Before hospitalization
First aid to the victim includes:
- stopping bleeding (pressing or packing the wound, applying cold);
- if necessary, cardiopulmonary resuscitation;
- pain relief (analgin, revalgin intramuscularly);
- immobilization of the jaw with the help of fixing bandages (contraindicated if the victim is unconscious, since this increases the risk of suffocation from the retraction of the tongue or vomit entering the respiratory tract).
Osteosynthesis
Indispensable for complex, comminuted and multiple fractures with displacement, loose teeth and complete absence of teeth, for periodontal disease and other inflammatory diseases of the gums in the area of injury. Osteosynthesis is also effective in cases of fracture of the condylar process complicated by dislocation of the articular head of the lower jaw.
Fastening materials can be steel knitting needles and rods, pins, nitride-tinan wire with shape memory, quick-hardening plastics, polyamide thread, special glue.
However, osteosynthesis with metal miniplates is considered the most convenient and safe method today. They allow you to cut through the skin and muscles on only one side, which simplifies the operation itself and shortens the recovery period. Another undeniable advantage is the ability to reliably fix fragments in areas with significant dynamic loads.
How to determine the type of fracture
Jaw fractures are classified by location into maxillary and mandibular, and by shape into open and closed.
According to the nature of the location of bone fragments, they are distinguished:
- Displaced fracture. Fragments, under the influence of internal or external factors, are displaced, deviating from the correct position.
- Fracture without displacement. It is characterized by the appearance of a fracture line and a gap, but the relationship of the fragments remains correct.
- Splintered occurs when there is a strong impact, many small fragments occur.
A mandibular fracture is the most common type and can be identified by the following clinical signs:
- Pain syndrome localized in the upper part of the jaw;
- Bleeding in open form;
- Inability to open the mouth to its full width;
- Pronounced facial asymmetry;
- Malocclusion;
- Edema and hematoma;
- Redness of the skin and local increase in temperature;
- Sensitization of teeth in the damaged area;
- Blurred vision;
- Local numbness of the face.
Injuries to the upper jaw are often accompanied by symptoms of concussion accompanying the injury. The clinical picture that makes it possible to identify this type is as follows: there is nausea, vomiting, high-intensity pain syndrome, breathing problems, malocclusion, chewing is accompanied by severe pain.
It is possible to diagnose a jaw fracture in a medical facility using an X-ray examination, MRI, CT scan or orthopantomography.
Types of jaw fractures
More detailed material on types in the article: Jaw fracture
The bone tissue of both jaws is not equally strong. For example, the lower one has the shape of a horseshoe, which is why it is easily crushed. Here, damage often occurs at the incisors, canines, at the corners, in the area of the coronoid process. The upper one is weakened in places where it meets other bones. Therefore, damage occurs without chipping, only in the form of displacement.
Based on severity, fractures are divided into:
- closed. The bone area is damaged, but the tissue is intact. The usual localization is the corners, branches of the jaw below. Recovery occurs faster than with open
- open. Shrapnel fragments are displaced into soft tissues, simultaneously damaging muscles, skin, mucous membranes, and the lower jaw suffers. Given the risk of bacterial infection of tissues, assistance is needed.
Taking into account the displacement of fragmentation fragments, the fracture is distinguished into types:
- without displacement. The bone is broken into pieces or damaged, but the fragments are in their anatomical places,
- with offset. There is a movement of fragments in relation to other bones and to each other,
- splintered. Characterized by the presence of bone fragments located randomly,
- full. The fragments of the broken bone are moved out of place and tilted. There are different types of fractures: single and double, comminuted and multiple.
Do you feel nervous before visiting the dentist?YesNo
Based on location, damage is divided into:
- incisal. Between the first and lateral incisor,
- mental. In the area of the mental foramen,
- average. In the area of the central incisors,
- canine. Near the fang,
- angular. In the corner of the lower jaw.
