C
Among algorithmic development tools, this language has become one of the most frequently used.
C found practical application in “low-level programming”: OS elements, drivers, programs for controlling various devices and systems. Specialists who speak the C language are now in, albeit small, but constant demand. However, due to the specifics of products created in C, the requirements for these developers are very high. Therefore, in the post-Soviet space, it is almost impossible for beginning C programmers to find a job.
However, you shouldn’t turn a blind eye to C, because it can be called the progenitor of most modern languages. Just set yourself up to the fact that knowledge of C will be a good foundation for long-term and successful career growth, and don’t expect to immediately deal with applied problems, such as creating websites or applications for mobile devices.
Simplified speech builds correct relationships in the family
A special “parent” language is spoken all over the world. This manner of speech is designed to attract the attention of a small child: simplified grammar and simple words, drawn out syllables. Adults switch to “parental” when communicating with children, almost without thinking about it.
But what if parents knew that speaking like this helps their child learn new skills faster? Scientists from the University of Washington found that parents who were well informed about the positive effects of "parenting" on children's development were more likely to use this special language when communicating with their children. Scientists also found that children with whom adults communicated in the “parent” language later demonstrated better language skills.
Previously, it was believed that the “parent” language helps children better master the adult language due to its simplified grammatical structure and emphatically clear pronunciation of syllables. According to the results of a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, scientists have suggested that the “parental” language plays the role of a kind of “social anchor” for young children - a high tone and a slow pace of speech invite the child to social interaction.
Evgenia Shishova, Candidate of Psychological Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Educational Psychology at the Institute of Psychology and Education of Kazan Federal University, head of the master’s program “Practical Psychology in Education”, international expert in the field of assessing the quality of preschool education ECERS:
— Currently, numerous studies are devoted to the problem of the influence of the “parental” language on the cognitive, emotional and communicative development of the child. Psycholinguists call “parental” language or speech addressed to a child, “native” language, “nanny” language. “Parental” language is, first of all, a form of communication with the child, in which the parents’ speech is adjusted to the child’s language. Most often it is considered as an instinctive mechanism of altered speech provided by nature. It manifests itself in a poorly controlled instinctive increase in the frequency of a person’s voice, emphasis on vowel sounds and simplification of speech structures when communicating with infants and children.
Research confirms that it is this kind of speech that children are most receptive to. Thus, verbal stimulation from parents, combined with a warm and positive parental speaking style, will have a positive effect on the child's development.
We are talking about research aimed at studying the role of an adult in the development of a child and the influence of these processes on the child’s speech development. The conducted studies show that such characteristics of coherent speech as thematic and semantic unity, interphrase connection, compositional and logical sequence of description, narration, reasoning, stylistic unity of speech depend on the speech environment and the linguistic environment. For example, the main conditions for the targeted formation of early bilingualism in children are the creation of balanced conditions for the simultaneous formation of bilingualism from birth (the language of the upbringing environment, the language of communication, the level of speech culture of others) and teaching a second language on the basis of steadily formed speech skills in the first language. These studies confirm the importance of social interaction, which Lev Vygotsky spoke about, and find experimental confirmation in modern foreign research. An analysis of works related to the problem under study suggests that there are several approaches to the influence of the “parental” language on the cognitive and linguistic development of the child: negative, neutral, positive.
Some psycholinguists do not deny the significant role of parents in the success of language acquisition, but note that if the needs for speech practice are not met, then the child becomes unable to acquire the language in sufficient quantities, and inattention to grammatical errors in children’s speech and lisping negatively affect speech development children and may contribute to speech therapy problems. Proponents of the second approach believe that the “parent” language does not play an important role. The third group of researchers confirmed the positive influence of the “parental” language on mental development, noting that it contributes not only to the speech, but also to the cognitive development of the child. However, it is important to remember that there are specifics to the role of an adult at different stages of development. Thus, the “parental” language will be effective only up to three years. This is due to the fact that early childhood (one to three years) is a sensitive period for speech development. The acquisition of the grammatical structure of the native language has its own periods of development. The first period, from one to two years, is the proposal period. In this period, one-word and two-word sentences are distinguished. The second period—up to three years—the child’s speech becomes quite coherent. The formation of active speech serves as the basis for the entire mental development of the child. A speech signal is a stimulus that activates a child’s brain, and without speech signals thinking does not develop.
