Cyst symptoms
If the cyst is not treated, it grows, preventing swallowing and chewing.
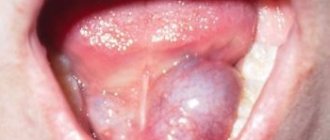
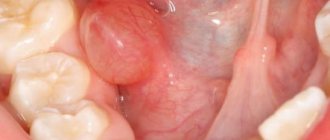
The growth of ranula can occur quite quickly, and in a short time it can reach a size of four to five centimeters (in diameter). It looks like a tumor-like formation, whose surface is a stretched mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth. The ranula is somewhat transparent due to its thin wall, but may have a bluish color.
It is usually located to the left or right of the lingual frenulum due to the pairing of the sublingual salivary glands, but in rare cases a bilateral lesion can be diagnosed. A sign of fluctuation is clearly visible against the background of the density of the formation, which gives reason to judge the liquid consistency of the ranula contents.
It is colorless, somewhat reminiscent of raw egg white due to its viscosity and stickiness. In terms of composition, the liquid can be divided into water, which occupies up to 95% of the total volume, and protein substances contained in it in the form of mucin. Palpation of the ranula does not cause discomfort to the patient, but its growth can cause a feeling of tightening of the oral mucosa under the tongue.
The advanced growth of the cyst leads to displacement of the tongue, disturbances in speech, swallowing and even breathing. Uncontrolled increase leads to thinning of the surface of the cyst, which inevitably provokes rupture with subsequent leakage of fluid into the oral cavity, after which the ranula will again begin to fill with salivary secretion. In the case of the inflammatory nature of cyst formation (due to a virus or bacteria), there is a high risk of secondary infection.
The danger of a malignant tumor
A lump under the tongue, unfortunately, is not always a safe lump. Any doctor can tell you why cancer develops in the oral cavity. Often, heavy smokers or workers in hazardous industries develop a cancerous tumor in the oral cavity. In 10% of cases, the tumor takes root under the tongue.
A cancer tumor develops in several stages:
- elementary;
- developed;
- launched.
At the initial stage, it is difficult to detect the disease due to the absence of symptoms. The patient begins to feel slight discomfort when eating or talking, lymph nodes and salivation increase. Pain is perceived as a symptom of sore throat or stomatitis.
At the second stage, severe pain, frequent numbness of the tongue, and bleeding occur. At the final stage, the disease metastasizes to other organs of the mouth and throat.
Signs of illness
At first, the patient has no idea that he has cancer. Over time, the seal grows and interferes with swallowing, speaking and chewing food. Pain can only occur during salivation or chewing food. Aching pain can also be constant. If any foreign formation appears in the oral cavity, you should immediately seek diagnosis and treatment from a specialist, especially if the lump changes color and grows.
How is cancer under the tongue diagnosed?
Detecting a malignant tumor in the early stages is often difficult due to the fact that the patient has no complaints. The doctor is faced with a fairly mature education, so he can already make a diagnosis only by palpation. The doctor orders a test to confirm suspected cancer. Histological examination is usually performed by biopsy. Using special tweezers, a piece of the body is pinched off, on which a laboratory test is carried out to find out whether the tumor is benign or not.
How is therapy carried out?
This disease is eliminated with the help of surgical treatment, which is combined with therapy with antibacterial drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs. When surgical treatment is performed, the recovery period can be long. This is due to the fact that the tissues of the mucous area under the tongue are thinned and are easily injured.
If there is an infectious process, the ulcer is additionally treated with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory medications prescribed by the doctor. When the salivary glands are blocked, the most optimal treatment method is surgical removal of the formation itself along with the gland that caused its appearance.
When talking about a cyst under the tongue, most often they mean a cyst of the sublingual salivary gland (ranula). This is a benign tumor-like neoplasm that develops against the background of blockage of the excretory duct of the gland. Less commonly, congenital dermoid cavities are found in the sublingual region.
