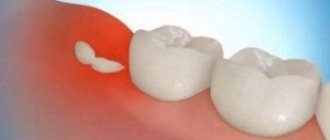
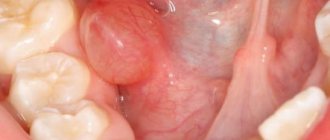
Often, enlarged tonsils in adults indicate infection of the throat mucosa by pathogenic microorganisms. This pathology is almost always accompanied by characteristic symptoms that cannot be ignored. It is important to find out the reasons why the tonsils are enlarged, and then, if necessary, begin drug treatment
. Sometimes conservative methods do not bring results; in such situations, the doctor decides to remove the tonsils that are hypertrophied.
Main reasons
In infants, the tonsils are undeveloped, but from birth they are constantly developing, and changes and improvements in their functions are also observed. But under the influence of negative factors, some people experience hypertrophy of the tonsils, accompanied by an increase in size and the addition of other pathological signs. Common reasons why tonsils become enlarged in an adult or child are:
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the nasopharynx;
- injuries, thermal or mechanical burns of the mucous membrane in the throat;
- chronic infectious diseases such as tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, caries;
- decreased protective functions of the body;
- hypothermia;
- hormonal, endocrine disorders;
- allergy.
Inflammation can be caused by an infection.
Enlarged tonsils in a child or adult can be a consequence of hypothermia, stress, or psycho-emotional overload. What reason influenced the progression of this pathology can only be determined by a doctor after a comprehensive diagnostic examination. If there is a clear change in the shape of the tonsils, you should not self-medicate, trying to eliminate the symptoms with medications and folk remedies
. It is important to treat the disease correctly, otherwise complications cannot be avoided.
Causes
Before talking about why the tonsils can enlarge and how this process objectively manifests itself, you need to imagine where these anatomical formations are located and what functional system of the body they belong to. The Pirogov-Waldeyer lymphadenoid ring, localized in the oropharynx, is an immune barrier at the entrance to the respiratory and digestive tract. It is formed by several tonsils:
- paired palatine, or tonsils, localized between the palatine arches;
- paired tubal, located at the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube;
- unpaired nasopharyngeal (pharyngeal), located in the vault of the nasopharynx;
- unpaired lingual in the mucous membrane of the root of the tongue.
Tonsils consist of lymphoid tissue, like peripheral organs of the immune system, they are formed at the stage of intrauterine development and remain throughout life. Moreover, some of them (pharyngeal, lingual, tubal) may undergo age-related involution, expressed in a decrease in size and functional activity.
Involution, in essence, means reverse development, transformation of an organ. This is of great importance for considering the reasons that explain the enlargement of the tonsils in an adult, since age-related functional hypertrophy is characteristic of children, and age-related involution occurs at the age of 13-15 years.
Hypertrophy, that is, an increase in the size of the amygdala, can be caused by various reasons. Why do tonsils and other lymphoid formations enlarge? This leads to:
- Congenital developmental anomalies.
- Absence of age-related involution.
- Constant trauma to the tonsil tissue (for example, rough food).
- Tonsillectomy (removal of the tonsils).
- Frequent infectious diseases, immunodeficiency.
- The presence of foci of chronic infection in the oropharynx.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Women taking hormonal contraceptives.
When the tonsils are enlarged, they interfere with adequate breathing and contribute to the formation of pathological changes. If in childhood hypertrophy tactics can be wait-and-see, in the treatment of adult patients it is necessary to take measures immediately after the diagnosis is established.
Thus, any of the tonsils can hypertrophy; The process in adults is irreversible and requires treatment.
Why does tonsil hypertrophy occur? An increase in lymphoid tissues in some cases is associated with an intensification of the synthesis of immunocompetent cells. Therapeutic treatment is prescribed only in case of catarrhal or purulent inflammation of organs. The protective mechanisms of the child's body are not fully regulated, so preschool children are more susceptible to infectious diseases than adults.
The causative agents of pathological processes in the tonsils can be:
- adenoviruses;
- rhinoviruses;
- herpes viruses;
- influenza virus;
- coronaviruses;
- staphylococci;
- meningococci;
- streptococci;
- diphtheria bacillus;
- mycoplasma;
- fungi;
- spirochetes.
Septic inflammation of lymphoid accumulations leads to swelling, hyperemia and tissue melting. A critical increase in the size of the tonsils makes breathing difficult, which can cause acute hypoxia in a child.
What symptoms are you worried about?
Depending on the degree of enlargement, the patient will be bothered by the following pathological signs:
- With progression of grade 1, the tonsils are expanded by 1/3 of the height between the palatine arch and pharynx. The patient complains of slight discomfort when swallowing, and a white coating forms on the mucous membrane.
- Hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils of the 2nd degree is characterized by expansion by 2/3 of the height. The tonsils become red and look inflamed and swollen.
- Hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils grade 3 is considered an advanced disease. The patient has a severe sore throat, pronounced problems with breathing and swallowing
. The tonsils become so huge that they prevent the normal penetration of air into the larynx, and an increase in body temperature is observed. Due to pressure on the vocal cords, the timbre of the voice changes, a constant feeling of a foreign object in the throat, soreness, and rawness appears.
The feeling of nasal congestion bothers me.
Adenoid hypertrophy is also accompanied by the following symptoms:
- violation of nasal breathing;
- decreased hearing function;
- speech disorder;
- sleep problems;
- often recurrent rhinitis.
Symptoms ↑
- Any exacerbation process begins with the fact that the tonsils increase in size, which means they take up more and more space in the oral cavity. At the same time, the pharynx itself does not enlarge, and as a result, the airways are partially or completely blocked;
- mucous discharge from the nasopharynx;
- systematic runny nose that cannot be treated with medications;
- snoring while the patient sleeps;
- open mouth at night;
- decreased hearing acuity;
- sometimes suffocation occurs;
- rhinitis, coughing attacks;
- nasal voice;
- the face takes on an adenoid shape;
- a certain apathy towards everything, indifference appears;
- constant headaches;
- irritability;
- failure to perceive information.
The degree of inflammation can be determined independently by the amount of accumulation of purulent deposits in the area of the palatine arches. To do this, you need to go to the mirror, press your finger or spatula on the tip of your tongue to open access to the gaps. Lacunae are cavities in the tonsils, which are located at the back of the oropharynx. At the initial stages, it is almost impossible to diagnose the presence of pus, since there will be a small amount of discharge in the lacunae. After some time, the number will increase and the affected area will expand.
What is the difference between tonsils and tonsils? On the one hand, they protect our body from pathogenic bacteria, on the other hand, they are a real threat when they themselves are affected.
Diagnostic methods
The fact that the tonsils have become enlarged and large can be noticed during self-diagnosis. If the condition worsens and pathological symptoms appear, it is better to visit a doctor and find out the causes of the disorder. At the initial examination, hyperemia, redness and swelling of the palatine tonsils will be noticeable.
. To determine an accurate diagnosis, a referral is given to undergo a number of additional diagnostic procedures, such as:
- general blood analysis;
- microbiological examination of a throat smear;
- allergy tests;
- immunogram;
- electrocardiography.
When examining the throat, the doctor should be alert to hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil on one side. Glands of different sizes often indicate the progression of malignant tumors, sexually transmitted diseases and other severe inflammatory processes
. In such a situation, the histology of the glands is examined in more detail, and an additional examination is prescribed by an oncologist, venereologist or pulmonologist. It is rare, but it happens that one tonsil is enlarged due to the individual characteristics of the body.
Tonsils - what are they?
Tonsils are small oval-shaped formations that are located in the oral cavity and nasopharynx.
They consist of lymphadenoid tissues involved in the process of synthesis of blood and immunocompetent cells. The pharyngeal, lingual, tubal and palatine tonsils are the main components of the pharyngeal ring, protecting the respiratory organs from the penetration of pathogens. In the absence of functional disorders in the functioning of the tonsils, medicinal and surgical intervention is not required.
Hypertrophy of lymphoid tissues most often occurs in childhood and affects mainly the pharyngeal tonsil and tonsils (palatine tonsils). In case of inflammation of organs, treatment begins with the use of conservative therapy. If drug treatment is ineffective, surgical intervention may be required, involving partial (tonsillotomy) or complete (tonsillectomy) removal of lymphoid accumulations.
How to treat?
Traditional
Not advanced stages are amenable to drug treatment.
At the first or second degree of hypertrophy, conservative treatment is prescribed, aimed at eliminating inflammation and pathological symptoms. Enlarged tonsils are treated with antiseptic medications that destroy the bacterial infection. When the tonsils are hyperemic, it is recommended to lubricate them with Collargol, Karotolin, and Tanid-glycerin.
.
If the tonsils are inflamed due to a bacterial infection causing a sore throat, an antibacterial drug is prescribed
.
Allergic manifestations are eliminated with the help of antihistamines
. Glucocorticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs will help remove swelling and inflammation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa. When the temperature rises, antipyretic drugs “Ibuprofen”, “Nurofen”, “Nise” are recommended.
