Pulpitis: symptoms and signs
In the percentage of patient visits to the dentist in dentistry, this disease accounts for more than thirty percent.
Pulpitis is an inflammatory process of the pulp - a nerve bundle with a large number of vessels and nerve endings that are located in the root canals, or in the coronal part.
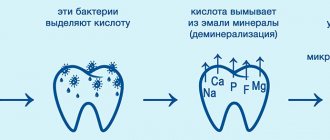
The main causes of this dental disease include infections and other irritants that enter the pulp through a cavity damaged by caries.
The main signs and symptoms of the disease are:
- throbbing pain spreading to the head and neck area;
- severe pain at night;
- sometimes a rotten smell appears from the mouth;
- cavities that are damaged by caries are of great depth.
In some cases, the causes of pulpitis may be the dentist’s mistakes during treatment or his incorrect actions. This includes improper grinding for a crown, careless opening of the pulp chamber and subsequent installation of a filling; during preparation, the tooth may overheat and other problems.
Today, there are two types of pulpitis:
- chronic;
- spicy.
During the acute form, paroxysmal pain is observed, which intensifies in the lying position. Symptoms are less typical in the chronic form, and are defined as complications after an untreated acute stage. The signs of acute and chronic pulpitis are based on a common clinical symptom - deep caries, which is the basis for all emerging dental diseases in humans.
Treatment methods for tooth inflammation
In dentistry, treatment of inflammatory lesions of the pulp is carried out only by conservative methods. True, in most cases it is not possible to maintain the viability of the pulp tissue. Depending on the diagnosis and prevalence of the pathology, doctors treat pulpitis in the following ways:
Biological technique
This method of therapy is indicated only for partial pulpitis or accidental opening of the pulp chamber. The doctor begins treatment by washing the carious cavity with an antiseptic solution (chlorhexidine, lysozyme or furatsilin).
The biological therapy regimen is as follows:
- local anesthesia, infiltration or conduction;
- tooth preparation using a water- and air-cooled drill;
- applying preparations with calcium hydroxide to the bottom of the carious cavity;
- in severe cases, the doctor installs corticosteroid and antibacterial medications into the cavity;
- tooth restoration using photopolymer filling material.
Vital amputation
This method is one of the types of biological therapy. Vital amputation involves the removal of coronal connective tissue and preservation of the integrity of the root pulp.
Vital amputation technique
Such treatment is carried out according to the following plan:
- anesthesia and preparation of carious defects;
- removal of coronal pulp with a sterile instrument;
- sealing the mouths of root canals with calcium-containing preparations;
- installation of a permanent filling.
Vital extirpation
This is the most common method of treating all forms of pulpitis. The technique involves the immediate extraction of coronal and root pulp from a previously anesthetized tooth.
Vital extirpation
This treatment ends with filling the root canals and restoring the crown of the tooth.
Devital extirpation
This method of therapy involves preliminary necrosis of the pulp using arsenic paste or paraformaldehyde. This is done under local anesthesia and after mechanical opening of the pulp chamber.
Preparation of devitalizing paste
After complete necrotization of the pulp, the dentist removes the connective tissue from the tooth and fills the tooth using the technology described above.
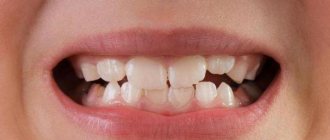
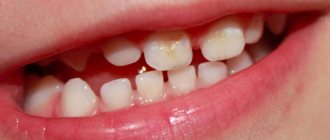
Caries: symptoms of appearance
The gradual destruction of dental tissues without characteristic signs is referred to as a disease such as caries.
Today, three types are considered the most common:
- deep;
- average;
- surface.
The formation of a rough spot on the surface of tooth enamel indicates the development of a superficial type of disease. The main symptom is high sensitivity to external stimuli. Short-term pain with damage to dentin is considered to be a moderate form of caries. During deep caries, complete destruction of dentin is observed, and the tooth also acquires a yellowish tint and reacts sharply to external irritants.
