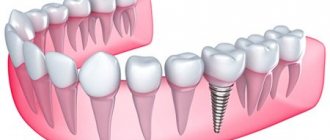
In dental implantation, a very important point is the initial planning and selection of an orthopedic design, including crowns for implants. It is for this reason that in our SDent clinic, the initial examination and consultation is carried out not by an implantologist, but by an orthopedic dentist. In order to correctly distribute the subsequent load on the teeth, the orthopedist clearly determines which dental implants to place, as well as the location and number of implants. Only after this does the implantologist give his opinion on the choice of types of implants, implantation techniques and the possibility of performing an operation without prior preparation for bone augmentation.
Unfortunately, it happens that some implantologists offer to install implants “without problems and quickly”, without taking into account all the subtleties of this process in combination with prosthetics.
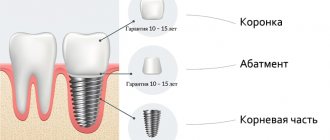
A tooth on an implant consists of three parts: the artificial root itself - the implant, an abutment, which is inserted into the implant and serves as a supporting stump for the crown on top.
Crowns for implants differ in the material from which they are made and in the type of fixation to the implant.
Purpose
During prosthetics, the procedure of tooth preparation is carried out and temporary crowns are necessary to protect the oral cavity from unwanted and even harmful influences; in addition, such crowns allow you to maintain the aesthetics of the dentition after grinding problem teeth. It should also be taken into account that when installed on the teeth, they relieve the patient from discomfort, since ground molars lose their main functionality, and also make it possible to correctly distribute the load during implantation.
Advantages
Considering the somewhat lengthy treatment process, issues of the aesthetic appearance of the patient’s oral cavity acquire particular importance and significance; it is these considerations that dictate the need to use provisional crowns. Their key advantages are:
- no pressure on the supporting tooth, which allows the patient not to feel pain;
- such crowns provide the patient with excellent protection from gum growth and the effects of various microorganisms;
- the tooth does not shift;
- while wearing such a crown, the patient gradually gets used to the foreign body in his oral cavity;
- there is no violation of diction;
- to some extent, restoration of lost functions is carried out, albeit to a small extent.
Materials for production
The most common and popular material for making temporary crowns in dentistry is now plastic or composite. This is explained by a large number of their advantages:
- speed of hardening;
- ease of modeling a plastic crown;
- almost zero toxicity level;
- high strength of the finished product;
- the ability to perform crown adjustments at almost any time;
- short production time;
- relatively short wearing period.
These advantages, of course, serve as serious arguments in favor of plastic crowns, but one cannot ignore their disadvantages, namely:
- the possibility of complications due to penetration of microorganisms deep into the porous structure of the crown;
- poor resistance to dyes and color changes;
- the maximum service life does not exceed two years.
Crown for implant price.
| Name of service | price, rub. |
| Making a temporary crown supported by an implant | from 5900 |
| Metal-ceramic crown (KHS) supported by an implant | from 27700 |
| Ceramic crown on a zirconium oxide frame supported by an implant | from 45900 |
| Custom titanium abutment | from 17300 |
| Custom Zirconium Oxide Abutment | from 28080 |
Ilgam Vagifovich Mamedov
Dentist, orthopedist
25
years of experience
As part of orthopedic treatment, we install crowns, bridges, removable and fixed dentures from various materials.
Sign up for a consultation
Methods, process and manufacturing steps
They can be produced with equal success both in the laboratory and in the dental office. The second option is good because it takes only two to three hours, but the shape and color of such a product will distinguish it from other teeth, but if the production takes place in a laboratory, the quality of the result will be higher, although it will take more time, approximately two or three days.
There are several methods for making crowns from plastic, in particular, the direct method, when the product is performed immediately in the dental chair according to the following algorithm:
- Taking an impression of the problematic tooth, its neighbors and the antagonistic jaw. The manufacturing material is softened silicone mass.
- After the silicone has hardened, the tooth is turned, on which a crown of both temporary and permanent properties will be installed.
- The material chosen for manufacturing is poured into the impression and it is placed on the ground tooth.
- Removing the impression, grinding and polishing the surface to bring it into proper shape, after which the final fixation of the prosthesis is performed using cement
This entire procedure lasts approximately one hour; the cement used to fix the prosthesis gradually dissolves under the influence of human saliva.
