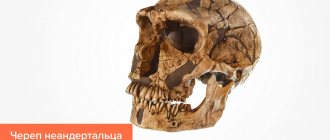
Teeth of ancient people
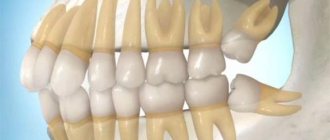
The dentofacial apparatus of prehistoric and modern humans differs significantly. Ancient people had more than 36 teeth, protruding fangs and a massive jaw. This was explained by the need to chew rough food and raw meat. With the addition of thermally processed foods to the diet, the dentition began to change. The canines were the first to transform, becoming aligned with the bite line. Then the jaw arch narrowed, the interdental spaces disappeared, and the teeth themselves decreased in size. Currently, 32 teeth in humans are the norm, but third molars are considered to be an atavism.
Interesting fact!
The teeth of ancient man cannot be called aesthetic, but they were healthy. According to scientists, cavemen never suffered from caries and other oral diseases.
What is a dental formula
A dental formula or diagram is a brief description of the dental structure of the human dentition using numbers and Latin letters. The letters are abbreviations from the Latin names of teeth accepted in medicine:
- I – these are dentes incisivi or incisors.
- C is for dentes canini or fangs.
- P stands for dentes premolars or premolars.
- M stands for dentes molars or molars.
This formula indicates that on each human jaw there is:
- 2 pairs of incisors;
- 1 pair of fangs;
- 2 pairs of premolars;
- 3 pairs of molars.
It is not difficult to correctly number dental units with a healthy dentofacial apparatus; it is much more difficult to indicate the location of the teeth if a person does not have any molars, incisors, canines or premolars. In this case, the dentist indicates the number 0 opposite a certain group of teeth, rather than shifting the number series.
If the patient has any anomalies in the development of the dentofacial apparatus, for example, teething in the wrong place (hyperdontia, polydontia), the dentist prescribes an individual formula. In addition to numerical designations, the doctor generates a detailed report on the structure of a person’s dentition.
Name of human teeth
Depending on the location and structure, dental units have their own functional characteristics and are called differently.
- Incisors.
On both jaws there are four front teeth in humans - medial and lateral incisors, which are used for biting food. - Fangs.
Sharp teeth designed for chewing hard foods. - Premolars.
"Fours" and "fives" on the left and right sides of each jaw arch grind soft or small pieces of food. - Molars.
Three large outer teeth in each row are aimed at grinding coarse substances. - The canines
and incisors are part of the anterior group, or the “smile zone,” and the human molars are part of the chewing segment.
In addition, teeth are divided into temporary and permanent. In the first case, we are talking about dairy products that appear in children from the fifth month of life to three years. The second refers to the final bite, which is formed between six and thirteen years of age. Milk teeth differ from permanent teeth only in size, but in structure they are identical.
Is straightening faster after removing quads?
The duration of treatment for teeth straightening depends on several factors:
- person's age;
- severity of pathology;
- the material from which the staples are made;
- type of correction system;
- anatomical features.
Important!
If alignment is impossible without prior removal, then it is performed. After this, the leveling process noticeably accelerates. There is room in the jaw for the correct placement of incisors, canines, premolars and molars.
How many teeth does a person have?
The number of teeth a person has depends on age and anatomical features. The child has a set of 20 primary teeth, which are replaced by a permanent bite of 28 teeth. Third molars erupt, as a rule, after twenty years or do not grow at all, which is not a pathology.
In dentistry, a single numbering of human teeth is adopted. Doctors classify teeth as lower and upper and distinguish the right and left segments of the jaws. Each of them includes two incisors, a canine, two premolars and three molars. The countdown starts from the first front tooth and ends, accordingly, with a figure eight. Sometimes a number is added to the serial number indicating the location zone. For example, the right canine of the top row is numbered 13. This order in the schematic representation is called the formula of human teeth.
Polyodontia
In rare cases, an anomaly such as polyodontia is observed - supernumerary, or extra teeth in a person. Dental units can appear in the primary and permanent dentition anywhere in the jaw, separate from or fused with the main teeth. The defect affects not only the aesthetics of the smile, but also leads to the formation of incorrect occlusion, impairs the quality of chewing food and diction. Most often, supernumerary teeth are removed in childhood or built into the dentition.
Edentia
There is also a deviation of the opposite meaning called edentia - congenital or acquired absence of dental units. The causes of the phenomenon include heredity or improper development of the embryo in the womb. People without teeth cannot fully eat and speak, have a deformed facial contour and weakened immunity.
Teeth numbering systems, what are they?
Today there is not one, but several schemes at once. Each of them has advantages and disadvantages. Let's take a closer look.