To solve this problem, you need to see a dentist and get treatment.
The deep development of the disease is accompanied by very severe toothaches and hypersensitivity to hot and cold foods. If the affected tooth is not treated in time, voids may appear in it over time.
Also, the presence of this dental disease is characterized by a loss of the ability to absorb nutrients due to impaired metabolism. Both baby and molar teeth can be affected. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully monitor the oral cavity of both children and adults.
Dental diseases: list and symptoms
Most dental diseases, photos and descriptions of which will be given below, are infectious in nature. Pathologies from this list are highly interrelated and often develop sequentially if treatment is not started in time.
| Diagnosis | The essence of the disease |
| Caries | It appears as small faded spots on the enamel, which darken over time and are subject to destruction. Most often it is provoked by insufficient hygiene, leading to the accumulation of plaque in the oral cavity, poor nutrition, and sometimes injuries. The superficial stages of the disease are accompanied by hyperesthesia - increased sensitivity. Deep caries is characterized by the appearance of holes in the hard tissues of the tooth , causing more acute pain and spoiling the appearance of the dentition. Bottle caries in children is associated with prolonged use of pacifiers and nipples, as well as with the retention of food debris in the mouth after night feeding. |
| Pulpitis | It can develop as a consequence of untreated deep caries, when the damage reaches the dentin, and then to the pulp chamber containing the neurovascular bundle. Sometimes the pulp becomes inflamed due to infection from the root, where it can be carried through the bloodstream from other organs. Pulpitis is accompanied by severe pain, sometimes by fever and discharge of pus. |
| Dental cyst | A cyst is an inflammatory process characterized by tissue proliferation near the root. Develops as a complication of inflammatory diseases – pulpitis, periodontitis. Accompanied by pain and swelling of the gums. |
Periodontal diseases: names and descriptions
Dentists call periodontal tissue the jaw tissue that surrounds the tooth root and fixes it in the alveolus. A list of dental periodontal diseases with names and photos is given in the table:
| Periodontitis | Inflammation of the periodontium - the structure that holds the root in the alveolus of the jaw. Provokes purulent inflammation, fever, and tooth mobility. |
| Periodontitis | Periodontal inflammation, manifested by bleeding and accumulation of pus in periodontal pockets. |
| Periodontal disease | Gradual loss of a strong connection between the root and the jaw due to atrophy of the dental process of bone tissue. Pus accumulates in periodontal pockets, and the neck gradually becomes exposed, until the tooth falls out completely. |
Anatomical dental diseases
Such diseases can occur at any time, but some of them begin during embryonic development. They are associated with improper formation of the dentofacial apparatus or changes in its anatomical structure in the future. Below are the most famous abnormal dental diseases with photos and descriptions.