According to Lefort, surgeons distinguish injuries to the jaw bones as follows:
Lefort I. The injury is localized at the base of the nose, then along the upper wall of the orbit, the zygomatic arch. Another name for damage is subbasal. There are complaints of painful swallowing, objects appear double in the eyes, swelling appears,
Lefort II. The damage occurs at the base of the nose, then along the lower wall of the orbit and the junction of the cheekbone with the upper jaw. Another name for trauma is suborbital. Typical complaints include lacrimation, numbness in areas of the face, bleeding from the nasopharynx,
Lefort III. The injury occurs at the base of the pyriform opening, then the bottom of the maxillary sinus is damaged. Another name for a fracture is inferior. Characteristic symptoms are problems with chewing, pain, difficulty biting, and bleeding.
Possible consequences of a jaw fracture
If you do not pay due attention to the resulting injury and do not contact specialists in time, a number of consequences are possible that may appear after removing the fixing bandage or directly during the healing period.
These consequences include:
- Difficulty breathing in and out.
- Difficulty swallowing saliva and chewing.
- Deformation of the angle of the lower jaw (cosmetic defect).
- Constant pain.
- The appearance of speech defects.
- Complete lignification of the entire lower facial area.
- Occurrence of problems with bite.
- Risk of tooth displacement.
A patient whose jaw fracture has not healed properly will constantly feel significant discomfort. It is noteworthy that the malaise may not be directly related to the maxillofacial area. For example, when the jaw is deformed, the patient often suffers from attacks of dizziness, nausea, and periodic headaches. Therefore, doctors warn that it is easier to cure a fracture than to eliminate the unpleasant consequences of improper treatment after it.
Splinting the jaw
This is the immobilization (fixation) of bone fragments using a special plastic or wire structure.
The technique, created by military doctors at the beginning of the 20th century, is successfully used by dentists today. The materials used to make the splint have changed, and the methods of applying it have been improved.
Today, a specialist has many types of tires in his arsenal:
- from standard Vasiliev tape splints, the simplest and cheapest method of treatment;
- to aluminum Tigerschdedt splints, which are made individually for each patient, due to which they are more effective. In addition, they evenly distribute the load and minimally injure the teeth.
The type of splinting depends on the type of injury and can be unilateral (when one jaw is fractured) or bilateral (when both are damaged).
If the teeth are preserved, it is not difficult to apply a bent dental wire splint. It is bent to the shape of the dental arch and fixed with bronze-aluminum wire ligatures, which, like a hairpin, cover the tooth on both sides. Manipulations are performed under local anesthesia.
Is it possible to do without splinting?
Even if the case is not severe - the fracture is one-sided, closed and without displacement - it is imperative to take measures to prevent the development of such unpleasant complications as:
- accidental displacement of fragments,
- re-injury
- development of inflammation of soft tissues,
- infection of the fracture site.
To do this, it is necessary to immobilize the jaw by any available method. This can be a sling bandage, but it is much more convenient and effective to use a splint. In case of a complicated fracture, splinting is absolutely indispensable, regardless of the location of the injury.
Rehabilitation after a jaw fracture
For successful treatment of a jaw fracture, anti-inflammatory and restorative therapy, physiotherapy, mechanotherapy and special oral hygiene are also important.
- Within 3-4 days after the injury, antibiotics must be prescribed to prevent inflammation, which are injected directly into the area of injury.
- General strengthening therapy is taking vitamins C, P, D and group B, drugs that stimulate tissue regeneration and restore the level of leukocytes in the blood.
- Among the effective physical procedures, we note UHF therapy, general ultraviolet irradiation, and magnetic therapy. After the third procedure, swelling and pain are noticeably reduced, swelling subsides. For better healing of fragments, 2 weeks after a jaw fracture, electrophoresis is performed using a two to five percent solution of calcium chloride.
- Mechanotherapy, or physical therapy, accelerates the restoration of jaw function and helps if, after an injury, the mouth opens poorly or does not open at all. It can also be practiced at home, starting 4-5 weeks after the fracture, when the splints are removed and a callus has formed.
- Special hygiene involves irrigation at least 8-10 times a day. For unconscious victims, their teeth and mucous membranes are treated with a special solution at least twice a day.
