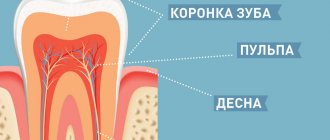
Could vomiting be caused by teething?
The process of teeth growth reduces the body's protective properties, and vomiting appears in the baby. Let's look at the possible reasons:
- Overfeeding.
- Disease.
- Heat.
- Profuse salivation.
In the absence of appetite, parents try to force feed the child; the body does not accept food, pushing it back with a gag reflex.
The baby fell ill with an infectious cold due to a weakened immune system, which resulted in vomiting.
Because of the teeth, excessive salivation occurs, the baby does not have time to swallow, saliva enters the lungs, and the body tries to remove it through vomiting.
When cutting, an increase in body temperature may occur, and uncomfortable conditions in the body cause vomiting.
He cries a lot from the pain, gasping for air, which results in vomiting.
Nausea is allowed up to three times a day. If there are no other symptoms, it is not necessary to call a doctor. Once you are sure that teeth are causing nausea, keep a close eye on your baby. Don't leave him alone indoors. Without supervision, he will choke on vomit and saliva. In a dream, the baby may choke on saliva. It is recommended to place it on its side and place a pillow under the back to prevent it from rolling off or turning over.
Vomiting is an unpleasant sensation; the taste of vomit remains in the mouth and is repeated. The parent rinses the baby's mouth with warm boiled water using gauze and a napkin.
You need to drink boiled water after vomiting to restore the water-salt balance of the fragile body.
Do not force the baby to eat, the appetite will resume after the body is restored, he will ask to eat.
Vomiting usually occurs when there are problems with the digestive tract, for example, due to toxic substances or infectious agents entering the stomach. Could vomiting be a harmless sign associated with teething? How to make sure that vomiting in a teething baby does not indicate an intestinal infection or other dangerous pathology and how to help the baby?
There is no direct connection between the appearance of vomiting and the process of teething in a baby, however, during the period when a child’s new teeth come out, there are many factors that contribute to the occurrence of vomiting. This happens especially often in situations where several teeth come out at the same time.
Teething is a lot of stress for a baby. Discomfort in the oral cavity leads to physical fatigue and emotional stress in the child. He sleeps poorly, eats little and is constantly capricious. Many parents, having noticed changes in the behavior of their baby, begin to worry, but most often their fears are in vain.
In the process of eruption of primary canines and molars, immunity decreases, and accordingly, the risk of infectious diseases increases. If a child has a fever, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, this condition may indicate the development of an intestinal infection. What manifestations are a natural reaction of the child’s body to teething, and when are we talking about a pathology that requires immediate treatment?
- The gag reflex in a teething baby becomes more pronounced and can be irritated by excess saliva that is secreted in the baby's mouth.
- Due to the child’s constant desire to rub his gums and chew on surrounding objects, the baby can introduce an infection into the digestive tract. This is also facilitated by decreased immunity.
- When a baby cuts a tooth, its nutrition may be disrupted, which can also provoke vomiting.
- If pain during teething bothers the baby very much and the baby constantly cries, he may swallow a lot of air, which will cause vomiting.
- Teething is often accompanied by high fever, which often results in vomiting.
- Attacks of vomiting in a teething baby can be triggered by force-feeding the child.
Can you vomit when teething?
The process of teeth growth reduces the body's protective properties, and vomiting appears in the baby. Let's look at the possible reasons:
- Overfeeding.
- Disease.
- Heat.
- Profuse salivation.
In the absence of appetite, parents try to force feed the child; the body does not accept food, pushing it back with a gag reflex.
The baby fell ill with an infectious cold due to a weakened immune system, which resulted in vomiting.
Because of the teeth, excessive salivation occurs, the baby does not have time to swallow, saliva enters the lungs, and the body tries to remove it through vomiting.
When cutting, an increase in body temperature may occur, and uncomfortable conditions in the body cause vomiting.
He cries a lot from the pain, gasping for air, which results in vomiting.
In the absence of disease, vomiting during teething occurs up to 3 times a day. If it is more, you should call the pediatrician, perhaps he is ill. The diagnosis will be made by a qualified specialist, prescribing appropriate treatment.
Nausea is allowed up to three times a day. If there are no other symptoms, it is not necessary to call a doctor. Once you are sure that teeth are causing nausea, keep a close eye on your baby. Don't leave him alone indoors. Without supervision, he will choke on vomit and saliva. In a dream, the baby may choke on saliva. It is recommended to place it on its side and place a pillow under the back to prevent it from rolling off or turning over.
Vomiting is an unpleasant sensation; the taste of vomit remains in the mouth and is repeated. The parent rinses the baby's mouth with warm boiled water using gauze and a napkin.
You need to drink boiled water after vomiting to restore the water-salt balance of the fragile body.
Do not force the baby to eat, the appetite will resume after the body is restored, he will ask to eat.
Why does a child vomit on his teeth?
The following factors can provoke vomiting:
- During teething, salivation increases. Due to the large accumulation of saliva in the mouth, the baby may choke.
- When a child is bothered by severe itching and irritation of the gums, he loses his appetite. Force-feeding or overeating leads to digestive disorders.
- Constant discomfort affects the psychological state of the baby, he becomes irritable. When a child cries for a long time, air is swallowed, which enters the digestive tract.
- An increase in temperature triggers the immune system. In an effort to protect the body from damage by toxins, harmful substances are released.
