Syphilis is a serious venereal disease, most often chronic and caused by bacteria of the genus Treponema pallida (treponema pallidum). The place of manifestation of syphilitic rashes is the mucous membranes of the genitals, mouth and larynx. By type of origin, syphilis is classified into congenital and acquired. In the first case, the infection enters the child’s body through the birth canal of a sick mother, in the second - through infection through sexual contact, contact with objects containing pathogen molecules (medical instruments, household supplies), as well as during various surgical interventions.
Is syphilis transmitted by mouth?
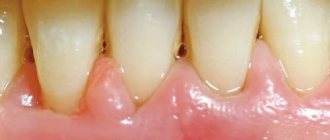
The mucous membrane of the oral cavity is affected by the spirochete in all forms of this infection. Frequent erosion and the formation of ulcers in the mouth only contribute to the spread of the disease. Their discharge contains a large number of pale treponema, therefore, upon contact with a healthy person, oral syphilis can develop. Infection occurs during oral sex, kissing, and oral sex.
Frequent nonspecific inflammatory processes in the oral cavity are important in the cross-transmission of syphilis. The development of syphilis in the mouth is promoted by:
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis;
- aphthous rashes;
- erosive forms of dermatoses.
Complications of syphilis
Mouth ulcers with syphilis often become infected, which complicates the course of the disease. However, this is not so scary compared to the damage to internal organs that occurs as a result of the long-term presence of Treponema pallidum in the body. Lack of proper treatment, violation of the regimen and duration of therapy established by the doctor can provoke the development of complications.
In the later stages of syphilis, important organs and systems of the body are affected, such as:
- brain;
- visual apparatus;
- heart;
- blood vessels;
- liver;
- bones and joints.
These complications can manifest themselves in different ways. Common symptoms include:
- impaired coordination of movements;
- paralysis;
- loss of sensation;
- blindness;
- dementia.
Diagnostic methods
After consulting a doctor, the following methods are used to determine syphilis in men and women:
- Treponema pallidum test;
- Wasserman reaction;
- Treponema immobilization;
- Immune fluorescence.
Diagnosis of the first stage
At the end of the first period, the following unpleasant symptoms appear: high fever, muscle weakness, bone aches, and terrible headaches. It is very important for an infectious disease specialist to distinguish a traumatic ulcer from a chancre.
Also, at the first stage, labial syphilis is often confused with herpes. With this infection, severe pain, swelling, and blisters appear, which is not typical for syphilis. Chancre is somewhat reminiscent of pyoderma, only with it there is severe pain and pus is released. Some people confuse syphilis with aphthous stomatitis, which causes inflammation of the mucous membrane and painful ulcers. It is important to differentiate chancre from cancer that deeply affects the lips.
Diagnosis of the second stage
The secondary form is difficult to diagnose. A scraping taken from the papules, as well as a serological reaction, will help determine the infection. The doctor prescribes all the necessary tests, because syphilis in its symptoms resembles other ailments:
- Leukoplakia, in which papules appear on the lips.
- Candidiasis. The difference here is that after removing the plaque, erosions appear in case of candidiasis, and treponema is found in case of syphilis.
- Exudative erythema.
Is it possible to diagnose the tertiary form?
It is almost always difficult to identify treponema in gummas and tubercles. In this case, the indicators RIBT and RIF are taken into account. It is important to distinguish syphilitic gummas from aphthous stomatitis, tuberculosis, and traumatic ulcers.
Treatment of syphilis in the mouth
Syphilis of the oral mucosa is treated in a specialized venereology department. To treat erosive damage to the mucous membrane, the following is carried out:
- local processing;
- rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions, chloramine-based products;
- granulations that rise above the surface of the mucosa are cauterized using a solution of chromic acid.
After the clinical symptoms subside, sequestrectomy is performed - a surgical intervention aimed at removing the formed sequesters.
During remission, sanitizing measures aimed at eliminating infection in the oral cavity are indicated:
- treatment of caries;
- removal of dental plaque.