Rehabilitation and nutrition of the patient
The effectiveness of the patient’s recovery largely depends on the chosen treatment and the timing of the operation relative to the moment of injury.
According to medical prescriptions, the following rehabilitation may be prescribed:
- physiotherapy;
- use of medicinal complexes;
- adherence to diet and daily routine;
- physiotherapy.
I would like to dwell on the last method in more detail, because when using physiotherapeutic procedures, the healing process of bones is accelerated and there is a beneficial effect on damaged tissues and the body as a whole.
For a fracture, several types are used, which we describe in the table below:
| View | Its medicinal features | Course duration |
| Low frequency magnetic therapy | When exposed to current, the properties of molecules and ions change and thereby eliminate the adverse effects. By reducing the activity of the inflammatory focus, the pain in the damaged area decreases | 1 session – 20-30 minutes, total course amount 9-10 |
| Calcium electrophoresis | At the fracture site, rapid delivery of calcium promotes rapid bone restoration, tissue regeneration and improvement of local immunity | 1 session – 20-30 minutes, course for 10-15 days |
| Electromagnetic therapy high frequency | High vibrations promote the production of heat, which improves blood circulation, reduces inflammation, reduces pain and swelling of the damaged area | After 3-4 days after surgery, a procedure is prescribed with a total course duration of 9-10 sessions |
| UFO of the fracture site | Ultraviolet light helps in the production of vitamin D, which is known to be necessary for the absorption of calcium from the gastrointestinal tract. Ca is needed for normal bone repair and metabolism | Session for 20-30 minutes every 3-4 days |
The main problem for a patient after a fracture is eating. Logically, this process is difficult due to the nature and area of the injury, as well as the resulting lack of chewing capabilities.
Nutrition is provided only in liquid form using parenteral administration, a gastric tube, a sippy cup with a tube, or special nutritional enemas. As healing progresses and the ability to open the mouth becomes possible, a second jaw table is prescribed, which includes high-calorie food. Alcohol is strictly contraindicated.
Causes of jaw fractures
The healing process is influenced by the reason why the injury occurred. The etiology is as follows:
- road accident,
- damage during the work process, at home,
- osteomyelitis,
- falling from height,
- fight,
- gunshot wound,
- perforation during tooth extraction,
- neoplasms,
- sports injuries (martial arts, gymnastics, etc.).
It is impossible to predict the development of an unfavorable situation, but risks should be avoided and reduced to a minimum. For example, when working at height, take care of a safety rope, follow the rules when moving on the road, avoid fights, do not abuse alcohol, treat foci of infection in a timely manner, observe TB at work and at home.
How to eat?
Since during intensive therapy and during the recovery period the jaws are rigidly fixed and habitual chewing of food is out of the question, correction of the diet is necessary during this period.
Food should have the consistency of low-fat sour cream. These are broths, pureed soups, carefully chopped vegetables and fruits, milk drinks, liquid cereals. Spices are excluded, salt consumption is limited. The temperature of the dish should not be higher than 45-50 °C. The most convenient way to eat food is through a straw.
You need to gradually switch to your usual diet after removing the splint. This is important not only for restoring chewing functions, but also for preventing disorders in the gastrointestinal tract.
How does healing occur after a jaw fracture?
Complete healing occurs in several stages. For a small fracture, an immobilizing splint is applied, so treatment should occur in a hospital.
After the necessary operations and fixation, the stages of fusion begin:
- Proliferation;
- Callus formation;
- Restoration of connective tissue.
After restoration, the new bone matter begins to adapt to its environment. After treatment, the patient's rehabilitation begins.
Proliferation
The stage is characterized by increased synthesis of lymphocytes, which help suppress infection. The rate of cell division at the fracture site increases. New vessels appear that nourish the damaged area of the bone and remove dead cells through filtration through the kidneys.
The appearance of a callus
During this period, the first layer of future bone grows. Connective cells begin to create tissue, the damaged area is finally destroyed, which is excreted through the blood. Gradually, cartilage tissue grows on the osteoblasts, which serves as a framework.
Negative factors in treatment
Prognosis depends on the condition of the patient's bone tissue, which depends on:
- from hereditary characteristics;
- the presence of chronic and acute inflammatory processes.