Why does a baby have a gag reflex during teething?
In many children, the appearance of the first baby teeth is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the gums;
- itching (so the baby puts objects around him in his mouth);
- salivation;
- gastrointestinal disorder;
- runny nose;
- loss of appetite;
- poor sleep, irritability and fatigue.
Can vomiting occur during teething? The answer to this question is clear - when a baby is teething, he may feel sick and vomit, but such a reaction is quite rare. This is usually preceded by a cough - due to excessive salivation, excess saliva accumulates in the baby’s nasopharynx and throat.
Teeth begin to erupt at 6-8 months of age. Six-month-old babies spend a lot of time in a horizontal position, which causes coughing and regurgitation.
The gag reflex during teething is considered normal and therefore does not require additional therapy. As a rule, unpleasant symptoms disappear within 2-3 days. If the child continues to vomit, it may be a secondary infection. In such a situation, it is necessary to urgently show him to a doctor.
Increased salivation
To allow the tooth to break through the gum tissue, the immune system temporarily weakens its defenses. This is why many babies show cold symptoms during this period. The gums swell, the temperature rises, and the oral mucosa becomes hyperemic. The baby experiences discomfort, refuses to eat and is constantly capricious. The receptors in the oral cavity are irritated, causing increased secretion of the salivary glands. Increased salivation helps soften the gum tissue a little.
How to help a child?
If the vomiting is one-time and the baby has no other symptoms of illness, you should simply monitor the baby, ensuring that he is in such a position that if vomiting recurs, the contents of the digestive tract cannot enter the respiratory organs. But the best option would still be to consult a pediatrician, so that the fact of the baby’s teething does not prevent timely diagnosis of the disease, a symptom of which may be vomiting.
- If the body temperature is high, you need to give the baby the antipyretic drug Ibufen and Paracetamol.
- To reduce pain when teeth begin to cut, doctors advise smearing the gums with special pain-relieving ointments.
- To speed up the growth process, rubberized chewing toys are given. First wash in water with baby soap, then rinse with boiling water.
- You cannot stop vomiting with medications - it will harm the child’s body.
- After vomiting, the baby is given fluids.
Differentiating “dental vomiting” from other diseases
A distinctive feature is the amount and composition of vomit. While waiting for a tooth, a child may vomit several times a day.
The amount of masses is small, with the absence of bile, mucus and blood. The temperature in this state rarely exceeds 37°C.
When an infection occurs, the urge to vomit often bothers the baby; the number of masses differs in their abundance and the presence of bile. The process of defecation is painful, the stool is liquid, often mixed with mucus. The toddler's belly is hard and swollen. Temperature can vary from 38 to 40°C.
It is very simple to distinguish vomiting and teeth from ordinary regurgitation:
- vomit consists mainly of leftover food from the child;
- regurgitation in infants is observed after each feeding, the urge to vomit, in turn, is not associated with food intake;
- the amount of masses during regurgitation is much less.
If vomiting occurs during teething, then the baby usually has other distinctive signs:
- A wet cough begins due to the accumulation of saliva. At night, it is recommended to place the child's head on a hill to improve the discharge of secretions.
- A runny nose does not require special treatment; it is enough to rinse the nose with saline solution and remove the snot with a baby aspirator. The nozzles should be transparent and colorless.
- The temperature should not exceed 38°C.
- Abnormal stool. The baby may experience constipation and diarrhea. This is due to the immaturity of the baby’s gastrointestinal tract; at this age, the body is not yet able to cope with the imposed load.
The presence of vomiting in babies should not be observed for more than 3 days. If after this time the baby’s condition does not improve, then you should consult a doctor. Associated symptoms - cough, runny nose and moderately loose stools - may persist for up to 7 days.
It should be remembered that frequent vomiting, high fever and bowel movements more than 7 times a day are characteristic of rotavirus infection. Green color of stool and a thermometer reading above 39°C indicate an intestinal infection. And the presence of yellow-green nasal discharge, weakness and high temperature indicate ARVI.
Popular fears of parents during teething
To prevent infection from entering the child’s body during teething, it is necessary:
- keep the baby's hands clean;
- clean teethers and toys before offering them to your little one;
- vests and bibs must be ironed on both sides with a hot iron before use, as children very often put them in their mouths;
- During this period, the child’s contact with pets should be excluded.
You can prevent vomiting by following these rules:
- You need to feed your baby in small portions as required. The consistency of the food should be liquid or medium thick. Lumps should be avoided.
- It is necessary to periodically blot accumulated saliva with a napkin. If excess fluid is not removed, the child may choke and vomit. It is also necessary to treat the corners of the mouth to prevent irritation of the baby’s delicate skin.
We suggest you read: Inflammation of the apex of the tooth root, treatment with antibiotics. Inflammation of the tooth root
Many parents are interested in how to behave when their baby is teething. Answers to pressing questions will help you find solutions in difficult situations.
What to do if a child starts vomiting?
In this case, it is necessary to lift the baby, ensuring that the masses are removed. After completing the process, the baby must be held in an upright position so that the baby does not choke on the remaining saliva. It is for this reason that the toddler is placed on his side during sleep.
Is it possible to introduce complementary foods during this period?
It is better to limit yourself to eating familiar dishes for a while. New products can aggravate the baby's condition.
Do I need to supplement if my baby vomits while eating?
