What to do if your teeth are crumbling?
Of course, it will not be possible to restore already crumbled teeth, but this process can be stopped, and only at the initial level of destruction.
Approaching the issue responsibly, instead of sweet candies, offer your baby finely chopped hard vegetables and fruits - they will help clean baby teeth and increase salivation.
Include foods containing calcium, fluorine, and phosphorus in your baby’s menu, after consulting with your pediatrician and pediatric dentist about a course of medications and vitamin complexes.
Gradually teach your child to brush his teeth in the mornings and evenings, and also talk about how important it is to rinse the mouth after meals, which does not require a special solution; it is enough to rinse with ordinary clean water.
Such prevention is also relevant for visible tooth decay. But still go to the dentist, although the child will not be entirely pleased, understand that treatment cannot be delayed.
A number of procedures will help stop tooth decay: fluoridation, silvering, fissure sealing.
For example, fluoridation on baby teeth needs to be done about once every 3 months; it is invisible, unlike silvering, although it is most effective.
Treatment methods
To select the treatment method necessary in each individual clinical case, the doctor is guided by the age of the child, the causes of tooth decay and their “status” - milk or molar, the severity of the pathology and other objective data.
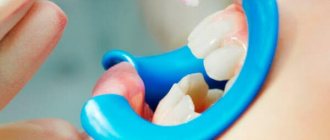
At the initial stage, when only the tooth enamel has crumbled (in whole or in part), fluoridation and remineralizing treatment can be used. The dentist treats the surface of the teeth with a special solution containing fluoride, and then applies a composition with calcium to the teeth.
It is also necessary to take a course of medications that improve the absorption of calcium and its digestibility by dental tissues. For this, vitamin and mineral complexes appropriate for the child’s age are most often used.
Here's what Dr. Komarovsky says:
If there is significant tooth decay, cosmetic or therapeutic restoration is performed. In the first case, the surface of the teeth is restored using photocomposite materials that imitate one’s own enamel and perform a protective function. This method is indicated for the initial destruction of dentin tissue.
In case of deeper damage, loosened tissues are first removed, the cleaned surface is thoroughly treated with antiseptic and remineralizing compounds, and only after this the tooth is restored using filling materials.
In addition to dental treatment, a consultation with a clinical psychologist may be indicated if the cause of the problem is an eating disorder (extremely low-calorie diets, bulimia, etc.).
How to prevent tooth decay
What to do to prevent chipping/decay of teeth:
- ensure high-quality oral hygiene;
- limit the amount of sweets in the children's diet;
- teach your child to brush their teeth and rinse their mouth after eating;
- take your child for preventive examinations to the dentist.
Expectant mothers need to eat well, take vitamins, and heal all their teeth that need it - after all, a child’s teeth are formed in the early stages of pregnancy. Vitamins that a child should receive from food:
- Group A – butter, yolk, offal, fish, fish oil;
- Group D – pork, salmon, yolk, beef liver, fish oil;
- Group E – meat by-products, nuts, seeds, green vegetables;
- Group K – liver, yolk, butter, nuts, seeds, broccoli.
As for babies, it is necessary, if possible, to eliminate night feedings and teach them to drink water at night. You can also use xylitol - containing wipes for treating teeth, if such feedings are still present.
What to do when children's baby teeth crumble?
Let's start with the fact that preventing such a serious problem is much easier than trying to fix it later. If you take care of the health of your baby’s baby teeth during pregnancy, then he shouldn’t have any difficulties cutting them out. To do this, you need to eat foods with calcium and fluoride, try not to take medications unless necessary, and do not smoke.
As soon as the baby's first teeth erupt, start cleaning the baby's mouth with chamomile decoction or a weak soda solution after each feeding. You can also use a small toothbrush and baby toothpaste and other cleaning tools. When your baby grows up, be sure to teach him how to perform oral hygiene without outside help.
To avoid bottle tooth decay, try not to feed your baby at night. After teething, you should give up the pacifier. And don’t forget to monitor your baby’s nutrition—from food he must receive all the substances necessary for a growing body. After the first baby teeth appear, fresh vegetables and fruits should be included in the child’s diet. Solid food will be beneficial, as it will strengthen and clean your teeth.
Non-carious causes
Often teeth are destroyed due to a lack of minerals in the enamel: calcium, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, which enter the body with food.