If the body has metabolic disorders, tuberculosis infection, or cancer, the prognosis may be disappointing.
Lack of vitamins and microelements affects the duration of treatment. The body needs correction of its general condition for successful recovery, including a jaw fracture.
The nature of the damage is of great importance in determining the healing period:
- Simple fractures are fixed with splints and plaster bandages for subsequent conservative treatment.
- Complex bone fractures require surgery to mechanically fix the parts using special plates and screws. Sometimes auxiliary elements are built in temporarily, sometimes for permanent wear.
Treatment
Surgical treatment of jaw fractures
Surgical treatment of a jaw fracture, which is indicated for most patients, and which in medicine is called osteosynthesis, is the main effective method of restoring bone integrity.
- External osteosynthesis is a method of treating fractures in which special wires are inserted through bone fragments perpendicular to the axis of the bone, which are then secured outside the bone on a special device. This tactic allows you to compare fragments and relieve the fracture site, thereby partially returning the functionality of the bone during treatment.
- Intraosseous osteosynthesis is carried out using a special conductor, which is inserted into the medullary canal of the bone and passed through the fracture site. Typically, this method is used to treat fractures of the diaphysis of long tubular bones.
- Bone osteosynthesis involves applying a metal plate to the fracture site after restoring the anatomical position of the fragments. To fix the plate, screws or screws are used that are screwed into the bone. This method allows you to quickly restore bone function and does not require the application of a plaster cast.
- Transosseous osteosynthesis. With transosseous osteosynthesis, pins, wires or nails fixing the fracture are passed at an angle through the fracture site so that both parts of the bone are fixed to the fracture line.
In addition to the listed methods used to fix fracture fragments, other methods are used in traumatological practice, the choice of which depends on the severity of the patient’s condition, the type and complexity of the fracture, as well as the skills of the surgeon.
- the presence of large and small bone fragments;
- strong displacement of fragments and, as a consequence, the impossibility of comparing them without surgical intervention;
- fractures behind the dentition;
- pathological inflammatory or neoplastic process in the fracture area;
- reconstructive operations;
- a small number of healthy, stable teeth on bone fragments.
Bone suture
To apply a bone suture, the fracture area is exposed from soft tissue on the lateral and internal sides. Holes are made in the fragments, through which, after comparison, a wire is passed, which is used to fix the fragments. The wire can be made of stainless steel or titanium. In some cases, synthetic threads are used instead of wire, however, due to their lower strength, this method has limited use.
- inflammatory process in the fracture zone;
- the presence of many small bone fragments;
- osteomyelitis;
- gunshot wounds in the area;
- presence of bone defects.
The advantage of this method is maintaining the ability to eat independently and perform oral hygiene, as well as eliminating complications in the temporomandibular joint.
Bony metal plates
Bony metal plates are widely used in maxillofacial surgery because, firstly, they reduce soft tissue trauma during surgery (
), which has a positive effect on the recovery period and the time of bone fusion, and secondly, they allow better fixation of fragments in areas subject to strong dynamic loads.
To fix bone fragments, small narrow plates made of titanium or stainless steel are used, which are screwed into the fracture area so that the fracture line is firmly fixed.
Also, fast-hardening plastics and special glue (
), metal staples with memory, Kirschner knitting needles.
For closed osteosynthesis, various extraoral wires and staples can be used. These include S-shaped and unified hooks, Kirschner wires, static and dynamic extraoral devices for immobilization, etc. The choice of fixation method is individual and is largely determined by the characteristics of the fracture.
Closed comparison of fragments
In addition to the above methods of surgical treatment, in some cases it is possible to achieve comparison of bone fragments non-surgically. This approach has a number of advantages, since, firstly, it does not require surgery and therefore is free of a number of risks, and secondly, it is not associated with soft tissue trauma in the fracture area, which disrupts blood microcirculation and slightly increases the time of bone healing.
However, the need for external bone fixation and limited jaw function are disadvantages of this method. Closed comparison of fragments of the lower jaw involves the application of a special fixing splint, which is attached to the teeth and stabilizes the bone fragments.