After vomiting, the child can be offered a few sips of water to wash away the remaining mass. It is better to postpone eating a little. Children usually do not want to eat after vomiting, and force-feeding will lead to the urge to vomit again.
- Special pain-relieving gels will help ease the condition of a teething baby. You can also wipe the inflamed gums with a swab containing chamomile infusion.
- Since the baby produces a lot of saliva, you need to wipe his mouth with a napkin in time so that saliva does not accumulate in large quantities in the mouth.
- To prevent infectious agents from getting into your baby’s mouth, let your baby chew on clean teethers and keep your baby’s hands clean.
- Do not force your child to eat, as this may lead to vomiting. Offer your baby food in small portions and preferably pureed.
specialist with medical education
auto RU
Prepared with the support of
medical
You can rate the article here
Share this article with your friends if you liked it
My weirdo had a temperature of 38.7 for two days. They knocked it down with Paracetamol and Ibufen. On the third day he was lethargic, didn’t eat anything all day, had seizures every 15-20 minutes, kicked his legs, cried and bent over. Then it let go and he fell asleep. Towards evening I drank a fennel decoction and immediately began to come to life. And later they fed him porridge, and after half an hour he gave up half of it in a fountain through his mouth and nose.
A little later they gave him dill water to drink, and he also vomited half of it. And now he sleeps for half an hour or an hour, then wakes up with his forehead, turns over the entire sheet in his bed and cries. It rears up straight! I take him in my arms (I am now 6 months pregnant), and he starts to vomit. I'm afraid it might be an intestinal infection!
I think maybe I’m just pressing on his tummy with my belly.. because of this.. Because in my husband’s arms he immediately calms down, but in mine he’s all squirming. We went to the pediatricians, and all three doctors unanimously said: don’t be afraid, it’s just the teeth. And they said that when teeth are cutting, they need help, they prescribed vitamins, active calcium, Vibrukol suppositories, Dentokid tablets and plenty of warm drinks. Decoctions of dill or fennel. I hope it helps. And to you all, patience girls and health to your children!!
My daughter is 10 months old and her top 4 teeth are coming out at once. And we had vomiting once each, for the second day already, the breast sucked for a long time and after a while the return. I had a high temperature for three days, in addition to this I had diarrhea (1-2 times a day), but it was very liquid. Refuses to eat. I don’t know when her torment will end.
Apparently we still have vomit on our teeth. I gave her a load, we sleep.
I was really scared at first. I hope that really everything is connected only with teething.
Pain in a child during tooth growth - when a symptom appears, a painkiller is given. The spasms will go away, the child will eat and sleep well, and his health will improve.
Example: one tooth, not an incisor, has come out - the parents begin to worry. Komarovsky warns that not all children have an incisor that comes out first; this is not a pathology, but a characteristic of the body.
Time of eruption of the first tooth - most parents are convinced that the appearance of the first tooth occurs no earlier than 6 months. If it doesn’t come out on time, there is a panic about the appearance of rickets. The tooth may appear later in a healthy baby.
When there is creaking, parents suspect bruxism. The disease appears in children and adolescents; infants have itchy gums.
The eruption of fangs is accompanied by fever and vomiting; after the teeth appear, the symptoms disappear without a trace. To get rid of it quickly, it is recommended to massage the gums and gently move your index finger along the gums towards the emerging tooth.
- Teething
- What does gum look like?
- Temperature
- Diarrhea
- Vomit
- Drugs
- Nurofen
- Gels
Purpose and method of treatment
Constant nausea brings discomfort to the baby. His mood worsens and he may become moody and lethargic. The main danger of vomiting is dehydration of the baby's body. Especially if the urge occurs frequently and with a large amount of vomit.
Treatment is aimed at alleviating the child's condition and preventing fluid loss. Restoring the water-salt balance involves feeding the baby an alkaline drink or Regidron.
If the urge is not associated with an infectious carrier, then no special therapy is required. The baby's condition should return to normal within three days. If the baby does not get better, the frequency and amount of vomit increases, then you need to consult a pediatrician.
You can alleviate the child’s condition with the help of special teethers and gum massage. Massage problem areas using a fingertip. Light circular movements help relieve itching and normalize blood circulation in the oral cavity. To eliminate inflammation of the gums, the crumbs are treated with chamomile decoction.
If the baby is painfully tolerant of teething and refuses to eat, the doctor may prescribe special cooling gels that are applied to the affected area.
Helping your child when vomiting
During the period of teething, it is necessary to especially closely monitor the child’s health and respond in a timely manner to the appearance of any warning symptoms. To identify the cause of fever, bowel dysfunction or vomiting during teething in children, the time of their appearance, duration and severity are of great importance. This information will help the doctor correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Excessive vomiting, and especially in combination with, is very dangerous for a child, since as a result, along with vomit and feces, his body loses a lot of fluid, which is fraught with dehydration and disruption of the water-salt balance. In the absence of timely assistance, the baby may experience complications from the nervous system and vital organs.
To alleviate the baby’s condition during the teething period, it is recommended:
- give your baby antipyretic drugs in the form of syrups based on paracetamol or ibuprofen when the temperature rises above 38°C;
- lubricate the gums with cooling and pain-relieving ointments or gels designed specifically for children;
- increase the number of breastfeedings for breastfed babies;
- offer the child a special chewing rod to facilitate teething and relieve discomfort in the mouth;
- massage the gums, making circular movements with your finger in the area of the erupting tooth;
- in case of vomiting and diarrhea, increase the amount of liquid consumed by the baby to replenish the water lost by the body;
- make compresses with chamomile for inflammation and redness of the gums.