Universal
It was originally adopted by the American Dental Association. Each tooth corresponds to a specific digital designation - from 1 to 32. The countdown starts from the upper jaw (right) strictly clockwise. To number primary dental elements in children, they use not only specific numbers, but also letters of the Latin alphabet.
Two-digit Viola system
It is one of the most popular due to its brevity. Each jaw has a pair of segments. There are four of them in total. For an adult, the numbering is calculated in numbers from one to four, for a child - from five to eight. Each dental element is assigned a two-digit number. The first one means the segment, and the second one means the sequence number. The Viola system is currently in active use, due to its relative simplicity. It allows you to easily transfer information from the dentist to the patient.
Dimensions of human teeth
The upper central incisors are twice as wide as their antagonists. The remaining dental units of the same name have approximately equal parameters. The size is determined using special tables with the optimal size and permissible deviations. Experienced doctors calculate proportions by dividing the length of a person’s teeth by the width. A result of about 0.75 millimeters is considered close to ideal. For more detailed diagnostics, other professional formulas and techniques are used.
Size deviations from the norm occur due to improper formation of the jaw, fusion of tooth buds, or genetic predisposition. Teeth that are too large are called macrodentia, and abnormally small teeth are called microdentia. Pathologies are accompanied by problems with bite and chewing functions, but can be successfully corrected by a dentist.
Interesting fact!
The longest tooth in the world belongs to an Indian teenager. The size of its crown is almost four centimeters. About a year ago, the tooth was removed, and the young man was included in the Guinness Book of Records.
The structure of the human tooth
Anatomy
From an anatomical point of view, a human tooth consists of three parts.
- Crown.
The visible part protruding above the gum. It has four sides: the occlusal, or cutting edge, in contact with the antagonist teeth; contact wall adjacent to adjacent dental units; vestibular and lingual surfaces facing the lips and tongue, respectively. - Root.
Fixed in the socket by connective tissue, located in the recess of the jaw. As a rule, premolars have two roots, and molars have three, four or even five. The remaining dental units have one root canal. - Neck.
It is located between the coronal part and the root of a human tooth, surrounded by periodontium.
Histology
What are human teeth made of? Let's look at the cross-section of the structure of a human tooth.
- Enamel.
A transparent protective coating of the crown, almost entirely consisting of inorganic microelements. - Dentine.
The hard base of the tooth, containing 80% mineral components and 20% organic substances. The shade of dentin is responsible for the color of dental units, as it shines through the enamel. - Cement.
The bone tissue covering the tooth root. Plays the role of a fastening element connecting the tooth to the alveolus. - Pulp.
Soft tissue filled with bundles of nerves and capillaries. Painful sensations during caries are explained precisely by the presence of nerve endings.
Internal structure
Figure 5: Internal structure
All teeth have a different anatomical structure, but they have a similar internal structure . When studying the histological structure, the following components are distinguished:
Enamel
This is a covering of the tooth that protects it from aggressive environmental influences . First of all, it protects the dentin of the crown from destruction. The enamel consists of microscopic elongated prisms glued together with a special substance.
With an insignificant thickness of the enamel layer, ranging from 0.01 to 2 mm, it is the strongest tissue of the human body . This is due to its special composition, 97% of which is mineral salts.
Strengthening the protection of enamel occurs due to a special shell - pelicule, which is resistant to acids.
Dentine
It is located immediately under the enamel and is a coarse fibrous tissue somewhat similar to porous bone. The main difference from ordinary bone tissue is its low hardness and a large amount of minerals in the composition.
The main structural substance of dentin is collagen fiber . There are two types of dentin: superficial and internal (peripulpal). It is the inner layer that determines the intensity of new dentin growth.
The surface layer of dentin has a high density, therefore it has a protective function and prevents infection from entering the tooth cavity.
Cement
This is bone tissue with a fibrous structure, consisting mainly of multidirectional collagen fibers impregnated with lime salts . Covers dentin in the neck and root area, acting as a link between periodontium and dentin.
The thickness of the cement layer depends on the area of location: on the neck it is up to 50 µm, on the apex of the root up to 150 µm. There are no vessels in the cement, so tissue nutrition occurs through the periodontium.
Unlike ordinary bone tissue, cement is not able to change structure and transform. There are two types of cement: cellular and acellular.
- Cellular is located in the first third of the root and the bifurcation area of multi-rooted teeth and ensures the regular deposition of new layers of dentin, ensuring a tight fit of the tooth to the periodontium.
- Acellular is located on the lateral surface of the roots, protecting them from damaging effects.
Crown cavity
Photo: opened crown cavity
Under the dentin there is a crown cavity that follows the shape of the crown. It is filled with pulp - this is a special tissue with a loose structure that nourishes the entire tooth and serves as an additional connection .