The cyst rarely becomes infected, however, and in the absence of inflammation, the neoplasm can cause significant discomfort to the person. The development of a cyst in a child during the formation of the speech apparatus can lead to speech disorders in the future. Treatment of the disease is only surgical, involving removal of the cavity along with the gland. After the operation, all unpleasant symptoms, as a rule, are completely eliminated, then the patient only needs to undergo preventive examinations.
Most sublingual cysts are retention-type neoplasms
, the cause of which is a blockage of the salivary gland duct. The human oral cavity contains many small salivary glands and 3 pairs of large ones:
- parotid;
- submandibular;
- sublingual.
The appearance of a “ball” under the tongue is most often associated with blockage of small glands (more than 55% of cases), the duct of the sublingual gland (35%), and less commonly, the submandibular gland (a more rarely diagnosed pathology, less than 5%).
In general, any cyst of the major salivary glands is a rare diagnosis.
From a localization point of view, we can highlight:
Since the glands are paired, the neoplasm is localized on the left or right; however, if the cyst is large, it can spread to the area of the healthy gland.
The cyst has a spherical or oval shape, it is soft-elastic to the touch with a distinguished two-layer capsule (on the outside - connective tissue, on the inside - epithelial). The mucous membrane covering the cyst may become thinner - then the “ball” acquires a white or bluish tint.
Cysts under the tongue are most often single-chamber, they are not multiple.
Most often, this tumor is found in people 20–30 years old.
, less often - after 40 years, there are cases of the development of retention sublingual cysts in children.
The size of the cavity (ranula, also called a “frog tumor”) rarely exceeds 3 cm, but a deep cyst can reach 5 cm in diameter.
In addition to retention cysts, dermoid cysts may be found under the tongue
– these are always congenital neoplasms that have a dense, elastic capsule and mushy contents. Dermoids are often located on the floor of the mouth, near the salivary glands. Their distinguishing feature is very slow growth. This is why these congenital cavities are often diagnosed in people over 30 years of age.
How does ranula appear under the tongue?
Ranula can be localized at the tip of the tongue, closer to one of the lateral surfaces, at the root; cyst formation often occurs in the sublingual area. Most often, such a cystic formation is formed in the area of the frenulum of the tongue, which can lead to its displacement to the side.
Ranula can form not only on the surface, but also under the mylohyoid muscle, which complicates the diagnosis of the tumor.
The size of ranula usually does not exceed 3 cm, and it grows quite slowly. Pain syndrome, as a rule, is not observed. However, the cyst may feel like a foreign body in the mouth. Large tumors cause discomfort when talking and can interfere with eating.
Possible causes of a lump in the mouth
In most cases, lump-shaped formations tend to increase in size over time. The structure of the lump and accompanying symptoms will depend on the reasons for its formation. For example, if it is black, it is a hematoma, the patient needs to see a surgeon. Common causes of lumps in the mouth include the following:
- injury;
- malignant neoplasm;
- cyst;
- lipoma;
- epithelioma;
- botryomyxoma;
- myoblastoma;
- papilloma;
- struma lingual.
Consequences of injury
Why does a ball appear on the tongue, under it or on the side? Often the cause is injury. The density and color of such a formation may vary - these factors depend on how severely the organ was injured. If a blood lump forms, it means the blood vessels have been damaged. If the vessels are not damaged, the formation in the form of a ball will not be red, but white. According to the nature of the injury, they are divided into the following types:
- chemical – result from exposure to very salty/spicy/acidic foods or household chemicals on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
- mechanical - a person bit his tongue or damaged it with a toothpick, fish bone, or seed shell (sometimes the injury is so minor that it may not be noticed);
- thermal - occur due to the consumption of too hot / cold foods.