Any medications can be given to the baby only after agreement with the pediatrician. If the cause of vomiting or other symptoms is only teething, then there is no need for special treatment. The child’s condition will normalize on its own after 2-3 days, when a new tooth appears in the mouth.
Important: During teething, babies especially need maternal care, warmth and attention.
Teething in a baby provokes changes in the toddler’s mood and well-being; moodiness, nausea, vomiting, etc. are frequent companions of this period.
This can be either a physiological norm for a child or the presence of an infection in the baby’s body. This is the most important point - to understand when a child is vomiting on his teeth, and when this is a sign of illness.
Nausea and vomiting are not the only ones that happen. You can distinguish gagging, which occurs, for example, during ARVI, from dental nausea by the presence of accompanying signs that can occur several months before the visual recognition of a tooth in the oral cavity:
- restlessness and moodiness of the child - the baby may experience itching and pain at the same time, which leads to changes in the baby’s mood;
- increased salivation, and the little one begins to put into his mouth everything that comes to hand.
When teething, the child's immunity weakens, which makes him vulnerable to infectious carriers. Intestinal disorders may be involved in the process.
When to worry
Adults should take steps to help with symptoms:
- The body temperature on the teeth rose above 38 degrees and lasted for a day. A child could catch a cold while walking outside.
- The baby refuses to eat or drink milk during the day. It happens against the background of teeth growth that stomatitis can be infected from a dirty toy or an unsterile pacifier.
- Cutting pain in the abdomen, gas.
You need to see a doctor for help and treat based on the diagnosis.
What to feed your child during this period
The period during teething is a reason to change the diet until the pain passes and the tooth comes out. Increased sensitivity of the body provokes unwanted reactions. Recommended:
- Feed thin cereals instead of thick ones.
- Refuse juices, offer compotes.
- Do not overload the body with heavy food.
- In a year, vegetable purees will come in handy.
- Milk and curd products will strengthen teeth during growth.
If the mother does not have breast milk, the infants are given special milk formulas that are age-appropriate. They contain a set of nutrients; when the baby refuses the offered complementary foods, they are replaced. These tips will help you get through difficult times with ease without losing vitamins and microelements that are beneficial to your body.
When a child is in the process of growing teeth, and there is no vomiting, diarrhea, or fever, preference is given to cottage cheese and dairy products. They contain a large amount of calcium necessary for the proper formation of teeth.
Preventive measures against vomiting and diarrhea during teething include observing the rules of personal hygiene and quality nutrition. Food for the child should be thermally processed, fresh fruits and vegetables should be well washed. All products must be fresh. If the baby is breastfed, the mother should follow a diet.
To prevent the development of acute intestinal infection, the child’s hands and toys should always be clean. You should strengthen your baby’s immunity, ventilate the room more often, walk more in the fresh air, and get a massage. The closeness of a loving mother and a favorable atmosphere in the home also contribute to the health of the child.
What to do with diarrhea
If your baby has diarrhea while teeth are growing, complementary foods in the form of purees and cottage cheese should be avoided for a short time. Rice porridge cooked in water will strengthen the stool. Soaked crackers and dryers will help you refresh yourself. The milk mixture thins the stool - during severe attacks, replace it with boiled water with added sugar. Sweet-salty solutions will help restore the water-salt balance of the body.
We suggest you read: Treatment of ulcers on the oral mucosa - ProfiMed
Doctors recommend giving a child bifidobacteria for indigestion to populate the body with beneficial microflora.
- Infection of the body with pathogenic microflora.
- An infectious disease associated with the growth of fangs.
- Digestive disorders due to poor nutrition.
You can avoid infectious diseases by walking outside, away from sick children. If the source of the disease is at home, you need to allocate a separate room for the baby and limit the access of the infectious patient.
If a child becomes ill, it is necessary to seek medical help.
Teething is a lot of stress for a baby. Discomfort in the oral cavity leads to physical fatigue and emotional stress in the child. He sleeps poorly, eats little and is constantly capricious. Many parents, having noticed changes in the behavior of their baby, begin to worry, but most often their fears are in vain.
In the process of eruption of primary canines and molars, immunity decreases, and accordingly, the risk of infectious diseases increases. If a child has a fever, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, this condition may indicate the development of an intestinal infection. What manifestations are a natural reaction of the child’s body to teething, and when are we talking about a pathology that requires immediate treatment?
How to alleviate the baby's condition?
If your baby refuses to sleep, use proven ways to lull him to sleep:
- Rocking him in his arms, pressing his head to his chest, he hears his mother's heartbeat. The rhythm of a heartbeat is great for calming babies.
- Place them on your chest and fall asleep together. The baby hears the beating of the heart, the breath of the parent lulls the baby to sleep.
- Children love to listen to their mother's voice; when rocked to sleep, they quietly hum a lullaby.
The methods work flawlessly, the parent and the child will calmly go through a difficult, inevitable period of life.
As a rule, vomiting during teething in children occurs due to dysfunction of the digestive tract, for example, as a result of toxic substances or microorganisms entering the child’s stomach that contribute to the development of infection. So, can vomiting during teething be just a feature of this period in children, or is it dangerous for the health of babies? How to make sure that a child is vomiting not due to an infection in the intestines or the development of some other dangerous disease?