Diagnosis of oral syphilis
The diagnosis of syphilitic lesions of the oral cavity is made based on the patient’s complaints, external examination and clinical research methods.
- Chancres, characteristic of the first stages of pathology, differ from aphthae, ulcers and other diseases in the absence of painful sensations upon touch and palpation.
- Secondary syphilis is characterized by polyadenitis, which resembles catarrhal tonsillitis, but patients do not have high fever and pain when swallowing.
- At the third stage of the disease, the lesions are usually specific and do not resemble the symptoms of other diseases. To confirm the diagnosis, an X-ray examination of the oral cavity is performed - the images show rarefaction and sclerotic changes in bone tissue.
If you notice the first signs of syphilis in the mouth, you should contact a dentist who will conduct an external examination of the oral cavity. If suspicions are confirmed, the patient is sent to the dermatovenerology department for additional examination.
Blood tests
The most effective way to detect syphilis is through laboratory blood tests. These include the Wasserman reaction, ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent method), immobilization reaction of Treponema pallidum, etc. Its essence lies in identifying antibodies to the causative agent of the disease - Treponema pallidum, or identifying specific signs that indicate the presence of a pathogenic microorganism. At the second and third stages, the diagnosis is made quite easily, since treponemes are present in the biological material in sufficient quantities.
What sexually transmitted diseases have no symptoms?
Many sexually transmitted diseases can occur without symptoms. Such infections include:
- Syphilis
- Chlamydia
- Myco- and ureaplasmosis
- HIV
- Hepatitis
Gonorrhea can also be asymptomatic in women.
Hidden infections often cause complications, through which a sexually transmitted disease is discovered.
For example, when a patient consults a doctor about arthritis, it may be a reason to identify chlamydia.
If it is impossible to conceive – ureaplasma infection or gonococcal infection.
Tertiary stage
Manifestations of syphilis at this stage include the formation of typical tissue nodules (gummy syphilides) and a lumpy rash on the oral mucosa. In parallel, degeneration of internal organs continues, as well as destabilization of the nervous system and bone destruction.
Gummous syphilides
They are represented by a dense knot formed on the tongue or soft palate in a single copy. Then it begins to grow, reaching an average size of 10-15 mm in diameter. An ulcer forms in the middle of the gumma, shaped like a crater and containing a necrotic core in the center. The circumference of the ulcer is strongly compacted, and the surface of nearby tissues is colored bluish-brown. The edges of the gumma are strewn with small granulations, which begin to bleed when touched. The ulcerative node itself is painful, but during the healing process the feeling of pain goes away. Over the course of 3-4 weeks, the crater gradually heals, and a retracted scar appears in place of the inflamed depression.
In the case of gumma localization on the tongue, the clinical picture may have some characteristic features:
- The process of diffuse infiltration begins, as a result of which the tongue thickens and increases in size, becoming “wooden”, but without the presence of visible nodules.
- The infiltrate is transformed into scar tissue, as a result of which the tongue loses mobility, furrows and cracks appear on the back, and the surface acquires a lumpy texture. As a result: impaired diction, difficulty eating, frequent injuries to the mucous membrane and possible infections with associated infections.
- The color of the tongue changes depending on the stage of sclerosis: from bright red to dirty gray with a pearlescent tint.
When the palate is affected by gumma, irreversible changes in the bone tissue and periosteum occur. Bone necrosis develops, accompanied by the opening of an ulcer in the area of the hard palate.
Tuberous syphilides
Unlike gummous syphilides, tuberculate ones are usually concentrated on the lips, palate and upper gum. They look like dense “mounds” with a diameter of about 5 mm with a smooth surface. Most often, they dislocate in groups, and subsequently have the property of breaking up into small but deep ulcers. The color of the tubercles is deep red with a bluish tint. The edges of ulcerative formations are compacted. After healing, scars appear in place of the bumps, which are never covered with new rashes.