Sometimes hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils and adenoids is not eliminated by conservative means. Then the doctor will recommend surgery to remove the pathological structures. The tonsils are completely or partially cut out, after which the condition should return to normal
. To prevent postoperative complications, rehabilitation is carried out, during which a restorative therapy regimen and auxiliary procedures are prescribed.
Sometimes parents insist that the child’s hypertrophied and loose tonsils be removed. However, such operations are carried out strictly according to indications.
. If the baby is 3 years old, the surgeon will recommend waiting until the child grows up. At an older age, the tonsils may become normal size without special treatment.
Therapy with folk remedies
Chamomile has an antiseptic effect.
Non-traditional methods can be used as adjuvant therapy. If you use natural medicines correctly, they will be of great benefit, and a person will be able to get rid of pathology faster. If the tonsils are very enlarged, it is recommended to gargle with solutions based on the following natural ingredients:
- tincture of propolis, mint;
- decoction of chamomile, sage, oak bark;
- soda, sea salt.
On the second or third day after removal, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids. This helps relieve inflammation, quickly remove toxins from the body, and moisturize the mucous membrane.
. To prepare a healthy drink, it is recommended to use the following recipe:
- Mix lingonberry leaves and meadowsweet flowers in equal proportions.
- Separate 2 tbsp. l. collection and pour 300 ml of boiling water.
- Leave the product for 20 minutes, then strain.
- Add 1 tsp to the infusion. honey, drink throughout the day as tea.
Other methods
Physiotherapeutic procedures help restore damaged tissue.
To eliminate the inflammatory process, it is recommended to use physiotherapeutic methods, which are prescribed in parallel with the drug therapy regimen. The following methods of physiotherapy are considered effective:
- ultrasound;
- electrophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- phonophoresis;
- mud baths.
Principles of treatment
Hypertrophy of the tonsils in children causes a number of disorders in the body. A constant lack of oxygen (hypoxia), caused by the blocking of the airways by hypertrophied tonsils, leads to children being retarded in physical development. Approximately 25% of patients with enlarged tonsils experience enuresis and associated mental disorders.
How to treat enlarged tonsils in a child? Komarovsky claims that it is possible to eliminate hypertrophy of lymphadenoid tissues without surgical intervention only if you undergo complex therapy. As a rule, the treatment plan for ENT diseases in children is as follows:
- cleansing the lacunae and follicles of the tonsils from pathological mucus and infectious agents with solution antiseptics;
- elimination of allergic manifestations and swelling with the help of antihistamines;
- increasing general and local immunity with vitamin-mineral complexes and immunostimulants;
- destruction of pathogens with etiotropic drugs - antibiotics, antifungal and antiviral agents;
- accelerating tissue healing processes using physiotherapeutic procedures.
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment are used only at the stage of resolution of inflammatory processes in lymphadenoid tissues.
Treatment for hypertrophy is mandatory if clinical symptoms occur. How to treat enlarged tonsils in adults? A combination of surgical and conservative methods is used, with surgery being the main method; other methods allow you to consolidate the result, prevent relapses (repeated episodes) and complications.
If the patient does not experience difficulty breathing, does not complain of poor sleep, snoring, or does not indicate other characteristic signs, hypertrophy is not dangerous for him. However, regular monitoring is mandatory - and it is advisable that the same attending physician examine the throat. This makes it easier to compare changes in dynamics.
If we are talking about paired lymphoid formations, but one tonsil is enlarged, before starting treatment, a differential diagnosis is carried out - chronic inflammatory processes, the presence of a cold abscess, and the presence of a neoplasm are excluded.
How to treat enlarged tonsils? For this purpose, methods of mechanical and physical influence are used:
- Tonsillotomy.
This is a surgical cutting off of part of the tonsil - during the operation, tissue is removed within the anterior palatine arches. The issue of tonsillotomy is considered for grade 3 hypertrophy.
- Diathermocoagulation.
Heating of tissues using high frequency current - this causes irreversible coagulation of proteins. The method is also called therapeutic cauterization. Can be shown at 2 degrees of magnification.
Adenoids in an adult patient must be removed because they cannot undergo involution and provoke irreversible changes in the nasal cavity. Adenotomy is carried out using a special instrument - an adenotomy. Laser removal is also currently practiced.
For hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil, surgical excision is not used, as this can increase the risk of bleeding. Preference is given to safer methods - cryosurgical treatment or diathermocoagulation. Radiation therapy is also used.
If we are talking about hypertrophy of tubal lymphoid formations, the left tonsil and/or the right tonsil are enlarged, curettage (curettage) of the growths, and radiation therapy are performed. At the same time, measures are taken to restore the patency of the auditory tube, and the throat and nasal cavity are sanitized, and foci of chronic infection in the teeth and gums are eliminated.