The main non-carious reasons why baby teeth crumble:
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Antiseptic for teeth and gums
Enamel hypoplasia is a serious problem in which the enamel layer on a tooth may be completely or partially absent due to abnormal processes that are formed during the formation of the rudiments of teeth. The reason is a difficult pregnancy, stress, bad habits and a lack of vitamins in the body of the expectant mother.
Visually, enamel hypoplasia looks like grooves on the enamel, through which dentin shines through. Such teeth are not protected and are more susceptible to physical and chemical stress.
Fluorosis is a disease that develops due to excess fluoride in the body. The child's teeth are covered with bright white spots. This problem is caused by drinking water with high levels of fluoride content.
Non-carious lesions also include:
- poor nutrition (lack of important substances);
- lack of fat-soluble vitamins;
- high levels of phytic acid;
- excessive sugar consumption;
- excess fluoride in the body;
- enamel defects or absence;
- heredity;
- taking antibiotics during the mother's pregnancy;
- poor oral hygiene;
- the habit of chewing on everything - pencils, pens, toys, nuts, candies;
- problems of intrauterine development;
- low quality of drinking water;
- jaw injuries resulting from a fall.
Not everything is so simple with the second reason.
Disturbances in the intrauterine development of dental tissue can be caused by the same medications taken by the mother during pregnancy or by a viral infection. Genetic predisposition can also play a role: if parents have abnormalities in the structure of teeth or their tissues, the same problem may subsequently appear in their children.
Another reason is disorders of mineral metabolism caused by deficiency or poor absorption of calcium, as well as vitamin D deficiency. Why teeth crumble in adolescents can be explained by some circumstances of early childhood. So, if a child has suffered from rickets, there is a high probability that the growth and formation of permanent teeth will be impaired.
Psychologists advise considering another potential cause of “unexplained” tooth decay. If the child did not have significant problems with his teeth, and suddenly they began to crumble, pay attention to the teenager’s diet.
Modern and excessively high demands on appearance often push a child to follow extreme diets and become the cause of the development of bulimia.
- In the first case, a critical lack of minerals and vitamins in the diet leads to the destruction of teeth that have not yet become stronger.
- In the second case, the tooth enamel crumbles in children who stimulate themselves to vomit after eating - regular exposure of teeth to aggressive stomach acids leads to such destructive consequences.
Professional treatments
To stop tooth decay, experts recommend strengthening the enamel with the help of remineralizing agents:
- fluoridation – periodic coating with solutions containing fluorine and other useful microelements;
- artificial saturation of the enamel surface with calcium and other minerals - the dentinal tubules are sealed and the density of the enamel increases;
- ozonation – destruction of bacteria in the affected tooth tissues without injuring soft tissues, helps stop destruction and cure caries at the initial stage;
- filling of dental defects;
- prosthetics – a decaying tooth is covered with a crown to isolate it from aggressive environments and stop crumbling.
- fissure sealing – sealing the chewing surface of molars with a special filling material;
We invite you to read Nimesil instructions for use
The dentist chooses the appropriate treatment method, depending on the condition of the teeth and the age of the patient.
If your teeth have already begun to decay/crumple or the first signs of caries have appeared (stains on the enamel, changes in its color), do not delay your visit to the dentist. This is when time matters!
Treatment
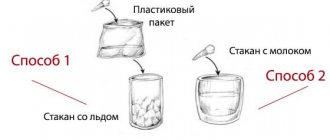
If crumbling is detected, you should immediately contact your dentist. He will ask you about your complaints in detail and then conduct a thorough examination of your oral cavity. After the examination, the doctor will prescribe treatment. There are three main methods: silver plating, fluoridation and ozonation.
Silvering
A fairly common treatment method, especially for children whose teeth have crumbled. The method is also applicable to children who are afraid of dental instruments.
A tooth that has been silvered can remain healthy and intact until new ones grow. In particular, the method helps fight caries and is effective in the initial stages of crumbling.
Effects of use:
- counteracting the growth of bacteria in the oral cavity;
- treatment of caries in the initial stages;
- helps those whose teeth are too sensitive;
- prevents carious relapse;
- if there is a filling, then silvering will have a positive effect on it.
Fluoridation
Few parents know that baby teeth differ from permanent teeth in the structure of their tissues and the presence of a loose surface. Therefore, on baby teeth, caries develops faster. In the case of fluoridation, fluoride molecules increase the density of enamel through the bonding of dentinal tubules. There are age restrictions for this method. This procedure is done only at the age of 4 years.