Today, closed comparison of bone fragments is used in cases where the bone fracture line allows it, when surgery is associated with high risks, as well as in fractures with a large number of small bone fragments, the surgical comparison of which is impossible.
Threats of complications
The fusion of the jaw bone depends on precise anchorage and recovery time.
Late visit to the doctor or incomplete rehabilitation hinder healing and cause complications such as:
- purulent processes at the fracture site;
- malocclusion, tooth damage;
- disorders of smell and vision;
- painful attacks;
- difficulty swallowing and chewing.
In order to prevent complications and achieve a favorable prognosis for recovery, it is important not to skip any stage of complex treatment:
- diagnostics;
- splinting or osteoplasty;
- restorative therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- therapeutic exercises;
- daily wound sanitation.
Treatment is not completed, as a rule, in a hospital - it continues at home. The duration of bone fusion depends on compliance with a special diet and doctor’s prescriptions.
How to develop a jaw after a fracture
After completion of treatment and removal of the splint or other treatment device, the person’s main task is to regain the previous functionality of the jaw. This is not always easy to do due to the complex anatomy of the organ. Recovery must be carried out strictly according to the recommendations of the attending physician. There is a set of measures and rules that will help the patient:
- Physical activity. Immediately after removing the device, it is necessary to begin making careful but constant movements of the jaws. Movements may cause discomfort or pain, but such procedures are necessary to restore quality of life;
- Heavy stress on bones and muscles should be avoided;
- At the beginning of rehabilitation, it may be necessary to use a spoon (spatula) to open the teeth;
- Therapeutic gymnastics includes exercises for the chewing, facial muscles, joints, and torso. A set of exercises is developed by a specialist individually for each clinical case;
- You should not eat solid foods;
- You can chew sugar-free gum frequently;
- You cannot suddenly open your mouth wide, the process should begin gradually;
- It is recommended to sing or make sounds that require forceful opening of the mouth.
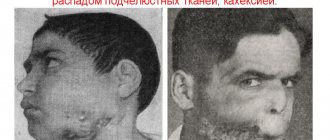
How to provide first aid to a victim
Severe swelling is one of the symptoms of a jaw fracture
Before the doctors arrive, a very important role is played by whether first aid was provided to the victim, and how well they were able to do it. Therefore, everyone should familiarize themselves with how first aid is carried out for a jaw fracture:
- stop bleeding if the fracture is open. You need to apply a sterile bandage to the wound. In addition, you can apply something cold;
- immobilize the bone. You can place a bar under the upper teeth, and then tie it to the head, or tie the lower jaw to the upper;
- numb . To relieve too much pain, you need to give an injection of a painkiller;
- carry out resuscitation actions if necessary.
It is important that resuscitation is carried out by a person who understands all the basic principles of the method.
more about how to treat arthrosis of the jaw joint here.
The first aid provider, at a minimum, must have special courses under his belt, in which the basic rules of this medical equipment were explained. Otherwise, resuscitating the victim is strictly prohibited. Otherwise, the desire to help will turn out to be disastrous.
Cure period
The question of how long it takes for a jaw fracture to heal does not have an exact answer. The minimum period for restoration of basic functions is 1.5 months.
There is no need to rush to remove the splint or constructive devices for restraining the bone, so as not to harm the weakened organ and not be left with displaced teeth or wide dental gaps.
Statistics reflect therapeutic treatment on average up to 60 days. Accurate forecasts are always individual. Removal of splints and fixing elements is carried out after 30-45 days.
The success and duration of treatment largely depends on the patient’s desire to overcome the illness and difficult situation.
You can enjoy your recovery both when the fixation is removed, discharged from the hospital, and when the functionality of the jaw is fully restored without pain.
How much does it cost to treat a broken jaw?
The cost of treatment for a jaw fracture is determined by the complexity of the injury and the measures taken to restore its integrity and functionality. Thus, the price of osteosynthesis can range from 15 to 70 thousand rubles. The starting price for splinting is about 14 thousand rubles.