Accordingly, the indirect method is based on laboratory production of the product. This procedure is carried out by a technologist who gets his hands on a cast for making plaster blanks. Taking into account all the features of his existing models, he produces a prototype using special wax. As a result of such painstaking work, the prosthesis is made in full accordance with the patient’s jaw and is highly reliable.
Fuji crown/post fixation
Fixing a crown with a pin is possible when the coronal part of the tooth is severely damaged, but the root is preserved. Pin inserts are microprostheses (screw and solid) that are installed into the root of the tooth.
Chewing pressure is transmitted not only to the pin insert, but is also distributed along the axis of the root. This will allow the patient with the crown to chew solid foods.
One of the disadvantages is that the fixation of the crown on the pin insert does not take place in 1 step, because its production takes place in the laboratory. Pin inserts are quite expensive.
It is impossible to install a post when there is periodontal disease and tooth mobility, when the roots are curvature and obstructed, or when the root is short in length.
When installing the pin insert, at the first appointment, a cavity is formed for the pin, unfilling and expansion of the channels and their polishing. Next, the dentist makes an impression - the cavity is filled with impression material. After 20 minutes, the impression is removed. A pin will be cast on it in the laboratory.
A temporary filling is placed in the canal.
When the pin is ready, the canal is unsealed at the second appointment. Its disinfection. Then a pin is installed and fixed with cement. Using light composite, a tooth stump is formed on which the crown will be fixed.
The main advantage of fixing a crown on pins is the preservation of the native root, due to which the native tooth covered with a crown will last longer.
Restrictions on use and prohibitions
The use of temporary crowns is not always feasible and possible; there are certain restrictions on their use in such situations:
- It is not recommended to install prostheses for children under 12 years of age;
- if you are allergic to the materials used in prosthetics;
- when a patient experiences a phenomenon such as teeth grinding or bruxism;
- in cases of inflammation of the problem area of the oral cavity;
- if the patient has a deep bite;
- when identifying certain mental disorders.
For those who do not pay enough attention to oral hygiene, it is not recommended to install plastic dentures due to the fact that the porous structure of the material itself serves as a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria.
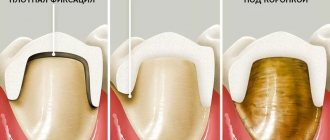
What is the difference between screw fixation of crowns on implants and cement, which is better?
First, we need to explain that with cement fixation we have an implant, to which an abutment is screwed with a screw, and a crown is placed on top of it on top of the cement, in fact, exactly the same as on your own tooth. With screw fixation, a crown is immediately made and fixed directly to the implant (without an abutment) with the same screw. This leaves a hole in the crown for the screw, which is closed with a conventional light filling material.
What's better? This question is akin to what is better: Mercedes or BMW, Canon or Nikon, Mac OS or Windows, Gucci or Prada... You should not contrast one type of prosthetic fixation with another. Although even among very advanced dentists there are ardent fans of one method or another, defending their position on the preferable use of one method over another. In fact, in my opinion, both of them have an equal right to life and selective use in certain conditions. Each has its own pros and cons. And I believe that in this matter the choice is up to the individual doctor. If he justified his choice to you, and you internally agree with his arguments, then simply trust. Otherwise, you can get to the point where you try to advise the implantologist during the implantation operation how to hold the tip correctly, what drills to choose, what thread to sew with, etc. In general, this usually only happens to one type of patient... the dentists themselves, when they find themselves on the other side of the drill machine.
And yet, if such a question arises, then for particularly interested patients I will very briefly explain the disadvantages of each fixation method.
Indications for installation of prostheses
Installation of temporary plastic prostheses is carried out for the following indications:
- in situations where various types of damage to teeth visible to others have occurred, for example, when the enamel has darkened or the patient is not satisfied with their size;
- crowns are placed on chewing teeth in order to preserve a person’s ability to eat well and eat any food;
- before a complete reconstruction of the teeth is carried out, temporary crowns are placed on the ground molars in order to protect them from various external influences;
- to prevent overgrowth of the gum bed;
- to prevent displacement of teeth in a row;
- If you have periodontal disease, you cannot splint your teeth without temporary crowns;
- in order to restore the patient’s diction;
- for the purpose of covering implants when installing a permanent prosthesis.
What is the difference between a custom abutment and a standard one?