Malignant formation
The cause of a lump on the surface of the tongue or under it may be the development of a malignant neoplasm. The risk group consists of men aged 40 years and older. However, the occurrence of pathology is not excluded in representatives of a different gender or age group. The development of a cancerous tumor is provoked by untreated or neglected benign formations. Malignant formation in the tongue goes through the following stages of development:
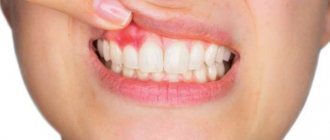
- the appearance of a white bumpy lump under the tongue (does not hurt, does not bother);
- education develops, pain appears;
- salivation increases, a putrid odor appears from the oral cavity;
- damage to all tissues of the tongue with the development of ulcers;
- tongue dysfunction (difficulty speaking or eating, loss of taste);
- inflammation and enlargement of nearby lymph nodes due to the spread of the disease through the lymphatic system;
- damage to the patient's internal organs.
The appearance of a salivary gland cyst
The development of a salivary gland cyst at the initial stage is almost invisible to the patient. Externally, the cyst under the tongue looks like a white lump filled with transparent liquid with a fibrous membrane, localized in the sublingual space. A cyst of the minor salivary gland or one of the large glands may appear. As the tumor grows, the patient experiences discomfort when chewing and swallowing, difficulty speaking, and in some cases the lump even interferes with breathing.
Types of benign neoplasms
Cysts, sialadenitis and lipomas most often form on the tongue and under it. Sometimes a doctor may diagnose a hemangioma, papilloma, or lymphangioma.
Sialadenitis . The disease occurs due to inflammation of the salivary glands. The development is caused by pathogenic bacteria and viruses that penetrate both from the inside and from the outside. Signs of sialadenitis:
- enlarged gland;
- pain in the salivary gland area;
- decreased salivation;
- pressure and tension in the duct area.
The disease causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient, including stabbing pain while eating. The disease does not stop there. If treatment is not started on time, the patient’s temperature rises, pus appears in the saliva, and an abscess develops. In the absence of medical care or incorrectly prescribed therapy, an ordinary pimple can develop into a chronic form.
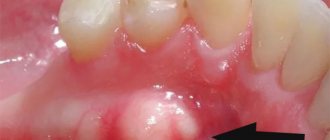
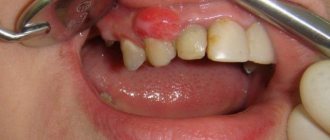
There is also a complicated form of this disease - calculous sialadenitis or salivary stone disease. This form is characterized by the formation of small stones in the salivary gland. The seal is presented in the form of a white bump. The disease most often manifests itself in the sublingual or submandibular salivary gland, near the frenulum, and less often in the parotid part. If the stones are large, the patient can feel them independently. These formations clog the duct, preventing secretion from coming out, which is why inflammation develops.
Types of formations
Traumatic cyst. Very rarely, the appearance of a sublingual cyst may be preceded by trauma. If a person is injured in the jaw area, this provokes hemorrhage. Most often it appears near the jaw bone. This release of blood provokes the formation of a cavity consisting of connective tissue. In cases where pus begins to form from the fistula, the pathology grows into the epithelium, from which the walls of the cyst are created. Moreover, the symptoms of such an anomaly are similar to those of variants that appear in the periodontal space. The only possible treatment option for such a disease is its complete removal, which is performed by cystotomy. Follicular type cyst. This kind of pathology is also called pericoronal. The fact is that it appears due to the degeneration of the remains of the tooth follicle into a cystic formation. It is because of this that such neoplasms always contain a tooth (in some cases it may be several teeth), normal or rudimentary type
It is important to note that such teeth will be completely mature and have ceased their development. Osteoma of the lower jaw (as well as the upper) can be treated exclusively by surgical methods.
Pathology in the tongue
When such a lump appears on the tongue, it causes a large number of problems for human health and requires mandatory treatment. Otherwise, it will gradually grow, and due to its increase in size, it will interfere not only with speaking, but over time even with eating and breathing. It can also spread to other areas of the mouth. Due to this, a tumor may also appear under the tongue. Removal of the abnormal growth is possible in most cases only by surgery. However, if diagnostics do not determine what type of pathology has formed in the mouth, doctors try to use strong medications to eliminate it.