The price is also affected by the quality of the tires used, physiotherapeutic procedures and postoperative observation. It is quite difficult to name the exact total cost of treatment, since this is only possible in a medical institution, when a specialist examines the victim. Services associated with recovery from such an injury are not cheap.
How long a jaw fracture takes to heal depends on the extent of the injury. The cause of damage will be various diseases or mechanical effects.
Symptoms include pain, visible deformation, swelling, and weakness.
Use search Are you having a problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease.
- How long does it take for a jaw fracture to heal?
- Easy degree
- Medium severity
- Severe degree
- How does healing occur after a jaw fracture?
- Proliferation
- The appearance of a callus
- Restoration
- How to speed up healing
- Jaw structure
- Structure of the upper jaw
- Structure of the lower jaw
- Complications from fractures
- Traumatic sinusitis
- Slowing down the consolidation of fragments
- Osteomyelitis
- False joint
- Fusion of fragments in the wrong location
- How to determine the type of fracture
- Nutritional Features
- Clinical study
- Causes
- Trauma with displacement
- Help at home
How does a fracture occur?
Human jaws have different structures. Due to these features, the symptoms of fractures and healing time will vary.
Table. Features of the structure of maxilla and mandibula:
The maxilla fracture occurs more easily than the mandibula. They can be broken in the following situations:
- direct or side blow to the jaw;
- with a sharp displacement of the jaws and slamming of the mouth;
- when colliding with a hard object or falling to the ground.
A specialist tells more about the causes and mechanism of the fracture in the video in this article:
Symptoms of a mandibula fracture are more severe than with a mandibular fracture. How long it takes the jaw to heal after a fracture will depend on which of them is broken. The lower one will take much longer to heal. How long a fracture of the lower jaw takes to heal depends on the nature of the damage and in what part of the bone it occurred.
If there is a fracture of the jaw area, what types exist?
When a jaw is fractured, bone damage occurs in various locations, as well as a violation of the integrity of surrounding tissues, blood vessels and nerves.
Depending on the cause of the injury, there are several types of such fractures:
- Complete with displacement of fragments . There are double, single or multiple (the specific case along the line of bone destruction is taken into account). A splintered version is also possible - this is when the jaw is broken into pieces.
- Closed. Externally, soft tissues are not damaged.
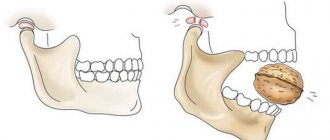
- Open . There is rupture of soft tissues and protrusion of fragments. See below for a photo of a displaced fracture.
- Incomplete . The most favorable type of fracture, because during injury the fragments do not move and it is possible to preserve bone tissue without surgical intervention.
Both the upper and lower jaw can be broken. The upper jaw is a paired bone located in the center of the face and is involved in the formation of the cavities of the nose, eye sockets and mouth.
Such a fracture can be very dangerous due to possible damage to the skull and brain and the development of inflammatory processes in the brain tissue against this background.
Open fracture with displacement
Attention: since it is the lower jaw that most often suffers from a fracture, frequent localizations of injury are the angle, the condylar processes of the chin area and the area of the molars. A rather rare pathology is the middle part of the lower jaw due to the maximum thickness of the bone in this area.
What causes this problem - common causes of fracture
To know how to avoid a jaw fracture, you need to have information about the causes of the injury.
The etiology is different and includes the following cases:
- falling from a height;
- strong blows during a fight;
- injuries in road accidents;
- gunshot wounds;
- injuries sustained at work or at home;
- malignant and benign neoplasms;
- osteomyelitis (inflammation of the jaw);
- perforation during tooth extraction;
- performing sports exercises and injuries during wrestling, boxing, etc.
Of course, it is impossible to predict the exact probability of eliminating the problem, but still, you need to try to reduce such risks to a minimum. Use insurance at height, follow traffic rules, do not get involved in fights, eliminate all inflammatory and infectious foci in a timely manner, and pay attention to safety precautions.
There is a lot that can be listed, but the main thing to understand here is that if you don’t take care of your health yourself, then no one will even think about this issue.