It is also interesting that the earlier a child comes into contact with a second language, the brighter the child’s potential in the future is revealed, the foundations are laid for the cognitive and communicative development of children. As E. Yu. Protasova notes, the foundations of language ability are laid in preschool age, and if it is formed in parallel in two languages, then we can expect better verbal development and cognitive effects. Inconsistent results across multiple studies make it necessary to conduct research that considers the benefits and limitations associated with the acquisition and use of two or more languages.
Irina Shlyapnikova, Candidate of Psychological Sciences, senior researcher at the Department of Developmental Psychology and Age Counseling, Higher School of Medical Biology, South Ural State University:
- In most cases, mothers seem to automatically switch to “parental” language, because they receive positive feedback from the child: the child reacts differently to such communication with him, listens as if spellbound, and enjoys such communication. “Parental” language is relevant for a very early age (infancy and early childhood), and at this age there is still a close physical connection between mother and child, due to the child’s helplessness and the round-the-clock need for each other, a strong emotional connection arises between mother and child, so mother almost unmistakably recognizes the child’s needs and builds a dialogue with him that corresponds to his capabilities.
In principle, any positive emotional communication between a parent and a child is developmental. The leading activity (the activity in which development occurs and without which development is inhibited) during infancy is called “direct emotional communication with an adult.” But the “parental” language is the most appropriate to the child’s capabilities and needs.
Such communication develops not only the brain and psyche, but also strengthens the emotional connection between parents and the child, which is a necessary foundation for the future development of the child’s personality and social abilities.
Anastasia Tabolina, Associate Professor at the Higher School of Engineering Pedagogy, Psychology and Applied Linguistics of Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU):
— In my understanding, “parental” language is a cultural form of oral dialogue with a child, which helps to build more competent child-parent relationships in the family. Such dialogue is most relevant at an early age, when speech centers and brain structures are being formed.
The most fruitful age is from one and a half to five years. It is most productive to use “parental” language with children who have weak communication skills and abilities.
It is important to moderate the “parental” language and stress when communicating with children; in conversation, do not switch to a simplified dialogue with the child and do not distort adult language.
That is, for example, when a child does not pronounce the letter “r” and other sounds, then parents may, out of kind-hearted feelings towards their child, begin not to pronounce it either. This can lead to permanent defects in speech development and perpetuate a negative pattern of incorrect pronunciation. At a later age, it may be difficult for a child to relearn, since the parent is a very significant “paternal” figure and what the parent conveys to the child through speech is learned very firmly and for a long time.
But the good thing about “parental” language is that an adult can, with the help of “soft intonations,” be in special contact with the child. In speech, it is important to use empathic listening techniques (for example, the phrases “Yeah, yeah, well done, continue / I’m listening to you / did I understand you correctly”). For each parent, their baby is unique, and it is the parent who knows how to communicate with their child. Even if there are several children in a family, parents adjust their speech to each child. Using parental language is most fruitful when communicating with boys. In boys, the speech zone is located in only one hemisphere of the brain, and therefore speech physiologically develops more slowly in most boys. Therefore, the longer and more often there is an open and confidential conversation with parents, the faster and more comfortable the boy’s speech will develop.
“Parental” language is not an instinctive form of communication, but is developed as a socially acquired skill. Of course, parental language is a value. It is very important to communicate on equal terms with the child. This affects the development of his intelligence. Speech should be understandable to the child; this will enhance the quality of interpersonal interaction with a significant adult and will contribute to the competent formation of a healthy attachment. Gradual load and expansion of vocabulary are very effective.
In 1958, Daniil Elkonin’s book “Speech Development in Preschool Age” was published, which does not lose its relevance in our time. The author notes that speech is actively formed in the game. There are a lot of games, and they are specific for each age, each type of game is important in its own way.
The “parental” language is capable of developing the child’s speech. Children begin to internalize the behavior patterns that their parents pass on to them. For example, children play the role-playing game “mothers and daughters” and, as a rule, use the speech of their parents, repeat, copy their parents, their behavior patterns, reactions, etc. The child, in a playful and comic form, broadcasts the linguistic means that he receives in the family. Therefore, it is very important to take care of the child’s psyche and his speech.