In general, as the name implies, in the first case the abutment is produced individually in a single copy and has a form strictly necessary for a particular case. In the second case, we are dealing with a factory stamped product. A standard titanium abutment is installed in the oral cavity. Such a standard “cylinder” does not follow the shape of a real tooth and does not maintain the correct shape of the gums. In addition, when fixing the crown to such an abutment, excess cement can easily penetrate deep into the gap between it and the gum. An individual zirconium abutment is made strictly according to the desired shape, which is usually what a central incisor should have. The gums are well supported. There is no space for cement to “drip” deep under the gum. The left crown is made on an individual abutment, the right one on a standard one. The difference in shape is obvious. The first has a more regular, natural profile.
Which is better and is there a difference for the patient? Imagine that you come to a shoe store and find a model you like. Everything would be fine, but fashionable boots are produced only in certain sizes, say, 37, 39, 41 and 43. And as luck would have it, yours is 40. Well, at the very least, you can take the 41st and wear your favorite stilettos with a woolen sock. Yes, it’s unaesthetic... but they don’t die from it, do they?! But what if you ate a lot of Rastishka as a child and your feet grew exactly 50? No extra socks will help here. And this is just a rough comparison. After all, your size may luckily be exactly 39. And so, it looks like the shoes are on, but you still don’t feel comfortable... the foot feels tight in width, but in the instep, on the contrary, everything somehow dangles... In general, it seems to fit, but it’s uncomfortable. Now, in contrast to this, imagine that your shoes will be made to order specifically for your foot, taking into account all its features. In such shoes, even with a 10-centimeter heel, you will feel like you are wearing house slippers. Almost the same can be said about the differences between standard and individual abutments. For work that does not claim to be high-class, especially in terms of aesthetics, in austerity mode, it will be possible to get by with standard ones. Well, for example, on chewing teeth. If we are talking about maximum aesthetics and service life, then custom ones are the best choice. It must be said that at the dawn of implantology, the difference in price between factory-made and individually made abutments was significant. Today, with the advent of more and more CAD/CAM* systems, the cost of producing individual abutments from all materials (primarily titanium and zirconium) has actually become equal to the cost of standard factory ones.
Designs for molars
Normal and nutritious human nutrition is impossible without chewing teeth, since the entire load during chewing food falls on them. Accordingly, as soon as the first problems with the condition of such teeth appear, you should immediately consult a doctor and arrange for the installation of dentures. However, it is necessary to understand that the choice of plastic crowns must be approached carefully and carefully; if you select unsuitable prostheses, this will not correct, but will only worsen the situation.
It is better to give preference to those prostheses that have the longest service life; we must not forget that the structures have to undergo very serious impacts and not the highest quality plastic can easily and quickly fail. Metal-ceramics and ceramics on paper look like a more preferable option, but, firstly, they are significantly more expensive, and, secondly, if you incorrectly calculate the bite or pressure force when installing them, then chips or cracks may form on the prosthesis, and this will cause serious inconvenience for the patient.
The process of removing temporary crowns
The very concept of “temporary crowns” means that after a certain period they must be removed, otherwise their functionality and appearance will no longer meet the requirements. How are such dentures removed? If metal ceramics were installed, then it must be sawed; this is not required for plastic, since this material does not have a high level of strength. First of all, the doctor will need to weaken the effect of the substances used to fix the prosthesis with the help of special drugs. Using a drill, a Copa apparatus and ultrasound, the process of gradual removal of the product is carried out. It is worth pointing out to patients that this procedure is painless and anesthesia is almost never required.
After the prosthesis is removed and the tooth is cleaned of the remaining fixing materials, the next temporary crown or a permanent one is installed. The decision in favor of one option or another must be made after consultation with a doctor. You also need to remember that a permanent crown is also limited in service life, but longer than a temporary one.
What does a custom abutment give us?
It is no longer just a round “stump”, but actually a full-fledged anatomical tooth stump. The same as if we simply treated an ordinary tooth for a crown.
In this photo you can see the stages of prosthetics for the lower 6th tooth. It was replaced with an implant (its installation in this clinical case was performed by my colleague, implant surgeon Dr. Ponomarev Oleg Yurievich). From left to right: first, the patient comes from the surgeon to the orthopedist with a gum former (Fig. 1). When we unscrew it, we can see the implant itself inside, in this case the Alpha-Bio system implant (Fig. 2). In order to take an impression, a special impression coping is temporarily screwed to the implant (Fig. 3). After taking the impression, the gum former is screwed back onto the patient, and the impressions are sent to the dental laboratory. There, based on the impression, the dental technician casts plaster models in a special way. The gums around the implant are modeled using special silicone to more realistically convey the state of “natural” gums. To model an individual abutment of the desired correct shape, the dental technician forms the contour we need by trimming the silicone gum. After this, a computer-controlled machine cuts out an individual abutment from a log of Buratino’s zirconium blank.