Conservative therapy is carried out mainly in the postoperative period and may include the prescription of drugs:
- antibacterial;
- antiseptic;
- vasoconstrictors;
- anti-inflammatory, etc.
The list of medications is determined in accordance with an assessment of indications and contraindications and is individual in each specific case. The drugs can be used systemically (tablets, injections), locally (lozenges, sprays, drops). During the treatment process, it is necessary to periodically examine the throat.
Tonsil hypertrophy in adults is treated by an otolaryngologist (ENT doctor). Timely seeking medical help will allow you to select the most gentle methods of treatment and avoid the formation of irreversible changes associated with enlargement of the tonsils and other lymphoid formations.
Preventive methods
If an adult, for unknown reasons, has enlarged tonsils and develops pathological symptoms, it is better to make an appointment with a doctor and find out the nature of the disorder. The doctor examines the test results, histology, and then selects the optimal treatment regimen that will help normalize the condition
.
To prevent tonsil hypertrophy, it is recommended to maintain the body’s protective functions at a high level, monitor health, promptly treat viral inflammatory diseases and prevent them from developing into a chronic stage. It is worth avoiding hypothermia, protecting the mucous membrane from injury, chemical and thermal damage, improving nutrition, and giving up bad habits
. These simple rules will help prevent inflammation of the tonsils and the development of dangerous consequences.
Professor, doctor of the highest category, MD. He defended his doctoral dissertation on the topic “Rare tumors of the ENT organs.”
26 years of experience, of which 10 years as head of the otorhinolaryngology department of City Clinical Hospital No. 67.
In 2010-2011 underwent advanced training in clinics in Italy and Holland in rhinosurgery and middle ear surgery
. Proficient in the techniques of functional endoscopic surgery of the paranasal sinuses (FESS - Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery), transoral robotic surgery of the hypopharynx (TORS - Trans Oral Robotic Surgery) and the technology of aesthetic robotic surgery of the thyroid gland without scars on the neck.
Sphere of professional interests:
— reconstructive and hearing-improving operations, — oncological diseases of the ENT organs, — cystosis, papillomatosis and polyposis of the ENT organs, — thyroid surgery.
Tel. for records: +7-495-933-66-55.
For some time now (long) one tonsil has been much larger than the other, I didn’t attach any importance to it, but then I got sick, started looking at my throat and, let’s say, it dawned on me that this is not normal) sometimes I cough up white lumps, also for a long period time, please tell me what it is and how it can be treated?
Hello. I've been having a lump in my throat for some time now.
.
Does not hurt. There's just something in my throat that's bothering me
.
Sometimes shooting pain in the jaw and ears
.
I looked into my throat a few weeks ago and discovered that the right tonsil is larger than the left
.
A couple of days ago I ate ice cream, and the next morning I had a sore throat on the right side. But it passed quickly
.
Strepsil sucked all day. I also noticed a small pimple on the uvula
.
A month ago I visited my family doctor about frequent heartburn and a stool test showed the presence of Helicobacter pylori
.
Based on this analysis, the doctor prescribed me a two-week course of antibiotics Amoxicillin and Metronidazole
.
Regarding the lump in the throat. I caught myself thinking that I had felt it for quite a long time (maybe half a year, a year), but did not attach much importance to it
.
I thought something was constantly dripping from my nose. I often have a stuffy nose and a deviated septum
.
Tell me, please, what can it be?
I'm very worried about this .
The lymph nodes do not seem to be enlarged
.
The condition is unclear. I don’t seem to have a fever, but I feel unwell
.
There is only an appointment for an ENT appointment on November 1st. Here in England, everything is very sad with this
.
According to quotas, you have to wait at least 2 months
.
Or for money (about $100 per appointment)
. I've been on edge for almost a month now. I really need your advice.
Indications for removal
The tonsils or palatine tonsils are an important organ in the nasopharynx that performs protective and hematopoietic functions. It is he who suffers the most during a sore throat and other throat diseases, taking the first blow. Removal of the tonsils is considered a forced step and is carried out when conservative methods do not lead to recovery. In addition, surgery is required if the tonsils become a strong source of infection that can spread to other organs.
The following indications for the procedure of complete or partial resection of the tonsils are distinguished:
- hypertrophy of the tonsils;
- malignant and benign neoplasms;
- chronic tonsillitis (more than 4 cases of the disease per year);
- the presence of streptococcal infection in the body;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system, respiratory system, liver and kidneys;
- active growth of lymphoid tissue, which causes difficulty in breathing and swallowing;
- sleep apnea syndrome;
- complication in the form of peritonsillar abscess.