Causes of neoplasms
The main harbinger of the formation of cysts on the root of the tongue and its other areas is clogging of the salivary glands and narrowing of their lumen. Similar conditions are observed during inflammatory processes that occur during the progression of sialadenitis and stomatitis. The following reasons may also provoke the development of ranula on the tongue:
- Increased mechanical impact on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
- Inappropriate manipulations by a dentist: infection, injury to tongue fibers;
- Clogging of the salivary glands by tartar;
- Hereditary predisposition to pathology;
- Abnormal intrauterine development of the baby (congenital tumor on the tongue);
- Blockage of salivary outflow by scars formed on the mucous membranes of the mouth.
Among all diseases of the oral cavity, a cyst under the tongue is considered one of the most problematic and common, as it progresses quite quickly and causes severe discomfort. It is not advisable to ignore this problem, because the larger the cyst, the higher the risk of its spontaneous rupture with subsequent relapse of the disease.
Benign cyst
The mechanism by which ranula occurs is that a blockage of the salivary gland duct (usually Bartholin's or Wharton's duct) prevents the resulting saliva from entering the oral cavity. It begins to accumulate in the gland, which gradually increases in size, at times reaching five centimeters in diameter.
Then there are two options for the development of the cyst: either the ranula spontaneously ruptures, releasing all its contents (water and mucus - mucin) into the oral cavity, or it is removed through surgery. With spontaneous rupture, the ranula forms again.
A dentist or maxillofacial surgeon, using a scalpel under local anesthesia, first drains the ranula (releases fluid) and then removes it from the bed.
This is necessary to prevent recurrence of the cyst.
Sutures are placed on the edges of the wound, which dissolve after a few days. The whole procedure takes a little more than half an hour. The question of whether the ranula needs to be removed is decided individually together with the attending physician.
Ranula can only be eliminated surgically. It is preferable to remove the cyst after making an incision in the oral mucosa. In cases where it is impossible to completely remove the cyst, only its anterior wall is excised, the cyst cavity is lubricated with tincture of iodine and tamponed for 5-7 days.
The timing of the operation depends on the size of the cyst. If there is difficulty swallowing or breathing, surgical intervention is carried out immediately upon diagnosis, including in infants. In the postoperative period, oral toilet is prescribed.
It makes no sense to pierce the ranula on your own and release the contents, since the cyst in such cases tends to recur. This is also dangerous because of the possibility of infection, which can subsequently lead to purulent inflammation and the formation of an abscess.
But this is not always necessary. To get started, you can try a few folk remedies.
Mix two tablespoons of eucalyptus essential oil and 200 ml of boiled water. Rinse your mouth with the resulting solution 3-4 times a day.
Also, eryngium herb is often used to rinse the mouth. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of the mixture and leave for about 2 hours. Afterwards, the broth needs to be cooled and strained.
Mix ½ teaspoon of soda and 200 ml of warm boiled water, add the same amount of iodized salt. You can also use a weak solution of potassium permanganate or furatsilin for rinsing.
Boil a liter of water, add 5 tablespoons of young pine needles to it and boil for about 30 minutes. Then cool, strain and take orally 2 times a day.
Oak bark decoction
Pour 300 g of dried oak bark with a glass of boiling water.
Rinse your mouth 3-4 times a day, store the broth for no more than two days.
Squeeze the juice from three lemons and leave in the refrigerator for 48 hours. Grind the remaining zest with 33 cloves of garlic. Pour the resulting mixture with two liters of boiled water and place in a warm place for a day. Then strain and add lemon juice. Rinse your mouth five or more times a day.
Cyst under the tongue: is it possible to do without removing the ranula?