Fluoridation happens:
- Superficial. Strengthening varnish and gel are applied to the enamel, which perform the task of preventing the disease.
- Deep. It is used when it is necessary to preserve baby teeth until they are completely replaced. The doctor applies a sealing gel-like liquid to the enamel. It penetrates deep into dense tissues and strengthens them.
- Manual. The dentist makes a composition of copper and calcium hydroxide. The resulting liquid is applied to the teeth and then washed off with water.
The advantages of this treatment:
- enamel density improves several times;
- counteracts caries;
- on average, several procedures per year are enough;
- has a positive effect even in the later stages of caries;
- affects the decrease in sensitivity.
Ozonation
This method plays more of a preventive role than a therapeutic one. Being a fairly strong oxidizing agent, ozone penetrates into the cracks inside the oral cavity without damaging soft tissues. On its way, it destroys harmful bacteria and also sterilizes the surface.
What can be achieved with this method:
- stopping the deformation of crumbling teeth;
- counteraction to caries;
- cleansing the oral cavity from microbes.
Children's teeth can be protected from problems if you regularly take care of them and eat a balanced diet. If crumbling does begin, the available treatment methods are simple, do not require surgical intervention, and their implementation does not take much time.
Manifestation of dental hypoplasia
Hypoplasia can be systemic or local. In the first case, the entire dentition is affected (the enamel of both milk and permanent teeth is damaged), in the second, one or more permanent teeth are damaged. Local hypoplasia is a consequence of mechanical trauma or an inflammatory process.
Clinical picture of hypoplasia:
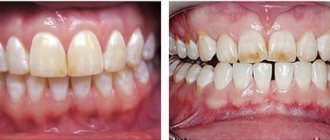
- The appearance of white spots on the child’s teeth. Such defects are white (less often yellowish) appear on the outside of the teeth, have a clear contour, and do not cause pain.
- Underdevelopment of enamel. Grooves or depressions appear on the teeth. Pain is usually not noted, but aesthetic defects are very noticeable.
- Lack of enamel (aplasia). A rare manifestation of the disease, the most severe form. The enamel may partially or completely peel off from the teeth, exposing dentin. In such cases, a painful reaction to thermal and chemical irritants is observed.
What affects the destruction of a child’s permanent teeth?
Many parents are interested in what affects the rapid destruction of permanent teeth . Let's talk today about what causes a child's permanent teeth to quickly become affected by caries and why they erupt with already altered, unhealthy enamel. The formation of the rudiments of permanent teeth begins from 5 months of pregnancy and continues until the child is 5 years old, and the mineralization of the rudiments of permanent teeth is completed by the age of 8 years of the child’s life. The first years of a child's life are very important in the formation of healthy permanent teeth. If a child is often sick during this period, does not receive enough microelements and vitamins from the diet, or takes a lot of antibiotics, all this will affect the health of permanent teeth. Taking antibiotics and especially tetracycline antibiotics (used in the treatment of intestinal infections) affects the formation of enamel and the child’s erupted teeth will have altered enamel. Depending on the degree of damage, the enamel may only change in color from light gray to dark yellow.
Or with a changed shape of the crown of the teeth.
We call these teeth “tetracycline teeth.” The severity of hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of tooth enamel depends on the severity of the disease, and the localization of hypoplasia on the crown of the tooth largely depends on the age at which the child suffered the disease.
During this period, the content of the microelement Fluorine in the soil and drinking water of the region where the baby was born and lives also has a great influence.
Fluoride is a microelement that, when insufficiently supplied to a child’s body, causes dental caries, and when in excess, causes the disease fluorosis.
The optimal fluoride concentration in water is considered to be 1-1.2 mg/l; if this concentration is exceeded, especially during the period of formation and mineralization of permanent teeth, the child develops fluorosis. The placenta delays the excessive supply of fluoride to the fetus, so fluorosis of baby teeth does not occur.
Symmetrical teeth are affected by fluorosis and the degree of damage depends on the concentration of fluoride in the water and the duration of the child’s consumption of such water (length of residence in an area with a high fluoride content).
The extent of the damage may range from small milky white spots or streaks on the enamel
Up to pronounced pigmentation in combination with structural disorders of the hard tissues of the tooth. The crown of the tooth is deformed, the enamel is easily erased, chipped, the tooth can be worn down to the edge of the gum.