| Diagnosis | The essence of the disease |
| Edentia | An acquired or congenital defect in which a person is missing all or some of his teeth. |
| Anomalies of the dentition and the teeth themselves | Irregularly formed dentofacial apparatus:
|
| Microdentia | Tooth size too small. |
| Macrodentia | Unusually large tooth. |
| Amelogenesis imperfecta, dentinogenesis | Improper formation of tissues - enamel or dentin. It manifests itself as darkening of the enamel, fragility, and increased sensitivity. |
| Hypercementosis | Proliferation of the cement layer with thickening of the roots. |
| Enamel hypoplasia | Underdevelopment of enamel, manifested by the appearance of stains or changes in the shape of the entire tooth: Hutchinson’s, Pfluger’s teeth. |
Other diseases: names and essence
The list of dental diseases associated with the action of chemicals, impaired cell division or jaw injuries is given in the table:
| Diagnosis | The essence of pathology |
| Tetracycline teeth | Violation of the structure and dark coloration of the enamel in children whose mothers took antibiotics during pregnancy. |
| Fluorosis | Violation of the structure and color of enamel and dentin in people whose body gets too much fluoride. |
| Denticles | The appearance of solid mineralized particles in the pulp. The disease is asymptomatic or causes pain due to compression of the pulp. |
| Odontoma | Benign growth of dental tissue. The tumor can become inflamed and bleed. |
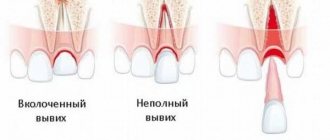
| Tooth luxation | Traumatic disruption of the normal position of the tooth. |
| Fracture of the tooth and its root | Traumatic damage to the integrity of the tooth, which is accompanied by pain and can lead to inflammation due to infection. |
| Tooth erosion | Erosion causes destruction of enamel that is not associated with caries. It can develop under the influence of chemicals and is manifested by the appearance of spots that lose the shine characteristic of the enamel, and then darken and become hypersensitive. |
Periodontitis: symptoms and causes
Inflammation in the area of the periosteum (the root membrane of the tooth), as well as adjacent tissues, is called a dental disease such as periodontitis. The process of inflammation appears as a result of carious lesions, as well as the passage of pathogenic bacteria through the hole from the root canal. The disease is characterized by pulsating and increasing painful sensations of a localized nature. Pain intolerance occurs when teeth are clamped together or when subjected to mechanical stress. In certain cases, patients experience an increase in temperature. Pulpitis has several forms of inflammation: chronic and acute.
In this case, the main signs of acute pulpitis are:
- suppuration of soft tissue;
- unbearable and severe pain;
- loosening of the tooth;
- swelling in the oral cavity.
The chronic form of pulpitis has such signs as:
- slight sensations of pain in a calm state;
- feeling of teeth bursting;
- pain while chewing food.
The main causes of dental diseases with inflammatory processes include traumatic exposure, carious damage, and inflamed pulp.
The inflammatory process can develop within a couple of hours or several days after infection enters the periodontium. An inflamed tooth reacts quite sharply to any touch, the pain is characterized as lingering and aching. Swelling of the lymph nodes and gums is likely, which often leads to the formation of gumboil, as well as complications such as phlegmon, osteomyelitis, and gingival fistula.
Treatment involves eliminating the causes of inflammation, getting rid of purulent accumulations with disinfection, cleaning the canals, administering medications, and filling. The dentist prescribes a course of antibiotics to patients that have an effective effect on pathogenic microorganisms.
Causes of pulpitis
Tooth inflammation is a tissue response to external irritants. In the overwhelming majority of clinical cases, the etiology of pulpitis is microorganisms of the carious cavity.
There is also a hematogenous route of infection into the tooth cavity. In this case, the disease develops in a completely healthy tooth.
Classification of pulpitis
In dentistry, it is customary to divide dental inflammation into the following categories:
| Acute forms | Chronic forms | Exacerbation of inflammation |
| Focal pulpitis |
|
|
|
| |
|
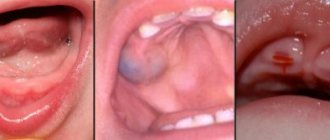
Granuloma: causes of the disease
Granuloma is one of the types of periodontitis with a characteristic inflammatory process of tissues.
The disease is asymptomatic and can be identified by a small tumor at the root of the tooth, which can only be detected on an x-ray. During the development of the inflammatory process, swelling, pain, and redness are noted. Taking into account the development of the disease, the dentist determines the method of treatment and may either prescribe the use of medications or recommend surgical intervention.
The danger of an advanced disease is that over time the granuloma turns into a cyst.
Cyst: signs and treatment of the disease
A cyst is a watery growth in the area of the tooth root. The cyst constantly increases in size and there is a corresponding decrease in bone tissue, and this is quite dangerous for the human body. It is necessary to immediately go to the doctor if such a tumor is identified.