Although a cyst under the tongue is a painless neoplasm, it still causes serious inconvenience to a person - it interferes with eating, talking, and even causes discomfort at rest. Externally, the cyst resembles a ball or lump, and these are the terms that patients most often describe it. Among doctors, other terms are used - ranula or retention cyst of the minor salivary glands. Sometimes you can hear another unofficial name - “frog tumor”. You will learn from our article about why a cyst forms under the tongue, how it is treated and how dangerous the tumor is.
2 style=”text-align: center;”>Ranula: features of pathology
A ranula is a mucous cyst that has formed in the sublingual space - at the bottom of the oral cavity. The main reason for its appearance is blockage of the salivary gland duct and filling of the submucosal space with saliva.
As you know, in the mouth there are ducts of three pairs of large and numerous additional small salivary glands. Through these ducts, saliva from the gland enters the oral cavity. If the duct becomes blocked for some reason (most often due to mechanical trauma), saliva accumulates in the lumen of the gland, forming a “bump” - a cyst. Due to the fact that saliva is produced continuously, the size of the tumor will grow.
Note: in approximately 60% of cases, ranulas are formed when the ducts of the minor salivary glands are blocked, in 35% - in the sublingual glands (Bartholin's duct) and in 5% of cases - in the submandibular glands (Wharton's duct).
Patients of both sexes are equally susceptible to the occurrence of neoplasms. More often, the pathology is diagnosed in people over the age of 40, but blockage of the salivary ducts also occurs in young children.
3 style=”text-align: center;”>Types and symptoms of ranula
There are 2 types of ranulas. The first type includes superficial cysts, located at the bottom of the oral cavity and having a soft structure. They may have a bluish tint, but more often the surface of the mucous membrane over the neoplasm is not changed. The second type of tumors forms under the mylohyoid muscle; the main symptom of their formation is swelling in the chin area.
In the early stages of development, neoplasms manifest themselves as a decrease in saliva production, which can lead to dry mouth. In the future, the ranula may increase in size, while the mucous membrane above it stretches and becomes thinner. As the ranula grows, it can cause more and more discomfort. Filling almost the entire sublingual space, it interferes with the movements of the tongue and disrupts the process of chewing, swallowing, and speaking.
We recommend reading about what disease burning lips can be a symptom of and how to cure it.
Read: what to do if the facial nerve is cold.
If the size of the cyst becomes too large, it may rupture. This is often preceded by injury to its shell with teeth, dentures, or deliberate opening of the bladder with a sharp instrument. The latter is not only dangerous, but also senseless. If a person deliberately opens a cyst at home, using, for example, a needle, he risks introducing an infection into the wound. But after the contents of the bubble spill into the oral cavity, its size will decrease only temporarily. The secretion will continue to be produced by the gland and fill the shell of the cyst, which will lead to its reappearance.
As you can see in the photo, a cyst under the tongue can reach impressive sizes, causing significant discomfort.
3 style=»text-align: center;»>Causes of cyst formation
As we have already said, the main reason for the formation of a cyst under the tongue is a blockage of the salivary gland duct. This can be caused by the formation of a stone in the duct, mechanical damage to the channel, or a change in the composition of saliva, as a result of which it thickens. It is rare, but it happens that the formation of a ranula occurs against the background of the development of cancerous tumors in this area. The malignant formation compresses the gland, leading to disruption of the flow of saliva from the duct.
Careless movement of the brush can cause the development of ranula.
Mechanical injury to the duct is considered the most common cause of blockage. The mucous membrane under the tongue is very thin and delicate, it can easily be damaged even during hygiene procedures if you are not careful when using floss or a toothbrush. Too hard foods or foreign objects in food (fish bones, nut shells) can also cause damage to the salivary ducts.
Blockage of the salivary gland can be caused by other dental diseases, including stomatitis, herpes, and accumulation of tartar. In addition, the cyst can be a congenital pathology. If it was found on the tongue of a newborn baby, it is called embryonic. There are also cysts of the root of the tongue, they are called radicular.
Bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol, as well as poor nutrition, which causes salt deposits in the ducts, can increase the likelihood of developing a cyst.
2 style=”text-align: center;”>Diagnostics of a cyst
When diagnosing ranula, it is differentiated from other diseases manifested by tumors in the floor of the mouth, including dermoid cyst, hemangioma, mucoepidermodal tumor of the salivary glands. The diagnosis is made based on a visual examination and a number of studies: ultrasound, MRI, sialography, biopsy.
2 style=”text-align: center;”>Treatment of a cyst under the tongue
The only effective treatment for a retention cyst is surgery, during which it is excised. It is worth immediately noting that for an experienced dental surgeon the operation is not particularly difficult, and its implementation does not take much time. The operation is performed using local anesthesia; as a rule, a 2% lidocaine solution is used as an anesthetic.
The only effective treatment is surgical excision of the cyst.
During the operation, the cyst shell is removed, while its bottom is left untouched; in the future it will degenerate into mucous tissue. The process of cyst removal - cystotomy - includes the following steps:
- the surface of the ranula is cut with scissors;
- the contents of the bladder are removed, its walls are excised;
- the wound is washed with antiseptics;
- the remaining wall of the capsule (bottom) is sutured to the mucous membrane along the edges of the ranula, applying catgut sutures.
To avoid relapses, the salivary gland can be removed along with the ranula. Removal of the gland can also be carried out if, after surgical excision of the cyst, it refills.
3 style=”text-align: center;”>Preventive measures in the postoperative period
In the postoperative period, careful oral hygiene is important. This will prevent infection from entering the wound and the development of complications. Hygiene procedures must be carried out extremely carefully so as not to injure the postoperative wound.
The patient is recommended to follow a diet in which it is prohibited to consume foods that provoke irritation of the oral mucosa. This includes too hot, cold, sour, spicy, spicy foods and drinks.
We advise you to find out what to do if your jaw is stuck.
Read: how to choose a battery-powered toothbrush.
Find out why bad breath occurs due to tonsillitis.
During tissue restoration, you need to stop smoking and drinking alcohol, since the tars and alcohols from alcoholic beverages contained in tobacco smoke irritate and dry out the oral mucosa, slowing down the processes of tissue regeneration.
Immediately after surgery, slight tissue swelling and pain may occur in the operated area. Tablet analgesics such as Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Ketanov will help relieve pain. Their use must be coordinated with your doctor.
Important: if severe swelling, numbness, suppuration or other signs of complications appear, consult a doctor immediately!
After successful surgical excision of the cyst, the mucous membrane at the operation site is completely restored in about a week.
A cyst under the tongue can cause many problems, and its size will only increase. Therefore, do not delay visiting the doctor. Traditional methods of treating ranula are ineffective; you can only get rid of the tumor by resorting to surgery. You should not be afraid of surgical intervention, since for an experienced specialist, removing ranula is not a difficult task. Be healthy!
Types of cysts and reasons for their appearance
There are several types of cysts that can form under the surface of the tongue, but the most common is considered to be ranula - a cystic tumor located in the sublingual area. In particular, it is localized at the bottom of the oral cavity, and is formed from the duct of the sublingual major salivary gland or the excretory ducts of the minor salivary glands located on the lower surface of the tongue.
Important! The formation of a ranula is always associated with a violation or complete cessation of the outflow of saliva from the corresponding gland, but the reasons for such a violation may be different. Among the main factors, we should mention blockage of the gland by a mucous plug and its narrowing as a result of the inflammatory process - usually stomatitis or sialadenitis
There are also less common reasons:
Among the main factors, we should mention the blockage of the gland by a mucus plug and its narrowing as a result of the inflammatory process - usually stomatitis or sialadenitis. There are also less common reasons:
- mechanical trauma (including from an orthodontic device or prosthesis);
- blockage of the salivary gland by a stone;
- blocking of the duct with scar tissue;
- compression by tumor;
- genetic inheritance.