A meager vocabulary, the use of jargon and profanity lead to underdevelopment of speech in a child; the richer and more intellectual the language environment in which the child develops, the faster and better the higher mental functions of the brain, such as speech, consciousness and thinking, develop.
So parental language lays down very important values, is aimed at supporting attachment and developing communicative abilities.
Prepared by Maria Gribova
C++
This is the case when the name reveals the whole essence: C++ is really an “improved version” of the C language. But modernization has made it more difficult to understand, learn and use. But even despite this, it has not ceased to be in demand for many years.
C++ is a developer’s ticket to the world of all the smart programs: games, antivirus software, search engines. And this is not a complete list of what is created through “C plus plus”.
As a rule, one begins to get acquainted with this language only after working with C or any other easier environment. Beginners definitely don't need to choose C++, especially if you don't have to work with complex mathematical algorithms. However, if in your dreams you see yourself as a developer of such amazing games as the legendary WarCraft and Doom, and not simple mobile Tetris, then you will still have to make friends with C++. But we strongly recommend starting with something more affordable.
You can view a large course on this language on our website:
How tongue helped vertebrates colonize land
It is not human nature to value language. The one in the mouth. We prefer eyes, arms, legs, hair... But this is not only a strange elastic muscle that allows us to taste food, make some sounds and express a playful mood. If we didn’t have a language, we would still be swimming in the seas and oceans and only dreaming of land - cozy, alluring, but completely inaccessible. Why? To understand this, we need to look at one of the lower rungs of the evolutionary ladder. It is there that the answer to the question of how one modest muscle became the key to planetary domination, the Internet, the sofa and all the other delights of human existence is found.
The first vertebrates were fish, but they did not have tongues. You may have always thought they had it, but they don't. Many of them have a hyoid body, a slightly protruding bone or cartilage at the bottom of the mouth. It is similar to a tongue, but does not move and has no taste buds. This is just a hard shield that protects sensitive nerves and blood vessels. This anatomy makes sense when you remember that most land animals use their tongues to catch and swallow food, but fish eat a little differently. Most of them suck food into themselves. Noticing a tasty morsel, the inhabitant of the depths of the sea swims up to it and sharply opens her mouth. The upper part of the skull goes up, the lower jaw goes down, and the hyoid bone goes deep into the throat. Thanks to this, a low pressure zone is created in the mouth, and water rushes there along with that very piece of food. Even those fish that take a bite of their prey often use suction to swallow the food. Those who do not use this technique open their mouths, accelerate and push the food inside with an oncoming flow of water. All this works great in the ocean, but the air is much less dense, so it can’t always push prey inside.
Macropod (Macropodus opercularis). Photo: André Karwath aka Aka
According to the fossil record, a group of bony fish known as lobe-finned fish started a wave of migration between 400 and 350 million years ago, during the Devonian period. The four-legged animals they evolved into, including all amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals, conquered the earth and sky, and in time, perhaps, will populate space. But first they got out of the water. The fossilized remains of early tetrapods, like the famous Tiktaalik, show how much had to come together for this transition to occur. This is a change in the limbs, spine, skull, eyes, lungs and much more. Including the way of eating. Unfortunately, paleontologists have not been able to find many remains of species that were in the early stages of language transformation, but we can see at what point it occurred by comparing the inhabitants of land and sea.
C#
The brainchild of Microsoft Corporation and another generation of the C language. C-Sharp differs from C++ in its relative simplicity, so courses on its study are suitable for novice developers. Web applications, products for the Windows OS, and even for smartphones with Windows Phone are now being written in C# (probably hoping that Microsoft will decide not to abandon its mobile OS completely).
In our country today there are enough vacancies for IT specialists-novices in C#. Having a good knowledge base, you can find more or less uncomplicated work in prestigious companies. So if you are looking for a stable and well-paid activity, the path of a “charpist” is quite a suitable option.