As you know, the period when a baby is teething brings a lot of inconvenience and anxiety to both the child and his parents and loved ones. Of course, there are exceptional cases when the child’s teething are just another reason for joy and are not characterized by the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms.
However, for the vast majority of children, in practice, the entire process occurs against the background of a painful state and whims. Often during this period, babies’ stool becomes liquid and their body temperature rises. The child suffers from vomiting, and sometimes the baby has a cough and redness of the throat. What worries parents most in this situation is vomiting and fever.
If the baby has vomited once and there are no other signs indicating the possible development of pathology, then it is enough to simply monitor him in order to prevent the contents of the digestive tract from entering the respiratory tract if repeated. However, in order to make sure that everything is in order and to exclude possible pathologies, it is still necessary to show the child to the pediatrician. Parents can help their baby in the following ways:
- To relieve pain, you can purchase special gels that have an analgesic effect. It is possible to wipe the baby's gums with a swab dipped in chamomile decoction.
- A mother or other relative, after putting on a fingertip, can massage the child’s gums in a circular motion, which will help alleviate his condition.
- Due to intense salivation, it is necessary to wipe the child’s mouth with a napkin in time to avoid the accumulation of large amounts of saliva in the oral cavity. It is recommended to regularly wash the baby's nasal opening and treat the chin and neck with special products. This will help relieve skin irritation caused by intense salivation.
- To exclude the possibility of infection entering the baby’s body, it is necessary to give the child a clean teether (changing it periodically), and regularly monitor the cleanliness of the baby’s hands.
- Do not force the child to consume food, otherwise this may also lead to vomiting.
Unfortunately, such an important moment in a child’s life as teething is accompanied by a number of unpleasant moments. During this period, the child usually has disturbed sleep, is restless and suffers from painful sensations in the gums and fever. During this period, some of the parents encounter such an unpleasant and worrying condition as vomiting. However, this is why parents are needed, to be there and help at such a difficult moment for the baby.
When children experience one-time vomiting or diarrhea, but there are no other symptoms indicating the development of pathology, parents should monitor the baby’s condition. If his behavior causes concern, it is better to call a doctor. Acute intestinal disorders in children under 3 years of age often lead to complications.
To make it easier for the child to endure the painful process, mothers and fathers should adhere to the following recommendations:
- put the baby to sleep on a small pillow so that excess saliva does not get into the throat and nasopharynx;
- refuse to introduce new complementary foods;
- do not force feed;
- monitor oral hygiene;
- use special teethers to prevent the child from putting foreign objects in his mouth and sucking his fingers;
- refuse self-medication (taking medications before the doctor arrives may distort the overall clinical picture).
First aid
To relieve pain, the pediatrician can prescribe anesthetic gels (Kalgel, Kamistad, Cholisal, etc.). Also, during teething, homeopathic remedies in the form of suppositories, syrup and tablets are widely used. At home, parents can alleviate the baby’s condition by rubbing the inflamed areas of the mucous membrane with chamomile decoction. If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, the child should be given antipyretic drugs.
Massage is effective during teething. To do this, the mother needs to put a fingertip on her finger and massage the swollen gums with soft circular movements.
To avoid rashes on the skin around the mouth due to excessive salivation, it is necessary to regularly wipe the baby's mouth with a napkin. It is advisable to apply baby cream to your face and neck.
According to the famous pediatrician, teething is a natural process that does not need to be interfered with. All children go through this. Komarovsky believes that the growing tooth does not bother the baby. The doctor recommends that parents completely stop taking medications during teething, unless there is a high fever. The doctor advises mothers to spend more time with their children - take walks more often, play fun, non-tiring games.
If there is increased salivation, frequent diarrhea or vomiting, the infant should be put to the breast more often, and bottle-fed children should be offered more liquid. These steps will help prevent dehydration.
Experts do not recommend introducing new foods into the diet of children over six months of age during teething. If possible, you should avoid fresh juices, fruits and dairy products. Preference should be given to boiled vegetables.
The baby's menu may include pureed vegetables with a high starch content, vegetable soups, and cereals. You can also add jelly to your diet - the drink coats the walls of the stomach, relieving irritation.
First aid
What to do when your baby is teething
If your baby refuses to sleep, use proven ways to lull him to sleep:
- Rocking him in his arms, pressing his head to his chest, he hears his mother's heartbeat. The rhythm of a heartbeat is great for calming babies.
- Place them on your chest and fall asleep together. The baby hears the beating of the heart, the breath of the parent lulls the baby to sleep.
- Children love to listen to their mother's voice; when rocked to sleep, they quietly hum a lullaby.
The methods work flawlessly, the parent and the child will calmly go through a difficult, inevitable period of life.
When children experience one-time vomiting or diarrhea, but there are no other symptoms indicating the development of pathology, parents should monitor the baby’s condition. If his behavior causes concern, it is better to call a doctor. Acute intestinal disorders in children under 3 years of age often lead to complications.
To make it easier for the child to endure the painful process, mothers and fathers should adhere to the following recommendations:
- put the baby to sleep on a small pillow so that excess saliva does not get into the throat and nasopharynx;
- refuse to introduce new complementary foods;
- do not force feed;
- monitor oral hygiene;
- use special teethers to prevent the child from putting foreign objects in his mouth and sucking his fingers;
- refuse self-medication (taking medications before the doctor arrives may distort the overall clinical picture).