A ranula most often forms under the tongue.
Ranulas are divided into two main types: superficial, which is much more common, is formed at the bottom of the mouth, and “diving” is located noticeably deeper, due to which the swelling protrudes not towards the tongue, but towards the chin. Ranula is formed with equal frequency in both men and women, but the main risk group is people over 40 years of age.
There are a group of factors that increase the risk of cysts: viral diseases, poor oral hygiene, smoking and poor nutrition. In the process of diagnosing ranula of the sublingual salivary gland, it is necessary to differentiate it from a number of other pathologies, which in some cases is difficult to do without additional tests.
First of all, we are talking about tumors of the salivary gland, among which the most common is the mucoepidermoid type. Such tumors are quite rare (less than 1% of all cancers), but they pose a danger to the patient’s life due to late diagnosis, which is due to their location hidden from early detection.
A swelling of the salivary gland may occur under the tongue.
Note! The development of such a tumor is facilitated by gene mutation, exposure to ionizing radiation and prolonged contact with harmful substances. Other types of tumors that can form in the salivary glands under the surface of the tongue include the following:
Other types of tumors that can form in the salivary glands under the surface of the tongue include the following:
Another probable formation under the tongue is considered to be a dermoid cyst: a congenital cystic form of teratoma that affects people of any age and can be localized not only under the tongue, but also on any other area of the skin.
It looks like a small, dome-shaped tumor of soft consistency, whose slow growth if left untreated can lead to tongue displacement and difficulty eating or speaking. Enucleation is the only way to get rid of a dermoid cyst, in which it is not excised, but removed from the oral cavity, keeping the tissue surrounding it intact.
Causes of cyst formation in the tongue area
The main reason why a tongue cyst forms is a disruption of the normal outflow of salivary secretions. Cysts that arise when the outflow of gland secretions is disrupted are called retention cysts. The problem can be either congenital or acquired. The formation of a sublingual cyst occurs gradually as fluid accumulates. First, the secretion accumulates in the salivary ducts; as its amount increases, the liquid penetrates the walls of the capillaries, which leads to the formation of a cavity filled with liquid. This is how a salivary gland cyst is formed.
What can have a negative impact on the ducts of the salivary glands and lead to their narrowing and blockage? The causes may be pathologies of fetal development, inflammatory processes or trauma to the tissues of the tongue and oral mucosa. Also, the causes of impaired outflow of salivary secretions include:
- Formation of a rudimentary salivary gland duct.
- Inflammation of the salivary gland (sialolithiasis).
- Stomatitis.
- Mechanical injuries.
The most common causes are inflammatory diseases, such as stomatitis and sialolithiasis, or rather, untimely treatment and inattention to the condition of the oral mucosa. Diseases in advanced form lead to tissue damage and scar formation. This process becomes the trigger for the development of a tumor under the tongue, as it disrupts the patency of the salivary glands (most often this happens with Wharton’s ducts).
Classification
Today there are two main classifications of seals. The first is related to the reason for their appearance. A retention cyst of the minor salivary gland or large (true) and post-traumatic (false) are distinguished. When an organ is injured, scars form, which cause blockage of the ducts.
The localization of retention cysts is associated with other causes of impaired secretion outflow. Depending on the location of a benign tumor, several types are distinguished:
- cyst of small glands (located on the inside of the cheeks, lips, palate, etc.);
- parotid cyst;
- sublingual;
- submandibular
Small
Cysts appear on the mucous membrane at the bottom of the lip, sometimes on the inside of the cheeks, palate, etc. This type of tumor rarely exceeds 1 cm in diameter and grows slowly. The patient feels a rounded thickening that moves slightly when the tongue touches it.
