromycin / 15 mcg
- Amoxicillin clavulanate / 20/10 mcg
- Metronidazole / 50 mcg
- Kanamycin / 30 mcg
What is the research used for?
- For a comprehensive diagnosis of periodontitis and periodontal diseases;
- for differential diagnosis of anaerobic and aerobic infections, for selection of adequate therapeutic treatment taking into account the detected microflora;
- to monitor the therapy of periodontitis or inflammatory processes in the gum canal.
When is the study scheduled?
- In case of inflammatory processes in the area of periodontal pockets;
- with bleeding gums, sore gums, bad breath;
- when the position of the teeth changes, gaps appear between the teeth;
- when purulent-inflammatory processes appear in the area of teeth, abscesses.
What do the results mean?
Normally, anaerobes are not sown in diagnostically significant quantities.
The reason for identifying microorganisms is the presence of growth of colonies of this type of microorganisms on a nutrient medium.
Also recommended
- Sowing for aerobic and facultative anaerobic flora
- Sowing wound discharge into aerobic and facultative anaerobic flora
Who orders the study?
Dentist, periodontist, infectious disease specialist, therapist, general practitioner, otorhinolaryngologist, pediatrician.
Literature
- Fermin A Carranza, Paulo M. Camargo. The Periodontal Pocket. / Carranza's Clinical Periodontology, 2012, 127-139.
- Mirela Kolakovic, Ulrike Held, Patrick R Schmidlin, Philipp Sahrmann. An estimate of pocket closure and avoided needs of surgery after scaling and root planning with systemic antibiotics: a systematic review. / BMC Oral Health. 2014; 14:159.
How is scraping performed for bile acids?
Such a scraping also allows for analysis of bile acids. The quality of the analysis is ensured by high-tech thin layer chromatography.
For such a high-precision analysis, the material is taken in the morning. The patient should not have time to eat, drink or take medications.
Don't be afraid of this simple procedure. It consists only in the fact that in the laboratory, using an ordinary teaspoon, the plaque that has accumulated overnight is carefully removed from the tongue. Then the material is placed in a test tube, filled with ethyl alcohol and left for a while under a tightly closed lid. All components must dissolve.
Then the material is evaporated in a water bath. It should decrease in volume by half. And only one drop of the resulting extract is applied to a heated chromatographic plate. Then the plate is dried again, cooled and developed. If there are few bile acids, the line will be solid, but if their concentration is high, dense spots will form.
For treatment to be effective and quick, it is necessary to identify the disease in its early stages. If the doctor has prescribed a scraping, there is no need to postpone this procedure. It is absolutely painless and safe. Moreover, such an analysis is very informative.
Scraping from the tongue - an informative diagnostic method
In the process of diagnosing various diseases, an analysis such as tongue scraping may be prescribed. We will figure out why it is performed, what information it provides about the state of the body and how it is carried out.
When can such an analysis be prescribed?
First of all, scraping is prescribed to diagnose the oral cavity and the state of the digestive system. If pathogenic microorganisms have settled in the gastrointestinal tract, they will certainly be found on the tongue. Indications for this analysis are:
- gingivitis;
- glossitis;
- stomatitis;
- somatic pathologies;
- immunity deficiency;
- HIV.
For the analysis to be successful, you need to follow simple rules:
- It is better to take it before breakfast.
- You can take it a couple of hours after your meal.
- Before collecting material, you should not brush your teeth, rinse your mouth, or carry out antifungal treatment.
First of all, scraping is prescribed to diagnose the oral cavity and the state of the digestive system.
Important! A dense white or yellow coating on the tongue is a direct indication for scraping. Additional indications are bad breath, discomfort and burning sensation, cracks in the corners of the mouth and on the surface of the lips.
Candidiasis
Most often, scraping is prescribed if there is a suspicion of infection with Candida fungus. It is he who provokes the development of thrush. The resulting material is examined under a microscope. In this case, very thin threads are revealed, which are formed by Candida pseudomycelium.
Thrush is a common oral lesion. It can provoke gingivitis, cheilitis, stomatitis, glossitis. Very often newborns suffer from such damage.
There are many reasons for infection in newborns:
- improper hygiene of the mother who is breastfeeding;
- insufficient sterilization of pacifiers and nipples;
- prematurity;
- infection during the passage of the birth canal;
- weak immune system;
- antibiotic treatment;
- avitaminosis;
- dysbiosis. Most often, scraping is prescribed if there is a suspicion of infection with Candida fungus.
And candidiasis of the mucous membranes often appears if there are dentures in the mouth. They darken and become covered with plaque. Two forms of Candida fungus can settle in the mouth - yeast and pseudomycelium. A fairly acidic environment (pH 5.8-6.5) becomes favorable for it. In this case, the fungus becomes a source of a number of enzymes and organic acids. They are so strong that they can even corrode plastic.
Therefore, they pose a real threat to acrylic dentures. Fungal plaque is also found on the prosthetic bed. If the prosthesis is made of metal, then its owner, when infected with the Candida fungus, begins to feel a burning sensation, a metallic taste in the mouth, and complains of paresthesia and bad breath.
If the owner of the prosthesis has a fungus, the following symptoms :
The resulting material is examined under a microscope.
All this resembles mechanical damage or an allergy picture. To avoid such surprises, you need to ensure high-quality hygiene of both the oral cavity and dentures. Most often, the fungus can be found on the palate, tongue, and corners of the mouth. At the same time, the tongue begins to become coated, and there may be cracks in the corners of the mouth.
Technology for scraping for candidiasis
2 hours before the procedure you should not drink, eat, brush your teeth, rinse your mouth or take medications. To get the most informative results, it is best to take this test right in the morning, immediately after sleep. The collected material will be sent for laboratory testing. It will be carefully examined under a microscope.
Thrush very often affects newborns and infants. Here the parents are faced with the question: “How to take the material correctly?” While this does not present any difficulties for an adult, taking a scraping from a small child can sometimes be difficult.
You need to take a special spatula for the surface of the tongue or a simple cotton swab and carefully rub it across the tongue several times. The taken material must be placed in a sterile flask and sent to the laboratory. The child will not feel any discomfort.
For high-precision analysis, the material is taken in the morning.
If the scraping shows signs of Candida fungus, the doctor will diagnose “oral candidiasis.” In this case, under a microscope, cells or filaments from pseudomycelium grouped into buds will be visible.
How is scraping performed for bile acids?
Such a scraping also allows for analysis of bile acids. The quality of the analysis is ensured by high-tech thin layer chromatography.
For such a high-precision analysis, the material is taken in the morning. The patient should not have time to eat, drink or take medications.
Don't be afraid of this simple procedure. It consists only in the fact that in the laboratory, using an ordinary teaspoon, the plaque that has accumulated overnight is carefully removed from the tongue. Then the material is placed in a test tube, filled with ethyl alcohol and left for a while under a tightly closed lid. All components must dissolve.
Then the material is evaporated in a water bath. It should decrease in volume by half. And only one drop of the resulting extract is applied to a heated chromatographic plate. Then the plate is dried again, cooled and developed. If there are few bile acids, the line will be solid, but if their concentration is high, dense spots will form.
For treatment to be effective and quick, it is necessary to identify the disease in its early stages. If the doctor has prescribed a scraping, there is no need to postpone this procedure. It is absolutely painless and safe. Moreover, such an analysis is very informative.
Source: https://skzub.ru/diagnostika/soskob-s-yazyka-informativnyj-metod-diagnostiki.html