You can view a large course on this language on our website:
Swift
Swift is a new language from Apple, designed to replace the inconvenient and receiving a lot of reproaches from Objective-C programmers. It cannot yet be said that Swift has fully lived up to the expectations placed on it.
However, the popularity of the language is constantly growing, at the same time Objective-C is also confidently losing its relevance. Therefore, if you plan to program for Apple devices, you don’t have to waste time and effort on outdated Objective C, but immediately start learning Swift.
How to learn new words correctly?
The most effective technique for memorizing words is spaced repetition. The idea is to return to the words you've learned at ever-increasing intervals, from a few days to a few weeks. At the end of the 19th century, psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus described the “forgetting curve” and proved that the rate of forgetting information decreases after each repetition.
Over time, the research of Ebbinghaus and his colleagues transformed into the card method, familiar to many, which is quite simple. The student goes through cards with foreign words and translations on the back side, correctly guessed words are put on one side, unguessed ones on the other. At the next stage, only cards with problem words are used.
Digital apps like Anki or Memrise follow in the footsteps of this method, setting special intervals between repetitions, helping you learn words faster without wasting time making flashcards by hand.
PHP
On the scale of large international projects, the once popular environment for developing web applications and websites, PHP, is now somewhat outdated. But due to the fact that this language is easy to learn and is still actively used for solving narrow-profile problems, you can start learning programming in general with it.
Career prospects for specialists with knowledge of PHP are quite good: at a minimum, a huge number of projects written in this environment need support and/or improvement. However, the level of salary even for experienced and highly competent PHP developers leaves much to be desired: their colleagues working with Java or C++ usually receive greater profits for the same amount of work.
You can view a large course on this language on our website:
Language exposure helps you learn a language
Today I will talk about what the concept of language exposure means, as well as how I discovered language exposure, and why it helps to learn languages.
Once upon a time, a very, very long time ago, I started learning Spanish. I purchased a textbook and began to study the material sequentially. First I learned to read, then I went through several lessons page by page. I remember how I wanted to quickly pick up some serious book with real Spanish. Or listen to a program in Spanish, or watch a movie. But I kept stopping myself. I said that now is not the time for this yet. What is the point, for example, of delving into a novel in Spanish if you still can’t read it without knowing a large number of words and having a good command of grammar? And what's the point of watching a video in Spanish if you don't have listening comprehension skills yet?
I stopped myself and said that first I had to go through the tutorial to the end. And only then proceed to the language in its natural performance. The moment came when I turned the last page of the tutorial. It seemed like it was time to start learning natural language, but... I suddenly realized that I had not yet mastered grammatical structures well enough. It was difficult for me, for example, to construct a sentence in a certain tense, because the patterns of tense formation had not yet completely settled into my mind. Well, how can you take on a natural language with such bad grammar?! No! It is necessary to memorize various grammatical schemes well.
Once the basic grammar was mastered, I finally picked up a serious literary text in Spanish. But I soon put it aside, since I had to look up almost every word in the dictionary. Then I decided that without a good vocabulary, touching natural language is useless.
For a long time, something constantly prevented me from switching to natural Spanish. Time passed, and I constantly learned something and did it until I finally realized that this could go on indefinitely. I always separated myself from Spanish literature, deprived myself of watching Spanish programs and films, all because I believed that I had not yet grown up to them. I was brought up with the mindset that first one thing, then another, then a third... Everything should go sequentially.
It was only recently that I realized my mistake. You cannot master any subject in isolation from it. You cannot, for example, learn to solve a Rubik's cube without the cube itself. You can read a lot of articles about how to select colors, watch pictures and videos... But without the cube itself in your hands, all this knowledge will not give a practical effect. To really learn how to solve a cube, you need to pick it up, spin it, changing the edges and remembering what you read in articles and saw in pictures and videos.
You can't learn to swim without water, and you can't learn to ride a bike without the bike itself. You can read and watch a lot about how to do this, but without interacting with real objects, mastering them is impossible.
To master a real foreign language, you need to be in constant contact with it. In this case, no prior knowledge of the language plays a role.
Many successful polyglots constantly listen to or watch something in the languages they are learning, even if their knowledge is not enough to fully understand the material. They do this in order to “get saturated” with the language, to get used to it. They understand some things right away, others become clear after a month or only after six months. But contact with the subject being studied is continuous.