Symptoms of a cyst
At the initial stage, there are no symptoms. But as the tumor begins to grow, swelling occurs, which leads to a change in the shape of the face. This form of the disease is dangerous because infection occurs through the blood vessels and can easily spread throughout the body.
Cyst treatment
There are two main methods of treatment:
- The surgical method is tooth extraction with further excision of the cyst. This method is used quite often, since a cyst is usually diagnosed when it reaches a large size;
- Non-surgical treatment - the cyst is filled with a special medicinal composition. However, this method is only suitable for cysts no larger than 8 cm in size.
In this case, after surgery, additional antibiotics are prescribed, as well as baths with antiseptic drugs.
Plaque on teeth
Plaque on teeth is a hard mass in the root area. The lesion appears from the development of a small layer of caked-on mucus from food debris that has hardened into a solid substance.
Experts call the main reasons for education:
- insufficient hygienic care;
- increased gum bleeding;
- imbalance of salt metabolism;
- burning sensation when eating.
Plaque formation is removed with special dental instruments. Direct treatment must be carried out in a timely manner, since this dental disease can contribute to the appearance of other ailments.
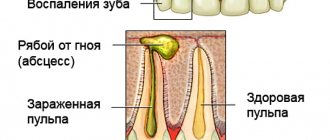
Abscess
As a rule, dentists name the reasons for the development of an abscess in the area of the tooth root:
- furunculosis in the jaw area;
- mechanical damage , fractures, dental trauma;
- dental treatment was not carried out in a timely manner, or the treatment was carried out incorrectly;
- infection during treatment and other problems.
If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, the infection is likely to spread to the jaw bone, which is fraught with a great threat to health.
Another serious inflammation of the submucosal area and subcutaneous tissue includes such an ailment as perimaxillary phlegmon without clear boundaries with purulent neoplasms.
The causes of this inflammatory process are the following factors:
- rashes with pus , which are formed by penetrated microorganisms, bacteria, infection, lack of treatment for ulcerative stomatitis;
- abscess at an advanced stage.
Clinical symptoms of the disease are the appearance of pain in the localized area, difficulty breathing, increased salivation, disturbances in jaw movements, and facial deformation.
Periodontitis
The inflammatory process that occurs within the connective tissue located around the tooth root is called periodontitis. The disease can be caused by many reasons, including:
- untreated caries;
- pulpitis;
- dental injuries (mechanical and those that develop gradually, when chewing hard objects, opening bottles with teeth, cracking seeds);
- improperly performed dental procedures - installation of fillings, dental reconstruction;
- penetration of the infectious agent through the general bloodstream, from infected maxillary sinuses, jaw bones;
- negative impact on periodontal tissue of strong toxins.
The most pronounced symptom of pathology is an “overgrown” tooth; to a person it seems too long and interferes with eating, talking and sleeping. If at the initial stage of the disease the pain is aching and of low intensity, then as it progresses it becomes more and more pronounced. In advanced stages, when a person suffers for a long time and does not see a doctor, the pain syndrome prevents normal life and radiates to the temple, eyeball, ear and neck on the affected side.
The lymph nodes under the lower jaw noticeably enlarge, and at the same time the temperature rises. If you touch a sore tooth, press on it, or drink a hot or cold drink, it responds with a flash of acute pain. Pus accumulates inside the connective tissue, which can lead to blood poisoning (sepsis).
Treatment involves removing the inflamed tissue, opening the canals of the affected tooth, placing medications in the cavities and subsequent filling. After which the doctor prescribes antibacterial and antiseptic drugs in order to eliminate inflammation and prevent its further development.
Periostitis
Dental periostitis or gumboil is a very unpleasant disease when microflora begins to multiply in a limited space of soft tissues, which grows without access to oxygen. Pus appears, nearby tissues become infected and die, periostitis increases in size.