First aid
To relieve pain, the pediatrician can prescribe anesthetic gels (Kalgel, Kamistad, Cholisal, etc.). Also, during teething, homeopathic remedies in the form of suppositories, syrup and tablets are widely used. At home, parents can alleviate the baby’s condition by rubbing the inflamed areas of the mucous membrane with chamomile decoction. If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, the child should be given antipyretic drugs.
Massage is effective during teething. To do this, the mother needs to put a fingertip on her finger and massage the swollen gums with soft circular movements.
To avoid rashes on the skin around the mouth due to excessive salivation, it is necessary to regularly wipe the baby's mouth with a napkin. It is advisable to apply baby cream to your face and neck.
According to the famous pediatrician, teething is a natural process that does not need to be interfered with. All children go through this. Komarovsky believes that the growing tooth does not bother the baby. The doctor recommends that parents completely stop taking medications during teething, unless there is a high fever. The doctor advises mothers to spend more time with their children - take walks more often, play fun, non-tiring games.
If there is increased salivation, frequent diarrhea or vomiting, the infant should be put to the breast more often, and bottle-fed children should be offered more liquid. These steps will help prevent dehydration.
Experts do not recommend introducing new foods into the diet of children over six months of age during teething. If possible, you should avoid fresh juices, fruits and dairy products. Preference should be given to boiled vegetables.
The baby's menu may include pureed vegetables with a high starch content, vegetable soups, and cereals. You can also add jelly to your diet - the drink coats the walls of the stomach, relieving irritation.
As a rule, vomiting during teething in children occurs due to dysfunction of the digestive tract, for example, as a result of toxic substances or microorganisms entering the child’s stomach that contribute to the development of infection. So, can vomiting during teething be just a feature of this period in children, or is it dangerous for the health of babies? How to make sure that a child is vomiting not due to an infection in the intestines or the development of some other dangerous disease?
As you know, the period when a baby is teething brings a lot of inconvenience and anxiety to both the child and his parents and loved ones. Of course, there are exceptional cases when the child’s teething are just another reason for joy and are not characterized by the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms.
However, for the vast majority of children, in practice, the entire process occurs against the background of a painful state and whims. Often during this period, babies’ stool becomes liquid and their body temperature rises. The child suffers from vomiting, and sometimes the baby has a cough and redness of the throat. What worries parents most in this situation is vomiting and fever.
If the baby has vomited once and there are no other signs indicating the possible development of pathology, then it is enough to simply monitor him in order to prevent the contents of the digestive tract from entering the respiratory tract if repeated. However, in order to make sure that everything is in order and to exclude possible pathologies, it is still necessary to show the child to the pediatrician. Parents can help their baby in the following ways:
- To relieve pain, you can purchase special gels that have an analgesic effect. It is possible to wipe the baby's gums with a swab dipped in chamomile decoction.
- A mother or other relative, after putting on a fingertip, can massage the child’s gums in a circular motion, which will help alleviate his condition.
- Due to intense salivation, it is necessary to wipe the child’s mouth with a napkin in time to avoid the accumulation of large amounts of saliva in the oral cavity. It is recommended to regularly wash the baby's nasal opening and treat the chin and neck with special products. This will help relieve skin irritation caused by intense salivation.
- To exclude the possibility of infection entering the baby’s body, it is necessary to give the child a clean teether (changing it periodically), and regularly monitor the cleanliness of the baby’s hands.
- Do not force the child to consume food, otherwise this may also lead to vomiting.
We suggest you read: Why does a child’s breath smell like iodine?
Unfortunately, such an important moment in a child’s life as teething is accompanied by a number of unpleasant moments. During this period, the child usually has disturbed sleep, is restless and suffers from painful sensations in the gums and fever. During this period, some of the parents encounter such an unpleasant and worrying condition as vomiting. However, this is why parents are needed, to be there and help at such a difficult moment for the baby.
First aid
Many parents are at a loss and don’t know what to do when their child begins to feel very sick. The well-being and safety of your baby depends on your behavior:
- during an attack, turn the baby face down, holding the body in weight;
- make sure that the child does not choke on vomit; to do this, he should not be on his back for a minute;
- after an attack, remove vomit from the mouth and nose using a cotton swab or aspirator;
- Offer your child some water.
Associated symptoms
Much more often, vomiting is caused by diseases, such as infection. You can identify it by the following signs:
- Vomiting more than once or twice.
- In addition to vomiting, the child has a high fever, diarrhea, and his condition has deteriorated greatly.
- The masses released during vomiting contain an admixture of blood or bile.
Could vomiting during teething be caused by an intestinal infection? Of course, these two processes can run in parallel. Food poisoning is a disruption of the gastrointestinal tract due to consumption of low-quality foods containing pathogens.
This disease can also be caused by some mushrooms, plants and their seeds. The habit of children putting various, not always clean, objects into their mouths is also dangerous.
Food poisoning, which is provoked and accompanied by the development of pathogenic microflora (bacteria, viruses, fungi) is called an intestinal infection. Among children, cases of dysentery, salmonellosis, escherichiosis, campylobacteriosis, and yersiniosis are common. Young children get sick more often, since the “habit of putting everything in their mouth” is more typical for children.
Once the pathogen enters the child’s body, it begins to secrete toxic substances in different parts of the digestive system. At this time, the first signs of intoxication appear: fever, diarrhea, vomiting. Inflammation begins in the intestines, and due to large loss of fluid, the body becomes dehydrated.