Punch to the jaw
Correctly recognizing symptoms is the first step towards recovery.
The clinical picture largely depends on the severity of the damage. This takes into account the degree of displacement of fragments, the type of injury and the number of fractures, damage to soft tissues, the presence of a brain contusion, etc.
After trauma to the jaw area, the following symptoms appear:
- at the site of the fracture, the patient feels severe pain, which only intensifies during movement, touching or talking;
- loss of sensitivity in the damaged area;
- tongue sinks;
- swelling of soft tissues is observed;
- abundantly secreted saliva contains streaks of blood;
- The victim’s mouth is slightly open, there is no way to swallow, speak, or even chew.
If there has been damage, it is best to immediately contact a medical facility, where the doctor will take an x-ray and, based on it, will be able to determine the presence of a fracture.
If such a problem is ignored, the following signs are added:
- an abnormal bite begins to form;
- the dentition shifts;
- large cavities form between the teeth;
- with an open fracture, the fragments spread out;
- I always feel a headache, severe weakness and irritability.
Fractures of the jaws can be different, and if the upper one is damaged, then the following additional symptoms can be noted:
- the cheeks are swollen, there is profuse bleeding between the teeth;
- blood also comes out of the nose, there is no sense of smell;
- numbness is felt in the eye area, and hematomas (bruises) appear;
- in severe situations, loss of vision is possible.
Quite often, patients complain of severe pain in the damaged area, as well as nausea. It is difficult for him to say anything, breathe or eat.
A broken jaw can also be diagnosed as a concussion. You can learn more about the causes, symptoms and treatment of jaw fractures from the video in this article.
Maxillofacial surgery cheekbone fracture
Classification
Damage is usually classified according to different criteria:
- The fracture line defines the injury as oblique, longitudinal, transverse, straight, zigzag, and comminuted.
- Jaw fracture with and without displacement.
- The number of fragments characterizes the fracture as multiple, single, double.
- The degree of soft tissue damage allows us to distinguish open and closed fractures.
- The cause of the pathology may be injury or diseases of bones and soft tissues. In the second case, a jaw fracture without displacement is more often recorded.
Depending on the location of the injury, a specific classification is used.
Classification of mandibular fractures
Injuries are usually divided into fractures:
- Body of the jaw. They are rarely closed. Depending on the location of the fault line, angular, median, mental and lateral fault lines are distinguished.
- Branches of the jaw. The fault line runs parallel or perpendicular to the longitudinal axis. This group also includes damage to the coronoid or articular process of the mandibular bone.
A fracture of the lower jaw may have one fracture line or several, forming fragments of different shapes. Unilateral and bilateral injuries are recorded, which can be open or closed.
Classification of fractures of the upper jaw
In medical practice, it is customary to distinguish 3 groups of injuries according to the Le Fort principle:
- Upper fracture. It is characterized by the absence of classic neurological symptoms for trauma. The cause of the pathology is considered to be an oblique blow to the vertical structures of the face or damage to the orbital area.
- Medium fracture. Characterized by separation of the mass with the bones of the nose and maxillary bone. The cause is a blow to the area of the nasal bones, or a reflection of a blow to the chin.
- Lower fracture. A violation of integrity in the area of the maxillary sinuses is typical. The injury occurs as a result of a blow to the upper lip area.
Jaw structure
A prerequisite for successful actions to restore the jaw is knowledge of its structure.
The upper jaw includes the body and processes.
The body contains 4 surfaces:
- The anterior one is curved and contains the canine fossa and infraorbital space.
- Posterior - includes the tubercle with the adjacent palatine groove, alveolar openings.
- Orbital, the functional elements of which are the infraorbital groove with the orbital canal and the lacrimal notch.
- Nasal surface with maxillary cleft.
The upper jaw consists of the palatine, zygomatic, frontal, and alveolar processes. On the latter there are alveolar openings adjacent to the maxillary tubercle, to which the lateral muscle is attached. The jaw includes a set of teeth: incisors, canines and premolars of the first and second orders.