Infection is possible with cystic jaw lesions, with inept pain relief and injections, with any open wounds of the oral mucosa, in rare cases with blood or lymph flow. There may be cases of development after a sore throat.
Painful sensations resemble periodontal ones, then increase in duration, become permanent, the facial part begins to change asymmetrically, swelling on the damaged side. Signs of septicemia appear and the general temperature increases. When the membrane ruptures, pus comes out or into the oral cavity; one way or another, surgical intervention is required. You should not delay with the flux; periostitis that does not break through can turn into diffuse phlegmon with blood poisoning or the development of a general septic picture.
Causes of development of diseases of the teeth and oral cavity
Dental diseases can occur due to the harmful effects of one factor or a combination of several. Most dental diseases develop for the following reasons:
- Violation of hygiene rules. We are talking not only about complete disregard for hygiene, but also about irregular or improper brushing of teeth. The accumulation and hardening of soft plaque ensures the rapid development of bacteria in the oral cavity, the waste products of which destroy even the hardest tissue in the body - enamel.
- Infectious diseases. Pathogens can enter dental tissues from the oral cavity, where inflammation occurs, through cracks in the crowns. In addition, bacteria can be introduced into them through the bloodstream from any diseased, infected organ.
- Insufficient supply of dental tissues with nutrients due to improper nutrition.
- Excessive intake of certain elements into the body, for example, fluoride.
- Taking medications.
- Metabolic disorder or hormonal shift.
- Low immunity.
- Hereditary predisposition to dental diseases and congenital anomalies.
- The effect of radiation and chemicals in contaminated places of residence or hazardous production.
- Injuries.
The main reasons for the development of dental diseases in children are the use of pacifiers and bottles with pacifiers, the habit of thumb sucking and putting dirty objects into their mouths.
Prevention of dental diseases
As a rule, dental diseases in humans are the result of insufficient attention to hygiene, to one’s health and to oneself. Rare visits to doctors and bad habits are very often the main cause of all ailments.
To keep your teeth healthy, you need:
- No smoking . Not many people know that smoking directly affects the blood vessels in the mouth. Vasoconstriction leads to poor blood supply, as well as a lack of nutrients. And as a result, problems with teeth and gums.
- Eat properly . Among the main causes of disease, the leaders remain a lack of nutrients and heat treatment. Less sour and sweet, more vegetables and fruits. Try to minimize the consumption of very cold and hot foods.
- Rinse properly . Most people still do not pay attention to such a smart invention of doctors. But in vain. Rinses are excellent antiseptic preparations that can access those areas of the tooth that are completely inaccessible to toothbrushes. Together, they will help restore the correct balance of acid and alkali in the mouth, and they are convenient to use even in public places where, for some reason, it is not possible to brush your teeth.
- Clean properly . It is best to consult your dentist about the specific stiffness of the brush you require. The dentist will be able to select a toothpaste that matches the condition of your teeth. This can help, at a minimum, preserve teeth, and even improve their condition.
In conclusion, it must be said that various dental diseases can be prevented by maintaining normal oral hygiene for any person at any age. Today, any dental disease can be treated quickly and painlessly, but regular visits to the dentist can help prevent any problems in a timely manner and prevent complications.
Gum diseases
Gums are soft mucous tissue that covers the alveolar process of the jaw and protects the roots of the teeth from environmental influences. The normal condition of the gums is the light pink color of the periodontium, the absence of erosions and other neoplasms.
Healthy gums
Due to the activity of pathogenic microflora and exposure to unfavorable irritants, the condition of teeth and gums changes. Unpleasant sensations appear in the oral cavity, indicating the development of dental disease.
Before studying dental problems, you should first know what gum diseases are. Inflammatory and non-inflammatory periodontal diseases include:
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis;
- periodontal disease.
The clinical pictures of periodontal diseases differ from each other. Therefore, before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis and establish the cause of the disease.