There is even a special phrase in the English language, which has almost become a term describing contact with a foreign language in its natural form - language exposure.
Renowned polyglot Steve Cowman says you should start exposing yourself to a language before you even start learning anything. And in this he is certainly right. From the very beginning, your ears should get used to the natural tempo of foreign speech, intonation patterns, merging of words, etc. The brain may not yet be able to comprehend the meaning of speech, but it will begin to form an image of the language. The meaning of speech will gradually emerge as you learn the language.
So, don't feel like you have to first learn words, understand grammar, and whatever else before you can watch or listen to anything in the language you're learning.
First of all, you should watch and listen to something in the language and secondly, of course, learn words and grammar. Now I only do this, because it is impossible to learn a language without a language. Alexey Ermakov
Java
In the world ranking of popular programming languages, Java takes an honorable second place. It is used as widely as C++, without many of its disadvantages. First of all, this environment is intended for creating extensive high-load products for transnational organizations and simple applications and games for Android devices.
Java programmers are in demand everywhere. In addition, their work is well paid. There are no prerequisites that this language will soon lose its position. And although it is not as easy to learn as PHP, the return on ownership will be worthy.
You can view a large course on this language on our website:
Why do you need to know the Russian literary language?
It would seem that in order to fully communicate, be understood and understand speech in Russian, it is not at all necessary to know all the spelling rules.
However, language serves us not only to communicate with friends and make purchases in a store. The native language is a whole huge world that contains the entire historical and cultural heritage of the people. Without knowing it, its bearers lose touch with this heritage, and, therefore, this cultural layer dies out and is forgotten. To understand our place in this world, from early childhood we learn our native language. When studying objects and phenomena in the environment, we do this through naming them. We cannot think otherwise than in our native language, we cannot perceive the reality around us otherwise than through words from our native language. And the richer our language, the better we know it, the richer and brighter the world inside and around us.
If a person cannot name an object or describe a phenomenon using words, it means that in reality he has no idea about them, since a person thinks in words.
Knowledge of the Russian literary language allows you to better and more correctly express your thoughts, choosing the right words. The Russian language is all around us - in every sphere of human activity, be it politics, art, culture, science or production.
JavaScript
JS got its name in the wake of the relevance of Java, and therefore they are often confused. In addition, JavaScript is now forced to fight for the status of an equal language. It is worth noting that he does this very well, because he has become the most popular among developers all over the world.
The demand for JS is due primarily to the development of the Web. It is used to write the user interface of all interactive web applications, thanks to which the browser has become a useful and convenient working tool, becoming on par with the Microsoft Office suite and hundreds of other standard applications for the Windows OS. In addition, JavaScript has found its place in server programming.
This language has been actively conquering new areas lately. Moreover, it is much easier to start in the profession with it than with Java, and salaries are often the same. The bottom line is that JavaScript is now one of the best options for newbie developers.
You can view a large course on this language on our website:
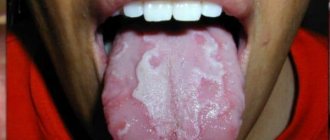
Meaning of the word language
m. a fleshy projectile in the mouth, serving to line the teeth with food, to recognize its taste, as well as for verbal speech, or, in animals, for individual sounds. Cow tongue, lick; fish, cuff; snake, sting, fork; dog, shovel; cat, grater. I broke my bite, my angry tongue; babbling, talkative; stirrer, childish; cloth tongue, burry. Other meanings of language are derived either from its external appearance, or as an instrument of speech. Toe with tongue, wedge.
The tongue of the bell, the beater, the rivet, the iron pestle, the flail hung inside under the shell of the bell for ringing. Coachmen like to tie a ring to a bell instead of a tongue. Without a tongue and the bell is mute. Get the tongue from the bell tower (when the tongue is removed, pour water over the bell tongue and give the patient something to drink).
The internal funnel of the merezha, ventera, through which the fish enters: detyty, detynets, ushinok.
Arch. underwater ice spit, from a hummock.
A tongue, the reed of an organ, a spring, a hook, which one hits when playing. The tongue of the bell, the beating, which walks between her cheeks.