But what a cyst on the tonsils looks like and what can be done about such a problem is indicated here.
The video describes the procedure for removing tonsils:
Only the attending physician can prescribe an operation based on the diagnostic results and the characteristics of the disease in each specific case. Complete removal of the tonsils is not always necessary; partial resection is more often performed, thanks to which the tonsils retain their functions. But is it possible to warm the throat when the tonsils are inflamed and how safe it is for health is indicated in the article at the link.
It is almost impossible to identify complications caused by tonsillitis in the early stages, since intoxication and weakening of the body occurs slowly. That is why in case of chronic sore throat it is extremely important to regularly undergo comprehensive diagnostics.
But what pus on the tonsils looks like and what can be done about such a problem is outlined here.
Removal methods and prices
Today, several methods of treating tonsillitis with laser have been developed, the choice of which is determined by the structural features of the tonsils, the age of the patient and the clinical picture of the disease. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, as well as restrictions on use.
Surgical excision
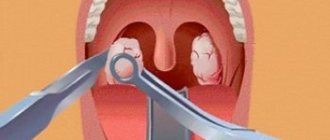
This is a classic method of removing tonsils, which has been used for several centuries. The operation is performed under general anesthesia and is therefore completely painless for the patient. The recovery period is the longest, during which severe discomfort is felt in the throat area, but the risk of relapse of the disease is minimized.
During the procedure, the doctor uses a scalpel, scissors and a snare to completely or partially remove the tonsil. Minor bleeding is stopped with a coagulator. The operation is considered a radical method; in recent years it has been replaced by more gentle methods. After complete removal, local immunity may decrease, and the likelihood of allergies increases. The average cost of the procedure is 10 thousand rubles.
You may also be interested in information about why a child’s tonsils are enlarged and which medications are the most effective.
Electrocoagulation
Using a special apparatus, the affected area is cauterized under high temperatures. Used for minor pathologies when there is no need to completely remove the tonsils. There is no risk of severe bleeding during the procedure and there is a short recovery period. Removal is carried out under local anesthesia. The cost of the procedure is from 15 thousand rubles.
The main disadvantage of this method is the likelihood of burns on nearby tissues if the coagulator temperature is incorrectly selected, which can cause discomfort during healing.
Removal with ultrasonic scalpel
It is an alternative to the classic method. For removal, an ultrasonic scalpel is used, the blade of which vibrates at high frequencies. During operation, a high temperature is created (up to 80 degrees), so the risk of bleeding is minimal. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, and after removal a neat suture remains. If the procedure is carried out correctly, the risk of burns is minimal. The rehabilitation period is up to 10 days. The cost of the procedure is from 15 thousand rubles. You may also be interested in information on how to treat inflammation of the tonsils.
Cryodestruction
A popular operation in recent years is to remove tonsils using liquid nitrogen.
During the procedure, lymphoid tissues are frozen, which then die. The procedure itself for cryodestruction of the tonsils takes place under local anesthesia, but subsequently many note a painful recovery period. During rehabilitation, antiseptic care is needed, as there is a possibility of infection. A repeat procedure is usually required after 5-7 years. The price of the procedure is from 1 to 6 thousand rubles.
Laser tonsillectomy
One of the most modern and safe methods for removing affected tonsils. Depending on the clinical picture, different types of laser can be used (holmium, infrared, fiber optic and others). During the procedure, not only tissue is excised, but also the risk of bleeding is prevented.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia and lasts no more than 30 minutes. It is used in most clinics around the world, but there are a number of contraindications for use (pregnancy, menstruation, tuberculosis, diabetes). Rehabilitation takes no more than 14 days, during which it is important to follow all doctor’s instructions. The average cost is 20 thousand rubles.
You may also be interested in information about why the tonsil and ear hurt on one side.
Liquid plasma method
The most high-quality and accurate method of complete or partial removal of tonsils. The operating principle is based on the mechanism of electrical potential difference. During the procedure, tissue ionization is caused, as a result of which the tonsils break down into lymph and low-molecular components.
This is a minimally invasive and reliable method with virtually no risk of bleeding or pain. The recovery period takes up to 10 days. Repeat surgery is usually not required. The cost of removing tonsils with a coblator is 45 thousand rubles.
When choosing a clinic for the procedure, you need to familiarize yourself with the qualifications of the surgeon and the availability of certificates for carrying out such activities, as well as look at the reviews of other patients.
But what the tonsils look like with a sore throat in the photo and how the operation to remove them is described here.