The duration of the process from the appearance of tubercular syphilides to their development into rough scars takes an average of 2-3 months. At the same time, regional lymph nodes remain in a normal state, do not enlarge, but can react when conjugate infections enter the body.
Diagnosis and treatment of syphilis is carried out in specialized inpatient medical institutions. The prognosis for recovery depends on the severity of the disease, as well as the stage at which the patient sought help from a doctor.
Syphilis and its symptoms are discussed in this video.
Prevention
The main route of infection with syphilis is sexual, in connection with this the following preventive measures can be distinguished:
- it is necessary to observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- use of contraception, namely condoms;
- You cannot have casual sex.
Not only the patient, but also the doctor treating him must take precautions:
- When examining a patient, disposable gloves should be used;
- medical instruments should be thoroughly sterilized;
- During procedures, trauma to the skin should not be allowed.
When visiting any public places, you should use only your own household items and sit on a closed surface. If you are not sure about the reputation of some places, then you should not visit them.
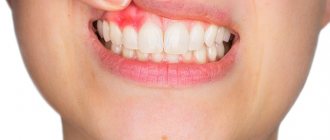
Syphilis on the lip can cause many complications. If you first suspect the occurrence of a disease, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. An accurate diagnosis can be made based on the examination results. Self-medication should not be allowed.
Symptoms
What does syphilis look like? The first sign of infection is a chancre, which often appears on the injured lip. The infection in men does not spread immediately; the following main stages can be distinguished:
- Infection during the incubation period - for one it lasts two weeks, for another - about a month. If a person takes antibiotics for too long, the disease does not manifest itself for a long time;
- The formation of a hard chancre, which resembles a subcutaneous pimple, is easy to feel. At an early stage of the disease, the patient rarely goes to the doctor immediately, because he is not bothered by the pain, he thinks that the pimple will go away on its own;
- Rash inside cracks on the lip after mechanical damage. As you can see in the photo of syphilis, chancre is not so easy to detect. It can be seen if you open the wound. The patient may feel a foreign body inside the wound;
- Spread of infection to other parts of the body. This stage is typical for those who do not treat the disease. In addition to all the symptoms described above, the submandibular lymph nodes become very inflamed. Chancre turns into roseola, papules. It is during this period that the patient infects others. The photo shows that the lips are covered with a red border. Sometimes papules appear in the corners of the mouth. At the same time, an unpleasant burning sensation is felt, the lips are very peeling.
Development of primary syphilis on the lips
At the beginning of the disease, blisters filled with pus appear; they are the source of infection. The patient must be urgently sent to the hospital, where a course of therapy will be prescribed. After the bubbles appear, men's body temperature rises. If the pathogen is not killed in a timely manner, syphilis will begin to spread to the throat and upper respiratory tract.
Attention! You should not wait for complications; it is better to treat the infection at the first stage.
If the disease starts, gummas and tubercles will begin to form instead of papules and roseolas. As a result, everything will end in an internal inflammatory process. The dark red bumps gradually increase in size, then begin to collapse, followed by ulcers. The affected area takes too long to heal, then scars appear.
In men, syphilis on the lips is accompanied by severe inflammation and tissue swelling. Subsequently, everything ends in necrosis and phimosis.
It is almost impossible to get rid of long-healing purulent ulcers. In addition to the fact that the mucous membrane of the lips is severely affected, deep tissue damage can be observed. It is dangerous when treponema begins to become active, enters the oral cavity, and gradually affects the entire body and genitals. Syphilis on the lips can be seen in the photo, which spoils the appearance; all damage after a while becomes the cause of various deformities.
What is the difference between syphilis and other infections
Features of the course of the disease include the following:
- painlessness of the rash, if there is no secondary infection
- no pain when palpating enlarged lymph nodes
- body temperature remains within normal limits
Read also Express test for syphilis
In case of secondary infection, the following complaints are added:
- soreness of the tonsils due to their enlargement
- formation of purulent deposits in the lacunae of the tonsils
- redness and swelling of the throat
- temperature rise