The tongue of a clarinet, oboe, peep, a thin wooden plate inserted into the mouthpiece for sound.
A tongue in a trap, a guard, a tongue, a longitudinal stick with a notch from which a sheer stand breaks off, a guard.
The tongue, the tongue of the lock, the bolt that fits into the eye of the padlock shackle, into the internal tenon: snych. The key locks the tongue with a bit. The tongue is also called the trigger, the pawl at the gun lock, and all the like.
Tongue, Chernomorsk fish Solea nasuta, half-fish.
The tongue, in the mouth, the tip of the palatine hanging in front of the pharynx; others call the laryngeal covering, under the root of the tongue, the uvula.
Tongue, plant Centaurea austriaka.
Language, verbal speech of a person, by nationality; vocabulary and natural grammar; the totality of all the words of the people and their correct combination to convey their thoughts; yasak. An adverb that has prevailed over other related adverbs is called a language. He knows many languages, speaks five languages. A proverb, a Psalter, or, more importantly, their setting and connection, an image, a way of expression, characteristic of someone personally. The language of Pushkin, Krylov, Derzhavin. Lermontov knew how to write in the language of each of our best poets. Gogol's language is motley, irregular, but bright, strong and expressive.
The structure, syllable and very choice of words, with their different formation, depending on the subject you are talking about and according to the accepted custom. The language is bookish, high, strict; - poems; spoken language, common language, command language, etc.
Language, military a prisoner from whom they ask questions to find out what is needed about the position and condition of the enemy. Get, get the tongue. The Cossacks went on a tour to get the language. Tongues spoke, old man. To catch your tongue, old man.
Star. order accuser, accuser before the court, slanderer during interrogation, taken and interrogated to search for the case. And in which people’s tongues are spoken from torture, and those people, according to pagan beliefs, are imati, Acts.
A people, a land, with its population of the same tribe, with the same speech. Samaritan tongue, Acts. Samaritans. Shout loudly (to all nations), for the Lord reigns, Psalm. The filthy Polovtsi bought up their entire language onto the Russian land, chronicle. The invasion of twelve languages in Rus', 1812.
Language, church foreign people, people of other faiths, foreigners;
pagans, idolaters. For God also gave repentance to the tongues, Acts. Every tongue praises God. He has a long tongue and talks too much. The tongue is sharp and mocking. Shorten your tongue! My tongue is my enemy: it speaks before the mind. Every bird dies from its tongue, it will tell itself. Eat the mushroom pie, but keep your mouth shut. The prince is spoken by the tongue, the chronicle. Use your tongue, but don’t give your hands free reign. You can't tell it with your tongue, you can't spread it with your fingers. Stuttering tongue, stutterer. Language will take you to Kyiv, you’ll question everything; and to the cue, to the beatings. The tongue is in agreement, the word is sacred, what is said, hold on to it, don’t give up. Trim the tongue, trim the hyoid frenulum; * stop excessive talkativeness. It’s good for the tongue to sit behind a bone palisade! May you choke on your tongue! You're lying. Evil tongue, slanderer. A cow's tongue is large and prevents her from speaking. The tongue is small, but it controls the whole body. She sewed and washed, ironed and rolled, spun and polished (all with her tongue). The tongue will lead you to the tavern. Whatever he knows, he will say, and whatever he doesn’t know, he will say (the tongue). The cow's tongue is great, and they call it licker. The tongue will not bring you any good. The tongue will insert into the sinner. Don’t be in a hurry with your tongue, and don’t be lazy in your deeds (be in a hurry with your deeds). You can't weave a bast with your tongue. Do not give free rein to your tongue at a feast, in conversation, or to your heart in anger. Give your tongue porridge, or wet your tongue, or feed your tongue, shut up. I should bite your tongue! If you bite your tongue, someone scolds you. Nobody pulls their tongue. As if the tongue is in jelly. His tongue is tied with a thread, his tongue is soaked. White hands with a tray, brisk legs with an approach, a head with a bow, a tongue with a sentence. The tongue feeds the head (it also leads to beatings). The tongue drinks and feeds, and spanks the back. There is honey on the tongue, and ice under the tongue. Dressed simply, but in the language of speeches with a hundred. Don't be afraid of the knife, but of the tongue. Tongue, adversary, my destroyer! The language is the same both on weekdays and on holidays. God gave two ears and one tongue. It took such a toll on my heart that I would have bitten my own tongue! Wine loosens the tongue. Hold your tongue and clench your heart into a fist. Keep your tongue short. Keep your tongue on a leash (on a string). Play with your tongue, but don’t give free rein to your hands. Hiss and click with your tongue, and keep your hand in your bosom. Use your tongue, but don’t wave your hands. You can’t escape the language (rumor). Don't be quick with your words, be quick with your actions. It feeds the tongue with bread and spoils the matter. The tongue gives the answer to the tongue, but the head realizes. Sole sole, Black Sea fish Solea nasuta. Sparrow's tongues, knotweed, grass, Corrigiola littoralis. Pig tongues, see love spell. Cow tongue, see scab. Ox tongues, licorice, bloodbath, Pulicaria dysenterica. Lamb tongue, blush plant, Onosma echioides. Ox tongue, Cynoglossum, larkspur. Deer tongue, plant Gymnogramma celerach.