All we have talked about now are systemic lesions. But there may also be local lesions and deformations of the crowns of the teeth associated with inflammatory processes in the area of the roots of baby teeth or injuries to baby teeth. But we'll talk about this next time
Tatiana Vedernikova
I also recommend
And again about silvering teeth...
Aphthous stomatitis (ARAS)
Acute periodontitis
About toothache with complicated...
Share link:
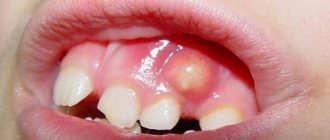
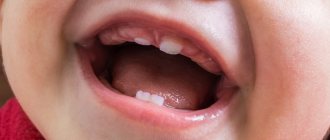
Symptoms of damage to baby teeth
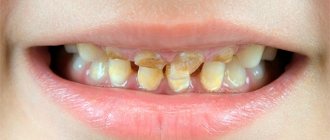
Periodic examinations carried out by parents may reveal the destruction of the crown of the tooth. The most common signs when a baby is developing a bite are:
- the appearance of depressions in the enamel,
- teeth look like they've been eaten
- the presence of chips and cracks on the incisors, as a result of which the edge becomes uneven,
- carious cavities are noticeable,
- if you eat cold or hot food or sour (sweet) dishes, the baby complains of pain,
- the presence of black or white spots on the enamel (enamel demineralization), but crumbling has not yet been noticed.
What to do
The condition of the oral cavity must be carefully monitored from the age of one.
If you notice any defects, you should seek dental help as soon as possible. It would also be a good idea to consult a pediatrician. Perhaps your child has a congenital endocrine pathology, a metabolic disorder, or a genetic predisposition to tooth decay. Timely treatment ensures the safety of not only baby teeth, but also permanent teeth in the future.
Advice: do not hesitate to ask questions to your doctor - this way you will understand how competent he is in these matters.
After 2 years, visit your dentist regularly, at least once every six months, for a preventive examination. After two years, crumbling is caused by infections of the oral cavity or congenital anomalies of the mandibular joint, as well as poor-quality water.
From this video you will learn how to easily brush your child's teeth:
What to do to stop the destruction
The destruction of dentin and enamel at an early age causes the child not only inconvenience and pain, but also causes a number of negative phenomena that will affect the child’s future life. Without treatment, the molars, which are in their infancy, can become infected and the child will have serious problems during the growth of permanent teeth.
Calcium deficiency
One of the main signs that a child does not have enough calcium in the body is his irresistible desire to eat chalk and chew plaster. If not every child can get to the chalk (it simply may not be in the house), then every child has plaster almost at hand. Don't scold your baby.
We suggest you read: Why does a tooth hurt when you press on it?
Bottle caries
The terrible diagnosis “bottle caries” is a sign of excessively long use of a bottle and pacifier or sippy cup. The presence of foreign objects in the mouth disrupts the correct formation of the bite, which can cause teeth to begin to decay faster.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to find out what caused the destruction of baby teeth. Only on this basis is the choice of treatment strategy made.
If the cause of tooth decay is heredity, then complete healing is impossible. You can only respond to the problem by providing symptomatic treatment.
If you have a problem such as crumbling baby teeth, you need to regularly take your child to the dentist and choose the right menu for him. These measures will slow down the destruction of enamel. A postponed visit and delay in solving the problem will lead to the development of serious pathologies in the child.
The doctor will treat all areas of caries and close all cracks in the enamel (including microcracks). If teeth deteriorate as a result of poor hygiene or poor nutrition, then changing the menu and regular (2 times a day) teeth brushing will partially solve the problem.
Preventive measures in case of dental problems include:
- keeping your baby in the fresh air (sunlight will help reduce vitamin D deficiency in the body), which will strengthen bone tissue,
- regular inclusion in the menu of dishes high in calcium and vitamins (fish, cottage cheese, fruits, vegetables, cheeses, etc.),
- closing fissures (microscopic grooves located on the enamel surfaces of molars and premolars) with special sealants,
- silvering of enamel, which allows to neutralize pathogenic bacteria and slow down the development of caries,
- fluoridation, which helps saturate the enamel of baby teeth with fluoride.
Silvering helps well in the early stages, but in the presence of advanced caries, this procedure is not recommended.