Vomiting in this disease is profuse, repeated, often accompanied by an increase in temperature to 38-39°, diarrhea, flatulence, and increased discharge of gases. The stool is not just loose, like when teething, but frequent, sometimes mixed with mucus and blood. The child becomes lethargic, weak, and refuses to eat.
Is vomiting during teething exactly the same as during an intestinal infection? No, the symptom is different both qualitatively and quantitatively. When teeth are being cut, the child vomits no more than 2 times during the day; the masses do not contain blood streaks, bile or mucus. But the temperature can be increased, but usually only up to 37°.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Maxillary first molar modeling
The first thing pediatricians pay attention to when examining a child is swollen and inflamed gums. In this case, the child’s whims and anxiety are explained by the beginning of the teething process. Many mothers also note that their babies cry often and for no reason and sleep little.
During this period, parents need to monitor stool consistency and frequency. Diarrhea during teething depends on the individual characteristics of the body (on average - 4-10 times a day). The general condition of the child needs to be assessed. If he has become lethargic and irritable, you need to show him to the pediatrician.
In addition to gastrointestinal disorders and increased salivation, some young patients experience symptoms of developing rhinitis. Sometimes teething leads to inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes. This condition is considered normal and treatment is not required. However, if the lymph nodes in the armpits and groin are simultaneously enlarged, you should immediately seek medical help.
It is a well-known fact that today's babies are developing much faster than their peers 10-20 years ago. Before a baby's teeth begin to erupt, the gums begin to swell around 6 months of age. This can be called one of the first symptoms of teething. Due to the discomfort caused by the process, the baby’s character changes and he becomes more capricious. Experts cite the following symptoms of a child’s condition when teething:
- elevated temperature;
- decreased appetite or complete refusal to eat;
- sudden crying for no apparent reason;
- excessive fatigue of the baby;
- more time the child is awake;
- excessive salivation;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- inflammation of the nasal mucosa.
Sometimes children experience enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes. This condition is considered normal. If the lymph nodes in the groin and axillary areas, as well as in the neck area, become enlarged, you should consult a pediatrician.
Occasional vomiting and fever in the baby have nothing to do with teething. This condition is caused by the development of the disease. Against the backdrop of changes occurring in the child’s body, the level of immunity decreases, and harmful microbes enter the body. And vomiting against the background of rising temperature is a completely normal reaction of the body to the processes taking place.
In this case, the following signs are observed:
- dry skin;
- exhausted state of the baby;
- sudden cessation of salivation;
- slight output of urine, which turns dark.
Main symptoms of teething
Early symptoms of teething can be detected several months before the first tooth appears. The child's salivation increases, his gums swell, he constantly holds his fingers in his mouth or tries to scratch his gums with other objects to relieve discomfort. On the eve of teething in the baby’s mouth, the following is observed:
- the appearance of a tubercle on the surface of the gum;
- redness, itching and inflammation of the gums in the eruption area;
- a white stripe visible under the gum.
In parallel with the listed signs, the following symptoms may be observed:
- diarrhea;
- loss of appetite;
- cough, runny nose;
- temperature;
- vomit;
- nervousness, moodiness;
- sleep disorders;
- mood swings;
- general malaise.
Symptoms such as cough and runny nose are not directly related to teething. Their appearance is most often caused by a cold, the likelihood of which children get during this period is very high due to decreased immunity and weakening of the body. If you experience a cough or runny nose, you should consult a doctor and not attribute these symptoms to teething. Lack of adequate timely treatment can result in bronchitis, otitis media or other serious complications.
Read also: Teeth symptoms at 3 months
Vomiting during teething is rare. In this case, its frequency does not exceed two times a day, and the duration is no more than two to three days. It must be taken into account that profuse vomiting is often a sign of an infectious disease and requires emergency medical attention.
Important: If your baby vomits frequently and profusely, and especially if the vomit contains bile or blood, you should urgently call a doctor!
Vomiting, diarrhea, fever and other symptoms resulting from teething appear in a mild form and last no more than two days. It is necessary to accurately determine the time of their appearance and monitor the dynamics of development. If symptoms worsen, you should immediately contact your pediatrician.
Causes of the phenomenon
It should be noted that there is no direct relationship between teething and the appearance of vomiting in a child. However, when teething, there are many factors that contribute to the appearance of vomiting. This situation is especially common when several teeth erupt at the same time.
So, there are the following reasons for vomiting in babies during teething:
- To begin with, it should be noted that during this period, vomiting becomes more pronounced and can occur due to excess saliva secreted into the oral cavity.
- Infection in the digestive tract can be caused by the child constantly trying to put surrounding objects in his mouth to scratch his gums. This leads to a decrease in the child’s immune defense level.
- A gag reflex can be triggered by poor nutrition due to teething.
- The cause of vomiting can also be the child swallowing a large amount of air when crying, which is a consequence of painful sensations;
- As a rule, as teething occurs, the baby’s temperature rises, which can trigger a gag reflex.
- Force-feeding a newborn during teething can also lead to vomiting.
Causes
It should be noted that there is no direct relationship between teething and the appearance of vomiting in a child. However, when teething, there are many factors that contribute to the appearance of vomiting. This situation is especially common when several teeth erupt at the same time.