Scolopendrium, family of ferns. Linguistic, related to language. Linguistic sciences related to languages and writing. Pagan man arch. quick-tongued, eloquent. Don't mess with a pagan man, Sire. Lingual muscles. He stood on a fragile spot on the wall, according to the language tale, where they would have a major attack, according to the language. Tongue milks (molkov), old. Same.
Pagan, more pagan, pertaining to idolaters and idolatry. Pagan rituals; pagan temple, temple, temple, shrine; - god, fool, idol, idol. Paganism cf. idolatry, idolatry, idolatry, adoration of nature or idols instead of God. If you are a Jew, you live like a pagan, and not like a Jew, why should tongues need to live like a Jew? Pagan, pagan, idolater, idolizer, adorer of earthly nature, fools, idols.
Linguist, scientist who knows many languages. Metzofanti was the greatest pagan.
Earpiece, carrier, gossip or evil tongue and secret slanderer.
Pagan, serpuha plant, Serratula tinctoria qat. Paganize arch. to speak, to say, to say, to speak (to pronounce), to be able to, to be able to speak. Yes, the patient does not speak, he is without a tongue. Paganize the East. carry, retell, gossip, gossip and bully people behind the eyes, fool someone's ears, tell lies. Paganism, paganism cf. sneak, slander; gossip, gossip. Linguistics, linguistics cf. philology and linguistics, the study of ancient or living languages. Linguist, linguist, philologist, linguist, pagan. Linguistics, language teaching. Linguistics related to this. Language teacher, language teacher, who teaches language. Language tamb. stand, look, yawn with your mouth open, tongue hanging out (?);
talk nonsense, talk idle, blather. Language vol. empty, absurd talker, empty-headed;
stripped, gaping.
Python
Python is versatile and relatively easy to learn. He has firmly settled down in the very promising field of data mining, or in Russian, intelligent data analysis. The essence of this activity is to use business information to search for implicit patterns of demand and then explore possible directions for business development.
Python is also used by creators of web services, developers of server architecture for multiplayer online games, and others. The need for professionals who know Python is increasing, so you can't go wrong if you start learning it.
You can view a large course on this language on our website:
You will be more courageous in speaking on sensitive topics
It is easier to discuss equality, ecology or musical tastes in English. It loosens the tongue and gives freedom to express an opinion on any controversial issue. Again, due to the characteristics of a liberal culture, for which it is natural to fight for one’s rights and agitate for the equality of all people.
This property of the English language was proved in 1968 by sociolinguist Susan Erwin in An Analysis of the Interaction of Language, Topic and Listener. She conducted an experiment involving women who emigrated from conservative Japan to the United States. Most of the subjects were married to Americans and spoke Japanese only during visits to their home country.
Erwin gave the women some simple tasks, such as “Answer the question” or “Complete the sentence.” They had to be completed first in Japanese, then in English. The answers turned out to be completely different. For example, when asked by a sociolinguist to complete the sentence “I want to become...”, a popular answer in Japanese was “housewife”, and in English “teacher”.