Thus, an individual zirconium abutment is almost no different from its “natural” neighbor prepared for a crown. After just 7-10 days, the technical work (custom zirconium abutment and all-zirconium crown) is completely ready, and we can fix it in the mouth. Before screwing the individual abutment, we first slightly correct the gum around the implant. Just like the technician did on the model.
Then you can screw the abutment to the implant. Notice how the gums around the abutment have turned white. This means that it fits very tightly to it, and when fixing the crown, excess cement, even if desired, will not be able to flow there. It is impossible to achieve the same tight fit of a standard abutment to the gum, no matter how hard you try.
And here is the final result. All-zirconium crowns are made for the Alpha-Bio implant and your tooth.
In all aspects, this design is superior to a standard titanium abutment + metal-ceramic crown pair. At the same time, the price of a standard metal spare part from a “cool” implantation system is actually equal to the cost of producing such an individual zirconium abutment. What to choose? The question, in my opinion, is now rhetorical. And metal-ceramic crowns now have a better and comparable price alternative.
So I advise both doctors and patients to perform prosthetics on implants only using individual spare parts. This will give a much more predictable beautiful and long-lasting result. And this is what dentists themselves usually want, and even more so, our patients!
Care and how long can you wear them?
The duration of use of a temporary prosthesis is limited not only by its performance characteristics, but is also determined by its proper care. There is nothing complicated about this, care should consist of such simple things as:
- lower level of load on the area of the oral cavity where the prosthesis was installed;
- in this place, when brushing your teeth, you should perform gentler actions, without applying much force;
- After using dental floss, you should not pull it out, but carefully and calmly pull it out.
When answering the question of how long you can wear temporary dentures, you should remember that delaying this procedure does not justify itself. As soon as the permanent structure is ready, it is rational to replace the temporary prosthesis with it.
Why is a custom zirconium abutment better than a standard titanium abutment?
Its most important advantage is its complete anatomy and individuality. This is not only important from an aesthetic point of view, but also allows you to avoid getting fixing cement under the gum when fixing the crown to the abutment. This is a very important plus, because... imperceptible penetration of even a thin film of cement between a standard abutment and the gum can after some time cause inflammation - peri-imlantitis. It is extremely difficult to treat, and often this inflammation ends in the loss of bone around the implant, and, therefore, the “screw” itself.
And that's why this happens.
Due to the fact that a standard abutment is much narrower than a crown, when fixing the latter, excess cement is literally pressed into the space between the abutment and the gum (the risk zone is marked in the figure). This situation can be aggravated by the fact that, in an effort to disguise the metal of the abutment, the technician places a ledge below the level of the gum so that the edge of the crown goes deeper and completely covers the metal abutment. This will inevitably lead to cement getting into an area from where it can no longer be removed. The occurrence of inflammation in this case is often only a matter of time.
This is exactly the problem that occurred in this situation: a “top” implant + a standard titanium abutment + a metal-ceramic crown instead of the lower 6th tooth.
After removing the crown and exposing the abutment, cement leakage under the gum was determined, which led to peri-implantitis approximately 1.5 years after installation of the implant and the need for its removal.
These images show the current level of bone tissue around the implant (blue line) and what it was originally (red line). This bone defect is caused by inflammation of the tissue around the implant as a result of cement getting under the gum.
What to do if it falls out?
It happens that the installed temporary crown comes off. It is quite natural that patients are concerned about this situation and if it has happened, what to do next? First of all, there is no reason to panic; you should return it to its place yourself, fixing it with Vaseline or toothpaste and be sure to consult a dentist. The structure returned to its place on its own will, of course, not have the same strength and reliability, but it will still perform its basic functionality. It should also be remembered that it is better to remove the prosthesis before going to bed, this will avoid the potential serious consequences of its night loss.
Voice of the people
If we analyze the reviews of patients who resorted to installing plastic crowns, we can say that for many of them they became a real salvation. They are perfect for young girls who, due to their age, cannot yet install metal-ceramics and do not have complexes about their smile, for example, at school.
It is also noted that it is necessary to use plastic structures only on a temporary basis, since it is not possible to fit such a crown tightly onto the tooth, and it becomes a breeding ground for harmful microorganisms. Many patients say that as a temporary measure, such prostheses are almost an ideal solution to the problem, plus, their cost is quite affordable.