The peculiarity of this variety is the absence of pain or any discomfort. Since a small cyst rarely reaches a significant size, it practically does not bother the patient. Some people don't pay attention to it until it opens spontaneously. In this case, the contents of the capsule flow out, but soon the cavity is filled with liquid again.
Sublingual
This type of lump occurs in the sublingual area, in the area of the major salivary gland. A benign tumor of a characteristic round or oval shape appears under the root of the tongue. You can distinguish a cyst by its color. It has a bluish tint, reminiscent of translucent veins.
Sublingual neoplasm contributes to the development of complications. As the cyst grows, it puts pressure on the frenulum of the tongue, causing it to shift. Because of this, the patient cannot eat or speak normally. When the capsule spontaneously opens, the unpleasant symptoms subside for a while, but as the cavity fills with saliva, the signs become more pronounced.
Submandibular
The submandibular salivary gland cyst is located in the lower jaw. The thickening is ball-shaped, soft. When pressed, you feel that the capsule is filled with liquid contents. If a benign tumor spreads to the sublingual area, it can provoke deformities of the oval of the face. As the formation increases in size, the contour becomes less clear, one side of the face may differ from the other.
Parotid
The next type is a parotid salivary gland cyst. It has certain features and symptoms:
- the parotid cyst in most cases is located only on one side (on the mucous membranes in the area of the right or left ear);
- a round neoplasm forms on the soft tissues;
- as the compaction increases in size, the contour of the face is deformed;
- a soft capsule filled with liquid contents is palpable inside.
In the absence of infection, a parotid cyst does not cause any inconvenience or discomfort to a person. The condition of the skin does not change, there is no pain. However, many people experience negative emotions due to changes in facial contour.
If an infection is added to the pathology, in addition to the main symptoms, temperature and swelling of the soft tissues appear, a feeling of neck tightness, and pain occurs. The patient cannot open his mouth normally.
Prognosis and prevention
In the postoperative period, special attention is paid to oral hygiene
Teeth brushing is done with the utmost care. Do not damage the mucous membrane with a toothbrush.
At first, you should follow a diet: sour, spicy, carbonated foods are prohibited.
Do not damage the mucous membrane with a toothbrush. At first, you should follow a diet: sour, spicy, carbonated foods are prohibited.
Excessively cold and hot foods should be avoided.
During rehabilitation, alcohol and nicotine are prohibited.
Adequate dental care will help prevent recurrence.
If the problem lies in an incorrectly selected denture or chipped teeth, then dental care cannot be avoided.
During the healing stage and in order to prevent cyst formation, rinse your mouth with a soda solution. For a glass of warm boiled water, take 1/2 spoon of soda and the same amount of iodized salt. It is useful to rinse with decoctions of herbs such as chamomile, sage, immortelle, and calendula.
A decoction of pine needles has anti-inflammatory properties. Take 5 tbsp per liter of water. l. chopped pine needles. Bring to a boil, infuse and filter. Take half a glass orally twice a day. The duration of treatment is 7-10 days.
For medicinal purposes, both eucalyptus essential oil and a decoction of the leaves are used.
In the first case, take a teaspoon of oil per glass of water.
There is no special prevention for ranula; primary prevention consists of maintaining oral hygiene. Brush your teeth regularly and use special mouthwashes. Secondary prevention consists of timely removal of ranulas and preventing their development. With proper and timely treatment of the disease, relapses are extremely rare.
Timely treatment of the disease results in a favorable outcome in 95% of all recorded cases. Complications can arise only when the tumor develops and grows rapidly, and the person does not pay attention to the unpleasant symptoms that appear.
To prevent the formation of tumors on the mucous membranes of the tongue, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Carefully monitor oral hygiene;
- Before eating various vegetables and fruits, wash them thoroughly;
- Do not eat unhealthy foods;
- Get rid of bad habits: smoking tobacco and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- Visit the dentist twice a year;
- Treat diseases of the oral cavity and teeth in a timely manner.