So, there are the following reasons for vomiting in babies during teething:
- To begin with, it should be noted that during this period, vomiting becomes more pronounced and can occur due to excess saliva secreted into the oral cavity.
- Infection in the digestive tract can be caused by the child constantly trying to put surrounding objects in his mouth to scratch his gums. This leads to a decrease in the child’s immune defense level.
- A gag reflex can be triggered by poor nutrition due to teething.
- The cause of vomiting can also be the child swallowing a large amount of air when crying, which is a consequence of painful sensations;
- As a rule, as teething occurs, the baby’s temperature rises, which can trigger a gag reflex.
- Force-feeding a newborn during teething can also lead to vomiting.
- The gag reflex in a teething baby becomes more pronounced and can be irritated by excess saliva that is secreted in the baby's mouth.
- Due to the child’s constant desire to rub his gums and chew on surrounding objects, the baby can introduce an infection into the digestive tract. This is also facilitated by decreased immunity.
- When a baby cuts a tooth, its nutrition may be disrupted, which can also provoke vomiting.
- If pain during teething bothers the baby very much and the baby constantly cries, he may swallow a lot of air, which will cause vomiting.
- Teething is often accompanied by high fever, which often results in vomiting.
- Attacks of vomiting in a teething baby can be triggered by force-feeding the child.
Vomiting in infants during teething
Every mother knows that teething is one of the most difficult periods in the first years of a baby’s life. For a few days the child changes completely: he becomes capricious, restless, often cries, refuses to eat and sleeps poorly. But mothers are more worried not about changes in the baby’s mood, but about the appearance of other symptoms, such as cough, runny nose, fever, diarrhea and vomiting during teething.
Often parents cannot determine exactly what exactly is causing the deviations in the child’s gastrointestinal tract: an intestinal infection or the appearance of teeth. Indeed, in the first case, urgent medical attention is necessary. To understand why a child is vomiting, you need to know the features of this process under various conditions.
Causes of vomiting
The occurrence of vomiting on the teeth in children is a common phenomenon, but before calmly waiting for an improvement in well-being, it is important to make sure that the problem condition is caused by this particular physiological process.
Teething
If your baby is vomiting and there are other signs of teething, symptomatic care can be provided. If the tooth does not appear after 2-3 days, and negative symptoms sometimes continue to bother the baby, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Often, excessive regurgitation is caused by the fact that the baby has no appetite when teething, but concerned parents force-feed the baby. As a result, this causes the child's stomach to try to empty itself of unwanted food. The baby begins to spit up, and this is directly related to the upcoming teething.
A baby may feel nauseous due to the fact that he swallows air when crying loudly. When there is little of it, the child expels it by burping. With frequent hysterical crying, a lot of air accumulates, which causes vomiting.
Although mothers know whether vomiting can occur during teething, they understand that there is no direct relationship between these phenomena. It is necessary to distinguish whether the negative symptoms are really caused by the natural processes of the baby growing up.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Gel for gums during teething in babies
You can suspect the presence of an infectious disease that causes nausea and vomiting if the condition is accompanied by the development of diarrhea, increased flatulence, and high fever. After diagnosis, an intestinal infection may be detected. It is important to urgently show the child to a pediatrician to maintain the baby’s health.
Why does vomiting occur during teething?
Vomiting during teething in children can occur for a number of reasons:
- During this period, the gag reflex intensifies, which is provoked by frequent irritation of the uvula with saliva, abundantly released in the oral cavity.
- The child constantly seeks to rub itchy and inflamed gums, so he chews on objects and sucks his fingers. All this increases the risk of infection in the digestive system. And due to reduced immunity, pathogenic microorganisms multiply quickly and symptoms of the disease appear.
- A baby with teething teeth does not eat well: he refuses food, and because of crying, he swallows food unevenly, sometimes in large quantities. Such disturbances can cause vomiting.
- Vomiting can be caused by a large accumulation of air in the digestive tract. Its ingestion occurs during crying due to pain in the gums.
- High fevers that occur during teething can also cause vomiting.
- Sometimes mothers, noticing that the child is refusing to eat, force-feed him. This method of eating can also cause vomiting.
The most dangerous among these causes is intestinal infection. If it develops, it is not necessary to help the child with teething, but complex treatment, including antibiotics. How to detect food poisoning?
Reasons for triggering the gag reflex
There are several main reasons that can cause vomiting during teething:
- Overfeeding or feeding against desire . Often, due to anxiety and pain, the baby refuses the breast and complementary foods. But concerned parents still actively try to feed him, which results in vomiting: the stomach simply rejects food, because the child does not want to eat at this moment.
- Profuse salivation . The baby sometimes does not have time to swallow saliva, which is released very abundantly, and it accumulates in the throat. If the baby chokes on it, the gag reflex is triggered.
- Increased body temperature . At high temperatures, the body directs all its forces to fight inflammation, and not to absorb food. In addition, the child may feel sick from intoxication if the process is complicated by the presence of a viral or bacterial infection.
- Long uncontrollable crying . A baby tired of pain and anxiety may cry a lot and loudly, during which he swallows air. A small amount of air can cause belching. But if the child swallows too much of it, vomiting will inevitably occur.
Photo gallery: what causes vomiting during teething
Vomiting occurs when a baby chokes on saliva
During high temperatures, provide your child with plenty of warm fluids and don’t be alarmed if he refuses to eat.
You should not overfeed your baby while teething.
Crying for a long time can cause vomiting