If there are tubercles on the chewing part of the tooth, pulp horns are formed in the crown cavity, completely copying them. Unlike other components, the pulp is penetrated by numerous fibers of nerve, blood and lymphatic vessels. It is because of this aspect that the penetration of infection into the tooth cavity leads to inflammation and severe pain.
Depending on the structure of the tissue, root and coronal pulp are distinguished.
- The root pulp has a dense structure with a predominance of voluminous bundles of collagen fibers that actively prevent the penetration of infections to the root apex.
- The coronal pulp is softer and contains a major network of blood vessels and nerve fibers. With age, the production of cells that form the pulp increases and the cavity narrows.
At the stage of tooth development, the pulp is directly involved in the formation of dentin . In addition, it is the pulp that performs trophic, sensory and reparative functions .
All pulp vessels are located in the root canal, into which they enter through the apical foramen of the apex of the root canal. Several nerve trunks and the pulpal artery from the upper jaw pass here.
The artery is located in the root canal in the center and comes into contact with the venous vessels. Nerve fibers closer to the pulp horns are transformed into a double plexus, spreading along the bottom of the cavity, penetrating into the initial layer of dentin.
The bottom of the cavity on single-rooted teeth passes into the canal in a funnel-shaped manner; on multi-rooted teeth it is strongly flattened, and has clearly defined openings in the canals.
Let's find out what antibiotics are usually prescribed for flu.
This article describes the popular Aquajet irrigator model.
Here: https://zubovv.ru/lechenie/yazyik-l/pochemu-poyavlyayutsya-krasnyie-pyatna-kak-ot-nih-izbavitsya.html - we’ll tell you why red spots appear on the tongue, give examples of photos.
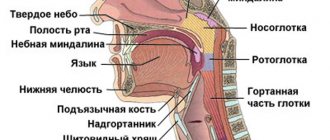
Gum
It is part of the periodontium, directly responsible for the preservation of the root system and neck of the tooth . It has a special structure.
Gum tissue consists of two layers: free (outer) and alveolar. Free gum tissue is located on the outer surface of the mucous membrane and is responsible for trophism and sensory.
In addition, they have a protective function, reducing the risk of mechanical damage or the spread of infection. The alveolar part of the gum is adjacent to the periodontal tissues and is responsible for the stability of the teeth.
Human wisdom teeth
A “wisdom tooth” is the third outer molar with three to five roots. In structure it is no different from its “neighbors”. To the question “How many wisdom teeth does a person have?” cannot be answered unambiguously. They erupt around the age of twenty, one on each side of both jaws. However, there are people without wisdom teeth. This is a variant of the norm, since in the process of human evolution the need for the “eight” disappeared, and the structure of the jaws underwent corresponding changes. Today, third molars are considered a vestigial organ.
Dairy
Figure 6: dairy almost identical to regular
A child's temporary teeth are practically no different in structure from the permanent teeth of an adult . And this applies not only to the histological, but also to the anatomical structure. There are still differences, but they are very minor.
It is worth noting here that temporary teeth are much smaller than permanent teeth. Moreover, their roots are much shorter than those of permanent ones.
Another small feature is that on baby teeth the cutting part has practically no teeth . As a rule, their surface is smoothed .
If we consider the difference in the histological structure, it can be noted that the structure of the enamel of temporary crowns is slightly different.
The enamel layer is slightly thinner and the amount of minerals it contains is significantly lower than in permanent crowns. In contrast, children's enamel is covered with a protective film - cuticle, resistant to aggressive environments.
A detailed study of the structure of teeth will allow us to understand the possible process of their destruction and stop it in time. Knowing the anatomy of crowns, you can not be afraid of the unknown and go to the dentist for treatment with less fear.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: baby teeth permanent teeth
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Dental health and human health
The connection between teeth and human organs is not obvious at first glance, but oral health directly affects the functioning of the entire body.
- Gastrointestinal tract.
Dental pathologies reduce the quality of chewing food, disrupting digestion. - The immune system.
Oral diseases weaken the overall immune system. As a result, it is difficult for the body to resist bacteria and viruses, which are especially active during epidemics. - Heart and blood vessels.
Inflammation of the tissues of the oral cavity can be accompanied by suppuration, which, in turn, causes intoxication, causing heart failure and angina attacks.
The health of the dentition itself is affected by nutrition, stress, environment and bad habits. The teeth of a smoker, for example, have a yellow coating and are prone to early loss.
Eating sweets provokes the development of caries - the destruction of hard dental tissues, starting with demineralization of the enamel. Poor dental care and untimely treatment contribute to the appearance of inflammatory complications of this disease such as pulpitis, periodontitis or dental cysts.
Healthy human teeth ensure not only the coordinated functioning of the whole organism, but also external attractiveness. A responsible attitude towards oral hygiene, quitting smoking and regular visits to the dentist for preventive examinations will help you maintain a perfect smile for many years.