The lower jaw consists of 2 surfaces (external, internal) of the body and 2 processes. On the inside there is a chin spine, to which the lingual and hyoid muscles are attached. Below is the digastric fossa, above is the hyoid fossa and the jaw line. On the outside there is the chin protuberance, the alveolar elevations above which the teeth are located.
Above the angle of the mandible there is a masticatory tuberosity, a retromolar fossa, a buccal ridge, a lingula, a condylar and a coronoid process. The branches of the jaw that pass into these processes determine the type of face.
Treatment methods
Instructions for treating fractures will vary depending on several factors:
- which jaw is broken;
- what kind of fracture - simple or complex, with or without displacement;
- patient’s age and presence of concomitant pathology;
- risk of complications.
All this will affect how long the injury site can take to heal:
- Conservative treatment. Used for simple fractures, in the absence of displaced fragments, against the background of good health. Plaster splints or splinting are used.
- Surgery. Indicated in the presence of displaced fractures, especially the mandibula. It is also recommended for people with concomitant pathologies, since healing may take much longer for them. Treatment consists of comparing the fragments and applying osteosynthesis.
The photo shows various types of restoration of broken bones.
The healing of the fracture is monitored periodically with x-rays. It is impossible to immediately answer how long such damage will take to heal, so several control images may be needed.
Recovery time
If a jaw fracture occurs, how long does it take for the damage to heal? This question cannot be answered unambiguously. There are only average periods. However, they are individual for each person and depend on many factors.
For example, how long does it take for a fracture to heal without displacement - the average recovery time is 30-35 days. During this time, the bone heals completely and the function of the organ is restored. And if we consider the question of how long it takes for a complicated fracture to heal, with displacement of fragments, here the time frame will be different and amount to at least two months.
Where to go and how to treat a fracture
If you are injured, you should immediately call an ambulance. While the emergency is awaiting, all measures must be taken to help the victim, because severe injuries may result in large blood loss, painful shock and difficulty breathing.
So, in front of you is a man with a broken jaw - your actions:
- We stop heavy bleeding by applying finger pressure to the jaw artery or applying cotton swabs (if there is copious bleeding, and this is possible due to the massive blood supply to the facial area, it is not always effective, but it’s worth a try).
- To restore breathing, you need to carefully cleanse the oral cavity of blood and vomit, thereby freeing the airways for oxygen to enter. Retraction of the tongue is also possible, so the victim should either be on their side or face down, or their tongue should be pulled towards the front of the jaw.
- If there is no breathing, immediately perform artificial ventilation through the nose.
- Carefully fix the jaw in a stationary position and wait for help.
In general, assistance provided by people who do not have certain knowledge should be carried out without fanaticism. There is no need to try to set a protruding bone, etc., because if handled ineptly, you can only aggravate the situation.
After the ambulance arrives, the patient is transported to the hospital. If relatives or the victim do not know where to go with a fractured jaw, the department of maxillofacial surgery deals with this issue. So, after an examination by a doctor and an x-ray, the doctor begins to collect the bones with his hands, but do not be afraid, general or local anesthesia is first administered.
The main treatment method, in addition to anti-inflammatory and symptomatic therapy, is splinting. In Russian, with this type of help, fragments are fixed using structures made of plastic or wire.
It can be of several types:
- With one-sided surgery, the wire is attached to the injured area, which is observed only on one half of the jaw bone.
- When double-sided, a stiffer wire is used, as well as additional rings and hooks.
- With double-jaw splinting, both jaws are fixed with displacement using copper wire, which is attached to the teeth and held in place by rubber rings.
Maxillofacial surgery deals with this; fracture of the zygomatic bone is also included in this group of care.
Attention: during treatment, the type of jaw displacement is an important point. It can be vegetal, sagittal and transversal. It is from this point that the type of equipment required to correct the fracture is based.
The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the damage and ranges from approximately 30 to 90 days. The main task of the doctor is to restore chewing functions and bite, as well as prevent the development of the inflammatory process and complications.
For complex fractures, plastic surgery with the installation of prostheses is also used. Providing assistance in paid clinics can be quite expensive; the price depends on many factors - geographical distance, degree of qualification of doctors, etc.
Splinting