Causes of gum disease
Problems with gums can be the result of poor oral hygiene, as well as a consequence of various somatic diseases of the body. Factors that provoke changes in the periodontium in adulthood and childhood include:
- vital activity of pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microorganisms;
- chemical, thermal and mechanical damage to the oral mucosa;
- decreased immunity;
- hormonal changes;
- acute viral and bacterial infections;
- avitaminosis;
- poor nutrition;
- bad habits (tobacco smoking).
Determining the cause of the disease, as well as its elimination, is the key to a quick recovery.
Gingivitis
Photo of gingivitis
Gingivitis is an acute inflammation of the gums, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- bleeding when brushing teeth;
- bad breath;
- presence of dental plaques;
- itching and pain from temperature stimuli;
- change in the shape and color of the gums.
According to the form of the disease, gingivitis is divided into catarrhal, hypertrophic and ulcerative. The description of the disease includes: discoloration of the periodontal tissue, swelling of the periodontal papillae, bleeding on palpation. There are no pathological gum pockets. Treatment of gums in adults and children is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a complication of gingivitis and develops in cases of untreated or improperly treated gum inflammation. The causes of periodontitis and gingivitis are the same. Despite this, gum disease has a specific clinical picture:
- the papillary-marginal-alveolar gum is swollen and hyperemic;
- periodontal pockets can reach up to 6 mm in depth;
- there is a lot of tartar and bacterial plaque;
- there is pronounced halitosis;
- gums hurt from all types of irritants;
- In the last stages of gum disease, tooth loss is possible.
In the photo of gum disease, you can see all the visible changes in periodontal tissue. Bacterial plaque on teeth occurs in 90% of cases.
Periodontitis
Periodontal disease
Periodontal disease can be called a non-inflammatory periodontal disease that occurs with exposure of the roots and loss of teeth. The disease develops most often in people aged 37–60 years, and has the following causes:
- bad habits (frequent smoking and drinking alcohol);
- changes in hormonal levels;
- immunodeficiency;
- HIV, all types of hepatitis, AIDS;
- non-compliance with a healthy lifestyle;
- hereditary predisposition to gum disease;
- age-related changes in the oral cavity.
The first signs of periodontal disease may be: exposure of dental roots, tooth mobility, the formation of deep gum pockets, and the presence of abundant plaque on the lower front incisors.
Symptoms of gum disease vary from person to person and appear in a person several months after the development of periodontal disease.
Many patients and doctors confuse periodontitis and periodontal disease with each other. Since further treatment depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis, you should know the main distinguishing signs of the two gum diseases.
| Features | Periodontitis | Periodontal disease |
| Signs of inflammation (gum hyperemia, bleeding, swelling) | Present | None |
| Presence of gum pockets | Present. Depth varies from 3 to 6 mm. | None |
| Tooth mobility and root exposure | Present in the last stage of the disease | Present |
| Degree of gum damage | The disease is localized, affecting the area of several teeth | The entire periodontal tissue of the upper and lower jaw is affected |
| Changes on the X-ray | None | Periosteal atrophy |
Treatment of gum diseases
Based on the symptoms of gum disease and their clinical picture, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
Gingivitis, periodontitis and other inflammatory diseases in the mouth are treated as follows:
- Eliminating the cause of inflammation.
- Rinsing with antiseptic solutions (miramistin, chlorhexidine).
- Intraoral baths with infusions of chamomile, oak bark and calendula.
- Local applications of vitamins A and E.
- Inside - vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Quitting smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
Treatment of periodontal disease in adults includes several stages:
- Carrying out professional oral hygiene.
- Splinting of mobile teeth.
- Physiotherapy (use of laser, hydromassage, depersonalization).
- Injection of antitoxic and sclerosing drugs into the gums.
- Rinse frequently with antiseptic solutions.
Remedies for gum disease are prescribed by the dentist based on the severity of the inflammatory process and the severity of the symptoms.